list的反向迭代器
文章目录
- list的反向迭代器
- reverse.h
- 疑问1:为什么在迭代器当中不需要写深拷贝、析构函数
- 疑问2:为什么在迭代器当中需要三个模板参数?
- 疑问3:反向迭代器是怎么实现的?
- 疑问4:为什么*解引用不直接返回当前值
- 为什么要加一些不认识的typedef
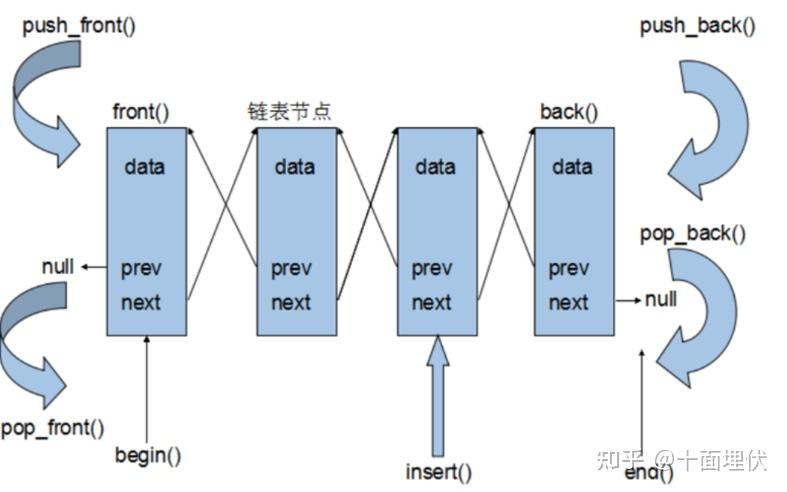
reverse.h
#pragma oncenamespace mudan
{template<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __reverse_iterator{Iterator _cur;typedef __reverse_iterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> RIterator;__reverse_iterator(Iterator it):_cur(it){}RIterator operator++(){--_cur;return *this;}RIterator operator--(){++_cur;return *this;}Ref operator*(){//return *_cur;auto tmp = _cur;--tmp;return *tmp;}Ptr operator->(){//return _cur.operator->();return &(operator*());}bool operator!=(const RIterator& it){return _cur != it._cur;}};
}
list.h
#include<assert.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include"reverse.h"
using namespace std;namespace mudan
{template<class T>struct list_node{T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& x = T()):_data(x), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};// typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;// typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;// 像指针一样的对象template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> iterator;typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;Node* _node;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}bool operator!=(const iterator& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const iterator& it) const{return _node == it._node;}// *it it.operator*()// const T& operator*()// T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}//T* operator->() Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*());}// ++ititerator& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}// it++iterator operator++(int){iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}// --ititerator& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}// it--iterator operator--(int){iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef __reverse_iterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef __reverse_iterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}void empty_init(){// 创建并初始化哨兵位头结点_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}template <class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){empty_init();while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}list(){empty_init();}void swap(list<T>& x)//void swap(list& x){std::swap(_head, x._head);}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end());swap(tmp);}// lt1 = lt3list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}void push_back(const T& x){//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//Node* newnode = new Node(x);_head tail newnode//tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = tail;//newnode->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newnode;insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);// prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}private:Node* _head;};void test(){list<int> ls;ls.push_back(1);ls.push_back(2);ls.push_back(3);ls.push_back(4);ls.push_back(5);ls.push_back(6);for (auto& e : ls){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;list<int>copy = ls;for (auto e : copy){cout << e << " ";}}
}
test.cpp
#include"list.h"
#include<list>int main(void)
{mudan::test();//list<int>ls;//ls.push_back(1);//ls.push_back(2);//ls.push_back(3);//ls.push_back(4);//ls.push_back(5);//ls.push_back(6);//for (auto e : ls)//{// cout << e << " ";//}//cout << endl;//list<int>lt(ls);//for (auto e : lt)//{// cout << e << " ";//}return 0;
}
疑问1:为什么在迭代器当中不需要写深拷贝、析构函数
1、因为迭代器就是希望做到浅拷贝,就是需要拿到地址而不是值,因为迭代器的修改是会影响对象中的内容的
2、因为迭代器并没有申请额外的空间,所以不需要析构,如果写了析构函数,那么调用一次迭代器那岂不是把对象都给销毁了😂😂😂
疑问2:为什么在迭代器当中需要三个模板参数?
其实这三个参数是被抽象出来的,__list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>等价于__list_iterator<T, T&, T>,其实在迭代器当中只有一个参数也可以正常推导,但是在list类当中只有一个参数就不行了,因为如果传递过来的是const修饰的类,然后用T&来接收的话会导致权限被缩小了,所以,为了解决这个const的问题,直接显示的定义模板参数*
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&,const T> const_iterator;**Ref就是reference
Ptr就是pointer
疑问3:反向迭代器是怎么实现的?
反向迭代器其实就是利用正向迭代器实现的,重载一下++、–等操作符,不过逻辑上功能要反过来写
疑问4:为什么*解引用不直接返回当前值

因为begin()和end()的位置和正常实现的不一样
为什么要加一些不认识的typedef
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
我也不知道,不加过不了编译,我太菜了😭😭😭😭😭😭