Title: Umeyama 算法之源码阅读与测试
文章目录
- 前言
- I. Eigen 中 Umeyama 算法源码
- 1. Eigen/src/Geometry/Umeyama.h 源码
- 2. 代码测试
- II. PCL 中 Umeyama 算法源码
- III. evo 中 Umeyama 算法源码
- 1. evo/core/geometry.py 源码
- 2. 代码测试
- 总结
- 参考文献
[相关博文介绍]
- 矩阵乘法可交换与可同时对角化的关系 —— Umeyama 算法推导的数学准备 (I)
- 旋转矩阵约束下的朗格朗日乘子 —— Umeyama 算法推导的数学准备 (II)
- 矩阵乘操作、三角化、开方特征值 —— Umeyama 算法推导的数学准备 (III)
- 奇异值分解之常用结论
- 旋转参数的最小方差估计 —— Umeyama 算法详细推导 (I)
- 相似变换参数 (旋转、平移、缩放) 的最小方差估计 —— Umeyama 算法详细推导 (II)
- Umeyama 算法之源码阅读与测试
前言
SLAM 轨迹的对齐和评估时, 多用 Umeyama 算法实现.
该算法从给定的两个欧几里得空间的关联点集中找出最小误差平方意义下的相似变换参数 (Similarity Transformation, 旋转+平移+缩放)[1].
在上一篇博文中, 我们已经详细推导了该算法的数学原理.
这里我们看一下实际应用中 Umeyama 算法的源码实现, 分别是
- Eigen[2] 中 Umeyama 算法源码
- PCL[3] 中 Umeyama 算法源码
- evo[4] 中 Umeyama 算法源码
(看现成的算法源码还是比推导公式稍微轻松一点.)
I. Eigen 中 Umeyama 算法源码
1. Eigen/src/Geometry/Umeyama.h 源码
/**
* \geometry_module \ingroup Geometry_Module
*
* \brief Returns the transformation between two point sets.
*
* The algorithm is based on:
* "Least-squares estimation of transformation parameters between two point patterns",
* Shinji Umeyama, PAMI 1991, DOI: 10.1109/34.88573
*
* It estimates parameters \f$ c, \mathbf{R}, \f$ and \f$ \mathbf{t} \f$ such that
* \f{align*}
* \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n \vert\vert y_i - (c\mathbf{R}x_i + \mathbf{t}) \vert\vert_2^2
* \f}
* is minimized.
*
* The algorithm is based on the analysis of the covariance matrix
* \f$ \Sigma_{\mathbf{x}\mathbf{y}} \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times d} \f$
* of the input point sets \f$ \mathbf{x} \f$ and \f$ \mathbf{y} \f$ where
* \f$d\f$ is corresponding to the dimension (which is typically small).
* The analysis is involving the SVD having a complexity of \f$O(d^3)\f$
* though the actual computational effort lies in the covariance
* matrix computation which has an asymptotic lower bound of \f$O(dm)\f$ when
* the input point sets have dimension \f$d \times m\f$.
*
* Currently the method is working only for floating point matrices.
*
* \todo Should the return type of umeyama() become a Transform?
*
* \param src Source points \f$ \mathbf{x} = \left( x_1, \hdots, x_n \right) \f$.
* \param dst Destination points \f$ \mathbf{y} = \left( y_1, \hdots, y_n \right) \f$.
* \param with_scaling Sets \f$ c=1 \f$ when <code>false</code> is passed.
* \return The homogeneous transformation
* \f{align*}
* T = \begin{bmatrix} c\mathbf{R} & \mathbf{t} \\ \mathbf{0} & 1 \end{bmatrix}
* \f}
* minimizing the residual above. This transformation is always returned as an
* Eigen::Matrix.
*/
template <typename Derived, typename OtherDerived>
typename internal::umeyama_transform_matrix_type<Derived, OtherDerived>::type
umeyama(const MatrixBase<Derived>& src, const MatrixBase<OtherDerived>& dst, bool with_scaling = true)
{typedef typename internal::umeyama_transform_matrix_type<Derived, OtherDerived>::type TransformationMatrixType;typedef typename internal::traits<TransformationMatrixType>::Scalar Scalar;typedef typename NumTraits<Scalar>::Real RealScalar;EIGEN_STATIC_ASSERT(!NumTraits<Scalar>::IsComplex, NUMERIC_TYPE_MUST_BE_REAL)EIGEN_STATIC_ASSERT((internal::is_same<Scalar, typename internal::traits<OtherDerived>::Scalar>::value),YOU_MIXED_DIFFERENT_NUMERIC_TYPES__YOU_NEED_TO_USE_THE_CAST_METHOD_OF_MATRIXBASE_TO_CAST_NUMERIC_TYPES_EXPLICITLY)enum { Dimension = EIGEN_SIZE_MIN_PREFER_DYNAMIC(Derived::RowsAtCompileTime, OtherDerived::RowsAtCompileTime) };typedef Matrix<Scalar, Dimension, 1> VectorType;typedef Matrix<Scalar, Dimension, Dimension> MatrixType;typedef typename internal::plain_matrix_type_row_major<Derived>::type RowMajorMatrixType;const Index m = src.rows(); // dimensionconst Index n = src.cols(); // number of measurements// required for demeaning ...const RealScalar one_over_n = RealScalar(1) / static_cast<RealScalar>(n);// computation of meanconst VectorType src_mean = src.rowwise().sum() * one_over_n;const VectorType dst_mean = dst.rowwise().sum() * one_over_n;// demeaning of src and dst pointsconst RowMajorMatrixType src_demean = src.colwise() - src_mean;const RowMajorMatrixType dst_demean = dst.colwise() - dst_mean;// Eq. (36)-(37)const Scalar src_var = src_demean.rowwise().squaredNorm().sum() * one_over_n;// Eq. (38)const MatrixType sigma = one_over_n * dst_demean * src_demean.transpose();JacobiSVD<MatrixType> svd(sigma, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);// Initialize the resulting transformation with an identity matrix...TransformationMatrixType Rt = TransformationMatrixType::Identity(m+1,m+1);// Eq. (39)VectorType S = VectorType::Ones(m);if ( svd.matrixU().determinant() * svd.matrixV().determinant() < 0 )S(m-1) = -1;// Eq. (40) and (43)Rt.block(0,0,m,m).noalias() = svd.matrixU() * S.asDiagonal() * svd.matrixV().transpose();if (with_scaling){// Eq. (42)const Scalar c = Scalar(1)/src_var * svd.singularValues().dot(S);// Eq. (41)Rt.col(m).head(m) = dst_mean;Rt.col(m).head(m).noalias() -= c*Rt.topLeftCorner(m,m)*src_mean;Rt.block(0,0,m,m) *= c;}else{Rt.col(m).head(m) = dst_mean;Rt.col(m).head(m).noalias() -= Rt.topLeftCorner(m,m)*src_mean;}return Rt;
}代码实现是完全按照 Umeyama 论文中的 [定理] 展开的, 理解了这些公式的来龙去脉, 就能很好的理解上面的代码. 我们没有多余的话要说的了.
2. 代码测试
我们根据 Eigen 中提供的单元测试代码 test/umeyama.cpp, 简单改写一下进行了测试.
// This file is part of Eigen, a lightweight C++ template library
// for linear algebra.
//
// Copyright (C) 2009 Hauke Heibel <hauke.heibel@gmail.com>
//
// This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla
// Public License v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed
// with this file, You can obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>#include <Eigen/LU> // required for MatrixBase::determinant
#include <Eigen/SVD> // required for SVD
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace Eigen;// Constructs a random matrix from the unitary group U(size).
template <typename T>
Eigen::Matrix<T, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> randMatrixUnitary(int size)
{typedef T Scalar;typedef Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> MatrixType;MatrixType Q;int max_tries = 40;bool is_unitary = false;while (!is_unitary && max_tries > 0){// initialize random matrixQ = MatrixType::Random(size, size);// orthogonalize columns using the Gram-Schmidt algorithmfor (int col = 0; col < size; ++col){typename MatrixType::ColXpr colVec = Q.col(col);for (int prevCol = 0; prevCol < col; ++prevCol){typename MatrixType::ColXpr prevColVec = Q.col(prevCol);colVec -= colVec.dot(prevColVec)*prevColVec;}Q.col(col) = colVec.normalized();}// this additional orthogonalization is not necessary in theory but should enhance// the numerical orthogonality of the matrixfor (int row = 0; row < size; ++row){typename MatrixType::RowXpr rowVec = Q.row(row);for (int prevRow = 0; prevRow < row; ++prevRow){typename MatrixType::RowXpr prevRowVec = Q.row(prevRow);rowVec -= rowVec.dot(prevRowVec)*prevRowVec;}Q.row(row) = rowVec.normalized();}// final checkis_unitary = Q.isUnitary();--max_tries;}if (max_tries == 0)eigen_assert(false && "randMatrixUnitary: Could not construct unitary matrix!");return Q;
}// Constructs a random matrix from the special unitary group SU(size).
template <typename T>
Eigen::Matrix<T, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> randMatrixSpecialUnitary(int size)
{typedef T Scalar;typedef Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> MatrixType;// initialize unitary matrixMatrixType Q = randMatrixUnitary<Scalar>(size);// tweak the first column to make the determinant be 1Q.col(0) *= numext::conj(Q.determinant());return Q;
}template <typename MatrixType>
void run_test(int dim, int num_elements)
{using std::abs;typedef typename internal::traits<MatrixType>::Scalar Scalar;typedef Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> MatrixX;typedef Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, 1> VectorX;// MUST be positive because in any other case det(cR_t) may become negative for// odd dimensions!srand((unsigned)time(NULL));const Scalar c = abs(internal::random<Scalar>());MatrixX R = randMatrixSpecialUnitary<Scalar>(dim);VectorX t = Scalar(50)*VectorX::Random(dim,1);MatrixX cR_t = MatrixX::Identity(dim+1,dim+1);cR_t.block(0,0,dim,dim) = c*R;cR_t.block(0,dim,dim,1) = t;std::cout << "[c]:\n" << c << "\n" << std::endl;std::cout << "[R]:\n"<< R << "\n" << std::endl;std::cout << "[t]:\n"<< t << "\n" << std::endl;std::cout << "[Original cR_t]:\n"<< cR_t << "\n" << std::endl;MatrixX src = MatrixX::Random(dim+1, num_elements);src.row(dim) = Matrix<Scalar, 1, Dynamic>::Constant(num_elements, Scalar(1));MatrixX dst = cR_t*src;MatrixX cR_t_umeyama = umeyama(src.block(0,0,dim,num_elements), dst.block(0,0,dim,num_elements));const Scalar error = ( cR_t_umeyama*src - dst ).norm() / dst.norm();// VERIFY(error < Scalar(40)*std::numeric_limits<Scalar>::epsilon());std::cout << "[cR_t_umeyama]:\n"<< cR_t_umeyama << "\n" << std::endl;std::cout << "[error]:\n"<< error << "\n" << std::endl;}int main(int argc, char** argv)
{std::cout << "\n----- First Experiment -----" << std::endl; run_test<MatrixXf>(3, 20);sleep(1);std::cout << "\n----- Second Experiment -----" << std::endl; run_test<MatrixXf>(4, 10);return 0;
}
这里我们进行了两组测试, 一组是 3 维空间中的 20 个随机数据点, 另一组是 4 维空间中的 10 个随机数据点.
将随机数据点保存为原始点云, 通过随机生成的相似变换 (旋转、平移、缩放) 从原始点云变换到目标点云.
利用 Umeyama 算法, 由原始点云和目标点云数据计算出该相似变换矩阵.
测试结果如下, 比较 [Original cR_t] 和 [cR_t_umeyama] 两个矩阵, 可以看出算法能够成功计算出相似变换参数.
----- First Experiment -----
[c]:
0.737838[R]:0.27562 -0.872498 0.403461
-0.780523 -0.448117 -0.4358620.561086 -0.194778 -0.804514[t]:4.90685
-11.29446.41211[Original cR_t]:0.203363 -0.643762 0.297689 4.90685
-0.575899 -0.330638 -0.321596 -11.29440.413991 -0.143715 -0.593601 6.412110 0 0 1[cR_t_umeyama]:0.203363 -0.643763 0.297689 4.90685
-0.575899 -0.330638 -0.321596 -11.29440.413991 -0.143715 -0.593602 6.412110 0 0 1[error]:
7.80264e-08----- Second Experiment -----
[c]:
0.0245536[R]:
-0.449366 -0.347432 -0.438747 0.696321
-0.449418 0.583524 -0.572782 -0.359784
0.0110775 -0.718994 -0.37278 -0.5864820.771991 0.147782 -0.583487 0.204285[t]:10.0548.1491
-14.796228.6888[Original cR_t]:-0.0110336 -0.0085307 -0.0107728 0.0170972 10.05-0.0110348 0.0143276 -0.0140639 -0.00883398 48.1491
0.000271992 -0.0176539 -0.00915309 -0.0144002 -14.79620.0189552 0.00362858 -0.0143267 0.00501594 28.68880 0 0 0 1[cR_t_umeyama]:-0.0110338 -0.00853069 -0.0107728 0.0170973 10.05-0.0110348 0.0143278 -0.014064 -0.00883401 48.1491
0.000271604 -0.017654 -0.00915301 -0.0144004 -14.79620.0189553 0.00362824 -0.014327 0.00501585 28.68880 0 0 0 1[error]:
7.49672e-08II. PCL 中 Umeyama 算法源码
registration/include/pcl/registration/impl/transformation_estimation_svd.hpp 源码如下:
template <typename PointSource, typename PointTarget, typename Scalar>
inline void
TransformationEstimationSVD<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::estimateRigidTransformation(ConstCloudIterator<PointSource>& source_it,ConstCloudIterator<PointTarget>& target_it,Matrix4& transformation_matrix) const
{// Convert to Eigen formatconst int npts = static_cast<int>(source_it.size());if (use_umeyama_) {Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, Eigen::Dynamic> cloud_src(3, npts);Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, Eigen::Dynamic> cloud_tgt(3, npts);for (int i = 0; i < npts; ++i) {cloud_src(0, i) = source_it->x;cloud_src(1, i) = source_it->y;cloud_src(2, i) = source_it->z;++source_it;cloud_tgt(0, i) = target_it->x;cloud_tgt(1, i) = target_it->y;cloud_tgt(2, i) = target_it->z;++target_it;}// Call Umeyama directly from Eigen (PCL patched version until Eigen is released)transformation_matrix = pcl::umeyama(cloud_src, cloud_tgt, false);}else {source_it.reset();target_it.reset();// <cloud_src,cloud_src> is the source datasettransformation_matrix.setIdentity();Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 4, 1> centroid_src, centroid_tgt;// Estimate the centroids of source, targetcompute3DCentroid(source_it, centroid_src);compute3DCentroid(target_it, centroid_tgt);source_it.reset();target_it.reset();// Subtract the centroids from source, targetEigen::Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> cloud_src_demean,cloud_tgt_demean;demeanPointCloud(source_it, centroid_src, cloud_src_demean);demeanPointCloud(target_it, centroid_tgt, cloud_tgt_demean);getTransformationFromCorrelation(cloud_src_demean,centroid_src,cloud_tgt_demean,centroid_tgt,transformation_matrix);}
}template <typename PointSource, typename PointTarget, typename Scalar>
void
TransformationEstimationSVD<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::getTransformationFromCorrelation(const Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic>& cloud_src_demean,const Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 4, 1>& centroid_src,const Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic>& cloud_tgt_demean,const Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 4, 1>& centroid_tgt,Matrix4& transformation_matrix) const
{transformation_matrix.setIdentity();// Assemble the correlation matrix H = source * target'Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3> H =(cloud_src_demean * cloud_tgt_demean.transpose()).topLeftCorner(3, 3);// Compute the Singular Value DecompositionEigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3>> svd(H, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3> u = svd.matrixU();Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3> v = svd.matrixV();// Compute R = V * U'if (u.determinant() * v.determinant() < 0) {for (int x = 0; x < 3; ++x)v(x, 2) *= -1;}Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3> R = v * u.transpose();// Return the correct transformationtransformation_matrix.topLeftCorner(3, 3) = R;const Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 1> Rc(R * centroid_src.head(3));transformation_matrix.block(0, 3, 3, 1) = centroid_tgt.head(3) - Rc;
}} // namespace registration
} // namespace pcl
PCL 中做的是 3 维欧式空间中刚体变换, 不涉及高维空间, 且只计算了旋转参数和平移参数, 而不涉及缩放.
实现方法分为一种直接调用 Eigen 中的 Umeyama 算法实现, 另一种在 PCL 内自己实现. PCL 自己实现的部分和 Umeyama 算法类似, 确切地说是 Umeyama 算法的上一代算法. 可参考文献 [5], 我们此处不展开.
III. evo 中 Umeyama 算法源码
1. evo/core/geometry.py 源码
def umeyama_alignment(x: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray,with_scale: bool = False) -> UmeyamaResult:"""Computes the least squares solution parameters of an Sim(m) matrixthat minimizes the distance between a set of registered points.Umeyama, Shinji: Least-squares estimation of transformation parametersbetween two point patterns. IEEE PAMI, 1991:param x: mxn matrix of points, m = dimension, n = nr. of data points:param y: mxn matrix of points, m = dimension, n = nr. of data points:param with_scale: set to True to align also the scale (default: 1.0 scale):return: r, t, c - rotation matrix, translation vector and scale factor"""if x.shape != y.shape:raise GeometryException("data matrices must have the same shape")# m = dimension, n = nr. of data pointsm, n = x.shape# means, eq. 34 and 35mean_x = x.mean(axis=1)mean_y = y.mean(axis=1)# variance, eq. 36# "transpose" for column subtractionsigma_x = 1.0 / n * (np.linalg.norm(x - mean_x[:, np.newaxis])**2)# covariance matrix, eq. 38outer_sum = np.zeros((m, m))for i in range(n):outer_sum += np.outer((y[:, i] - mean_y), (x[:, i] - mean_x))cov_xy = np.multiply(1.0 / n, outer_sum)# SVD (text betw. eq. 38 and 39)u, d, v = np.linalg.svd(cov_xy)if np.count_nonzero(d > np.finfo(d.dtype).eps) < m - 1:raise GeometryException("Degenerate covariance rank, ""Umeyama alignment is not possible")# S matrix, eq. 43s = np.eye(m)if np.linalg.det(u) * np.linalg.det(v) < 0.0:# Ensure a RHS coordinate system (Kabsch algorithm).s[m - 1, m - 1] = -1# rotation, eq. 40r = u.dot(s).dot(v)# scale & translation, eq. 42 and 41c = 1 / sigma_x * np.trace(np.diag(d).dot(s)) if with_scale else 1.0t = mean_y - np.multiply(c, r.dot(mean_x))return r, t, c
很直接地由 Umeyama 论文中的 [定理] 翻译成了 Python 代码进行实现, 不做过多解释了.
2. 代码测试
根据 doc/alignment_demo.py 示例程序, 简单修改并测试.
import copy
import logging
import sysimport evo.core.lie_algebra as lie
from evo.core import trajectory
from evo.tools import plot, file_interface, logimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltlogger = logging.getLogger("evo")
log.configure_logging(verbose=True)traj_ref = file_interface.read_kitti_poses_file("../test/data/KITTI_00_gt.txt")
traj_est = file_interface.read_kitti_poses_file("../test/data/KITTI_00_ORB.txt")# add artificial Sim(3) transformation
traj_est.transform(lie.se3(lie.so3_exp([-0.7,2.3,1.2]), np.array([-215.7, -114.1, -198.3])))
# traj_est.transform(lie.se3(np.eye(3), np.array([0, 0, 0])))
traj_est.scale(0.7)logger.info("\nUmeyama alignment without scaling")
traj_est_aligned = copy.deepcopy(traj_est)
traj_est_aligned.align(traj_ref)logger.info("\nUmeyama alignment with scaling")
traj_est_aligned_scaled = copy.deepcopy(traj_est)
traj_est_aligned_scaled.align(traj_ref, correct_scale=True)logger.info("\nUmeyama alignment with scaling only")
traj_est_aligned_only_scaled = copy.deepcopy(traj_est)
traj_est_aligned_only_scaled.align(traj_ref, correct_only_scale=True)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plot_mode = plot.PlotMode.xyzax = plot.prepare_axis(fig, plot_mode, subplot_arg=221)
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_ref, '--', 'red')
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_est, '-', 'blue')
fig.axes.append(ax)
plt.title('not aligned')ax = plot.prepare_axis(fig, plot_mode, subplot_arg=222)
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_ref, '--', 'red')
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_est_aligned, '-', 'blue')
fig.axes.append(ax)
plt.title('$\mathrm{SE}(3)$ alignment without scaling')ax = plot.prepare_axis(fig, plot_mode, subplot_arg=223)
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_ref, '--', 'red')
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_est_aligned_scaled, '-', 'blue')
fig.axes.append(ax)
plt.title('$\mathrm{Sim}(3)$ alignment')ax = plot.prepare_axis(fig, plot_mode, subplot_arg=224)
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_ref, '--', 'red')
plot.traj(ax, plot_mode, traj_est_aligned_only_scaled, '-', 'blue')
fig.axes.append(ax)
plt.title('only scaled')fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
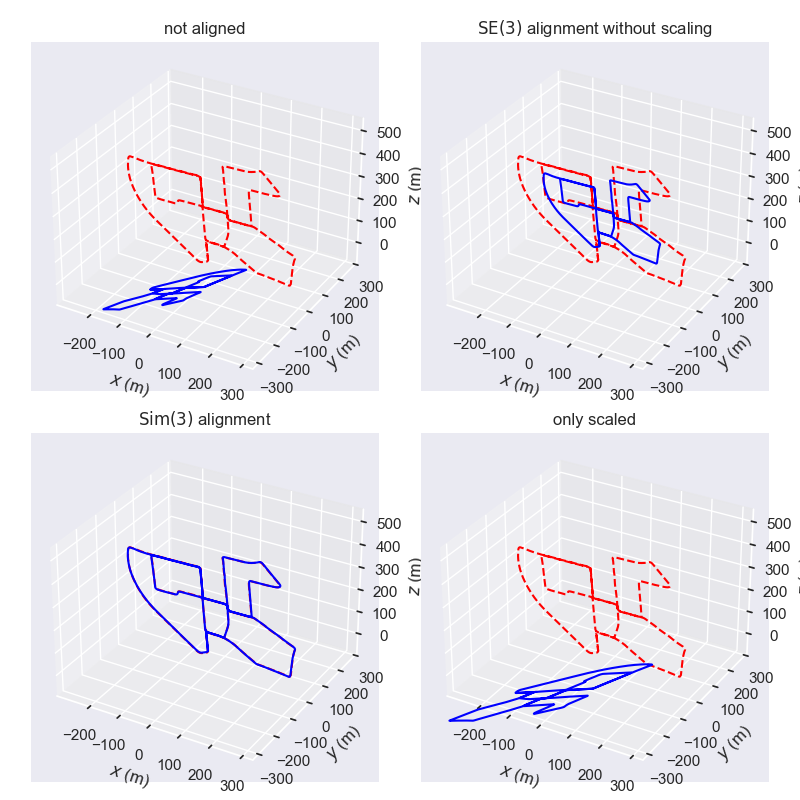
结果如下图所示, 左上角是原始的两组数据 (未对齐), 右上角仅计算了平移和旋转 (没有缩放) 后的 “对齐” 结果, 右下角仅计算了缩放 (没有旋转和平移) 后的 “对齐” 结果, 左下角是计算了相似变换 (旋转、平移、缩放) 后的对齐结果. 可以看出相似变换后的对齐效果比较好, 体现 Umeyama 算法的较好的特性.
总结
本篇博文中
- 查阅了 Eigen 中 Umeyama 算法源码并简单测试
- 查阅了 PCL 中 Umeyama 算法源码 (基于 Eigen)
- 查阅了 evo 中 Umeyama 算法源码并简单测试
到此, 我们完成了对 Umeyama 算法的数学推导和源码阅读, 可以暂时画个休止符了.
(如有问题, 请指出)
参考文献
[1] S. Umeyama, “Least-squares estimation of transformation parameters between two point patterns,” in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 376-380, April 1991
[2] Eigen, https://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
[3] The Point Cloud Library (PCL), https://pointclouds.org/
[4] Grupp Michael, “evo: Python package for the evaluation of odometry and SLAM”, https://github.com/MichaelGrupp/evo
[5] Kaxlamangla S. Arun and Thomas S. Huang and Steven D. Blostein, “Least-Squares Fitting of Two 3-D Point Sets”, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1987, PAMI-9, pages 698-700