1、背景
看图片
_calloc_r ->_malloc_r ->heap_caps_malloc_default->heap_caps_malloc->multi_heap_malloc->multi_heap_malloc_impl->get_next_block
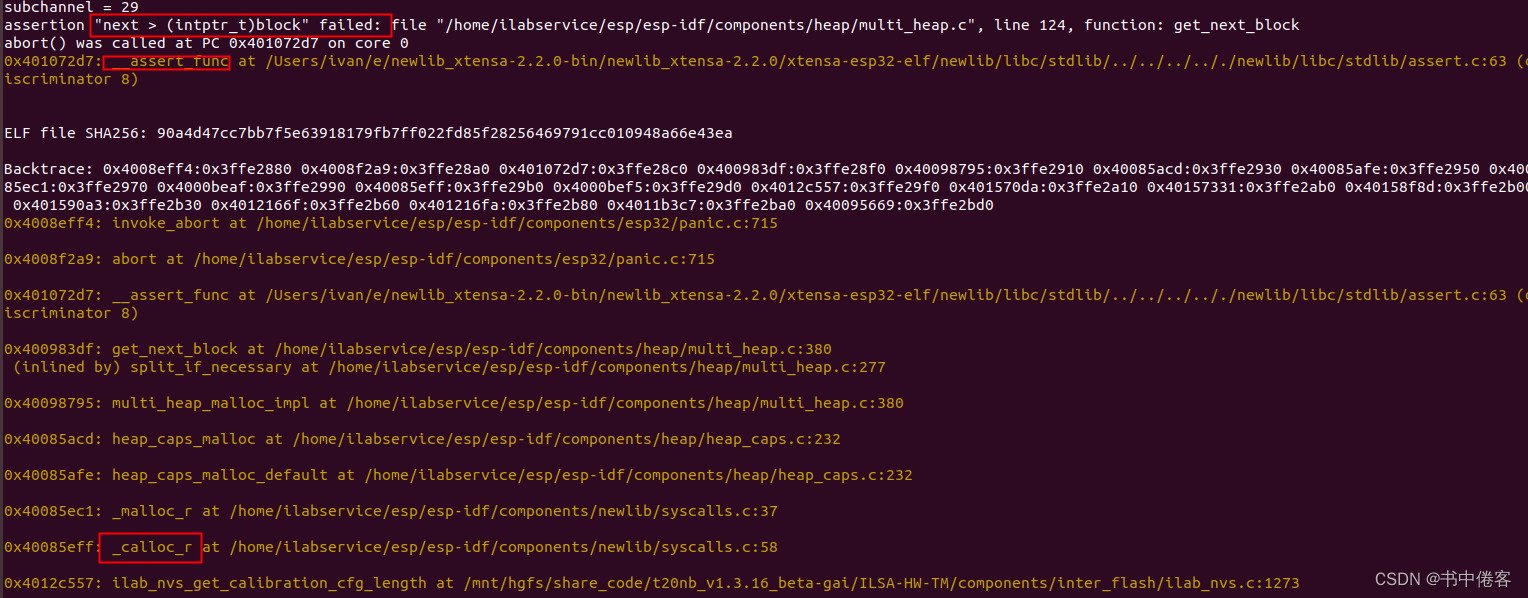
/* Return the next sequential block in the heap.*/ static inline heap_block_t *get_next_block(const heap_block_t *block) {intptr_t next = block->header & NEXT_BLOCK_MASK;if (next == 0) {return NULL; /* last_block */}assert(next > (intptr_t)block);return (heap_block_t *)next; }在分配堆内存时,碰上了这个断言,触发应用程序反复重启。
1.1 参考文档
ESP32 程序的内存模型 - 知乎MCU 中的内存资源可能是其最宝贵的资源,因为它在芯片中占据最大的面积。更新的应用程序对内存的需求正在不断增长。为了充分利用硬件资源,理解内存架构并能针对应用程序的实际用例进行内存优化变得至关重要。特别…![]() https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/345915256?utm_id=0
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/345915256?utm_id=0
https://www.cnblogs.com/sinferwu/p/17253138.html![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/sinferwu/p/17253138.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/sinferwu/p/17253138.html
esp32 heap 内存管理简析-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读1.2w次,点赞2次,收藏29次。嵌入式系统运行时的内存情况是非常值得关注的。本文档用于分析乐鑫ESP32 SDK(版本esp-idf-v3.0-rc1) Heap (堆内存)管理的实现。 1:Heap管理主要函数接口与数据结构 1.1主要函数接口ESP32的SDK对于heap部分管理的源码位于路径\esp-idf-v3.0-rc1\components\heap下,可以简单的认为分为两层:heap_caps_init.c与hea..._esp32 heaphttps://blog.csdn.net/abc517789065/article/details/79680214https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/latest/esp32/api-reference/system/mem_alloc.html
![]() https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/latest/esp32/api-reference/system/mem_alloc.html
https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/latest/esp32/api-reference/system/mem_alloc.html
2.理论知识
2.0 内存管理
ESP-IDF 应用程序使用常见的计算机架构模式:由程序控制流动态分配的内存(即 栈)、由函数调用动态分配的内存(即 堆)以及在编译时分配的 静态内存。
由于 ESP-IDF 是一个多线程 RTOS 环境(FreeRTOS的变种),因此每个 RTOS 任务都有自己的栈,这些栈默认在创建任务时从堆中分配。在FreeRTOS的实现中,每个任务用到两个内存块,其中一块用来保存任务自身的数据结构--类似Task_t(process control block);另一块内存块用作任务的栈。xTaskCreate()两个内存块都是内部实现从堆中动态分配的,而xTaskCreateStatic的两个内存块都需要程序控制流作为参数传递给它。
2.1 ESP32内存类型和特性
ESP32包含多种类型的RAM
DRAM:是连接到 CPU 数据总线上的内存,用于存储数据。这是作为堆访问最常见的一种内存(用作bss段、data段和堆)。
IRAM:是连接到 CPU 指令总线上的内存,通常仅用于存储可执行数据(即指令,text段)。如果作为通用内存访问,则所有访问必须为 32 位可访问内存。---4字节地址严格对齐
D/IRAM:连接到 CPU 数据总线和指令总线的 RAM,因此可用作指令 RAM 或数据 RAM
ESP32 还可外扩SPI RAM,通过缓存将 片外 RAM 集成到 ESP32 的内存映射中,访问方式与 DRAM 类似。
2.2 ESP32内存图

520K SRAM = 192KSRAM0 + 128KSRAM1 +200KSRAM2
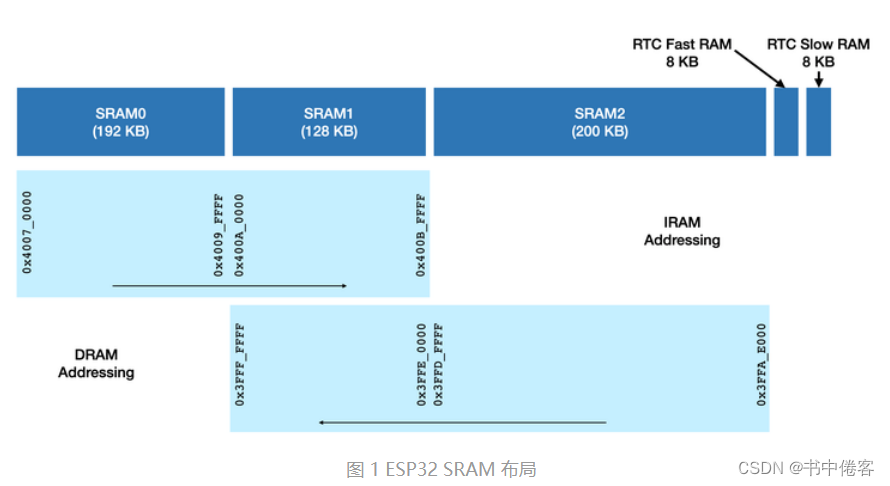
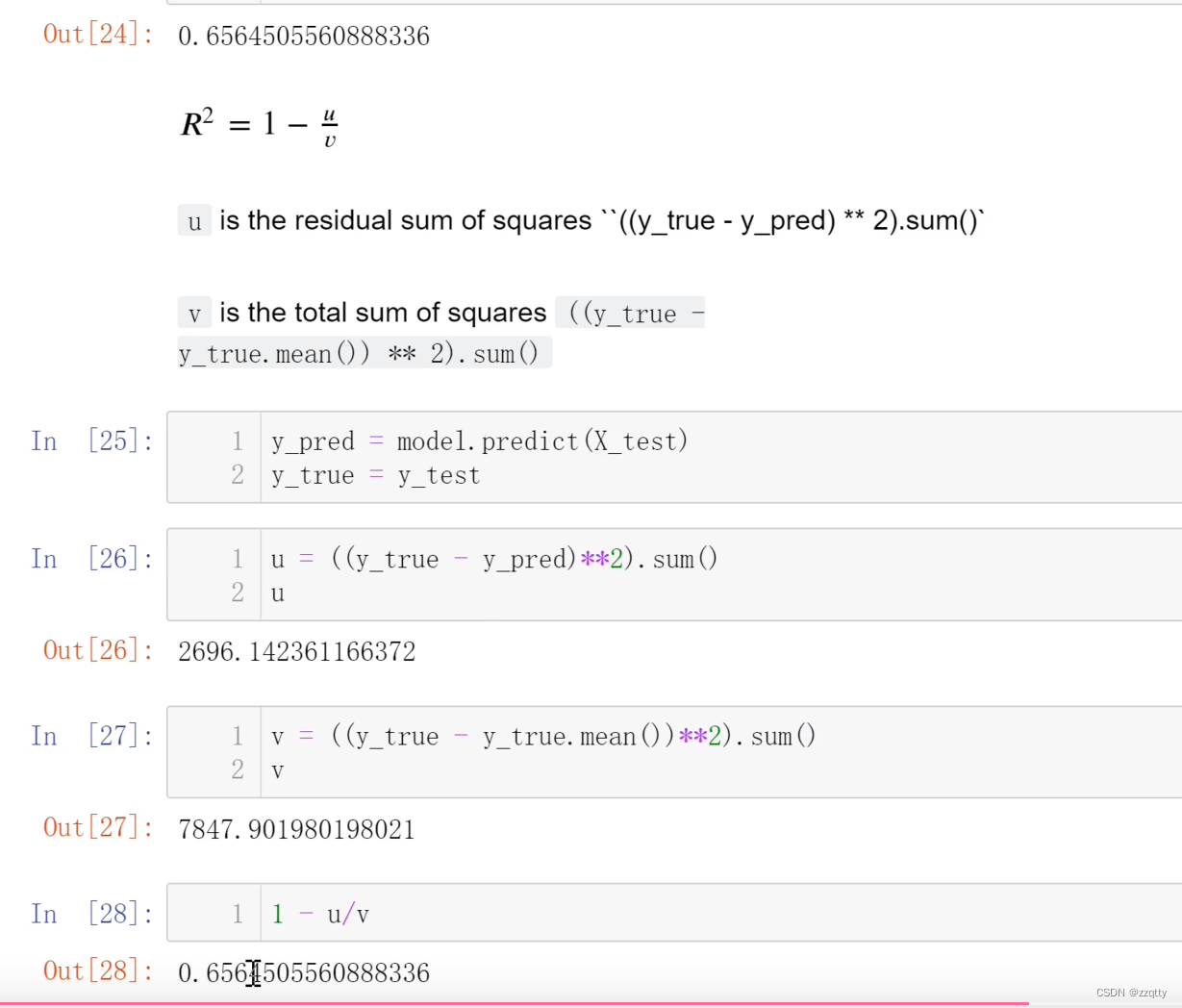
由上图可知,SRAM0被用作IRAM,SRAM2被用作DRAM,SRAM1既可被用作IRAM,也可被用作DRAM。SRAM1默认被用作DRAM,以补充应用程序中数据空间的紧缺。
2.3 基于内存属性的堆内存分配器
ESP32 使用多种类型的 RAM,因此具备不同属性的堆,即基于属性的内存分配器允许应用程序按不同目的进行堆分配。
2.3.0 堆内存分配器管理的DRAM大小和初始化过程
启动时,DRAM 堆包含应用程序未静态分配的所有数据内存,减少静态分配的缓冲区将增加可用的空闲堆空间。静态分配和其他特殊目的保留的内存外,其他内存均受到堆内存分配器的管理。
/* Initialize the heap allocator to use all of the memory notused by static data or reserved for other purposes*/
void heap_caps_init()系统调用heap_caps_init实现Heap空间初始化的过程,实质就是初始heap_t数据结构的过程。简单的看可以分为三个步骤:
<1> 遍历当前系统的可用内存区域,并对类型相同的相邻区域进行合并
<2> 将可用内存区域通过register_heap初始化为Heap分区的结构(建立Meta Data头以及数据区的链表)
<3> 将所有Heap分区信息通过链表连接到registered_heaps
2.3.0.1 步骤1
heap_caps_init中的关键代码段1
/* Get the array of regions that we can use for heaps(with reserved memory removed already.)*/size_t num_regions = soc_get_available_memory_region_max_count();soc_memory_region_t regions[num_regions];num_regions = soc_get_available_memory_regions(regions);//The heap allocator will treat every region given to it as separate. In order to get bigger ranges of contiguous memory,//it's useful to coalesce adjacent regions that have the same type.for (int i = 1; i < num_regions; i++) {soc_memory_region_t *a = ®ions[i - 1];soc_memory_region_t *b = ®ions[i];if (b->start == a->start + a->size && b->type == a->type ) {a->type = -1;b->start = a->start;b->size += a->size;}}/* Count the heaps left after merging */size_t num_heaps = 0;for (int i = 0; i < num_regions; i++) {if (regions[i].type != -1) {num_heaps++;}}
其中有一个关键的数据结构体soc_memory_region_t,其成员包括region的起始地址、大小、类型。
/* Region descriptor holds a description for a particular region of memory on a particular SoC.*/
typedef struct
{intptr_t start; ///< Start address of the regionsize_t size; ///< Size of the region in bytessize_t type; ///< Type of the region (index into soc_memory_types array)intptr_t iram_address; ///< If non-zero, is equivalent address in IRAM
} soc_memory_region_t;什么叫类型相同的相邻区域,就是前region和当前region的内存类型相同,前region的起始地址+大小=当前region的起始地址,那么就是类型相同的相邻区域,可以合并。
2.3.0.2 步骤2
/* Type for describing each registered heap */
typedef struct heap_t_ {uint32_t caps[SOC_MEMORY_TYPE_NO_PRIOS]; ///< Capabilities for the type of memory in this heap (as a prioritised set). Copied from soc_memory_types so it's in RAM not flash.intptr_t start;intptr_t end;portMUX_TYPE heap_mux;multi_heap_handle_t heap;SLIST_ENTRY(heap_t_) next;
} heap_t;关键数据结构heap_t,描述注册heap的类型,成员有caps--功能,起始地址和结束地址、互斥锁等等
ESP_EARLY_LOGI(TAG, "Initializing. RAM available for dynamic allocation:");for (int i = 0; i < num_regions; i++) {soc_memory_region_t *region = ®ions[i];const soc_memory_type_desc_t *type = &soc_memory_types[region->type];heap_t *heap = &temp_heaps[heap_idx];if (region->type == -1) {continue;}heap_idx++;assert(heap_idx <= num_heaps);memcpy(heap->caps, type->caps, sizeof(heap->caps));heap->start = region->start;heap->end = region->start + region->size;vPortCPUInitializeMutex(&heap->heap_mux);if (type->startup_stack) {/* Will be registered when OS scheduler starts */heap->heap = NULL;} else {register_heap(heap);}SLIST_NEXT(heap, next) = NULL;ESP_EARLY_LOGI(TAG, "At %08X len %08X (%d KiB): %s",region->start, region->size, region->size / 1024, type->name);}关键在于register_heap(),注册这些可用region
2.3.0.3 步骤3
找到第一个DRAM,分配永久堆数据,用作运行时的链表--数组。设置锁并将之加入到链表中。
heap_t *heaps_array = NULL;for (int i = 0; i < num_heaps; i++) {if (heap_caps_match(&temp_heaps[i], MALLOC_CAP_8BIT|MALLOC_CAP_INTERNAL)) {/* use the first DRAM heap which can fit the data */heaps_array = multi_heap_malloc(temp_heaps[i].heap, sizeof(heap_t) * num_heaps);if (heaps_array != NULL) {break;}}}assert(heaps_array != NULL); /* if NULL, there's not enough free startup heap space */memcpy(heaps_array, temp_heaps, sizeof(heap_t)*num_heaps);/* Iterate the heaps and set their locks, also add them to the linked list. */for (int i = 0; i < num_heaps; i++) {if (heaps_array[i].heap != NULL) {multi_heap_set_lock(heaps_array[i].heap, &heaps_array[i].heap_mux);}if (i == 0) {SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(®istered_heaps, &heaps_array[0], next);} else {SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(&heaps_array[i-1], &heaps_array[i], next);}} 有一个疑问,这个heap_t 链表是不能扩容的,用来表述可用的堆空间。这个链表和后面分配的总链表和free链表有什么关系?
有一个疑问,这个heap_t 链表是不能扩容的,用来表述可用的堆空间。这个链表和后面分配的总链表和free链表有什么关系?
2.3.0.4 void register_heap(heap_t *region)
register_heap(heap)
->multi_heap_register((void *)region->start, heap_size)
->multi_heap_register_impl(start, size)
register_heap将普通的内存区域初始化为Heap分区结构,multi_heap_register_impl是其最终实现功能的接口.
multi_heap_handle_t multi_heap_register_impl(void *start_ptr, size_t size)
{uintptr_t start = ALIGN_UP((uintptr_t)start_ptr);uintptr_t end = ALIGN((uintptr_t)start_ptr + size);heap_t *heap = (heap_t *)start;size = end - start;if (end < start || size < sizeof(heap_t) + 2*sizeof(heap_block_t)) {return NULL; /* 'size' is too small to fit a heap here */}heap->lock = NULL;heap->last_block = (heap_block_t *)(end - sizeof(heap_block_t));/* first 'real' (allocatable) free block goes after the heap structure */heap_block_t *first_free_block = (heap_block_t *)(start + sizeof(heap_t));first_free_block->header = (intptr_t)heap->last_block | BLOCK_FREE_FLAG;first_free_block->next_free = heap->last_block;/* last block is 'free' but has a NULL next pointer */heap->last_block->header = BLOCK_FREE_FLAG;heap->last_block->next_free = NULL;/* first block also 'free' but has legitimate length,malloc will never allocate into this block. */heap->first_block.header = (intptr_t)first_free_block | BLOCK_FREE_FLAG;heap->first_block.next_free = first_free_block;/* free bytes is:- total bytes in heap- minus heap_t header at top (includes heap->first_block)- minus header of first_free_block- minus whole block at heap->last_block*/heap->free_bytes = size - sizeof(heap_t) - sizeof(first_free_block->header) - sizeof(heap_block_t);heap->minimum_free_bytes = heap->free_bytes;return heap;
}发现了吧返回值类型是multi_heap_handle_t,在函数实现中用的是heap_t,怎么回事?
typedef struct multi_heap_info *multi_heap_handle_t;
/* Block in the heapHeap implementation uses two single linked lists, a block list (all blocks) and a free list (free blocks).'header' holds a pointer to the next block (used or free) ORed with a free flag (the LSB of the pointer.) is_free() and get_next_block() utility functions allow typed access to these values.'next_free' is valid if the block is free and is a pointer to the next block in the free list.
*/
typedef struct heap_block {intptr_t header; /* Encodes next block in heap (used or unused) and also free/used flag */union {uint8_t data[1]; /* First byte of data, valid if block is used. Actual size of data is 'block_data_size(block)' */struct heap_block *next_free; /* Pointer to next free block, valid if block is free */};
} heap_block_t;/* These masks apply to the 'header' field of heap_block_t */
#define BLOCK_FREE_FLAG 0x1 /* If set, this block is free & next_free pointer is valid */
#define NEXT_BLOCK_MASK (~3) /* AND header with this mask to get pointer to next block (free or used) *//* Metadata header for the heap, stored at the beginning of heap space.'first_block' is a "fake" first block, minimum length, used to provide a pointer to the first used & free block inthe heap. This block is never allocated or merged into an adjacent block.'last_block' is a pointer to a final free block of length 0, which is added at the end of the heap when it isregistered. This block is also never allocated or merged into an adjacent block.*/
typedef struct multi_heap_info {void *lock;size_t free_bytes;size_t minimum_free_bytes;heap_block_t *last_block;heap_block_t first_block; /* initial 'free block', never allocated */
} heap_t;
一段可用的连续内存被初始化为Heap分区时,分区起始地址会写入一个MetaData头(即是multi_heap_info类型)。MetaData头后紧接着是第一个真正可以用来分配的内存块block0,block0包含一个信息头heap_block_t以及实际数据区。
在Heap分区的最后,有一个heap_block_t的信息头作为整个分区的结尾。heap_block_t结构中有指向下个节点的指针,这样分区所有block组成链表用于访问。
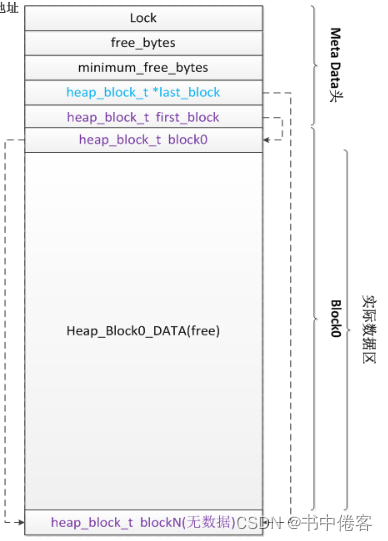
最后可用的就是Heap_Block0_DATA的。
由此可知,管理内存就通过这两级。先通过遍历heap_t链表查找符合申请内存类型的heap_t,在从heap遍历以找到最优满足大小的Heap_Block。
2.3.1 Heap空间分配
Heap空间是系统运行期间用户通过函数申请的,如何分配与释放是关键问题。本节描述关于Heap空间如何分配的问题?
2.3.1.3 C标准函数库malloc()和free()----MALLOC_CAP_DEFAULT属性
调用 malloc() 时,ESP-IDF malloc() 内部调用 heap_caps_malloc_default(size),使用属性 MALLOC_CAP_DEFAULT 分配内存。该属性可实现字节寻址功能,即存储空间的最小编址单位为字节。
对于Heap空间的分配过程,通过对代码的理解,可以简单的概括为三个步骤:
当用户向系统通过malloc申请Heap内存空间时:
<1>系统会遍历每个Heap分区(通过registered_heaps),找到满足申请内存类型(如MALLOC_CAP_DEFAULT属性)的分区;再依次遍历分区下所有可用的Heap Block,找到可用空间满足申请内存大小的Heap Block。
<2>遍历所有Heap Block期间,会出现几种可能:
A:若Heap Block的可用空间小于用户申请的内存大小,显然不能使用,继续查找下一个Heap Block;
B:若Heap Block的可用空间正好等于用户申请的内存大小,这时系统出现了最佳的分配选择,策略选择该Heap Block作为本次分配的Best Heap Block,停止遍历。
C:若Heap Block的可用空间大于用户申请的内存大小,则先行记录下这个Heap Block的位置以及它的实际可用空间大小,然后继续遍历查找;在找到下一个满足条件的Heap Block时,比较两者,选取可用空间较小的记录下来。策略的目的即是保证最终得到一个既满足用户申请需求又最不浪费空间的Best Heap Block。
<3>对应步骤<2>选出的Best Heap Block:
A:若Best HeapBlock不存在,意味着用户申请失败;
B:若Best HeapBlock空间正好满足用户申请的需求,则无需另做处理,直接给到用户即可;
C:若Best HeapBlock的空间除去用户申请的需求还有盈余,则需要进行分割。盈余部分需要分割成为新的可用(空闲)Heap Block,等待下次内存申请。
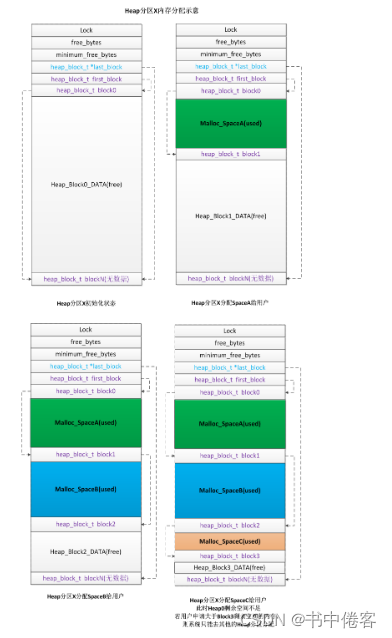
三次分配,从初始化、分配SpaceA、SpaceB、SpaceC。
3、问题分析
回归到背景中问题,malloc分配中出现问题_calloc_r,从中看出调用关系
_calloc_r ->
_malloc_r ->
heap_caps_malloc_default->
heap_caps_malloc->
multi_heap_malloc->
multi_heap_malloc_impl->
split_if_necessary->
get_next_block
void *multi_heap_malloc_impl(multi_heap_handle_t heap, size_t size)
{heap_block_t *best_block = NULL;heap_block_t *prev_free = NULL;heap_block_t *prev = NULL;size_t best_size = SIZE_MAX;size = ALIGN_UP(size);if (size == 0 || heap == NULL) {return NULL;}multi_heap_internal_lock(heap);/* Note: this check must be done while holding the lock as bothmalloc & realloc may temporarily shrink the free_bytes valuebefore they split a large block. This can result in false negatives,especially if the heap is unfragmented.*/if (heap->free_bytes < size) {MULTI_HEAP_UNLOCK(heap->lock);return NULL;}/* Find best free block to perform the allocation in */prev = &heap->first_block;for (heap_block_t *b = heap->first_block.next_free; b != NULL; b = b->next_free) {MULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(b > prev, &prev->next_free); // free blocks should be ascending in addressMULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(is_free(b), b); // block should be freesize_t bs = block_data_size(b);if (bs >= size && bs < best_size) {best_block = b;best_size = bs;prev_free = prev;if (bs == size) {break; /* we've found a perfect sized block */}}prev = b;}if (best_block == NULL) {multi_heap_internal_unlock(heap);return NULL; /* No room in heap */}prev_free->next_free = best_block->next_free;best_block->header &= ~BLOCK_FREE_FLAG;heap->free_bytes -= block_data_size(best_block);split_if_necessary(heap, best_block, size, prev_free);if (heap->free_bytes < heap->minimum_free_bytes) {heap->minimum_free_bytes = heap->free_bytes;}multi_heap_internal_unlock(heap);return best_block->data;
}/* Split a block so it can hold at least 'size' bytes of data, making any sparespace into a new free block.'block' should be marked in-use when this function is called (implementation detail, this functiondoesn't set the next_free pointer).'prev_free_block' is the free block before 'block', if already known. Can be NULL if not yet known.(This is a performance optimisation to avoid walking the freelist twice when possible.)
*/
static void split_if_necessary(heap_t *heap, heap_block_t *block, size_t size, heap_block_t *prev_free_block)
{const size_t block_size = block_data_size(block);MULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(!is_free(block), block); // split block shouldn't be freeMULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(size <= block_size, block); // size should be validsize = ALIGN_UP(size);/* can't split the head or tail block */assert(!is_first_block(heap, block));assert(!is_last_block(block));heap_block_t *new_block = (heap_block_t *)(block->data + size);heap_block_t *next_block = get_next_block(block);if (is_free(next_block) && !is_last_block(next_block)) {/* The next block is free, just extend it upwards. */new_block->header = next_block->header;new_block->next_free = next_block->next_free;if (prev_free_block == NULL) {prev_free_block = get_prev_free_block(heap, block);}/* prev_free_block should point to the next block (which we found to be free). */MULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(prev_free_block->next_free == next_block,&prev_free_block->next_free); // free blocks should be in order/* Note: We have not introduced a new block header, hence the simple math. */heap->free_bytes += block_size - size;
#ifdef MULTI_HEAP_POISONING_SLOW/* next_block header needs to be replaced with a fill pattern */multi_heap_internal_poison_fill_region(next_block, sizeof(heap_block_t), true /* free */);
#endif} else {/* Insert a free block between the current and the next one. */if (block_data_size(block) < size + sizeof(heap_block_t)) {/* Can't split 'block' if we're not going to get a usable free block afterwards */return;}if (prev_free_block == NULL) {prev_free_block = get_prev_free_block(heap, block);}new_block->header = block->header | BLOCK_FREE_FLAG;new_block->next_free = prev_free_block->next_free;/* prev_free_block should point to a free block after new_block */MULTI_HEAP_ASSERT(prev_free_block->next_free > new_block,&prev_free_block->next_free); // free blocks should be in orderheap->free_bytes += block_data_size(new_block);}block->header = (intptr_t)new_block;prev_free_block->next_free = new_block;
}看看heap_block这个结构体,包括一个总的block 链表和一个空闲block列表
/* Block in the heapHeap implementation uses two single linked lists, a block list (all blocks) and a free list (free blocks).'header' holds a pointer to the next block (used or free) ORed with a free flag (the LSB of the pointer.) is_free() and get_next_block() utility functions allow typed access to these values.'next_free' is valid if the block is free and is a pointer to the next block in the free list.
*/
typedef struct heap_block {intptr_t header; /* Encodes next block in heap (used or unused) and also free/used flag */union {uint8_t data[1]; /* First byte of data, valid if block is used. Actual size of data is 'block_data_size(block)' */struct heap_block *next_free; /* Pointer to next free block, valid if block is free */};
} heap_block_t;block的信息被损坏,查看block信息。
3.1 问题原因和解决方法
原因在于内存溢出,申请的空间不足放下,强制填入导致后一个block的信息被破坏。
检查每个内存申请。