多线程
0.基本概念
程序:为完成特定任务,用某种编程语言编写的一组指令的集合(静态)
进程:程序的一次执行过程,或正在执行的一个程序(动态过程)
线程:程序内部的一条执行路径,若某个程序支持同一时间执行多个线程,即支持多线程
1.多线程的创建和使用
继承Thread类创建多线程
- 一个线程只能执行一次
start() - 不能通过
Thread类的run方法去启动一个线程
例:
package thead; //1.创建继承于Thread的子类
class SubThread extends Thread{//2.重写Thread类的run方法,方法内实现此子类线程要完成的功能public void run() {for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i); }}
}
public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//4.创建子类对象SubThread s = new SubThread();//5.调用start()方法,启动线程;再调用相应的run方法s.start();//主线程执行for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);}}
}实现Runnable接口创建多线程
package thead;
//创建多线程的方式二:通过实现的方式
//1.创建实现Runnable接口的类
class PrintNum implements Runnable{//2.重写run的方法public void run() {for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);}}
}
public class test4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//3.创建一个Runnable接口的实现类的对象PrintNum p = new PrintNum();//4.将此对象作为形参传递给Thread类的构造器中Thread t1 = new Thread(p);//想启动多线程,必须调用start()t1.start();Thread t2 = new Thread(p);t2.start();}}
继承Thread类与实现Runnable接口的区别
- 1.都继承
了Runnable接口(Thread类实现Runnable接口) - 2.实现的方式优于继承的方式(避免Java单线程的局限性;如果多个线程要操作同一份资源(或数据),更合适使用实现的方式)
案例:模拟火车站售票,开启三个窗口,总票数100张
继承
package project;
//模拟火车站售票,开启三个窗口,总票数100张
class Window extends Thread{static int ticket = 100; //总票数public void run() { while(true) {if(ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售票口:票号为:" + ticket--); }else {break;}}}
}
public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Window w1 = new Window();Window w2 = new Window();Window w3 = new Window();w1.setName("1号");w2.setName("2号");w3.setName("3号");w1.start();w2.start();w3.start();}
}
实现
package project;
//模拟火车站售票,开启三个窗口,总票数100张
class Window1 implements Runnable{int ticket = 100; //总票数public void run() { while(true) {if(ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售票口:票号为:" + ticket--); }else {break;}} }
}
public class test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Window1 w = new Window1();Thread t1 = new Thread(w);Thread t2 = new Thread(w);Thread t3 = new Thread(w);t1.setName("1号");t2.setName("2号");t3.setName("3号");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}
多线程的优点
- 1.提高应用程序的响应,对图形化界面更有意义,可增强用户体验
- 2.提供计算机CPU利用率
- 3.改善程序结构,将复杂的进程分为多个线程,独立运行,利于理解和修改
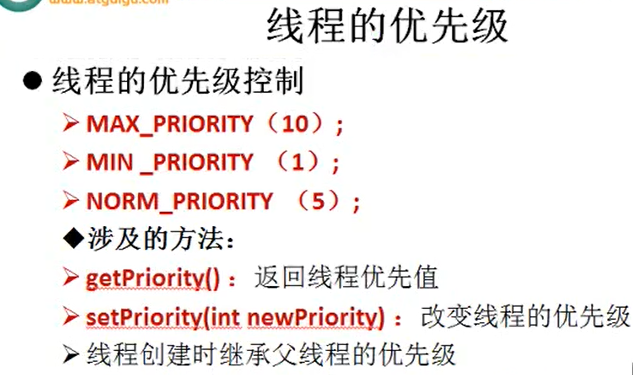
Thread类的主要方法与配置线程优先级
package thead;
/** 线程的主要方法* 1.start():启动线程并执行相应的run()方法* 2.run():子线程要执行的代码放入run()方法中* 3.currentThread():静态的,调取当前的线程* 4.getName():获取线程的名字* 5.setName():设置线程名* 6.yield():调用此方法的线程释放当前CPU的执行权* 7.join():在A线程中调用B线程的join()方法,当执行到此方法时,A停止,B执行,等B全部执行完后,A再继续执行剩下的任务。* 8.isAlive():检测线程是否存活* 9.sleep(long l):显式的让当前线程睡眠l毫秒* 10.线程通信:wait() notify() notifyAll()后续介绍* 11.线程优先级(默认5,最大10,最小1):只是提高了抢到的CPU执行权的概率* getPriority():返回线程的优先级* setPriority(int newPriority):改变线程的优先级*/class SubThread1 extends Thread{public void run() {for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {
// try {
// Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
// }System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority() + ":" + i);}}
}
public class test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {SubThread1 s1 = new SubThread1();s1.setName("线程1号");s1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);s1.start();Thread.currentThread().setName("======主线程=====");for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority() + ":" + i);
// if(i % 10 == 0) {
// Thread.currentThread().yield();
// }
// if(i == 10) {
// try {
// s1.join();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }}System.out.println(s1.isAlive());}
}
练习

package thead; class SuThread1 extends Thread{//1-100奇数public void run() {for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i = i + 2) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i);}}
}class SuThread2 extends Thread{//1-100偶数public void run() {for(int i = 2;i <= 100;i = i + 2) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " : " + i); }}
}class test3{public static void main(String[] args) {SuThread1 st1 = new SuThread1();SuThread2 st2 = new SuThread2();st1.setName("子线程1号");st1.start();st2.setName("子线程2号");st2.start();// //继承Thread类的匿名类的对象
// new Thread() {
// public void run() {
// for(int i = 2;i <= 100;i = i + 2) {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " : " + i);
// }
// }
// }.start();}
}
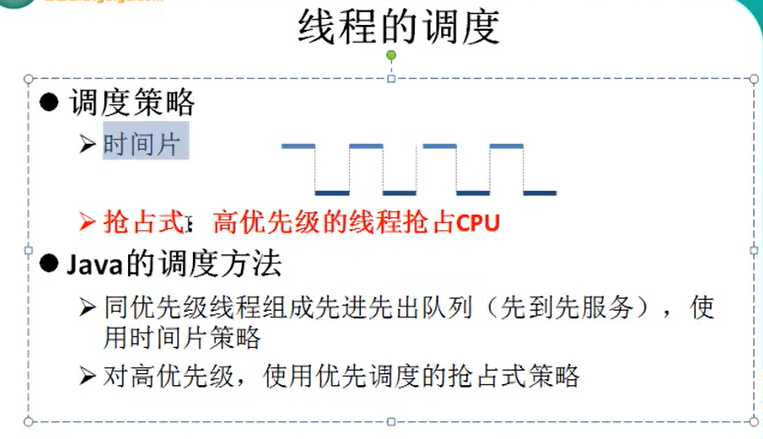
2.线程的生命周期
生命周期中通常要经历的5种状态
新建:当一个Thread类或子类的对象被声明并创建时,新生的线程对象处于新建状态
就绪:处于新建状态的线程被start()后,将进入线程队列等待CPU时间片,此时它已具备运行的条件
运行:当就绪的线程被调度并获得处理器资源时,便进入运行状态,run()方法定义了线程的操作和功能
阻塞:在某种特殊情况下,被人为挂起或执行输入输出操作时,让出CPU并临时中止自己的执行,进入阻塞状态
死亡:线程完成全部工作或线程被提前强制中止

3.线程的同步(重点)
在上面列举的火车售票案例中存在售错票,重票等的情况,存在线程安全问题
原因:由于线程在操作共享数据过程中,未执行完毕的情况下,另外的线程参与进来,导致共享的数据存在安全问题
解决:必须让一个线程操作共享数据完毕以后,其他线程才有机会参与共享数据的操作
Java利用线程同步来解决线程安全问题
方法一:同步代码块
synchronized(同步监视器){//需要同步的代码(即为操作共享数据的代码);}
- 1.同步监视器:由一个任意类的对象来充当。哪个线程获此监视器,谁就执行括号中被同步的代码。俗称:锁
- 2.共享数据:多线程共同操作的同一个数据(变量)
- 要求:所有的线程必须共用同一把锁
例:
package project;
//模拟火车站售票,开启三个窗口,总票数100张
class Window2 implements Runnable{int ticket = 100; //总票数(共享数据)Object obj = new Object();public void run() { while(true) {synchronized(obj){if(ticket > 0) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售票口:票号为:" + ticket--); }else {break;}}}}
}
public class test4 {public static void main(String[] args) {Window2 w = new Window2();Thread t1 = new Thread(w);Thread t2 = new Thread(w);Thread t3 = new Thread(w);t1.setName("1号");t2.setName("2号");t3.setName("3号");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}
注:在实现方式中可以用this表示当前对象(同步监视器),若在继承的方式中慎用this
方法二:同步方法
public synchronized void show() {//需要同步的代码(即为操作共享数据的代码);}
例:
package project;
class Window3 implements Runnable{int ticket = 100; public void run() { while(true) {show();}}public synchronized void show() { if(ticket > 0) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售票口:票号为:" + ticket--); }}
}
public class test3 {public static void main(String[] args) { Window3 w = new Window3();Thread t1 = new Thread(w);Thread t2 = new Thread(w);Thread t3 = new Thread(w);t1.setName("1号");t2.setName("2号");t3.setName("3号");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}
互斥锁

单例之懒汉式的线程安全
例:
package thead;
/* 单例之懒汉式的线程安全:使用同步机制 */
//对于静态方法而言,使用当前类本身充当锁
class Singletion{private Singletion() {}private static Singletion instance = null;public static Singletion getInstance() {if(instance == null) {synchronized(Singletion.class) {if(instance == null) {instance = new Singletion();}}}return instance;}
}
public class test5 {public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSingletion s1 = Singletion.getInstance();Singletion s2 = Singletion.getInstance();System.out.println(s1 == s2);}
}
- 线程同步的弊端:同一时间只能有一个线程访问共享数据,效率变低


练习

package project;
//线程安全练习
//存在多线程,存在共享数据,需同步
class Account{double balance;//余额public Account() {}//存取public synchronized void deposit(double amt) {balance += amt;try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + balance );}
}
class Customer extends Thread{Account account;public Customer(Account account) {this.account = account;}public void run() {for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++) {account.deposit(1000);}}
}public class test5{
public static void main(String[] args) {Account acct = new Account();Customer c1 = new Customer(acct);Customer c2 = new Customer(acct);c1.setName("甲");c2.setName("乙");c1.start();c2.start();}
}
线程死锁

例:
package thead;
/* 死锁:处理线程同步时容易出现 */
//一个线程抓住一半锁,另一个线程抓住一半锁,互不相让
public class test6 {static StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer();static StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer();public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread() {public void run() {synchronized(sb1) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}sb1.append("A");synchronized(sb2){sb2.append("B");System.out.println(sb1);System.out.println(sb2);}}}.start();new Thread() {public void run() {synchronized(sb2) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}sb1.append("C");synchronized(sb1){sb2.append("D");System.out.println(sb1);System.out.println(sb2);}} }.start();
}
}
4.线程的通信
wait()
让当前线程挂起并放弃CPU,同步资源,使用别的线程可访问并修改共享资源,而当前线程排队等候再次对资源的访问
notify()
唤醒正在排队等待同步资源的线程中优先级最高者结束等待
ontifyAll()
唤醒正在排队等待资源的所有线程结束等待
以上三个方法(Java.lang.Object提供)只有在synchronized()方法或synchronized代码块中才能使用,否则会报异常
例1:
package thead;
/* 两个线程交替打印1~100的数 */
//线程通信:wait(),让当前线程停止;notify(),notifyAll()唤醒wait()停止的1个或多个线程
class PrintfNum implements Runnable{int num = 1;public void run() {while(true) {synchronized (this) {//解决线程安全问题notify();if (num <= 100) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();} //使隐藏的线程安全问题暴露处理System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + num);num += 1;} else {break;}try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
public class test7 {public static void main(String[] args) {PrintfNum p = new PrintfNum();Thread t1 = new Thread(p);Thread t2 = new Thread(p);t1.setName("A");t2.setName("B");t1.start();t2.start();}}
生产者/消费者问题
生产者(Productor)将产品交给店员(Clerk),而消费者(Customer)从店员处取走。店员一次只能持有一定数量的产品(如:20).如果生产者试图多生产会被叫停,如果店中有空位才会通知生产者生产;如果店中没有产品,店员会告诉消费者等一下,有产品后在通知消费者取走产品。
注:可能会出现的问题:
-
1.生产者比消费者快,消费者会漏掉一些数据没有取到
-
2.消费者比生产者快,消费者会取到相同的数据
package thead;
//生产者/消费者问题
//多线程:生产者,消费者;共享数据:产品数量;存在数据通信//店员
class Clerk{int product; public synchronized void addProduct() {if(product < 20) {product += 1;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":生产到第" + product + "产品了!" );notify();}elsetry {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}public synchronized void consumProduct() {if(product <= 0) {try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}else {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":消费到第" + product + "产品了!" );product -= 1;notify();}}
}
//生产者
class Producer implements Runnable{Clerk clerk;public Producer(Clerk clerk) {this.clerk = clerk;}public void run() {System.out.println("生产者开始生产产品");while(true) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}clerk.addProduct();}}
}//消费者
class Customer implements Runnable{
Clerk clerk;public Customer(Clerk clerk) {this.clerk = clerk;}public void run() {System.out.println("消费者开始消费产品");while(true) {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}clerk.consumProduct();}}
}public class test8 {public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubClerk clerk = new Clerk();Producer producer = new Producer(clerk);Customer customer = new Customer(clerk);Thread t1 = new Thread(producer);//一个生产者线程Thread t3 = new Thread(producer);//一个生产者线程Thread t2 = new Thread(customer);//一个生产者线程t1.setName("生产1号");t2.setName("消费者");t3.setName("生产2号");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}
练习
在上次练习的基础上,实现交替存款
package project;
//线程安全练习
//存在多线程,存在共享数据,需同步
//扩展实现交替打印class Account{double balance;//余额public Account() {}//存取public synchronized void deposit(double amt) {notify();balance += amt;try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + balance );try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}
}
class Customer extends Thread{Account account;public Customer(Account account) {this.account = account;}public void run() {for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++) {account.deposit(1000);}}
}public class test5{
public static void main(String[] args) {Account acct = new Account();Customer c1 = new Customer(acct);Customer c2 = new Customer(acct);c1.setName("甲");c2.setName("乙");c1.start();c2.start();}
}
感谢大家的支持,关注,评论,点赞!
参考资料:
尚硅谷宋红康20天搞定Java基础下部