题目非常典型,很适合学算法。
1111 第 3 场算法双周赛 - 蓝桥云课
双十一的祈祷
题意:求的个位数。
思路:只需要求个位数,因此此题等效于求 ,可用快速幂或者直接看出为1。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod = 10;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
LL qpow(LL a , LL b)//快速幂
{LL sum=1;while(b){if(b&1){sum=sum*a%mod;}a=a*a%mod;b>>=1;}return sum;
}
void solve()
{cout<<qpow(11,1111);
}
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t=1;
// cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
疯狂的促销
题意:三个电商平台优惠不同,现有若干商品,每个商品可以任选平台,求购买所有商品的最低价格。
思路:直接模拟。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int algo(int cost){int cost1 , cost2 , cost3;cost1 = cost >= 500 ? cost - cost / 10 : cost;cost2 = cost >= 1000 ? cost - 150 : cost;cost3 = cost == 1111 ? 0 : cost - cost / 20;return min(cost1 , min(cost2 , cost3));
}
int main()
{// 请在此输入您的代码int n;cin>>n;long long sum = 0;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){int num;cin>>num;sum += algo(num);}cout<<sum;return 0;
}被替换的身份证
题意:两个人有两张牌,根据规则谁先出完牌谁赢。
思路:还是模拟,考虑先手获胜情况:1、有对子/王炸。2、自己最大的牌比对面能打的最大的牌要大。其余都是后手赢。
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{// 请在此输入您的代码int n;cin>>n;map<char , int>mp;string mask = "3456789XJQKA2MF";for(int i = 0 ; i < mask.size() ; i ++){mp[mask[i]] = i;}while(n--){string s1 , s2;cin >> s1 >> s2;int sd_1 , sd_2 , j_1 , j_2;sd_1 = mp[s1[0]];sd_2 = mp[s1[1]];j_1 = mp[s2[0]];j_2 = mp[s2[1]];if(sd_1 > sd_2){swap(sd_1 , sd_2);}if(j_1 > j_2){swap(j_1,j_2);}if(sd_1 == 13 && sd_2 == 14){cout<<"ShallowDream";}else if(sd_1 == sd_2){cout<<"ShallowDream"; }else if(j_1 == 13 && j_2 == 14){cout<<"Joker";}else if(sd_2 >= j_2){cout<<"ShallowDream";}else{cout<<"Joker";}cout<<endl;}return 0;
}迷宫逃脱
题意:迷宫问题,从左上角走到右下角,只能往右或者往下走,每个格子中含有一个数字,若从 走到
的两个格子中的数字互质,则需要一把钥匙才能走。现在共有 k 把钥匙。求从左上角走到右下角的路径上数字之和的最大值。
思路:观察到迷宫格子数(1e6), 钥匙数(3)因此考虑 来做。定义
为走到第
行的第
列,消耗了
把钥匙的路径之和最大值。状态转移方程:
(互质情况)
(非互质情况)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int n , m , q;cin >> n >> m >> q;LL a[n + 5][m + 5];LL dp[n + 5][m + 5][q + 5];memset(dp , -0x3f3f, sizeof dp);for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i ++)for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++)cin >> a[i][j];dp[1][1][0] = a[1][1];for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++){for(int k = 0 ; k <= q; k ++){//从上方转移if(i > 1){if(gcd(a[i - 1][j] , a[i][j]) == 1){if(k > 0){dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k] , dp[i - 1][j][k - 1] + a[i][j]);}}else{dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k] , dp[i - 1][j][k] + a[i][j]);}}//从左侧转移if(j > 1){if(gcd(a[i][j - 1] , a[i][j]) == 1){if(k > 0){dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k] , dp[i][j - 1][k - 1] + a[i][j]);}}else{dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k] , dp[i][j - 1][k] + a[i][j]); }}}}}LL maxx = -1e18;for(int i = 0 ; i <= q; i ++){maxx = max(maxx , dp[n][m][i]);}if(maxx > 0)cout<<maxx;elsecout<<-1;return 0;
}
深秋的苹果
题意:给定一个数组,要求分成m段连续子序列,定义一段子序列的价值为,求分成m段连续子序列中子序列价值的最大值的最小值。
思路:最值问题考虑二分来解答,二分子序列价值的最大值即可。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n , m;
int a[N];
bool check(long long c){long long cnt = 1;long long sum = 0;long long tt = 0;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){if(tt + sum * a[i] > c){cnt ++;tt = 0;sum = a[i];}else{tt += sum * a[i];sum += a[i];}}if(cnt <= m){return true;}else{return false;}
}
int main()
{// 请在此输入您的代码cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)cin>>a[i];long long l = 0 , r = 3e18;while(l < r){long long mid = (l + r) / 2;if(check(mid)){r = mid;}else{l = mid + 1;}}cout<<l;return 0;
}鲜花之海
在一个幻想的王国中,有一个美丽的花园,花园里开满了各种不同颜色的鲜花。现在花园里一共有 朵鲜花,这些鲜花都有一个独特且 唯一 的编号,编号由
两个数字组成。
这些鲜花按如下规则摆放在花坛中(花坛可以视作一条直线):
- 如果第
朵鲜花的编号之和
小于第
朵鲜花编号之和
,则 XX 朵鲜花放在 YY 朵鲜花前面。
- 如果第
朵鲜花的编号之和
等于第
朵鲜花编号之和
,则哪一朵鲜花的编号
更小,哪一朵鲜花就摆在前面。
现在小蓝需要找到花园中的第 朵鲜花,但鲜花实在是太多了,他不想一朵朵的去找,你可以快速的告诉他第
朵鲜花的编号吗。
思路:参考曼哈顿距离,将原正方形顺时针旋转90°之后再镜像一下得到一个菱形,其中第一行只有一个元素 , 第二行有两个元素
....共有
行,且上面一行的两坐标之和必然小于下面一行。由于N很大,因此无法通过遍历N来找出第
朵花。对于整个菱形而言,前x行的总数是能够快速得到的,因此考虑二分第
朵花所在的行,然后再快速求出其坐标。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long long n , k;
long long cnt(long long r){long long res = 0;if(r > n){res += (n + 1) * n / 2;res += (n - 1 + (n - (r - n))) * (r - n) / 2; }else{res += (1 + r) * r / 2;} return res;
}
bool check(long long r){long long res = cnt(r);if(res >= k){return true;}else{return false;}
}
int main()
{// 请在此输入您的代int t;cin >> t;while(t--){cin >> n >> k;long long l = 0 , r = 2 * n - 1;while(l < r){long long mid = (l + r) / 2;if(check(mid)){r = mid;}else{l = mid + 1;}}k -= cnt(l - 1);if(l <= n){int sum = l + 1;int x = k;int y = sum - k;cout << x << " " << y << endl;}else{int sum = l + 1;int x = k + (r - n);int y = sum - x;cout << x << " " << y << endl;}}return 0;
}斐波拉契跳跃
题意:博弈游戏,小蓝和小桥在玩一个数学游戏,游戏规则如下:有一个长度为 的 排列
和一个棋子,两个人轮流按照游戏规则在排列上移动这个棋子,由小蓝先手,最先不能移动棋子的人判为输。对于某一次移动,设棋子的移动起点为
,移动的终点为
,两人移动棋子均需要满足以下游戏规则:
1、。
2、是一个斐波那契数。且跳跃的距离要严格大于上一次所跳跃的距离。
思路:建立函数,定义
为第
个点,上一步已经跳了第
个斐波那契数的距离之后是否能走出最后一步,若移动之后无法再移动了,则
= 1(代表了必胜), 反之
(代表必输).。其中
表示自身状态,若
, 则该点必输。由于每个点所能跳跃的点十分有限,因此考虑dfs+记忆化搜索来遍历所有可能情况。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n;
int fib[30];
int sg[N][30];
int a[N];
int dfs(int x , int l){if(sg[x][l] != -1)return sg[x][l]; int vis[2] = {0};for(int i = l + 1 ; i < 30 ; i ++){int v = fib[i];if(x - v >= 0 && a[x] < a[x - v]){dfs(x - v , i);vis[sg[x - v][i]] = 1;}if(x + v < n && a[x] < a[x + v]){dfs(x + v , i);vis[sg[x + v][i]] = 1;}}if(vis[0])return sg[x][l] = 1;elsereturn sg[x][l] = 0;
}
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);fib[0] = 0;fib[1] = 1;fib[2] = 2;for(int i = 3 ; i < 30 ; i ++){fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];}cin>>n;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> a[i];}memset(sg , -1 , sizeof sg);for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){if(dfs(i,0) == 0)cout<<"Little Qiao"<<endl;else cout<<"Little Lan"<<endl;} return 0;
}星石传送阵

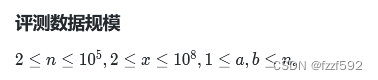
思路:首先答案显然是建完图之后BFS。对于求,需要求出所有的质因子之和(由于要求价值之和最小,假设有一个能量为x * x的星石,那么将其拆为x + x 两块星石的总价值会更小)。需要先把1 ~ 1e4上所有的素数都找出来。然后再对 x 分解质因子。 接下来考虑如何去建图,对于规则2而言,编号为
和编号为
的相连,那么总共只会有最多
条边(每个编号一条边)。但是对于规则1而言,若每个能量阵的
都相同,那么需要建
条边,这是无法接受的。因此不能用操作1来建边。因为其边权值都为1,那么无需存边,只需要将
相等的点放一起即可。在BFS的过程中,对于能量值为 x 的传送阵而言,下一步只需要将
相等的所有的点全部放进去即可,然后又因为此次操作做完以后所有
的点全都放进去了,下次再碰到
时无需再遍历
相等的所有的点,如此便能无需建边且不重复的BFS。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 2e05+10;
const LL NN = 1e4;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
vector<LL>prime;//存储素数
bool vis[N+5];
vector<int>mp[N];
int depth[N];
int vi[N];//x是否进去
int v[N];//f[i]是否进去
int n , A , B;
struct Node{int x;int fx;
}a[N];
vector<int>f[N];
void su()
{for(int i = 2;i <= NN;i++){if(!vis[i])prime.pb(i);for(int j=0;j < prime.size() && prime[j] * i <= NN;j ++){vis[prime[j]*i]=1;if(i % prime[j]==0)break;}}
}
int fun(int a){int len = prime.size();int sum = 0;for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){int x = prime[i];if(a < x){break;}while(a % x == 0){sum += x;a /= x;}}if(a > 1){sum += a;}return (sum % n) + 1;
}
void dfs(){queue<int>q;q.push(A);vi[A] = 1;depth[A] = 0;while(!q.empty()){int x = q.front();q.pop();for(auto it : mp[x]){if(!vi[it]){depth[it] = depth[x] + 1;q.push(it);vi[it] = 1;}}int F = a[x].fx;if(v[F] == 0){for(auto it : f[F]){if(!vi[it]){depth[it] = depth[x] + 1;q.push(it);vi[it] = 1;} }v[F] = 1;}}
}
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);su();cin >> n >> A >> B;for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){depth[i] = -1;}for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){cin >> a[i].x;a[i].fx = fun(a[i].x);mp[i].pb(a[i].fx);mp[a[i].fx].pb(i);f[a[i].fx].pb(i);}dfs();cout<<depth[B];return 0;
}