目录
- bind1st和bind2nd什么时候会用到
- bind1st和bind2nd的底层实现原理
- function函数对象类型的应用示例
- lambda表达式的应用实践
橙色
绑定器和函数对象operator()
函数对象就是对象拥有()运算符重载函数,这个对象使用起来就跟函数调用特别相似。
1.C++ STL中的绑定器
bind1st:operator ()的第一个形参变量绑定成一个确定的值
bind2nd:operator ()的第二个形参变量绑定成一个确定的值
2.C++11从Boost库中引入了bind绑定器和function函数对象机制
3.lambda表达式,底层依赖函数对象的机制实现的
bind1st和bind2nd什么时候会用到
bind1st和bind2nd这两个函数在functional库中。这两个函数都是用在二元函数对象身上的
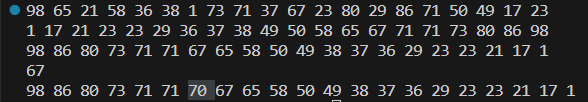
注意代码第36行,find_if的第三个参数是需要一个一元的函数对象,因为它需要一次从容器中取出一个元素与70进行比较。因此没法直接使用algorithm库里的greater()等函数对象,因为它们都是二元的。
所以就引入了bind1st和bind2nd
绑定器+二元函数对象=一元函数对象
下面的例子中,通过find_if找到了小于70的第一个数,并把70插在了它的前面。greater()函数对象的逻辑是a>b,通过bind1st(greater(), 70)其函数对象的逻辑就变成了70>b,依此来寻找小于70的第一个元素。
同样也可以用less()来实现寻找小于70的第一个数的功能,因为该函数对象的逻辑是a<b,所以bind2nd(greater(), 70),其逻辑就变成了a<70。同样是寻找小于70的第一个元素
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;template<typename Container>
void showContainer(Container &con)
{typename Container::iterator it = con.begin();for (; it != con.end();it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main(){vector<int> vec;srand(time(nullptr));for (int i = 0; i < 20;i++){vec.push_back(rand()% 100 + 1);}showContainer(vec);sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); //默认从小到大showContainer(vec);//greater 二元函数对象sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), greater<int>());showContainer(vec);/*把70按顺序插入到vec容器当中 找第一个小于70的数字*/auto it1 = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind1st(greater<int>(), 70));cout << *it1 << endl;if (it1 != vec.end()) {vec.insert(it1, 70);}showContainer(vec);return 0;
}
bind1st和bind2nd的底层实现原理
这段代码是很精妙的,下面有详细的解释,可以好好看看
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;template<typename Container>
void showContainer(Container &con)
{typename Container::iterator it = con.begin();for (; it != con.end();it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}template<typename Iterator,typename Compare>
Iterator my_find_if(Iterator first,Iterator last,Compare comp)
{for (; first != last;++first){if(comp(*first))//comp.operator()(*first){return first;}} return last;
}template<typename Compare,typename T>
class _mybind1st
{
public:_mybind1st(Compare comp,T val):_comp(comp),_val(val){}bool operator()(const T&second){return _comp(_val, second);}
private:Compare _comp;T _val;
};template<typename Compare,typename T>
_mybind1st<Compare,T> mybind1st(Compare comp,const T &val)
{return _mybind1st<Compare, T>(comp, val);
}int main(){vector<int> vec;srand(time(nullptr));for (int i = 0; i < 20;i++){vec.push_back(rand()% 100 + 1);}//greater 二元函数对象sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), greater<int>());showContainer(vec);/*把70按顺序插入到vec容器当中 找第一个小于70的数字*/auto it1 = my_find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), mybind1st(greater<int>(), 70));cout << *it1 << endl;if (it1 != vec.end()) {vec.insert(it1, 70);}showContainer(vec);return 0;
}
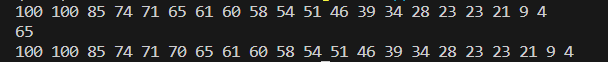
上面这段代码是对bind绑定器函数的一个实现。我的目标是在已经按降序排列的容器中把70按顺序插入到容器中,其实也就是找到小于70的第一个数字。my_find_if函数的形参有三个,分别是初始的迭代器,末尾的迭代器和一个二元函数对象。这个二元函数对象形参实际上传入的参数是mybind1st(greater(), 70),也就是传入的是mybind1st函数的返回值。
mybind1st函数返回的是一个二元函数对象_mybind1st<Compare, T>(comp, val),看本文最开始函数对象的定义,其实返回的就是一个有()运算符重载的类对象,因为_mybind1st<Compare, T>(comp, val)已经算是调用了构造函数对这个类对象进行初始化了。其类成员变量_comp为greater(),_val为val
所以呢,my_find_if中的第3个形参cmp在本代码中实际上就是_mybind1st<Compare, T>(comp, val)。my_find_if函数内的comp(*first)其实就是调用了_mybind1st类对象的()运算符重载。也就是下面这段代码:
bool operator()(const T&second){return _comp(_val, second);}
也就是挨个把_val(为70)和迭代器所指向的元素一起传入到_comp函数对象(也就是greater())中,看70是否大于该迭代器所指向的元素,是的话就返回该迭代器(也就是寻找到小于70的第一个元素,代码中容器初始顺序是从大到小)。
function函数对象类型的应用示例
使用functioal函数对象类型需要头文件< functional >.
下面是几个简单的应用:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include<string>
using namespace std;/*
function :绑定器,函数对象,lambda表达式它们只能使用在一条语句中
*/
void hello1()
{cout << "hello world!" << endl;
}void hello2(string str)
{cout << str << endl;
} int sum(int a,int b)
{return a + b;
}
int main()
{//从function的类模板定义处,看到希望用一个函数类型实例化functionfunction<void()> func1 = hello1;func1(); //func1.operator()()=>hello1()function<void(string)> func2 = hello2;func2("hello hello2"); //func2.operator()(string str)=>hello2(str)function<int(int, int)> func3 = sum;cout << func3(20, 30)<<endl;function<int(int,int)>func4=[](int a,int b)->int {return a+b;};cout << func4(20, 30) << endl;return 0;
}
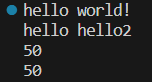
上面这些例子都是通过function函数对象指向函数的,但function函数对象不仅可以指向函数,也可以指向类中的成员函数,但就没办法直接指向了,而是必须依赖于一个对象,参考下面的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Test
{
public://必须依赖一个对象void hello(string str) { cout << str << endl; }
};
int main()
{//因为类对象自带一个this指针,所以参数是两个function<void(Test *, string)> func5 = &Test::hello;Test a;func5(&a, "call Test::hello!");return 0;
}
看完上面这些内容,那function到底强大在哪里呢?直接用函数不也可以吗?看下面这个例子:
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;void doShowAllBooks() { cout << "查看所有书籍信息" << endl; }
void doBorrow() { cout << "借书" << endl; }
void doBack() { cout << "还书" << endl; }
void doQueryBooks() { cout << "查询书籍" << endl; }
void doLoginOut() { cout << "注销" << endl; }
int main()
{int choice = 0;map<int, function<void()>> actionMap;actionMap.insert({1, doShowAllBooks});actionMap.insert({2, doBorrow});actionMap.insert({3, doBack});actionMap.insert({4, doQueryBooks});actionMap.insert({5, doLoginOut});for (;;){cout << "---------------------" << endl;cout << "1、查看所有书籍信息" << endl;cout << "2、借书" << endl;cout << "3、还书" << endl;cout << "4、查询书籍" << endl;cout << "5、注销" << endl;cout << "---------------------" << endl;cout << "请选择:";cin >> choice; auto it=actionMap.find(choice);if(it==actionMap.end()){cout << "输入数字无效,重新选择" << endl;}else{it->second();}}return 0;
}
假如直接在主函数中通过switch来实现也可以,但就不符合写代码的开闭原则;而且后面想加减功能就必须在主函数中改动。但像我们这么写,清晰明了,无论后续对功能作何种改动,都可以直接在相应函数上该,而不需要对主函数进行大的改动。
lambda表达式的应用实践
lambda表达式的语法:


举个例子
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> vec = {9, 7, 4, 2};//寻找第一个小于5的数字,并按照降序插入其中auto it = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [=](int a) -> bool{ return a < 5; });if(it!=vec.end()){vec.insert(it, 5);}for(int val:vec){cout << val << " ";}cout <<endl;//找vec中的偶数并输出for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a){if(a%2==0)cout << a << " "; });cout << endl;return 0;
}
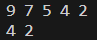
既然 lambda 表达式只能使用在语句当中,如果想跨语句使用之前定义好的lambda表达式,怎么办?用什么类型来表示lambda表达式?
当然是用function类型来表示函数对象的类型了
下面是一个函数对象方面应用的例子
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;//lambda表达式=》函数对象int main()
{map<int, function<int(int, int)>> caculateMap;caculateMap[1]=[](int a,int b)->int{return a+b;};caculateMap[2]=[](int a,int b)->int{return a-b;};caculateMap[3]=[](int a,int b)->int{return a*b;};caculateMap[4]=[](int a,int b)->int{return a/b;};cout << "选择:";int choice;cin >> choice;cout << "10+15:" << caculateMap[choice](10, 15) << endl;return 0;return 0;
}
再举一个智能指针自定义删除器方面的例子:
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<memory>
using namespace std;int main()
{unique_ptr<FILE, function<void(FILE *)>> ptr1(fopen("data.txt", "w"), [](FILE *pf){ fclose(pf); });return 0;
}
再举一个优先队列的例子:
下面的代码是会报错误的,因为优先队列默认的情况下维护的是一个大堆,即权值以从高到低排列。但此时传入的是一个自定义变量Data,所以就不知道该怎么排了
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;class Data
{
public:Data(int val1=10,int val2=10):ma(val1),mb(val2){}int ma;int mb;
};int main()
{priority_queue<Data> queue;queue.push(Data(10, 20));queue.push(Data(15, 15));queue.push(Data(20, 10));return 0;
}
我们可以通过lambda匿名函数这么写:
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;class Data
{
public:Data(int val1=10,int val2=10):ma(val1),mb(val2){}int ma;int mb;
};int main()
{using FUNC = function<bool(Data &, Data &)>;priority_queue<Data, vector<Data>, FUNC>maxHeap([](Data &d1, Data &d2) -> bool{ return d1.ma > d2.ma;});maxHeap.push(Data(10, 20));maxHeap.push(Data(15, 15));maxHeap.push(Data(20, 10));return 0;
}