文章目录
- 前言
- 项目结构
- Sort算法实现
- 卡尔曼跟踪器
- 工具类
- 多目标跟踪器
- 整合
前言
昨天挖了个坑,那么今天的话把坑填上,只要是实现Sort算法和Yolov5-Lite的一个整合。当然先前的话,我们在Yolov3–Tiny的时候,也做了一个,不过当时的话,有几个问题没有解决。第一就是当时以中心点进行预测的,这样做的结果就是如果目标框的波动比较大的话,影响会很大,同时,当时设计是为了应对直线旋转平移这样的运动进行捕捉。所以效果比较差。同时就是对于目标点的匹配不合理。那就是,我是按照,当预测点和识别点进行距离计算,计算当前点的最小距离。在同一个类别之下,但是这里有个问题,就是,假设有一个的A,和点B,C,由于B点先进行计算,那么假设A,B匹配了,当C进来的时候,由于C可能和A点的距离更小,但是由于B,A已经匹配导致C没有和A匹配。那么这样一来明明C是最合适A的,但是由于B先来,导致A和B先匹配了(淦,有点像极了人生)
所以,这里的话,还是要引入匈牙利算法,当然这个算法的话,在先前的算法刷题专栏当中已经说过了,那么这里就不重复了,其实就是简单的应用。
项目结构
这里先说一下,这个项目的基本原理还是类似的:
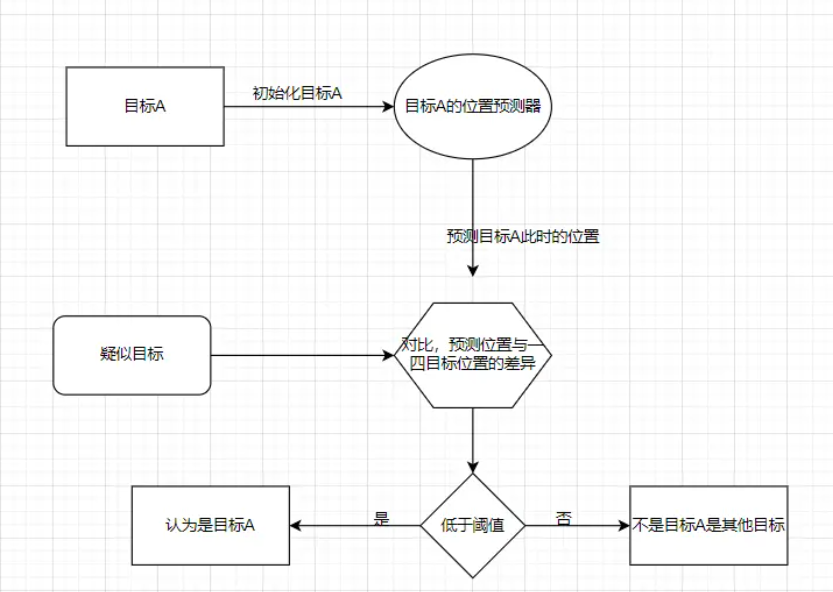
只是,现在匹配我们换成了匈牙利算法。
Sort算法实现
那么,在这里的话,我们先来实现Sort算法。本来是打算嫖个开源的做整合的,但是没想到,他们的代码有很多问题,改别人的bug,还不如自己手写,所以的话,这里的话,我自己手写了一个Sort算法。这里注意的是,Sort算法只是一个匹配算法,通过IOU,和卡尔曼滤波做预测,来匹配当前的跟踪器和新产生的目标框是不是同一个目标。如果你的目标识别算法不准确的话,也就是目标框不稳定,会不断生成新的目标框,那么你的Sort算法就会不断认为这是新的目标的。解决办法的话,可以考虑使用deepsort。 但是的话,我们这里是边缘设备,如果没有deepsort-lite的话实在是不好搞。而且,比如一些简单场景,比如车流量检查,行人检测啥的,机位固定倒也用不上。
卡尔曼跟踪器
那么首先,在这里要实现的就是卡尔曼跟踪器。
这里的话,原理就不扯了,我这里都提到好几次了。
import numpy as np
from filterpy.kalman import KalmanFilter
import cv2
from sort.utils import convert_bbox_to_z, convert_x_to_bbox
np.random.seed(0)@DeprecationWarning
class ObjectTrackerKF:"""这个滤波是只跟踪中心点坐标,不过,还是会还原为[x1,y1,x2,y2]的"""def __init__(self,bbox, dt=1, sigma=10):# 每次创建新的kalman滤波器时,计数ID都会加1self.id = 0self.hit_streak = 0self.bbox = bbox# 自上次未匹配成功,经过的帧数self.time_since_update = 0# 自上次未匹配成功,连续成功匹配的帧数self.hit_streak = 0self.dt = dtx_init, y_init = (bbox[0]+bbox[2])/2 ,(bbox[1]+bbox[3])/2# 状态向量,包含位置和速度信息self.state = np.array([[x_init], [y_init], [0], [0]], np.float32)# 系统矩阵,将状态向量映射为下一时刻的状态向量self.A = np.array([[1, 0, self.dt, 0],[0, 1, 0, self.dt],[0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]], np.float32)# 测量矩阵,将状态向量映射为测量向量self.H = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0]], np.float32)# 过程噪声,表示模型中未考虑的外部因素产生的偏差self.Q = np.array([[self.dt ** 4 / 4, 0, self.dt ** 3 / 2, 0],[0, self.dt ** 4 / 4, 0, self.dt ** 3 / 2],[self.dt ** 3 / 2, 0, self.dt ** 2, 0],[0, 0, 0, self.dt ** 2]], np.float32) * sigma ** 2# 测量噪声,表示测量器的误差self.R = np.array([[1, 0],[0, 1]], np.float32) * sigma ** 2# 卡尔曼滤波器初始化self.kf = cv2.KalmanFilter(4, 2, 0)self.kf.statePost = self.stateself.kf.transitionMatrix = self.Aself.kf.measurementMatrix = self.Hself.kf.processNoiseCov = self.Qself.kf.measurementNoiseCov = self.Rdef predict(self):self.state = self.kf.predict()t = self.state[:2].reshape(-1)t = list(t)w = self.bbox[2] - self.bbox[0]h = self.bbox[3] - self.bbox[1]box = [(t[0]-w/2),t[1]-h/2,t[0]+w/2,t[1]+h/2,self.bbox[4]]self.bbox = boxif self.time_since_update > 0:self.hit_streak = 0return self.bboxdef update(self,bbox):x, y = (bbox[0]+bbox[2])/2 ,(bbox[1]+bbox[3])/2self.time_since_update = 0# 表示连续匹配成功的次数加一if(self.hit_streak<=30):self.hit_streak+=1self.kf.correct(np.array([[x], [y]], np.float32))return self.state[:2].reshape(-1)class KalmanBoxTracker(object):# 利用bounding box初始化Kalman滤波轨迹def __init__(self, bbox):self.id = 0#注意这里的bboxs是[x1,y1,x2,y2,conf]是list类型self.bbox = bbox# 定义恒定速度模型,7个状态变量和4个观测输入self.kf = KalmanFilter(dim_x=7, dim_z=4)# 状态向量 X = [检测框中心的横坐标,检测框中心的纵坐标,检测框的面积,长宽比,横坐标速度,纵坐标速度,面积速度]# SORT假设一个物体在不同帧中检测框的长宽比不变,是个常数,所以速度变化只考虑横坐标、横坐标、检测框面积self.kf.F = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]])self.kf.H = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]])# R是测量噪声的协方差矩阵,即真实值与测量值差的协方差# R = diagonal([1, 1, 10, 10])self.kf.R[2:, 2:] *= 10.# [[ 1. 0. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 1. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 10. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 0. 10.]]# P是先验估计的协方差,对不可观测的初始速度,给予高度不确定性# P = diagonal([10,10,10,10,1000,1000,1000])self.kf.P[4:, 4:] *= 1000.self.kf.P *= 10.# [[ 10. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 10. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 10. 0. 0. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 0. 10. 0. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 10000. 0. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 10000. 0.]# [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 10000.]]# Q是系统状态变换误差的协方差# Q = diagonal([1, 1, 1, 1, 0.01, 0.01, 0.0001])self.kf.Q[-1, -1] *= 0.01self.kf.Q[4:, 4:] *= 0.01# [[1.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 1.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 0.e+00 1.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 1.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 1.e-02 0.e+00 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 1.e-02 0.e+00]# [0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 0.e+00 1.e-04]]# Kalman滤波器初始化时,直接用第一次观测结果赋值状态信息self.kf.x[:4] = convert_bbox_to_z(self.bbox)# 自上次未匹配成功,经过的帧数self.time_since_update = 0# 自上次未匹配成功,连续成功匹配的帧数self.hit_streak = 0def update(self, bbox):# 重置,每次匹配成功,则会调用update函数,即自上次未匹配成功,经过的帧数变为了0self.time_since_update = 0self.kf.update(convert_bbox_to_z(bbox))self.bbox = bboxif(self.hit_streak<=30):self.hit_streak+=1def predict(self):# 如果边界框面积+面积变化速度<=0,就将面积变化速度赋值为0# 因为下一时刻边框面积数值,就等于边界框面积+面积变化速度,这样处理可以防止出现面积小于0的情况if (self.kf.x[6]+self.kf.x[2]) <= 0:self.kf.x[6] *= 0.0self.kf.predict()self.time_since_update += 1if(self.time_since_update>0):self.hit_streak=0t = list(convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x)[0])#将置信度设置为上一次的被击中的conft.append(self.bbox[4])self.bbox = t#[x1,y1,x2,y2,conf]return self.bboxdef get_state(self):# 返回当前边界框估计值return convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x)工具类
当然,这里还有一些工具类。在这里:
import numpy as np
# 将 [x1,y1,x2,y2] 形式转化为 [center_x,center_y,s,r] 形式
def convert_bbox_to_z(bbox):w = bbox[2] - bbox[0]h = bbox[3] - bbox[1]x = bbox[0] + w/2.y = bbox[1] + h/2.s = w * hr = w / float(h)return np.array([x, y, s, r]).reshape((4, 1))# 输入的x是一个7维的状态向量,我们只用前4维的边框信息
# 将 [center_x,center_y,s,r] 形式转化为 [x1,y1,x2,y2] 形式
# s = w * h , r = w / h
def convert_x_to_bbox(x):w = np.sqrt(x[2] * x[3])h = x[2] / wreturn np.array([x[0]-w/2., x[1]-h/2., x[0]+w/2., x[1]+h/2.]).reshape((1, 4))import numpy as npdef calculate_iou(bbox1, bbox2):"""计算两个边界框的IOU(Intersection over Union)参数:bbox1: 第一个边界框 [x1, y1, x2, y2]bbox2: 第二个边界框 [x1, y1, x2, y2]返回:iou: IOU值"""# 确保输入的边界框为浮点数类型bbox1 = np.array(bbox1, dtype=np.float32)bbox2 = np.array(bbox2, dtype=np.float32)# 计算两个边界框的交集区域x1 = np.maximum(bbox1[0], bbox2[0])y1 = np.maximum(bbox1[1], bbox2[1])x2 = np.minimum(bbox1[2], bbox2[2])y2 = np.minimum(bbox1[3], bbox2[3])intersection = np.maximum(0, x2 - x1 + 1) * np.maximum(0, y2 - y1 + 1)# 计算两个边界框的面积area_bbox1 = (bbox1[2] - bbox1[0] + 1) * (bbox1[3] - bbox1[1] + 1)area_bbox2 = (bbox2[2] - bbox2[0] + 1) * (bbox2[3] - bbox2[1] + 1)# 计算IOUiou = intersection / (area_bbox1 + area_bbox2 - intersection)return iou多目标跟踪器
之后就是我们的Sort算法的具体实现了,也就是多目标跟踪器。这个其实好办,做组装就好了,原理也不复述了,代码当中有注释。
from sort.kalman import ObjectTrackerKF,KalmanBoxTracker
from sort.utils import calculate_iou
import numpy as np
import cv2class SortMulObjectTracker():def __init__(self, max_age=1, min_hits=1, iou_threshold=0.3):self.max_age = max_ageself.min_hits = min_hitsself.iou_threshold = iou_threshold # 0.3self.trackers = {}self.counts = {}self.colours = np.random.rand(32, 3) * 255#本次匹配的情况self.match_curr = {}"""trackers的数据类型是{类别:[tracker1,tracker2,tracker3]}在进行跟踪的时候,需要输入的数据结构为:{类别:[bbox,bbox]}其中bbox:[x1,y1,x2,y2,conf]为了进行匹配,我们将实现匈牙利算法进行匹配"""def __match(self,st,match,a,pre_bboxs,bboxs,trackers_cls):for j in range(len(pre_bboxs)):iou_a_j = calculate_iou(pre_bboxs[j], bboxs[a][:4])if (not st.get(j,False)):st[j] = True"""没有被匹配,iou超过阈值,并且被命中次数大于最小命中次数,进行匹配"""if (match.get(j,[False,False]) == [False,False]):if(iou_a_j>=self.iou_threshold):match[j] = [a,iou_a_j]return Truereturn Falseelse:if(iou_a_j > match[j][1] andself.__match(st, match, match[j][0],pre_bboxs,bboxs,trackers_cls)):match[j] = [a,iou_a_j]return Truereturn Falsedef HunagerWithTrackers(self,bboxs,trackers_cls,cls):"""右侧的集合元素和左侧的谁进行了匹配,这里记录的是下标,这个算法模板在图算法专栏当中出现了现在将其运用在实际项目当中,不同的是,这里匹配的时候,还要计算一下甜蜜值‘iou'以前我们是默认,只要女方匹配的男嘉宾可以找到新欢,就让那个男嘉宾找新欢,现在是,按照亲密度最高来匹配因此match:{1:[1,0.9]}"""match = {}hit_set = []bboxs_ids = [i for i in range(len(bboxs))]pre_bboxs = [trackers_.predict() for trackers_ in trackers_cls]for i in bboxs_ids:# 表示右边的那个集合元素有没有遍历,因为每次新上场的男嘉宾不知道女嘉宾的情况,# 都需要问一遍。st = {}if(self.__match(st, match,i,pre_bboxs,bboxs,trackers_cls)):hit_set.append(i)new_bbox = set(bboxs_ids) - set(hit_set)self.match_curr[cls] = [match,new_bbox,bboxs_ids]def __gc(self,items):"""先处理,我们这边已经出现的跟踪器:param items::return:"""for cls in items.keys():match,new_bbox,bboxs_ids= self.match_curr[cls]trackers_cls = self.trackers.get(cls,[])bboxs = items[cls]#先更新for m in match.keys():trackers_cls[m].update(bboxs[match[m][0]])#然后删除need_romve = {}for i in range(len(trackers_cls)):if(trackers_cls[i].time_since_update>=self.max_ageor trackers_cls[i].hit_streak<self.min_hits):need_romve[i]=1new_trackers_cls = []for i in range(len(trackers_cls)):if(not need_romve.get(i)):new_trackers_cls.append(trackers_cls[i])#然后加入新的跟踪器for i in new_bbox:new_tracker = KalmanBoxTracker(bboxs[i])new_tracker.id = len(new_trackers_cls)new_trackers_cls.append(new_tracker)self.counts[cls] = self.counts.get(cls, 0) + 1#最后生效self.trackers[cls] = new_trackers_clscur_keys = set(items.keys())have_keys = set(self.trackers.keys())#没有出现的类别进行处理not_go = have_keys-cur_keysfor n_key in not_go:trackers_cls = self.trackers[n_key]#全部预测一下,刷新_ = [trackers_.predict() for trackers_ in trackers_cls]#执行删除操作即可need_romve = {}for i in range(len(trackers_cls)):if (trackers_cls[i].time_since_update >= self.max_ageor trackers_cls[i].hit_streak < self.min_hits):need_romve[i] = 1new_trackers_cls = []for i in range(len(trackers_cls)):if (not need_romve.get(i)):new_trackers_cls.append(trackers_cls[i])#完成更新self.trackers[n_key] = new_trackers_clsdef drawTracks(self,frame):for cls in self.trackers.keys():cls_trackers = self.trackers.get(cls)for cls_tracker in cls_trackers:frame = self.drawTrack(frame,cls_tracker,cls)return framedef drawTrack(self,frame,tracker,cls):#根具当前的跟踪器返回的情况,进行跟踪color = self.colours[tracker.id % 32]cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(tracker.bbox[0]), int(tracker.bbox[1])), (int(tracker.bbox[2]),int(tracker.bbox[3])), color, thickness=2)label = '%.2f' % tracker.bbox[4]label = '%s:%s' % (cls, label)label = label+"-ID:"+str(tracker.id)# Display the label at the top of the bounding boxlabelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)top = max(int(tracker.bbox[1]), labelSize[1])# cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine), (255,255,255), cv.FILLED)cv2.putText(frame, label, (int(tracker.bbox[0]), top - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, color, thickness=1)return framedef tracker(self,items):#注意这里的cls都是指标签名for cls in items.keys():trackers_cls = self.trackers.get(cls,[])items_bbox = items.get(cls)self.HunagerWithTrackers(items_bbox,trackers_cls,cls)self.__gc(items)到此,Sort算法实现完毕。
整合
之后的话,就是我们的算法整合了。这个很重要,但是也不难。
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import argparse
import onnxruntime as ort
from sort.tracker import SortMulObjectTrackerclass yolov5_sort():"""同时实现目标检测和目标跟踪"""def __init__(self, model_pb_path, label_path, confThreshold=0.5, nmsThreshold=0.5, objThreshold=0.5):so = ort.SessionOptions()so.log_severity_level = 3self.net = ort.InferenceSession(model_pb_path, so)self.classes = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open(label_path, 'r').readlines()))self.num_classes = len(self.classes)anchors = [[10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23],[30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119],[116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]]self.colours = np.random.rand(32, 3) * 255self.nl = len(anchors)self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2self.no = self.num_classes + 5self.grid = [np.zeros(1)] * self.nlself.stride = np.array([8., 16., 32.])self.anchor_grid = np.asarray(anchors, dtype=np.float32).reshape(self.nl, -1, 2)self.confThreshold = confThresholdself.nmsThreshold = nmsThresholdself.objThreshold = objThresholdself.input_shape = (self.net.get_inputs()[0].shape[2], self.net.get_inputs()[0].shape[3])self.sortMulTrackers = SortMulObjectTracker(max_age=10, min_hits=1, iou_threshold=0.3)def resize_image(self, srcimg, keep_ratio=True):"""根据网络的输入要求,将图片进行resize:param srcimg::param keep_ratio::return:"""top, left, newh, neww = 0, 0, self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1]if keep_ratio and srcimg.shape[0] != srcimg.shape[1]:hw_scale = srcimg.shape[0] / srcimg.shape[1]if hw_scale > 1:newh, neww = self.input_shape[0], int(self.input_shape[1] / hw_scale)img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)left = int((self.input_shape[1] - neww) * 0.5)img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 0, 0, left, self.input_shape[1] - neww - left, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,value=0) # add borderelse:newh, neww = int(self.input_shape[0] * hw_scale), self.input_shape[1]img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)top = int((self.input_shape[0] - newh) * 0.5)img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, self.input_shape[0] - newh - top, 0, 0, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0)else:img = cv2.resize(srcimg, self.input_shape, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)return img, newh, neww, top, leftdef _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20):xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(ny), np.arange(nx))return np.stack((xv, yv), 2).reshape((-1, 2)).astype(np.float32)def postprocess_sort(self, frame, outs, pad_hw):newh, neww, padh, padw = pad_hwframeHeight = frame.shape[0]frameWidth = frame.shape[1]ratioh, ratiow = frameHeight / newh, frameWidth / neww# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.classIds = []confidences = []box_index = []boxes = []outs = outs[outs[:, 4] > self.objThreshold]for detection in outs:scores = detection[5:]classId = np.argmax(scores)confidence = scores[classId]if confidence > self.confThreshold: # and detection[4] > self.objThreshold:center_x = int((detection[0] - padw) * ratiow)center_y = int((detection[1] - padh) * ratioh)width = int(detection[2] * ratiow)height = int(detection[3] * ratioh)left = int(center_x - width / 2)top = int(center_y - height / 2)classIds.append(classId)confidences.append(float(confidence))boxes.append([left, top, width, height])# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with# lower confidences.# print(boxes)indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold)for ix in indices:box_index.append(ix)items = {}for i in box_index:box = boxes[i]x1 = box[0]y1 = box[1]x2 = box[2]+x1y2 = box[3]+y1conf = confidences[i]cls = self.classes[classIds[i]]items[cls] = items.get(cls,[])items[cls].append([x1,y1,x2,y2,conf])#完成目标跟踪self.sortMulTrackers.tracker(items)frame = self.sortMulTrackers.drawTracks(frame)print(self.sortMulTrackers.counts)return frame,boxesdef detect_sort(self, srcimg):img, newh, neww, top, left = self.resize_image(srcimg)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0blob = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)), axis=0)t1 = time.time()outs = self.net.run(None, {self.net.get_inputs()[0].name: blob})[0].squeeze(axis=0)cost_time = time.time() - t1# print(outs.shape)row_ind = 0for i in range(self.nl):h, w = int(self.input_shape[0] / self.stride[i]), int(self.input_shape[1] / self.stride[i])length = int(self.na * h * w)if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != (h, w):self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(w, h)outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + np.tile(self.grid[i], (self.na, 1))) * int(self.stride[i])outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * np.repeat(self.anchor_grid[i], h * w, axis=0)row_ind += lengthsrcimg,boxes = self.postprocess_sort(srcimg, outs, (newh, neww, top, left))infer_time = 'Inference Time: ' + str(int(cost_time * 1000)) + 'ms'cv2.putText(srcimg, infer_time, (5, 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), thickness=1)return srcimg,boxesdef postprocess(self, frame, outs, pad_hw):newh, neww, padh, padw = pad_hwframeHeight = frame.shape[0]frameWidth = frame.shape[1]ratioh, ratiow = frameHeight / newh, frameWidth / neww# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.classIds = []confidences = []box_index = []boxes = []outs = outs[outs[:, 4] > self.objThreshold]for detection in outs:scores = detection[5:]classId = np.argmax(scores)confidence = scores[classId]if confidence > self.confThreshold: # and detection[4] > self.objThreshold:center_x = int((detection[0] - padw) * ratiow)center_y = int((detection[1] - padh) * ratioh)width = int(detection[2] * ratiow)height = int(detection[3] * ratioh)left = int(center_x - width / 2)top = int(center_y - height / 2)classIds.append(classId)confidences.append(float(confidence))boxes.append([left, top, width, height])# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with# lower confidences.# print(boxes)indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold)for ix in indices:box_index.append(ix)for i in box_index:box = boxes[i]left = box[0]top = box[1]width = box[2]height = box[3]frame = self.drawPred(frame, classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)return frame,boxesdef drawPred(self, frame, classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):# Draw a bounding box.color = self.colours[classId % 32]cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), color, thickness=2)label = '%.2f' % conflabel = '%s:%s' % (self.classes[classId], label)# Display the label at the top of the bounding boxlabelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)top = max(top, labelSize[1])# cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine), (255,255,255), cv.FILLED)cv2.putText(frame, label, (left, top - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, color, thickness=1)return framedef showFps(self,frame,fps):cv2.putText(frame, 'FPS:{}'.format(int(fps)),(50, 50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.6, (255, 0, 255), 2)return framedef detect(self, srcimg):img, newh, neww, top, left = self.resize_image(srcimg)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0blob = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)), axis=0)t1 = time.time()outs = self.net.run(None, {self.net.get_inputs()[0].name: blob})[0].squeeze(axis=0)cost_time = time.time() - t1# print(outs.shape)row_ind = 0for i in range(self.nl):h, w = int(self.input_shape[0] / self.stride[i]), int(self.input_shape[1] / self.stride[i])length = int(self.na * h * w)if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != (h, w):self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(w, h)outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + np.tile(self.grid[i], (self.na, 1))) * int(self.stride[i])outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * np.repeat(self.anchor_grid[i], h * w, axis=0)row_ind += lengthsrcimg,boxes = self.postprocess(srcimg, outs, (newh, neww, top, left))infer_time = 'Inference Time: ' + str(int(cost_time * 1000)) + 'ms'cv2.putText(srcimg, infer_time, (5, 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), thickness=1)return srcimg,boxesclass RunTime:def __init__(self):self.net = yolov5_sort(args.modelpath, args.classfile, confThreshold=args.confThreshold,nmsThreshold=args.nmsThreshold)def run(self):"""打开摄像头:return:"""cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)if not cam.isOpened():raise RuntimeError("无法打开摄像头")# 循环读取和处理每一帧图像while True:ret, frame = cam.read()if not ret:break# 进行目标检测start = time.time()#进行推理检测,返回的是绘制好的图片frame,boxes = self.net.detect(frame)end = time.time()fps = 1 / (end - start)# 绘制边界框,也是返回绘制好的图篇,把这个图片进行发布即可frame = self.net.showFps(frame,fps)# 显示图像cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)# 检测按键来退出循环if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):break# 释放摄像头资源cam.release()# 关闭所有窗口cv2.destroyAllWindows()def run_sort(self,fps):"""打开摄像头注意,这里的话,会受到fps的影响:return:"""cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)if not cam.isOpened():raise RuntimeError("无法打开摄像头")# 循环读取和处理每一帧图像p_time = (1/fps)while True:ret, frame = cam.read()if not ret:break# 进行目标检测start = time.time()# 进行推理检测,返回的是绘制好的图片frame, boxes = self.net.detect_sort(frame)end = time.time()s_p = (end - start)time.sleep(p_time-s_p)end = time.time()t_fps = 1/(end-start)# 绘制边界框,也是返回绘制好的图篇,把这个图片进行发布即可frame = self.net.showFps(frame, t_fps)# 显示图像cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)# 检测按键来退出循环if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):break# 释放摄像头资源cam.release()# 关闭所有窗口cv2.destroyAllWindows()if __name__ == '__main__':parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument('--modelpath', type=str, default=r'F:\projects\PythonProject\YOLOv5-Lite-master\weights\v5lite-e.onnx', help="onnx filepath")parser.add_argument('--classfile', type=str, default='coco.names', help="classname filepath")parser.add_argument('--confThreshold', default=0.5, type=float, help='class confidence')parser.add_argument('--nmsThreshold', default=0.6, type=float, help='nms iou thresh')args = parser.parse_args()runner = RunTime()# runner.run()runner.run_sort(30)
这样的话,就完成了基本的算法整合,后面按照自己的需求去修改定制即可。
具体流程就不搞了,因为比较简单。

![[Visual Studio 报错] error 找不到指定的 SDK“Microsoft](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f453b0ee14720ffeb38cc9cf2febf1eb.png)