目录
1.简介
1.1 intel D4系列深度相机 (D455)
1.2 yolo算法
2.功能实现
2.1构思:
2.2 主代码
这篇文章还是接着前面的几篇文章的项目延申,这个是最初的方案,因为太贵被否了。
1.简介
1.1 intel D4系列深度相机 (D455)
Intel RealSense D435、D455等D4系列:
Intel D4系列深度相机是由英特尔(Intel)公司推出的一款深度感知摄像头,专为实现计算机视觉和深度学习应用而设计。这款相机使用了英特尔的深度感知技术,结合了摄像头和红外(IR)传感器,可以提供高质量的深度图像和 RGB 彩色图像,为开发者提供了丰富的数据源,用于各种应用,包括虚拟现实(VR)、增强现实(AR)、手势识别、人脸识别、姿势识别、3D 扫描等。
以下是Intel D4系列深度相机的一些主要特点和优势:
1. 深度感知技术:
D4系列相机具备高质量的深度感知功能,能够获取场景中各个物体的精确距离信息,而不仅仅是RGB图像。
2. 多模式操作:
相机支持多种操作模式,包括手势识别、人脸识别、物体追踪等。这使得它非常适合于需要人机交互的应用领域。
3. 低光环境适应:
D4系列深度相机在低光环境下也能够提供准确的深度信息,这使得它在各种不同的环境中都能够稳定工作。
4. 易于集成:
相机提供了丰富的软件开发工具,开发者可以方便地将其集成到自己的应用中,快速开发深度感知应用。
5. 多平台支持:
D4系列深度相机支持多种操作系统,包括Windows、Linux等,也提供了各种开发语言的API,方便开发者在不同平台上使用。
6. 精准度和稳定性:
相机具有高精度和稳定性,能够在不同距离范围内提供准确的深度信息,这对于需要精确度的应用非常重要。
1.2 yolo算法
YOLO(You Only Look Once)是一种实时目标检测算法,它的主要思想是将目标检测问题转化为一个回归问题。相较于传统的目标检测算法,YOLO具有更快的处理速度和较高的准确性。
YOLO算法的基本原理如下:
将输入图像划分为一个固定大小的网格。每个网格负责预测该网格中是否包含目标以及目标的边界框。
每个网格预测多个边界框(一般为5个)以适应不同形状的目标。
每个边界框预测目标类别的概率。
对每个边界框的位置和类别进行综合预测。
使用非极大值抑制(NMS)处理重叠的边界框,以获取最终的目标检测结果。
YOLO算法相较于其他目标检测算法的优势在于其端到端的设计,能够实现实时目标检测,并且减少了检测过程中的多次重复计算。然而,由于YOLO将图像划分为网格,对于小尺寸目标和密集目标的检测效果可能会稍差。
此外,YOLO还有不同版本的改进,如YOLOv2、YOLOv3和YOLOv4等,这些改进版本在准确性和速度方面有所提升,同时也引入了一些新的技术和网络结构,如多尺度预测、锚框、Darknet-19等。
2.功能实现
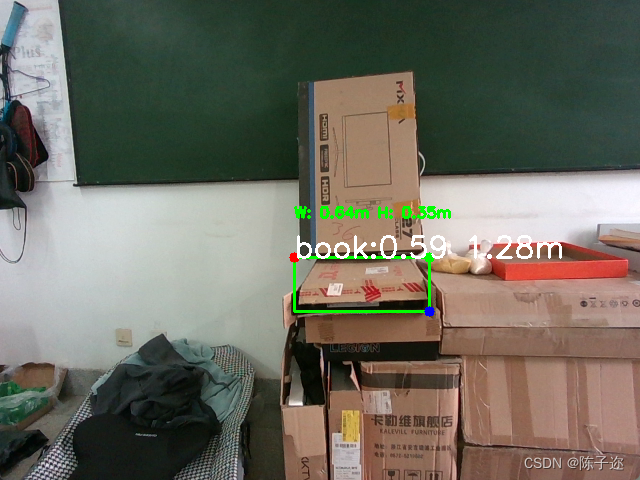
这是实验室的一个项目,用于未来试智能立体停车场的视觉部分,需要检测车俩位置信息和尺寸信息,摄像头在库的顶上,俯拍视角,图如下:
2.1构思:
因为是俯拍,所以这里就考虑了用2D框实现的可行性,通过yolo拿到粗定位框,将框手动扩大一点,确保物体完全包裹,对框内区域提取轮廓在进行多边形拟合,使用拟合后数据重新画框,拿到角点坐标,进行坐标变换,将像素坐标转为真实坐标,求出距离。(仅限俯拍情况,如果是其他场景,框的坐标和现实坐标不在一个面上,这样就需要用三维目标检测算法画框)

2.2 主代码
这里就不完全开源了,因为这个项目还在做,不过有底子的道友,可以参考我前面有一篇opencv里dnn推理yolov5的代码,结合一下下面这个代码就可以用了。
import pyrealsense2 as rs
# import numpy as np
# import cv2
import random
# import torch
from ours import *
import time# model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
#
# model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5l6')
# model.conf = 0.5
def get_mid_pos(frame,box,depth_data,randnum):distance_list = []mid_pos = [(box[0] + box[2])//2, (box[1] + box[3])//2] #确定索引深度的中心像素位置min_val = min(abs(box[2] - box[0]), abs(box[3] - box[1])) #确定深度搜索范围#print(box,)for i in range(randnum):bias = random.randint(-min_val//4, min_val//4)dist = depth_data[int(mid_pos[1] + bias), int(mid_pos[0] + bias)]cv2.circle(frame, (int(mid_pos[0] + bias), int(mid_pos[1] + bias)), 4, (255,0,0), -1)#print(int(mid_pos[1] + bias), int(mid_pos[0] + bias))if dist:distance_list.append(dist)distance_list = np.array(distance_list)distance_list = np.sort(distance_list)[randnum//2-randnum//4:randnum//2+randnum//4] #冒泡排序+中值滤波cv2.imshow('1', frame)return np.mean(distance_list)
def dectshow(org_img, boxs,depth_data):img = org_img.copy()for box in boxs:cv2.rectangle(img, (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3])), (0, 255, 0), 2)intrinsics = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics## x1, y1 = (box[0] ,box[1])# print((x1,y1))# x1, y2 = (box[1] ,box[1])# x2, y1 = (box[0] ,box[1])# x2, y2 = (box[0] ,box[1])x1 = box[0]y1 = box[1]x2 = box[2]y2 = box[3]cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1) # 红色圆点cv2.circle(img, (x2, y1), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1) # 绿色圆点cv2.circle(img, (x2, y2), 5, (255, 0, 0), -1) # 蓝色圆点depth1 = depth_frame.get_distance(x1, y1) # 获取第一个点的深度值depth2 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y1) # 获取第二个点的深度值depth3 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y2) # 获取第三个点的深度值point1 = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intrinsics, [x1, y1], depth1)point2 = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intrinsics, [x2, y1], depth2)point3 = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intrinsics, [x2, y2], depth3)cv2.imshow('1', img)# 计算两点之间的距离width = np.linalg.norm(np.array(point2) - np.array(point1))height = np.linalg.norm(np.array(point3) - np.array(point2))print("宽 is:", width, "m")print("长 is:", height, "m")cv2.putText(img, f'W: {str(width)[:4] }m H: {str(height)[:4]}m', (int(box[0]), int(box[1]) - 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5,(0, 255, 0), 2)# if not depth_frame.is_depth_frame():# continue## # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x1 >= 0 and x1 < depth_image.shape[1] and y1 >= 0 and y1 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth1 = depth_frame.get_distance(x1, y1) # 获取第一个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth1 = None### # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x2 >= 0 and x2 < depth_image.shape[1] and y1 >= 0 and y1 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth2 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y1) # 获取第二个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth2 = None## # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x2 >= 0 and x2 < depth_image.shape[1] and y2 >= 0 and y2 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth3 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y2) # 获取第三个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth3 = None# if x1 < 0 or x1 >= depth_image.shape[1] or y1 < 0 or y1 >= depth_image.shape[0]:# # 处理超出范围的情况# continue # 跳过该点的处理# if x2 < 0 or x2 >= depth_image.shape[1] or y2 < 0 or y2 >= depth_image.shape[0]:# # 处理超出范围的情况# continue # 跳过该点的处理dist = get_mid_pos(org_img, box, depth_data, 24)cv2.putText(img, box[4] + ' ' + str(dist / 1000)[:4] + 'm' ,(int(box[0]), int(box[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)# if not depth_frame.is_depth_frame():# continue## # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x1 >= 0 and x1 < depth_image.shape[1] and y1 >= 0 and y1 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth1 = depth_frame.get_distance(x1, y1) # 获取第一个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth1 = None### # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x2 >= 0 and x2 < depth_image.shape[1] and y1 >= 0 and y1 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth2 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y1) # 获取第二个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth2 = None## # 确定坐标值是否在depth_image的范围之内# if x2 >= 0 and x2 < depth_image.shape[1] and y2 >= 0 and y2 < depth_image.shape[0]:# depth3 = depth_frame.get_distance(x2, y2) # 获取第三个点的深度值# continue# else:# depth3 = Noneif x1 < 0 or x1 >= depth_image.shape[1] or y1 < 0 or y1 >= depth_image.shape[0]:# 处理超出范围的情况continue # 跳过该点的处理if x2 < 0 or x2 >= depth_image.shape[1] or y2 < 0 or y2 >= depth_image.shape[0]:# 处理超出范围的情况continue # 跳过该点的处理cv2.imshow('dec_img', img)if __name__ == "__main__":# Configure depth and color streamsonnx_path = 'yolov5s.onnx'model = Yolov5ONNX(onnx_path)pipeline = rs.pipeline()config = rs.config()config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 60)config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 60)# Start streamingpipeline.start(config)pTime = 0try:while True:# Wait for a coherent pair of frames: depth and colorframes = pipeline.wait_for_frames()depth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frames.get_color_frame()depth_intrinsics = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicsif not depth_frame or not color_frame:continue# Convert images to numpy arraysdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())im = color_image.copy() # 备份原图cTime = time.time()fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime)pTime = cTimecv2.putText(color_image, str(int(fps)), (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,(255, 0, 255), 3)results , boxs = model.detect(color_image)dectshow(im, boxs, depth_image)# Apply colormap on depth image (image must be converted to 8-bit per pixel first)depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)# Stack both images horizontallyimages = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))# Show imagescv2.namedWindow('RealSense', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv2.imshow('RealSense', images)key = cv2.waitKey(1)# Press esc or 'q' to close the image windowif key & 0xFF == ord('q') or key == 27:cv2.destroyAllWindows()breakfinally:# Stop streamingpipeline.stop()请忽略yolo这个笨蛋把他识别错了,但是效果还是可以的,精度也没问题,关键是很省事,就是相机费钱。这个方案被否了。




![[ROS2系列] ubuntu 20.04测试rtabmap 3D建图(二)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f01360f12f9b4ad7854fea51c0e87f76.png)