我们在上一节以手动的方式实现了一个词法解析器的 c 语言源码。它主要包含若干部分,第一部分就是输入缓存系统,用于从磁盘文件或者控制台上获取要解析的字符串。第二部分是数据读入逻辑,它主要通过调用输入系统的接口获得要解析的字符串;第三部分是 DFA 状态机的代码实现,它主要通过输入字符实现不同状态的跳转,最后得出被识别字符串是否可以被状态机接收;最后一部分是接收状态执行代码,当状态机识别字符串进入接收状态后,程序将执行对应接收状态的执行代码。
在以上四个部分中,第 3,4部分代码由我们动态生成,DFA 状态机的代码是由我们 golang 代码在解析 input.lex 输入文件后产生,第 4 部分则是在 input.lex 中直接设置,golang 代码主要是在生成第 3 步代码后,然后从 input.lex 中读取第 4 步的代码,然后将第 1,2步的代码结合起来,形成一个可以编译成可执行文件的 c 语言项目。
我们在上一节手动生成了第 3 步的代码,然后手动从 input.lex 中抽取出第 4 步的代码,然后手动将 1,2 部分的代码结合起来,形成一个 c 语言源程序项目,编译通过后,可执行文件就能从给定文件中识别input.lex 中正则表达式规定的字符串,本节我们通过代码的方式来取代上一节手动方式,完成本节工作后,我们就相当与完成了编译器工具链中的Flex词法解析工具。
由于我们在前面章节中已经完成了输入系统的c语言代码,在这里我们先固定第二部分的代码,这部分代码我们写入到一个名为lex.par的模板文件中,后面我们完成第3,4步后,将他们对应的c代码和lex.par 中的代码拷贝在一起,然后跟输入系统的代码放在一起,形成词法解析器的c项目代码。
首先我们看lex.par 文件的内容,它主要包含三部分,一部分是注释,它以@字符开始,当我们以一行行的方式读取lex.par的内容时,如果读入的一行以字符@开始,那么我们就直接忽略它。第二部分是单个字符‘ /f’,当我们拷贝 lex.par 的内容时,如果遇到该字符,那意味着我们需要拷贝第3或第4步对应的代码,首先我们看看lex.par 的内容,首先开始部分如下:
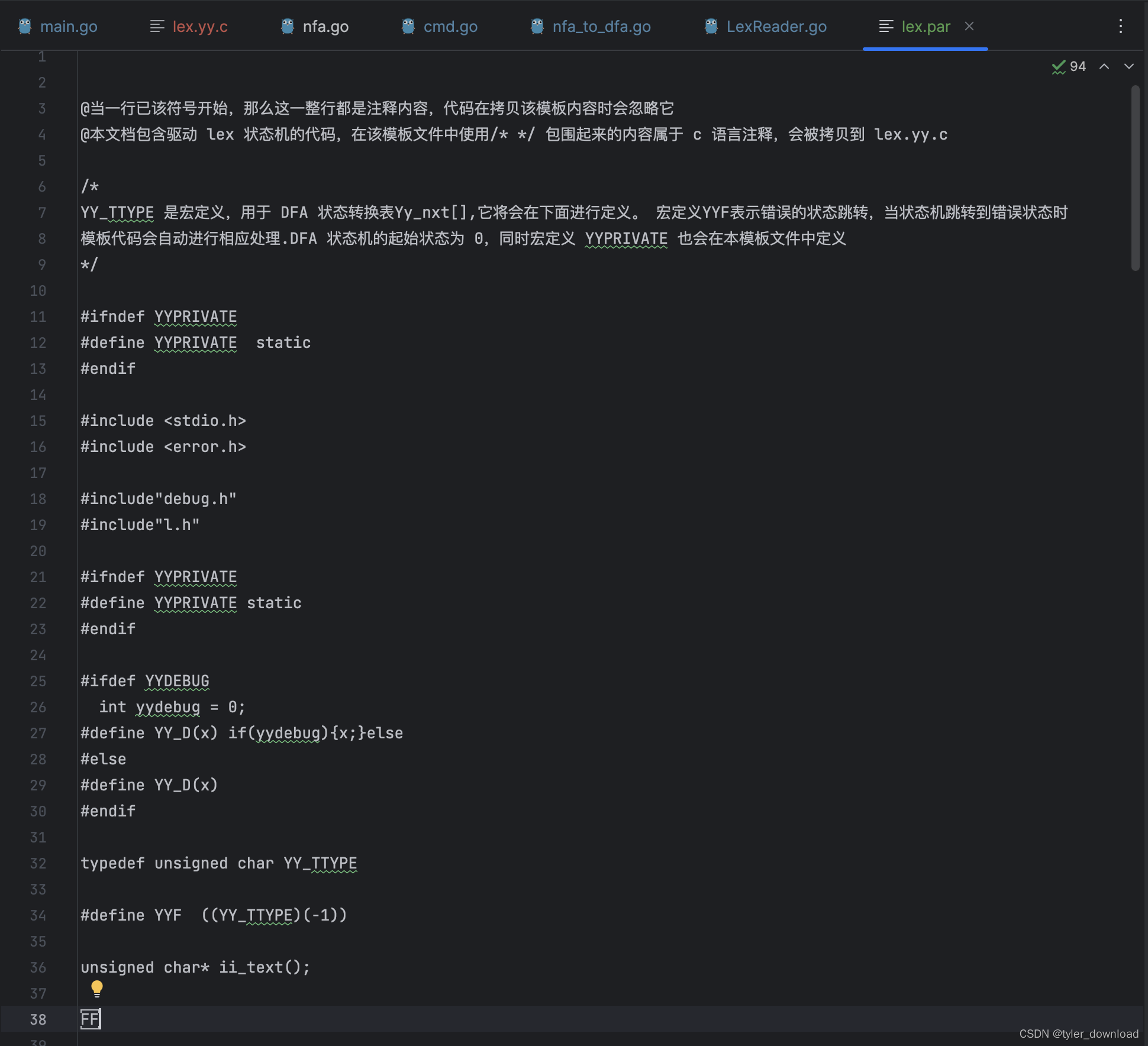
文件的最开头两行都以@开始,这意味着他们是注释,我们在读取该文件时将忽略掉这些以@开始的行,接下来的部分直到 “FF"标记处的内容都属于 c 语言的模板内容,我们将会把他们直接拷贝到 lex.yy.c 源代码文件中,符号"FF"其实就是’/f’,遇到它时就表明下面我们需要拷贝状态机代码或者是进入接收状态时的处理代码,我们继续看下面部分:
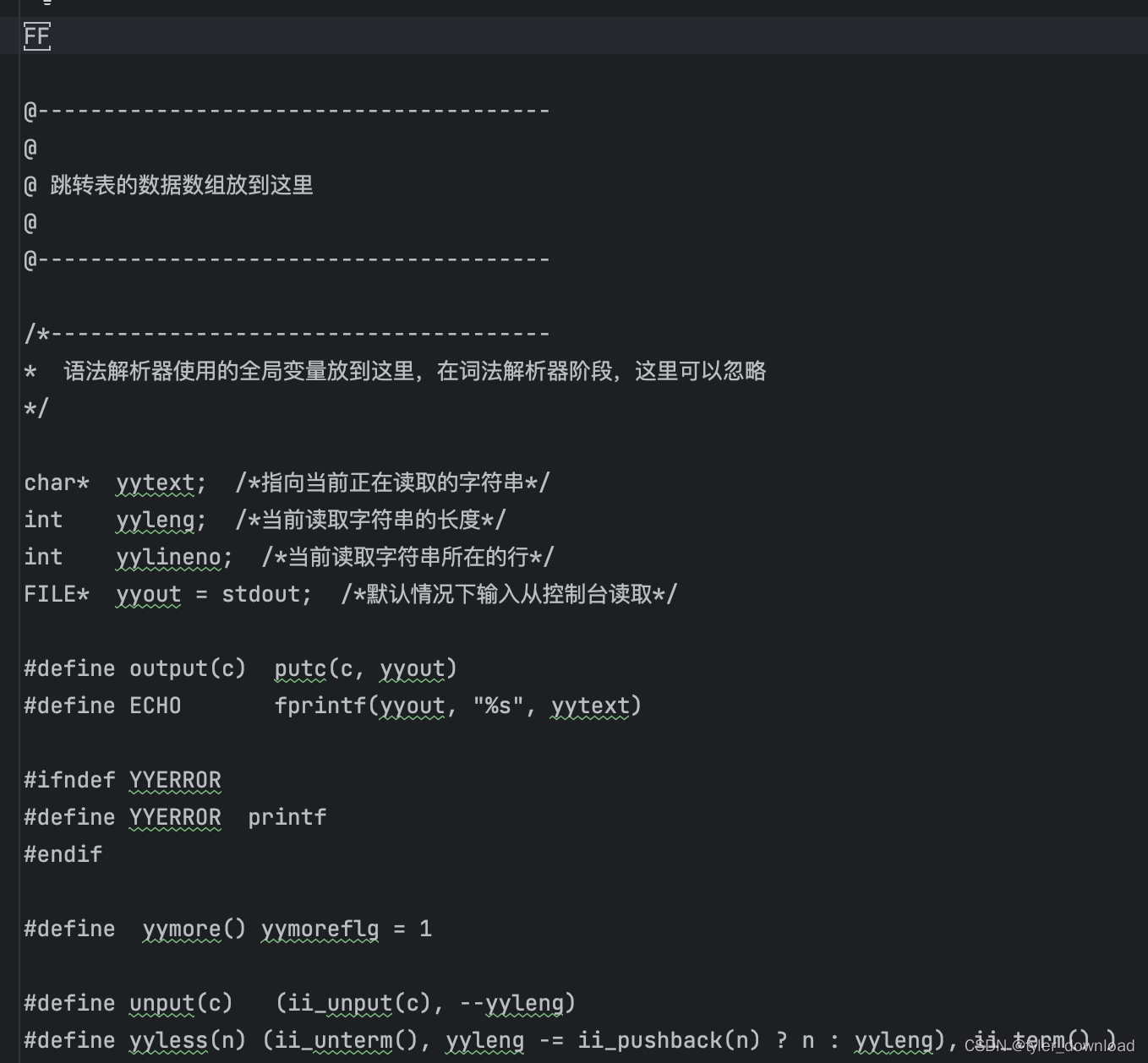
从上面内容我们看到,在“FF”下面是一段注释,它告诉我们那里需要写入的是状态机的代码,我们 golang 代码中会创建状态机,然后将其转换为 c 语言代码,那么这段转换的 c 语言代码就会替换到上面@符号注释的部分,接下来还是一系列 c 语言模板代码,他们将直接拷贝到 lex.yy.c文件,其中 unput, yyless 等宏定义是对输入系统接口的一些封装。我们继续往下面:
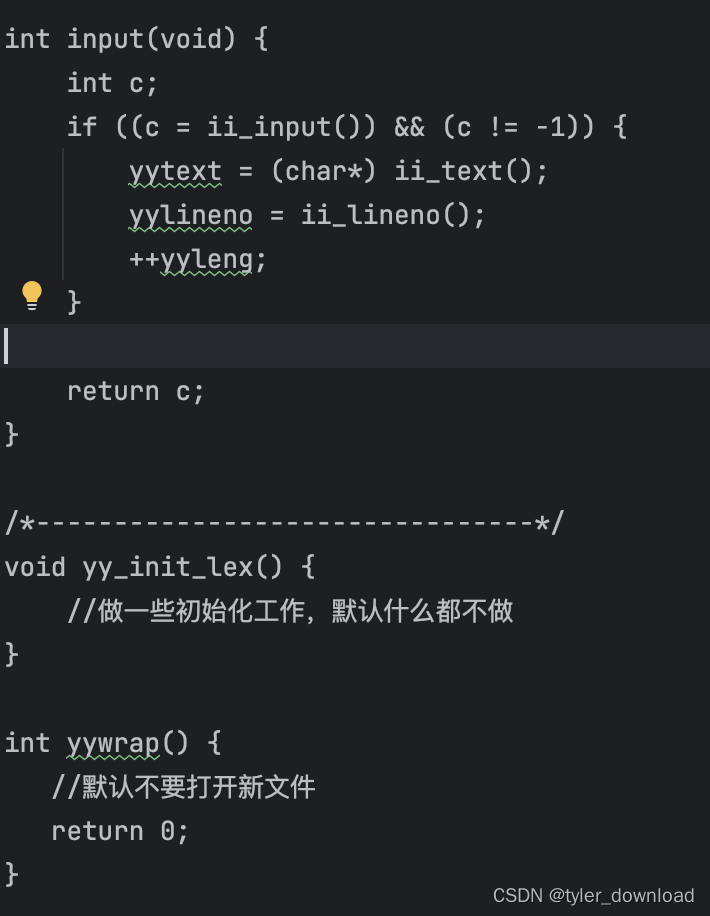
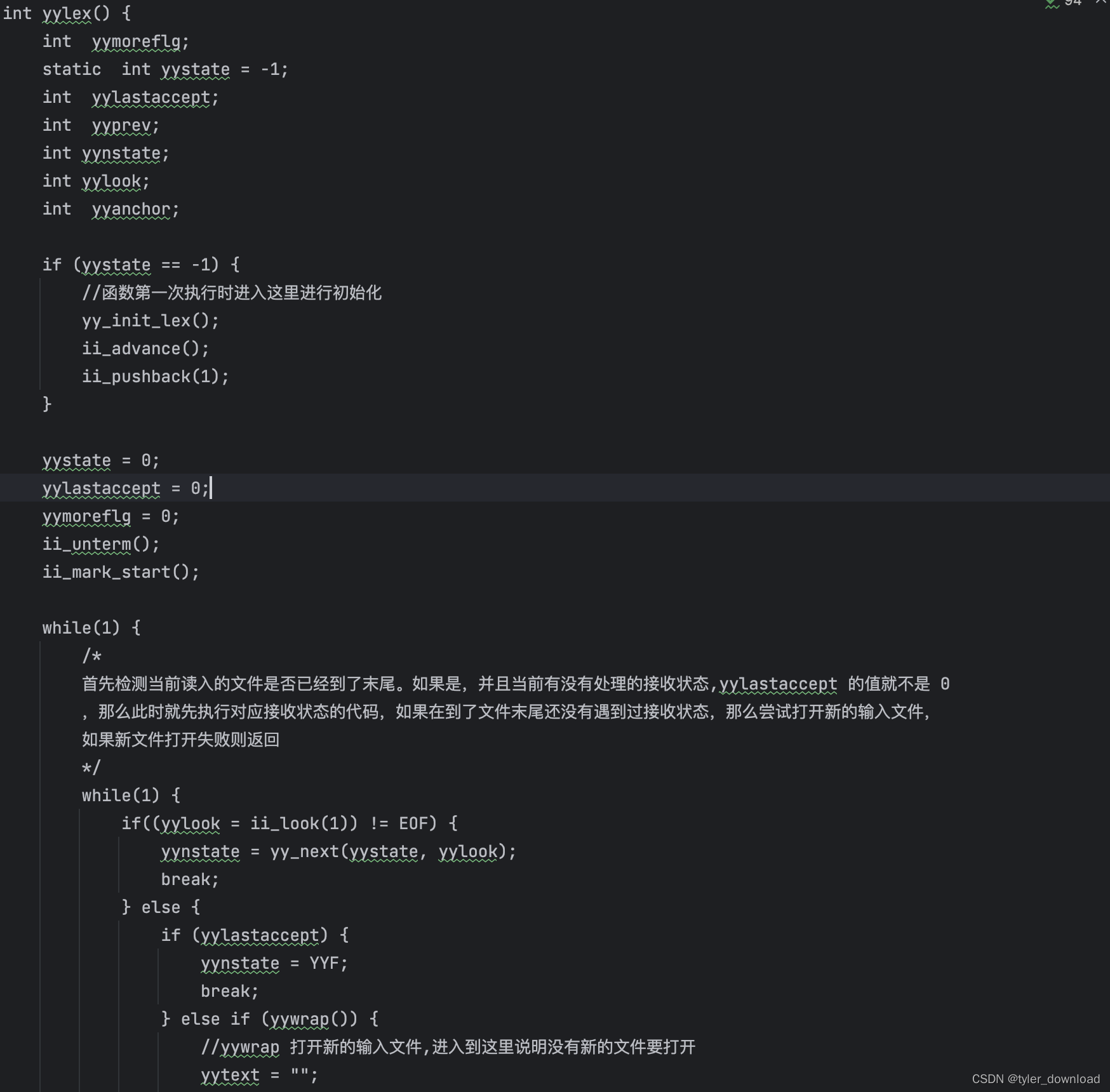
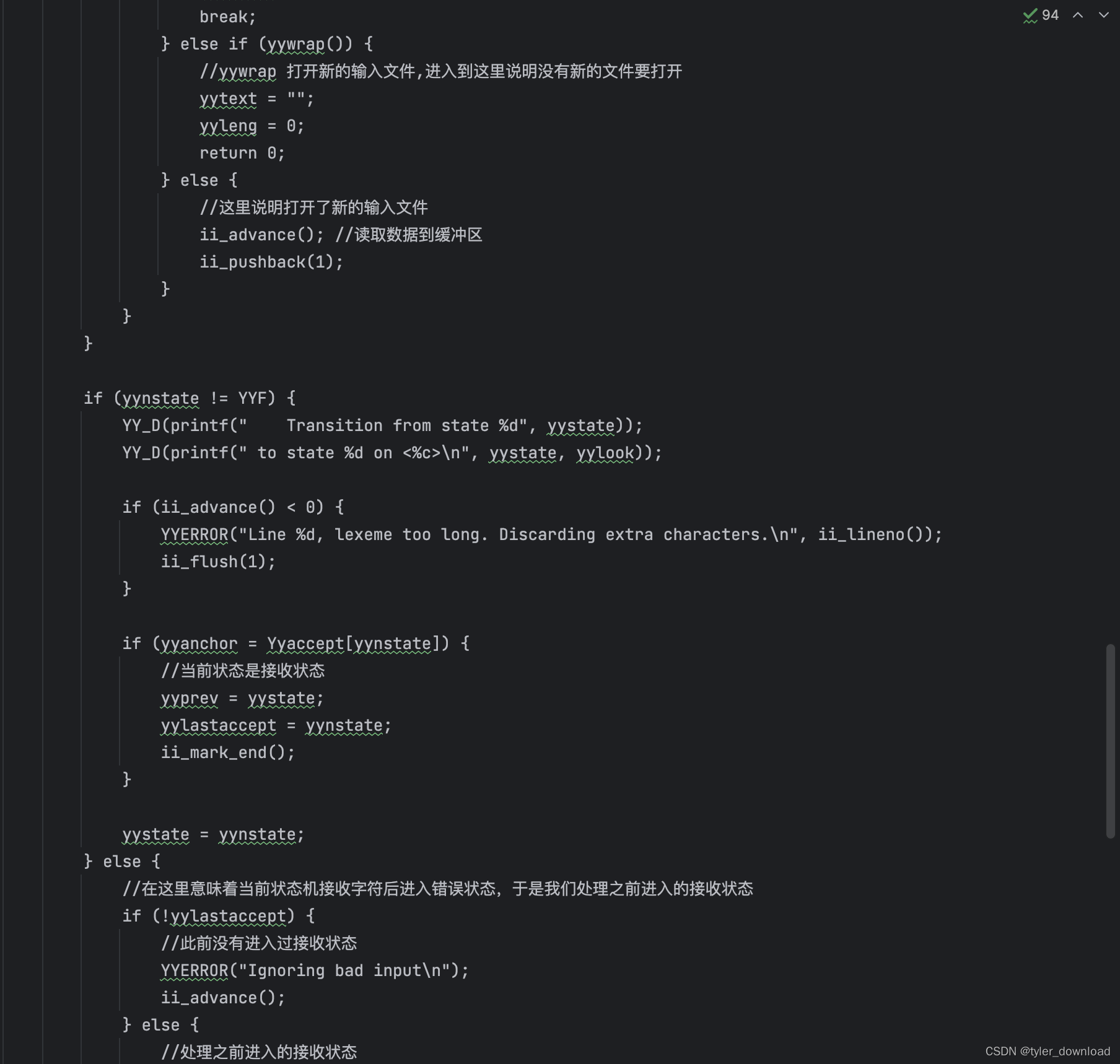
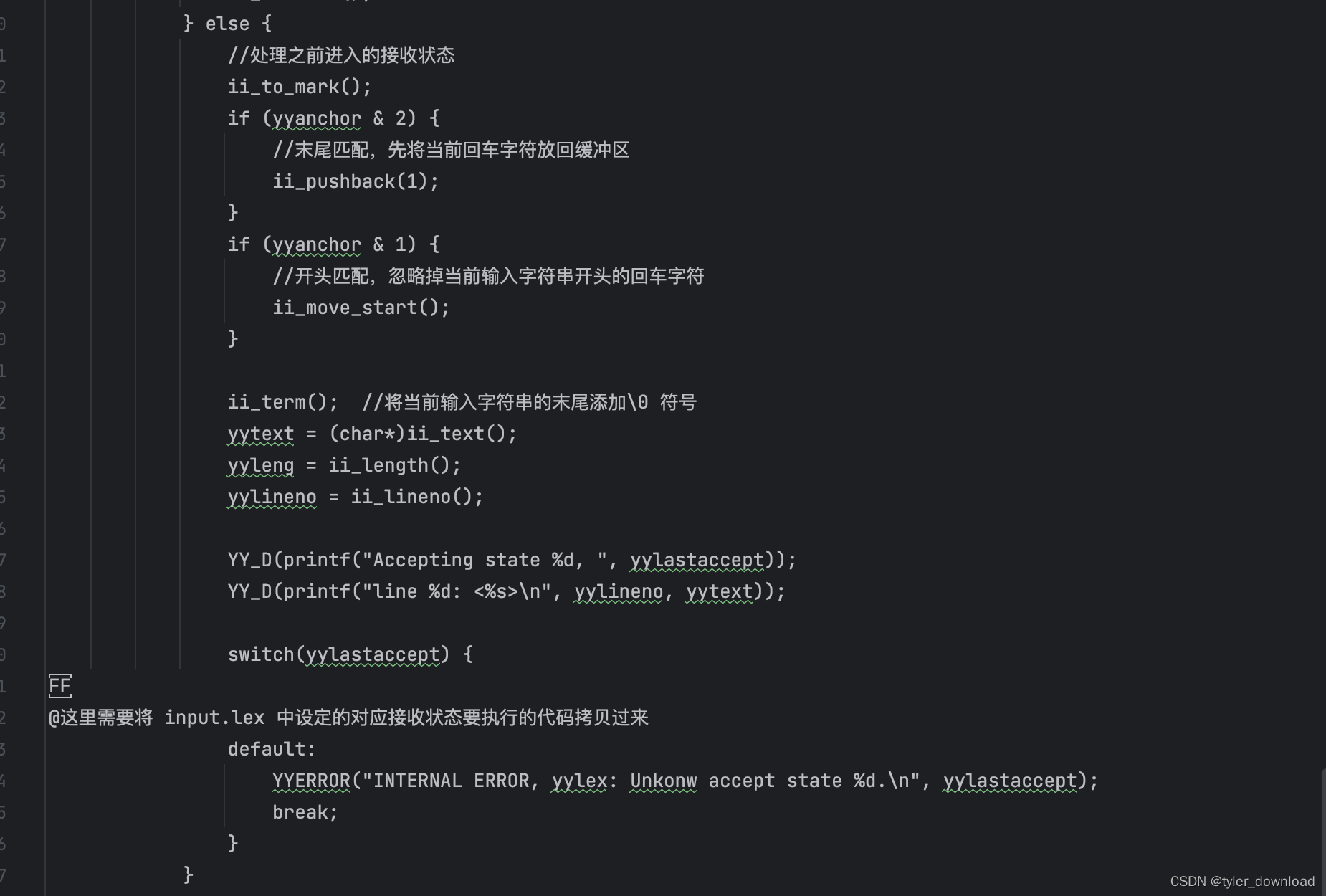

在上面代码中,主要是函数 yylex 的实现,它主要调用输入系统代码,读入要解析的字符串,然后调用状态机代码识别读入字符串,这里需要主要的是,我们再次遇到了符号"FF”,那里提示我们需要将进入接收状态后需要执行的代码拷贝过来,这两处 "FF"对应的代码拷贝,我们将使用 golang 代码来实现。
接下来我们实现对应 golang 代码,首先在原工程中将 cmd.go 挪到 nfa 目录,这样 cmd.go 中的代码就能直接访问 NfaConverter 类的数据,其次将原来实现在NfaConverter.go 中的PrintUnCompressedDFA,pnext,cnext, 等函数挪到 cmd.go 中,我们先看修改后 cmd.go 的第一部分:
type CommandLine struct {lexerReader *LexReaderparser *RegParsernfaConverter *NfaDfaConverter//打开 lex.par 文件对应的句柄tempFile *os.File//记录lex.par 读到第几行inputLines intscanner *bufio.Scanner
}func NewCommandLine() *CommandLine {lexReader, _ := NewLexReader("input.lex", "lex.yy.c")parser, _ := NewRegParser(lexReader)nfaConverter := NewNfaDfaConverter()nfaConverter.fp = lexReader.OFilereturn &CommandLine{lexerReader: lexReader,parser: parser,nfaConverter: nfaConverter,}
}func (c *CommandLine) head() {//先读取 input.lex ,识别其中的正则表达式c.lexerReader.Head()
}func (c *CommandLine) miniDFA() {//构建 DFA 状态机并最小化状态机start := c.parser.Parse()c.nfaConverter.MakeDTran(start)c.nfaConverter.PrintDfaTransition()c.nfaConverter.MinimizeDFA()fmt.Printf("%d out of DFA states in miminized machine\n", c.nfaConverter.nstates,DFA_MAX)}func (c *CommandLine) PrintHeader() {//针对未压缩的 DFA 状态就,输出对应的 c 语言注释c.PrintUnCompressedDFA()
}func (c *CommandLine) Signon() {//这里设置当前时间date := time.Now()//这里设置你的名字name := "yichen"fmt.Printf("GoLex 1.0 [%s] . (c) %s, All rights reserved\n", date.Format("01-02-2006"), name)
}func (c *CommandLine) PrintUnCompressedDFA() {fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, "#ifdef __NEVER__\n")fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, "/*------------------------------------------------\n")fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, "DFA (start state is 0) is :\n *\n")nrows := c.nfaConverter.nstatescharsPrinted := 0for i := 0; i < nrows; i++ {dstate := c.nfaConverter.dstates[i]if dstate.isAccepted == false {fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "* State %d [nonaccepting]\n", dstate.state)} else {//这里需要输出行数//fmt.Fprintf(n.fp, "* State %d [accepting, line %d <", i, )fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "* State %d [accepting, line %d, <%s>]\n", i, dstate.LineNo, dstate.acceptString)if dstate.anchor != NONE {start := ""end := ""if (dstate.anchor & START) != NONE {start = "start"}if (dstate.anchor & END) != NONE {end = "end"}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, " Anchor: %s %s \n", start, end)}}lastTransition := -1for j := 0; j < MAX_CHARS; j++ {if c.nfaConverter.dtrans[i][j] != F {if c.nfaConverter.dtrans[i][j] != lastTransition {fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\n * goto %d on ", c.nfaConverter.dtrans[i][j])charsPrinted = 0}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s", c.nfaConverter.BinToAscii(j))charsPrinted += len(c.nfaConverter.BinToAscii(j))if charsPrinted > 56 {//16 个空格fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\n * ")charsPrinted = 0}lastTransition = c.nfaConverter.dtrans[i][j]}}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\n")}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "*/ \n\n")fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "#endif\n")
}
在上面代码中,CommandLine 结构体先构建 LexerReader 用于读取 input.lex,并识别其中的正则表达式,nfaConverter 负责构建 DFA 状态机,上面代码的逻辑在前面章节我们都详细讲述过,我们继续看接下来的代码:
func (c *CommandLine) PrintDriver() {text := "输出基于 DFA 的跳转表,首先我们将生成一个 Yyaccept数组,如果 Yyaccept[i]取值为 0," +"\n\t那表示节点 i 不是接收态,如果它的值不是 0,那么节点是接受态,此时他的值对应以下几种情况:" +"\n\t1 表示节点对应的正则表达式需要开头匹配,也就是正则表达式以符号^开始," +"2 表示正则表达式需要\n\t末尾匹配,也就是表达式以符号$结尾,3 表示同时开头和结尾匹配,4 表示不需要开头或结尾匹配"comments := make([]string, 0)comments = append(comments, text)c.nfaConverter.comment(comments)//YYPRIVATE YY_TTYPE 是 c 语言代码中的宏定义,我们将在后面代码提供其定义//YYPRIVATE 对应 static, YY_TTYPE 对应 unsigned charfmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "YYPRIVATE YY_TTYPE Yyaccept[]=\n")fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "{\n")for i := 0; i < c.nfaConverter.nstates; i++ {if c.nfaConverter.dstates[i].isAccepted == false {//如果节点i 不是接收态,Yyaccept[i] = 0fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\t0 ")} else {anchor := 4if c.nfaConverter.dstates[i].anchor != NONE {anchor = int(c.nfaConverter.dstates[i].anchor)}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\t%-3d", anchor)}if i == c.nfaConverter.nstates-1 {fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, " ")} else {fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, ", ")}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "/*State %-3d*/\n", i)}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "};\n\n")// 先处理 switch cases 之前的内容c.driver_2()//如果遇到接收状态,我们将接收状态对应的操作代码拷贝到switch(yylastaccept)里面的 case 分支for i := 0; i < c.nfaConverter.nstates; i++ {if c.nfaConverter.dstates[i].isAccepted {fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\t\tcase %d:\t\t\t\t\t/* State %-3d */\n", i, i)fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\t\t %s\n", c.nfaConverter.dstates[i].acceptString)fmt.Fprint(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\t\t break;\n")}}//输出 switch case 之后内容c.driver_2()
}func (c *CommandLine) driver_1() {/*打开名为 lex.par 的代码模板文件,这里我们将模板文件名字写死为 lex.par 是为了简单,它的名字完全可以设计成从命令行输入,driver_1 函数的作用主要是打开文件,真正实现内容拷贝操作的是在 driver_2*/tempFile, err := os.Open("lex.par")if err != nil {panic("error for open lex.par file")}c.inputLines = 0c.tempFile = tempFilec.scanner = bufio.NewScanner(tempFile)//开始拷贝模板内容c.driver_2()}func (c *CommandLine) readTempFile() (string, bool) {res := c.scanner.Scan()textLine := ""if res == true {textLine = c.scanner.Text()}return textLine, res
}func (c *CommandLine) driver_2() bool {processingComment := falsetextLine, endOfFile := c.readTempFile()for endOfFile != false {if len(textLine) == 0 {textLine, endOfFile = c.readTempFile()continue}c.inputLines += 1if textLine[0] == '\f' {/*读取到符号\f 表示 lex.par 中一个特定区域的内容已经读取完毕*/break}idx := 0for textLine[idx] == ' ' {//忽略掉空格idx += 1}if textLine[idx] == '@' {//读取到@表示当前模板内容属于注释processingComment = truetextLine, endOfFile = c.readTempFile()continue} else if processingComment {//上一行是注释,当前行不是processingComment = false}//把当前读到的模板内容写入 lex.yy.cfmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s\n", textLine)textLine, endOfFile = c.readTempFile()}return endOfFile
}func (c *CommandLine) pnext(name string) {/*这里输出一段c语言代码,它们的作用是根据输入字符,查询上面生成的压缩跳转表后,跳转到下一个状态节点*/toptext := []string{"unsigned int c ;", "int cur_state;", "{","/*给定当前状态和输入字符,返回跳转后的下一个状态节点*/",}boptext := []string{" int i;",""," if ( p ) "," {"," if ((i = *p++) == 0)"," return p[ c ];",""," for(; --i >= 0; p += 2)"," if( c == p[0] )"," return p[1];"," }"," return unsigned char (-1);","}",}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "\n/*------------------------------------*/\n")fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s %s yynext(cur_state, c)\n", SCLASS, TYPE)for _, str := range toptext {fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s\n", str)}fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, " %s *p = %s[cur_state];\n", TYPE, name)for _, str := range boptext {fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s\n", str)}
}func (c *CommandLine) cnext(name string) {text := []string{"yy_next(state,c) is given the current state number and input","character and evaluates to the next state.",}c.nfaConverter.printComment(text)fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "#define yy_next(state, c) (%s[Yy_rmap[state]][Yy_cmap[c]])\n", name)
}func (c *CommandLine) tail() {//忽略掉含有 %% 的行c.readTempFile()//将%% 后面的内容直接拷贝到 lex.yy.ctextLine, endOfFile := c.readTempFile()for endOfFile != false {fmt.Printf("t%d: %s", c.inputLines, textLine)c.inputLines += 1fmt.Fprintf(c.nfaConverter.fp, "%s\n", textLine)}c.nfaConverter.fp.Close()
}func (c *CommandLine) DoFile() {c.head()c.miniDFA()c.PrintHeader()c.driver_1()//压缩 DFA 状态机c.nfaConverter.DoSquash()c.cnext("Yy_nxt")//输出跳转表c.PrintDriver()c.tail()
}函数 PrintDriver 用于将状态机的跳转信息输出到控制台,我们以前也调试过该函数,它相比以前的不同之处在于调用了函数 driver_2,这个函数将我们生成的状态机 c 语言代码和 input.lex 中进入接收状态要执行的代码拷贝到 lex.yy.c 的对应处,第一次调用它时,它将我们生成的状态机 c 语言代码拷贝到 lex.yy.c,第二次调用将 input.lex 中对应的接收态代码放置到 lex.yy.c 中 switch case 对应位置,tail 函数负责把 input.lex 中最后一个 %% 后面的内容直接拷贝到 lex.yy.c中,上面代码完成后,运行起来,在本地会生成 lex.yy.c 文件,其中内容如下所示:
#define YYPRIVATE#line 1 "input.lex"int FCON = 1;int ICON = 2;ifdef __NEVER__
/*------------------------------------------------
DFA (start state is 0) is :*
* State 0 [nonaccepting]* goto 2 on .* goto 4 on 0123456789
* State 1 [nonaccepting]* State 2 [nonaccepting]* goto 1 on 0123456789
* State 3 [accepting, line 6, < {printf("%s is a float number", yytext); return FCON;}>]* goto 3 on 0123456789
* State 4 [accepting, line 6, < {printf("%s is a float number", yytext); return FCON;}>]* goto 3 on .* goto 5 on 0123456789
* State 5 [nonaccepting]* goto 2 on .* goto 5 on 0123456789
*/ #endif
/*
YY_TYPE 是宏定义,用于 DFA 状态转换表Yy_nxt[],它将会在下面进行定义。 宏定义YYF表示错误的状态跳转,当状态机跳转到错误状态时
模板代码会自动进行相应处理.DFA 状态机的起始状态为 0,同时宏定义 YYPRIVATE 也会在本模板文件中定义
*/
#ifndef YYPRIVATE
#define YYPRIVATE static
#endif
#ifndef NULL
#include <stdio.h>
#endif
#include<debug.h>
#include<l.h>
#ifndef YYDEBUGint yydebug = 0;
#define YY_D(x) if(yydebug){x;}else
#else
#define YY_D(x)
#endif
typedef unsigned char YY_TYPE;
#define YYF ((YYTYPE)(-1))
unsigned char* ii_text();/*--------------------------------------
* The Yy_cmap[] and Yy_rmap arrays are used as follows:
*
* next_state= Yydtran[ Yy_rmap[current_state] ][ Yy_cmap[input_char] ];
*
* Character positions in the Yy_cmap array are:
*
* ^@ ^A ^B ^C ^D ^E ^F ^G ^H ^I ^J ^K ^L ^M ^N ^O
* ^P ^Q ^R ^S ^T ^U ^V ^W ^X ^Y ^Z ^[ ^\ ^] ^^ ^_
* ! " # $ % & ' ( ) * + , - . /
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : ; < = > ?
* @ A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
* P Q R S T U V W X Y Z [ \ ] ^ _
* ` a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o
* p q r s t u v w x y z { | } ~ DEL
*/static unsigned char Yy_cmap[128]=
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
};static unsigned char Yy_rmap[6]=
{0,1,2,3,4,5
};static unsigned char Yy_nxt[6][3]=
{
/* 0 */ {-1, 2, 4},
/* 1 */ {-1, -1, -1},
/* 2 */ {-1, -1, 1},
/* 3 */ {-1, -1, 3},
/* 4 */ {-1, 3, 5},
/* 5 */ {-1, 2, 5}
};/*--------------------------------------
* yy_next(state,c) is given the current state number and input
* character and evaluates to the next state.
*/#define yy_next(state, c) (Yy_nxt[Yy_rmap[state]][Yy_cmap[c]])/*--------------------------------------* 输出基于 DFA 的跳转表,首先我们将生成一个 Yyaccept数组,如果 Yyaccept[i]取值为 0,那表示节点 i 不是接收态,如果它的值不是 0,那么节点是接受态,此时他的值对应以下几种情况:1 表示节点对应的正则表达式需要开头匹配,也就是正则表达式以符号^开始,2 表示正则表达式需要末尾匹配,也就是表达式以符号$结尾,3 表示同时开头和结尾匹配,4 表示不需要开头或结尾匹配*/YYPRIVATE YY_TTYPE Yyaccept[]=
{0 , /*State 0 */0 , /*State 1 */0 , /*State 2 */4 , /*State 3 */4 , /*State 4 */0 /*State 5 */
};/*--------------------------------------
* 语法解析器使用的全局变量放到这里,在词法解析器阶段,这里可以忽略
*/
char* yytext; /*指向当前正在读取的字符串*/
int yyleng; /*当前读取字符串的长度*/
int yylineno; /*当前读取字符串所在的行*/
FILE* yyout = stdout; /*默认情况下输入从控制台读取*/
#define output(c) putc(c, yyout)
#define ECHO fprintf(yyout, "%s", yytext)
#ifndef YYERROR
#define YYERROR printf
#endif
#define yymore() yymoreflg = 1
#define unput(c) (ii_unput(c), --yyleng)
#define yyless(n) (ii_unterm(), yyleng -= ii_pushback(n) ? n : yyleng), ii_term() )
int input(void) {int c;if ((c = ii_input()) && (c != -1)) {yytext = (char*) ii_text();yylineno = ii_lineno();++yyleng;}return c;
}
/*--------------------------------*/
yy_init_lex() {//做一些初始化工作,默认什么都不做
}
int yywrap() {//默认不要打开新文件return 0;
}
yylex() {int yymoreflg;static int yystate = -1;int yylastaccept;int yyprev;int yynstate;int yylook;int yyanchor;if (yystate == -1) {//函数第一次执行时进入这里进行初始化yy_init_lex();ii_advance();ii_pushback(1);}yystate = 0;yylastaccept = 0;yymoreflg = 0;ii_unterm();ii_mark_start();while(1) {/*首先检测当前读入的文件是否已经到了末尾。如果是,并且当前有没有处理的接收状态,yylastaccept 的值就不是 0,那么此时就先执行对应接收状态的代码,如果在到了文件末尾还没有遇到过接收状态,那么尝试打开新的输入文件,如果新文件打开失败则返回*/while(1) {if((yylook = ii_look(1) != EOF) {yynstate = yy_next(yystate, yylook);break;} else {if (yylastaccept) {yynstate = YYF;break;} else if (yywrap()) {//yywrap 打开新的输入文件,进入到这里说明没有新的文件要打开yytext = "";yyleng = 0;return 0;} else {//这里说明打开了新的输入文件ii_advance(); //读取数据到缓冲区ii_pushback(1);}}}if (yynstate != YYF) {YY_D(printf(" Transition from state %d", yystate));YY_D(printf(" to state %d on <%c>\n", yystate, yylook));if (ii_advance() < 0) {YYERROR("Line %d, lexeme too long. Discarding extra characters.\n", ii_lineno());ii_flush(1);}if (yyanchor = Yyaccept[yynstate]) {//当前状态是接收状态yyprev = yystate;yylastaccept = yynstate;ii_mark_end();}yystate = yynstate;} else {//在这里意味着当前状态机接收字符后进入错误状态,于是我们处理之前进入的接收状态if (!yylastaccept) {//此前没有进入过接收状态YYERROR("Ignoring bad input\n");ii_advance();} else {//处理之前进入的接收状态ii_to_mark();if (yyancor & 2) {//末尾匹配,先将当前回车字符放回缓冲区ii_pushback(1);}if (yyanchor & 1) {//开头匹配,忽略掉当前输入字符串开头的回车字符ii_move_start();}ii_term(); //将当前输入字符串的末尾添加\0 符号yytext = (char*)ii_text();yyleng = ii_length();yylineno = ii_lineno();YY_D(printf("Accepting state %d, ", yylastaccept);YY_D(printf("line %d: <%s>\n", yylineno, yytext));switch(yylastaccept) {case 3: /* State 3 */{printf("%s is a float number", yytext); return FCON;}break;case 4: /* State 4 */{printf("%s is a float number", yytext); return FCON;}break;default:YYERROR("INTERNAL ERROR, yylex: Unkonw accept state %d.\n", yylastaccept);break;}}ii_unterm();yylastaccept = 0;if (!yymoreflg) {yystate = 0;ii_mark_start();} else {yystate = yyprev; //记录上一次遇到的状态yymoreflg = 0;}}}
}我们将上面代码直接拷贝的 c语言项目中的 main.c 文件中 main 函数的上方,然后直接编译 c 语言项目,那么我们就得到了一个能直接对浮点数进行词法解析的可运行程序,更多详细的演示和调试讲解,请在 b 站搜索 coding 迪斯尼,本节代码下载路径如下:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1LPpw2HbtXuu8FFtlMrxtFQ 提取码: 7wxg
或者:
https://github.com/wycl16514/golex-flex-final.git