原文链接:麒麟KYSEC使用方法05-命令设置密码强度
hello,大家好啊,今天给大家带来麒麟KYLINOS的kysec使用方法系列文章第五篇内容----使用命令设置密码强度,密码强度策略有两个文件需要修改,pwquality.conf/login.defs,今天给大家介绍一下使用命令设置密码强度的文章,欢迎大家点个赞并点个在看。关注我吧!
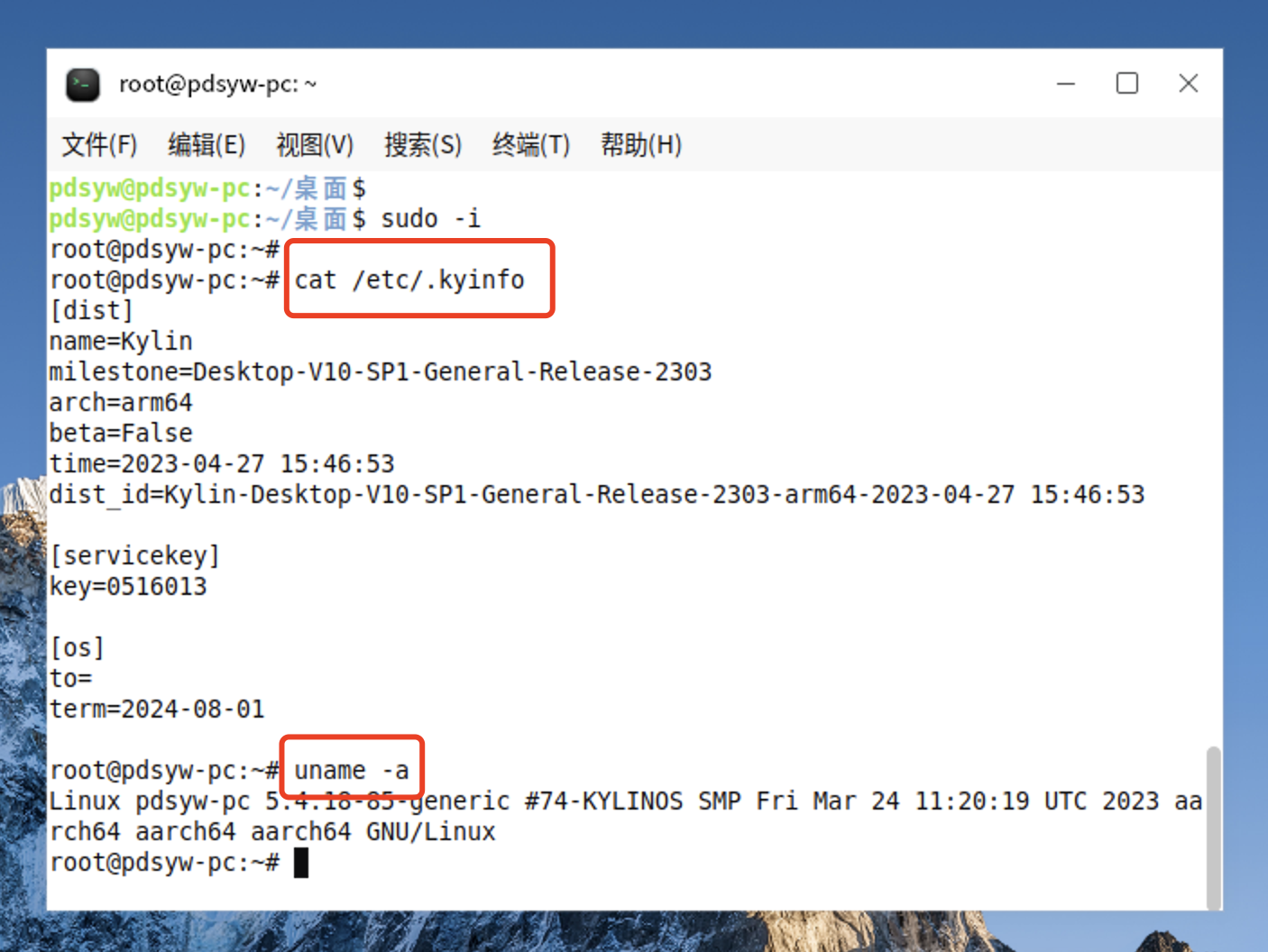
1、查看系统信息
pdsyw@pdsyw-pc:~/桌面$ sudo -i
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# cat /etc/.kyinfo
[dist]
name=Kylin
milestone=Desktop-V10-SP1-General-Release-2303
arch=arm64
beta=False
time=2023-04-27 15:46:53
dist_id=Kylin-Desktop-V10-SP1-General-Release-2303-arm64-2023-04-27 15:46:53[servicekey]
key=0516013[os]
to=
term=2024-08-01root@pdsyw-pc:~# uname -a
Linux pdsyw-pc 5.4.18-85-generic #74-KYLINOS SMP Fri Mar 24 11:20:19 UTC 2023 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/Linux
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
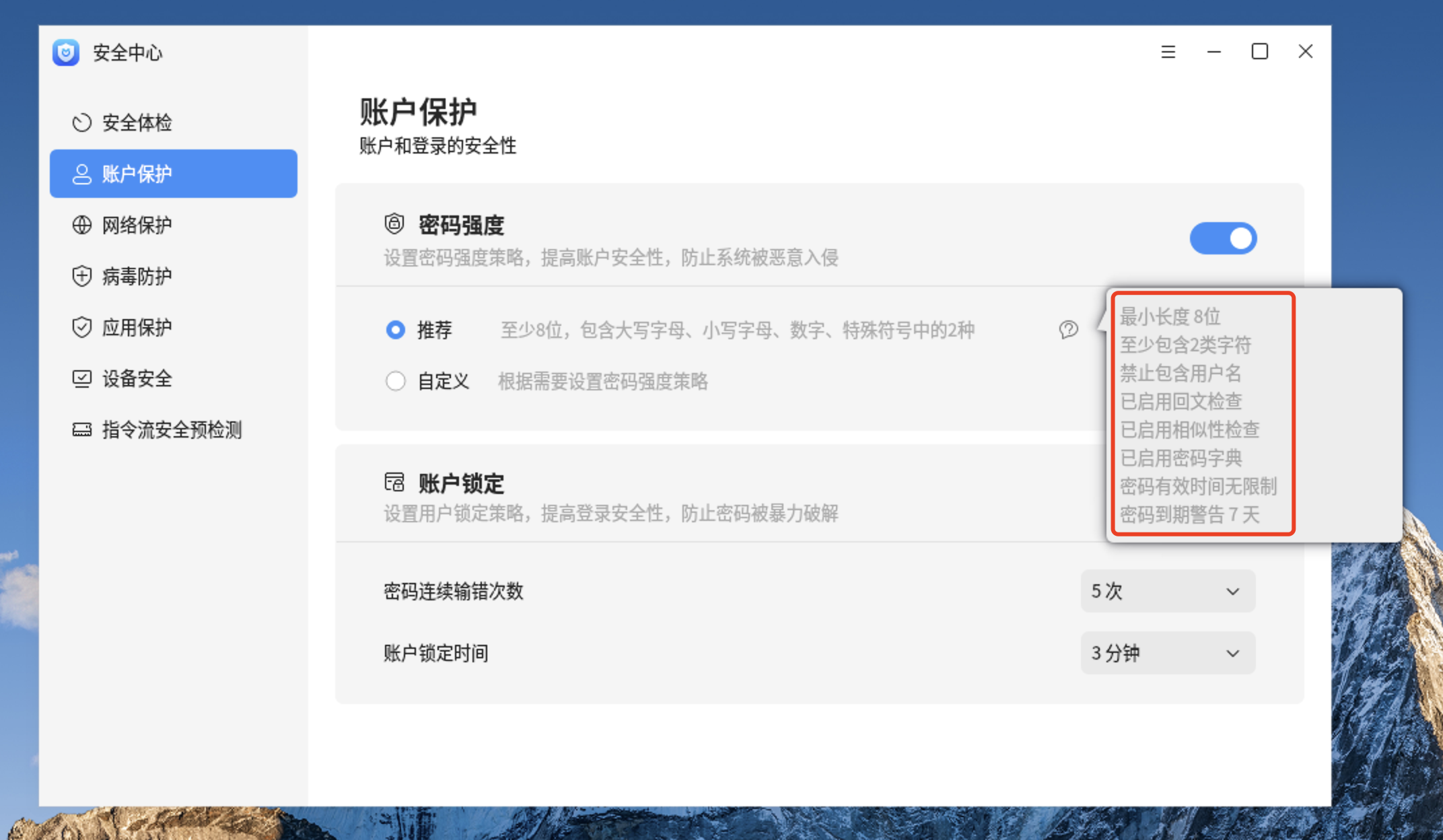
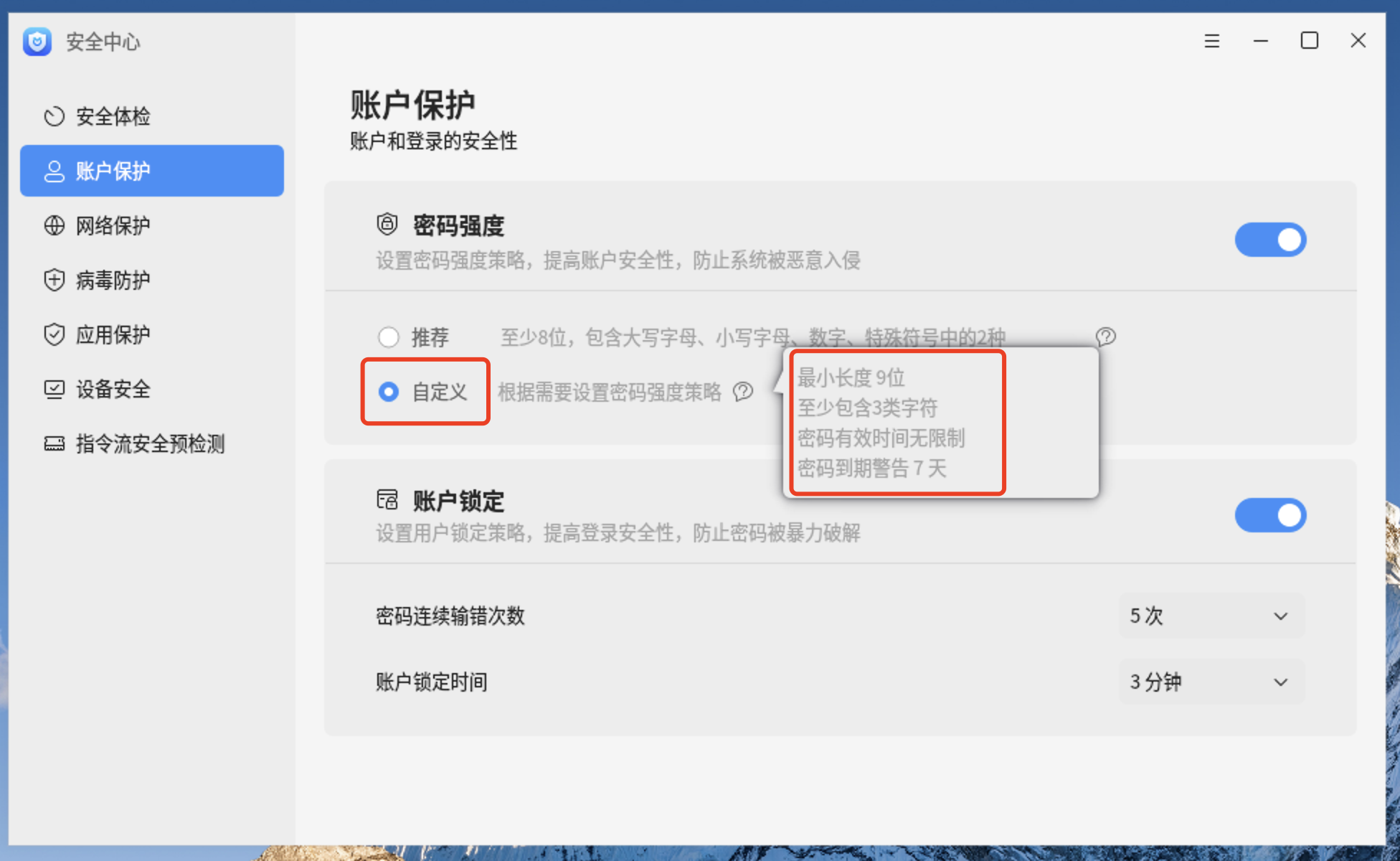
2、查看推荐的密码策略
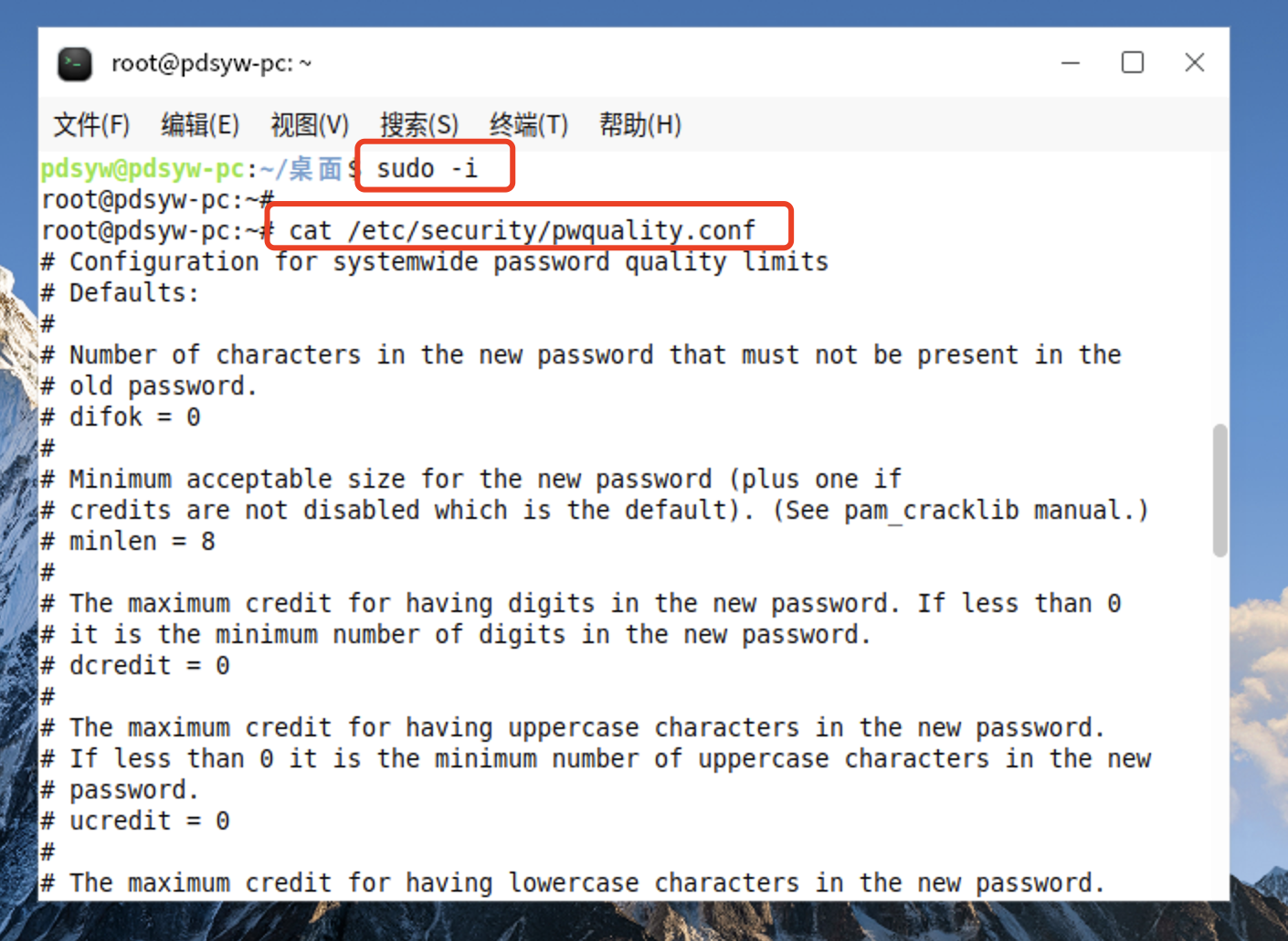
3、查看密码策略配置文件
pdsyw@pdsyw-pc:~/桌面$ sudo -i
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# cat /etc/security/pwquality.conf
# Configuration for systemwide password quality limits
# Defaults:
#
# Number of characters in the new password that must not be present in the
# old password.
# difok = 0
#
# Minimum acceptable size for the new password (plus one if
# credits are not disabled which is the default). (See pam_cracklib manual.)
# minlen = 8
#
# The maximum credit for having digits in the new password. If less than 0
# it is the minimum number of digits in the new password.
# dcredit = 0
#
# The maximum credit for having uppercase characters in the new password.
# If less than 0 it is the minimum number of uppercase characters in the new
# password.
# ucredit = 0
#
# The maximum credit for having lowercase characters in the new password.
# If less than 0 it is the minimum number of lowercase characters in the new
# password.
# lcredit = 0
#
# The maximum credit for having other characters in the new password.
# If less than 0 it is the minimum number of other characters in the new
# password.
# ocredit = 0
#
# The minimum number of required classes of characters for the new
# password (digits, uppercase, lowercase, others).
# minclass = 2
#
# The maximum number of allowed consecutive same characters in the new password.
# The check is disabled if the value is 0.
# maxrepeat = 0
#
# The maximum number of allowed consecutive characters of the same class in the
# new password.
# The check is disabled if the value is 0.
# maxclassrepeat = 0
#
# Whether to check for the words from the passwd entry GECOS string of the user.
# The check is enabled if the value is not 0.
# gecoscheck = 0
#
# Whether to check for the words from the cracklib dictionary.
# The check is enabled if the value is not 0.
# dictcheck = 0
#
# Whether to check if it contains the user name in some form.
# The check is enabled if the value is not 0.
# usercheck = 0
#
# Whether the check is enforced by the PAM module and possibly other
# applications.
# The new password is rejected if it fails the check and the value is not 0.
# enforcing = 1
#
# Path to the cracklib dictionaries. Default is to use the cracklib default.
# dictpath =
#
# Prompt user at most N times before returning with error. The default is 1.
# retry = 1
#
# Enforces pwquality checks on the root user password.
# Enabled if the option is present.
# enforce_for_root
#
# Skip testing the password quality for users that are not present in the
# /etc/passwd file.
# Enabled if the option is present.
# local_users_only
#
# Whether to check the new password is a palindrome or not
# Enabled if the option is present
palindrome
#
# Whether to check the new password is simliar with old one
# Check include only case changes and rotated
# Disabled if the option is present
# no_similar_check
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
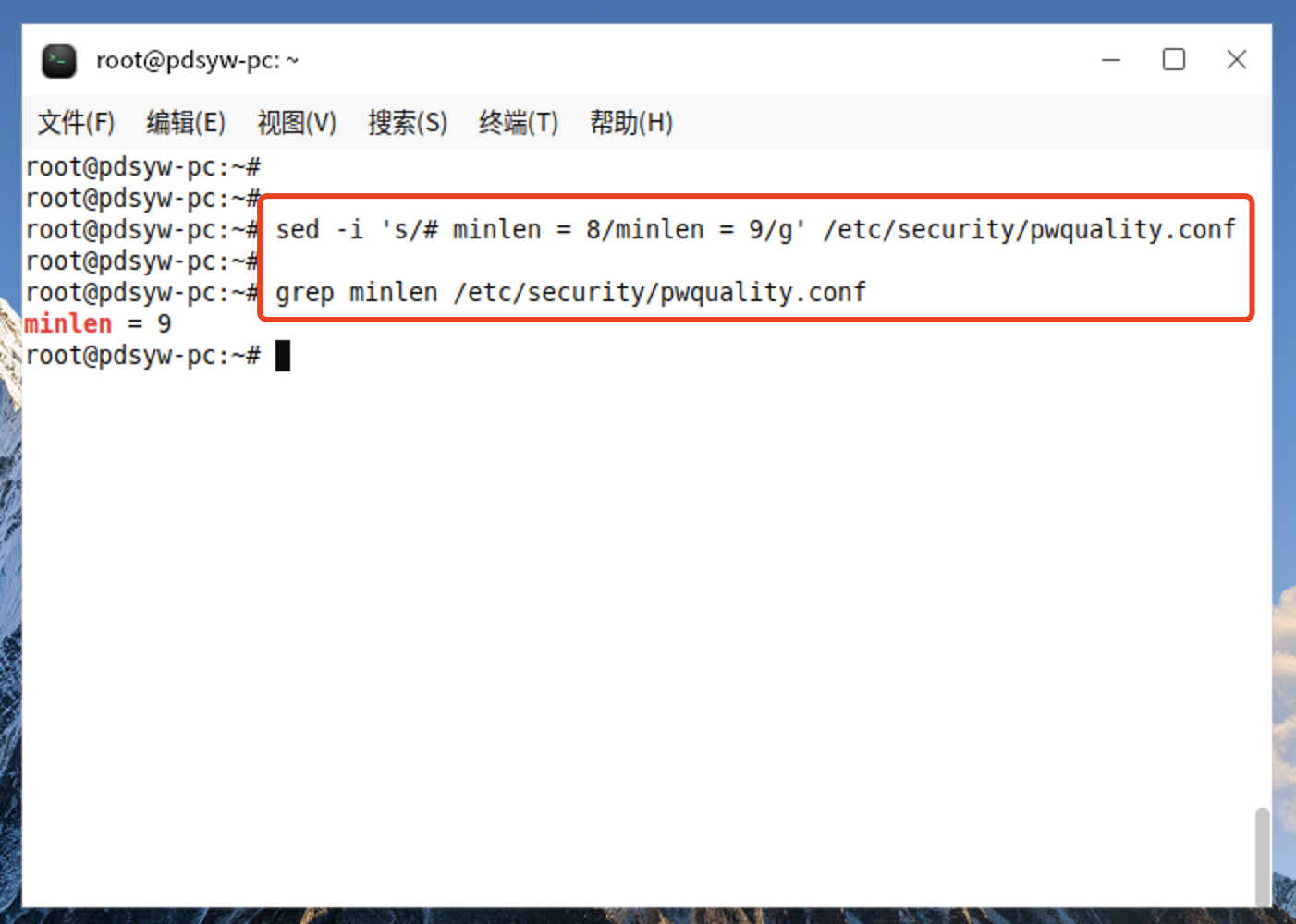
4.1、更改最小长度为9位
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/# minlen = 8/minlen = 9/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep minlen /etc/security/pwquality.conf
minlen = 9
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
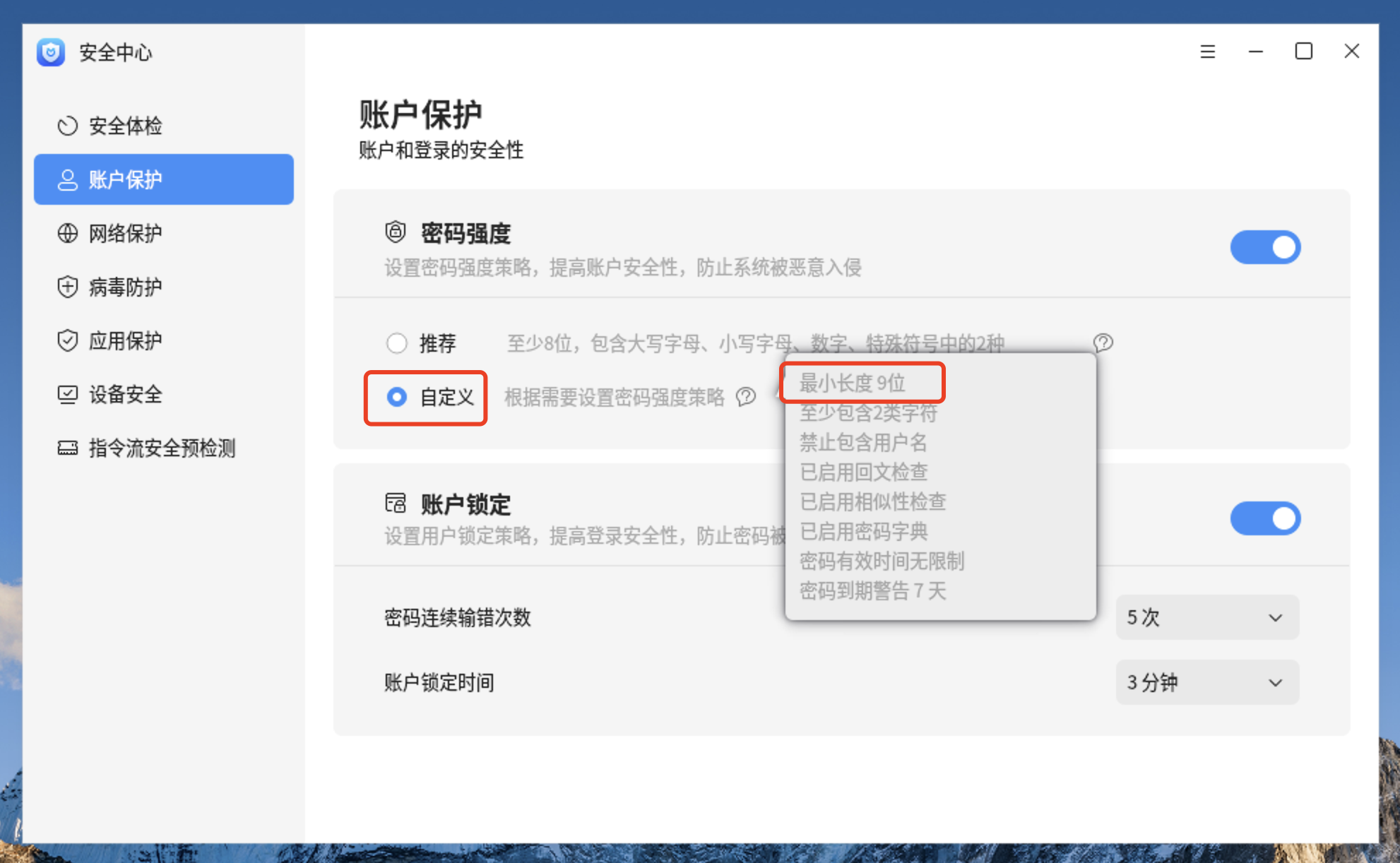
4.2、更改后的内容
5.1、更改至少包含3类字符
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/# minclass = 2/minclass = 3/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep minclass /etc/security/pwquality.conf
minclass = 3
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
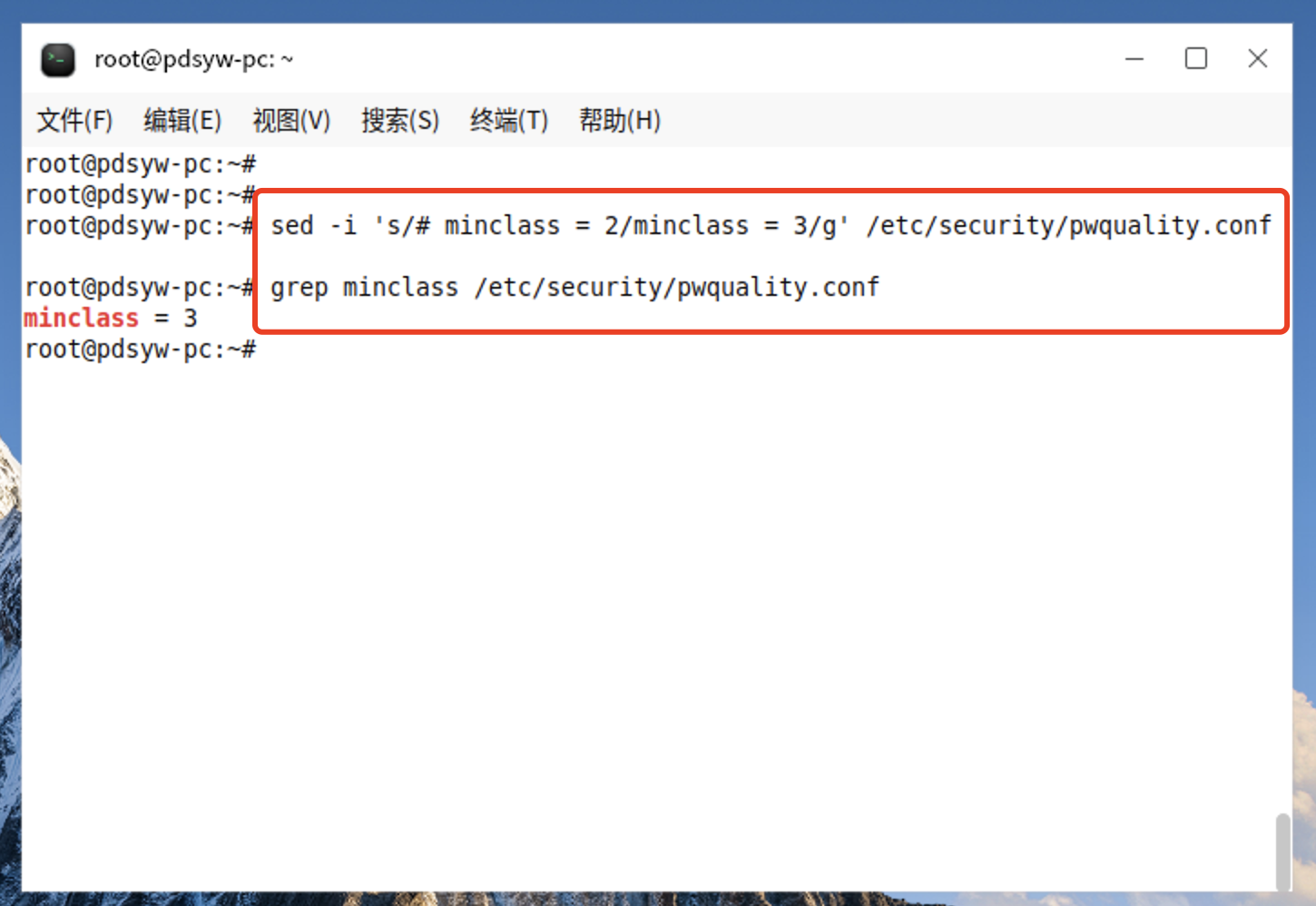
5.2、更改后的内容
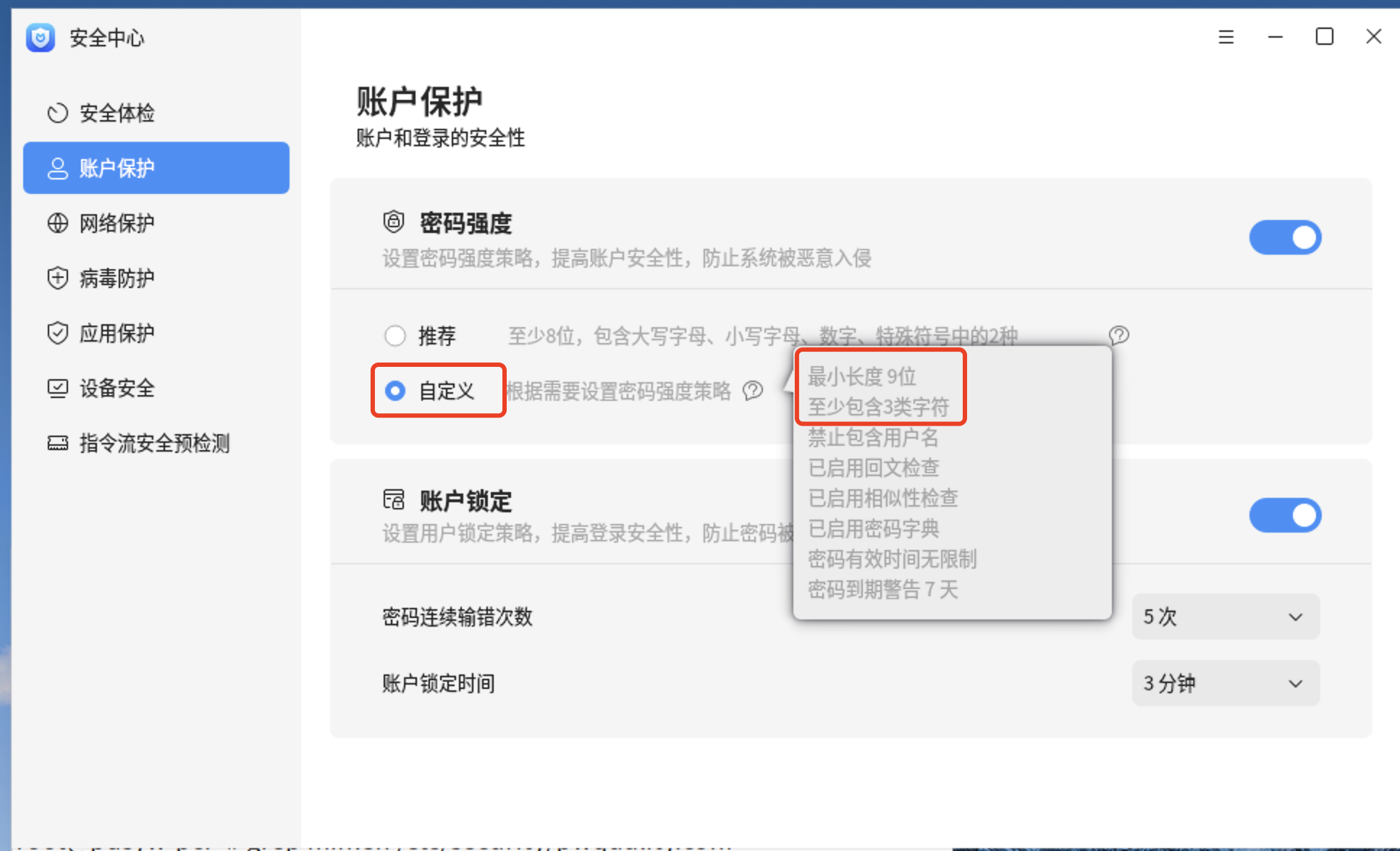
6.1、更改允许包含用户名
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/# usercheck = 0/usercheck = 0/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep usercheck /etc/security/pwquality.conf
usercheck = 0
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
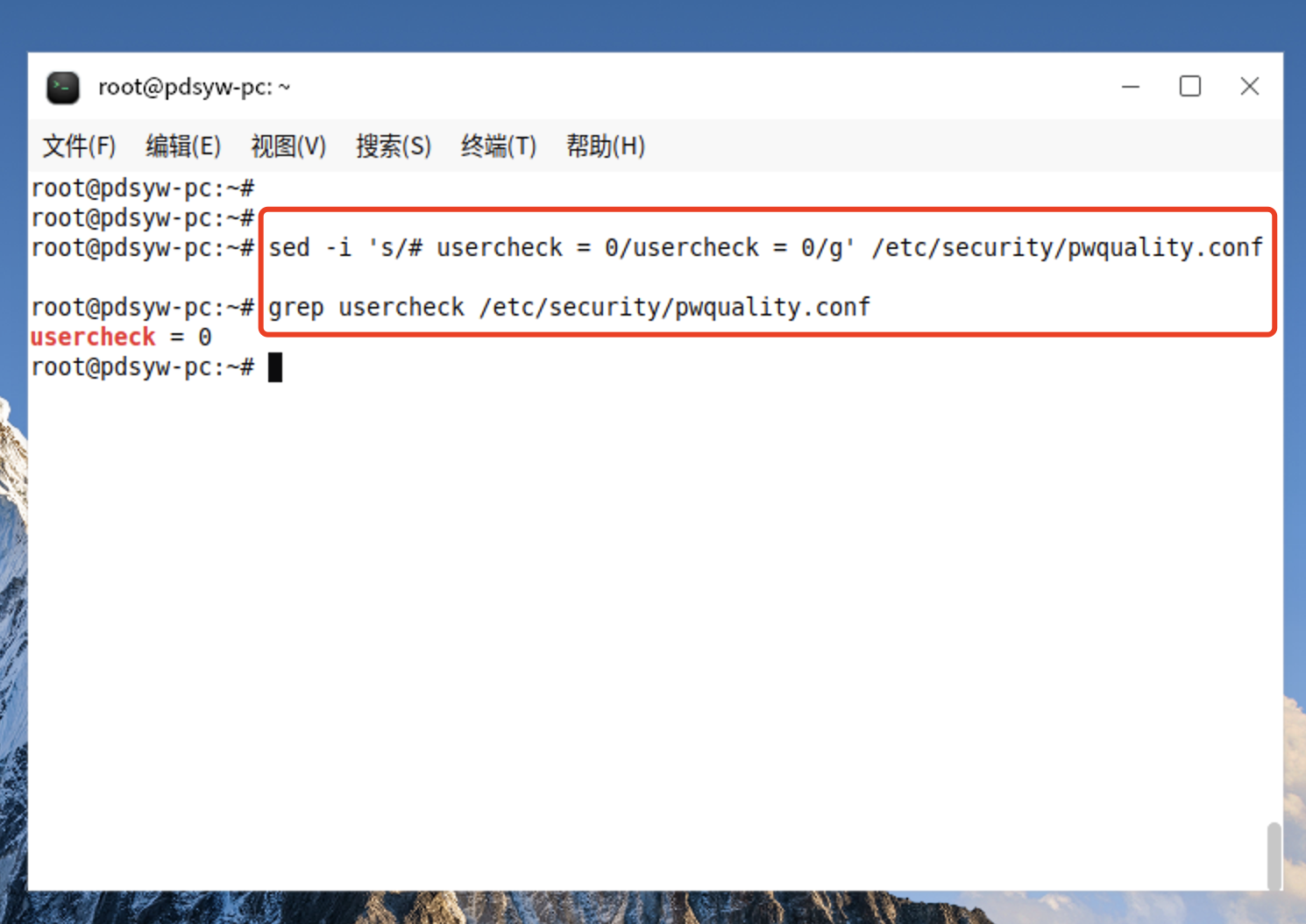
6.2、更改后的内容
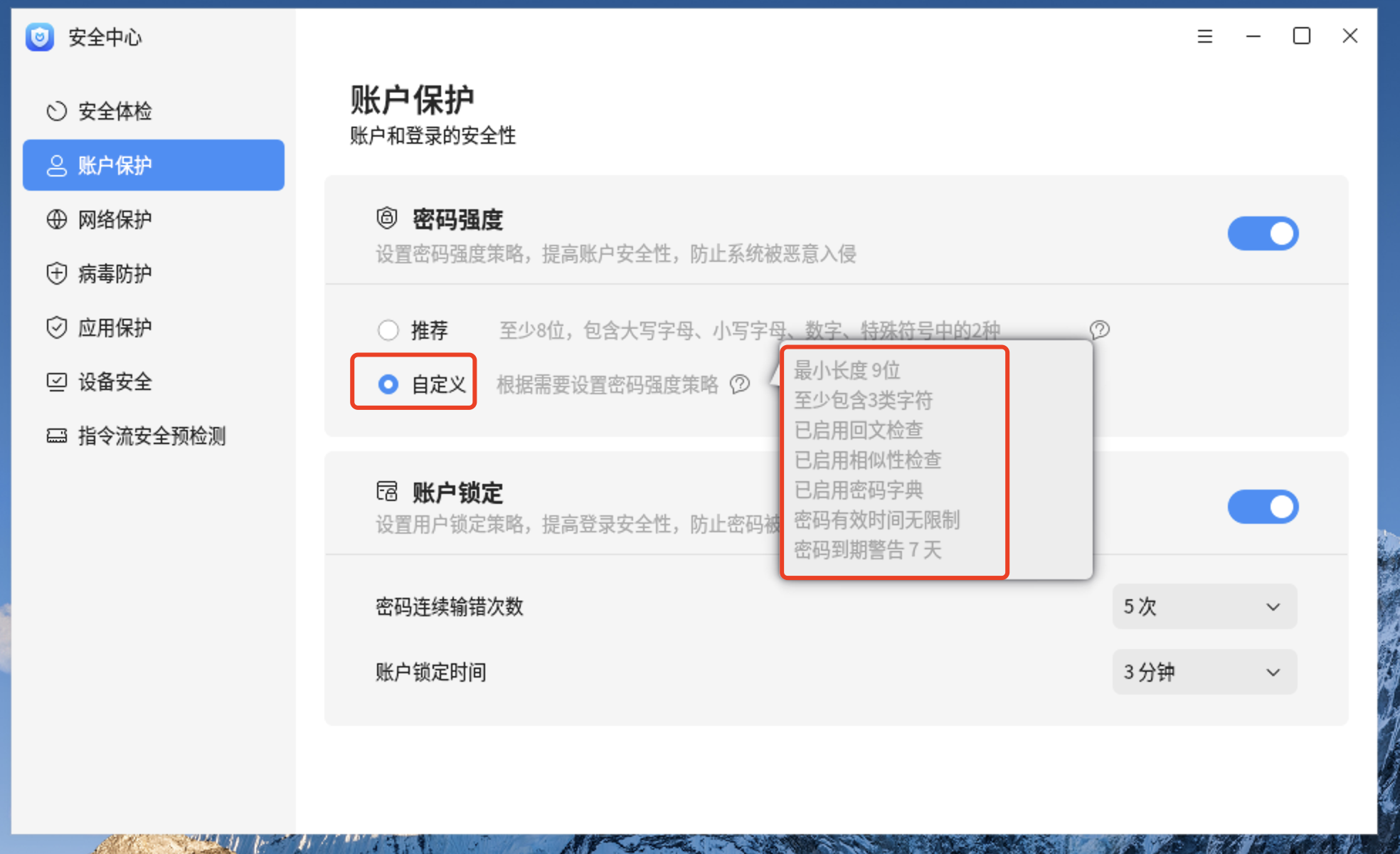
7.1、更改不启用回文检查
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/palindrome/#palindrome/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep palindrome /etc/security/pwquality.conf
# Whether to check the new password is a #palindrome or not
#palindrome
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
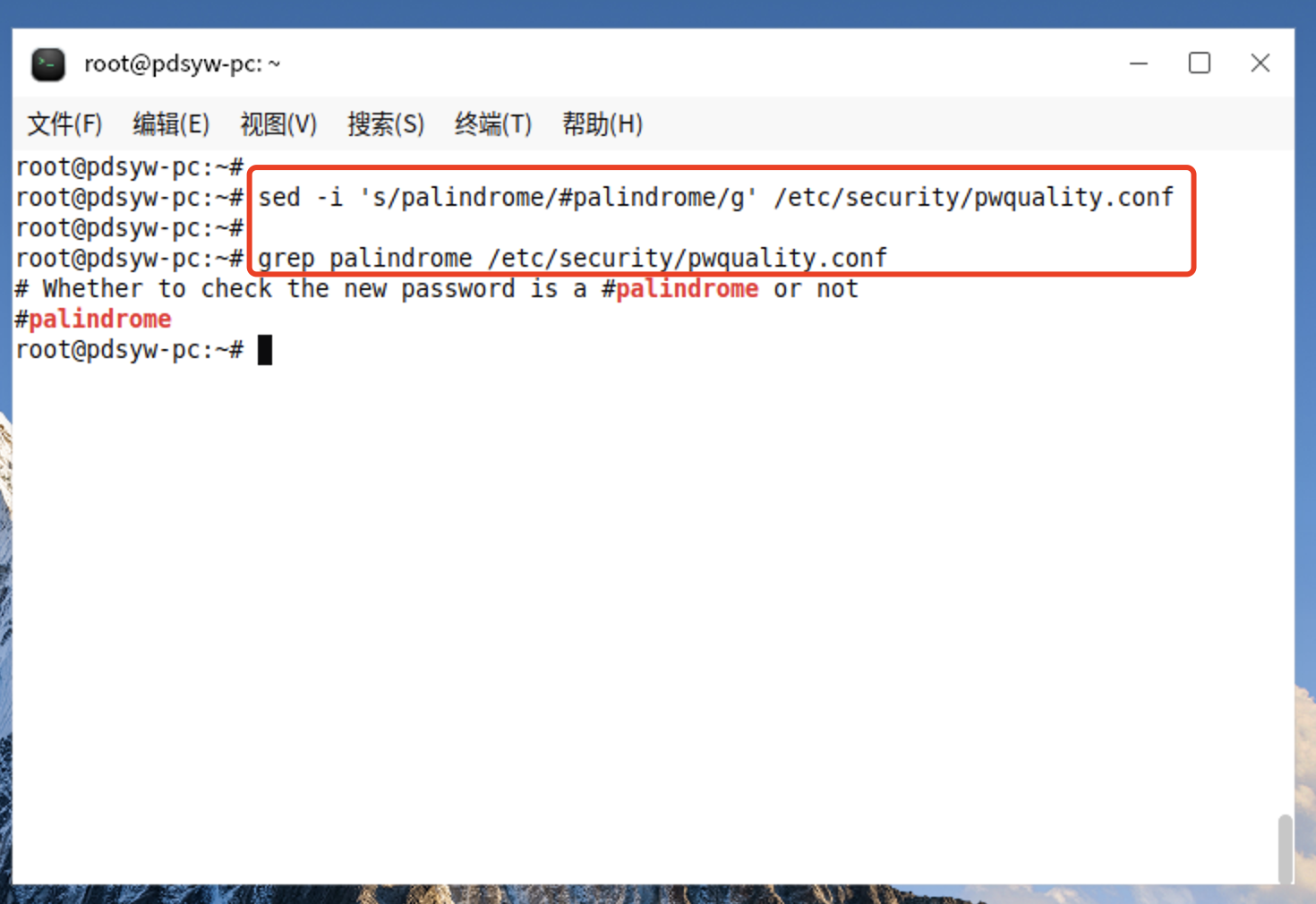
7.2、更改后的内容
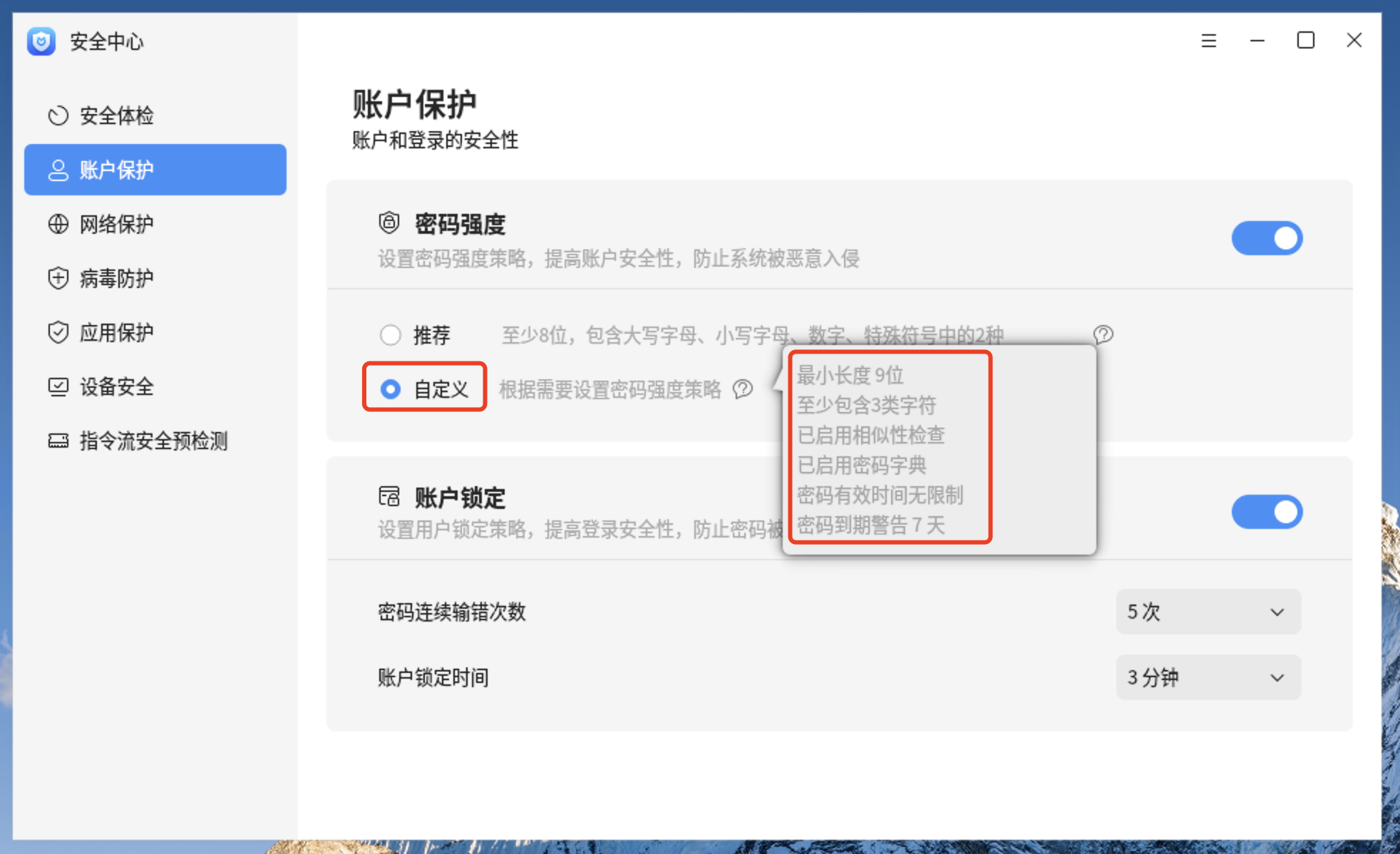
8.1、更改不启用相似性检查
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/# no_similar_check/no_similar_check/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep no_similar /etc/security/pwquality.conf
no_similar_check
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
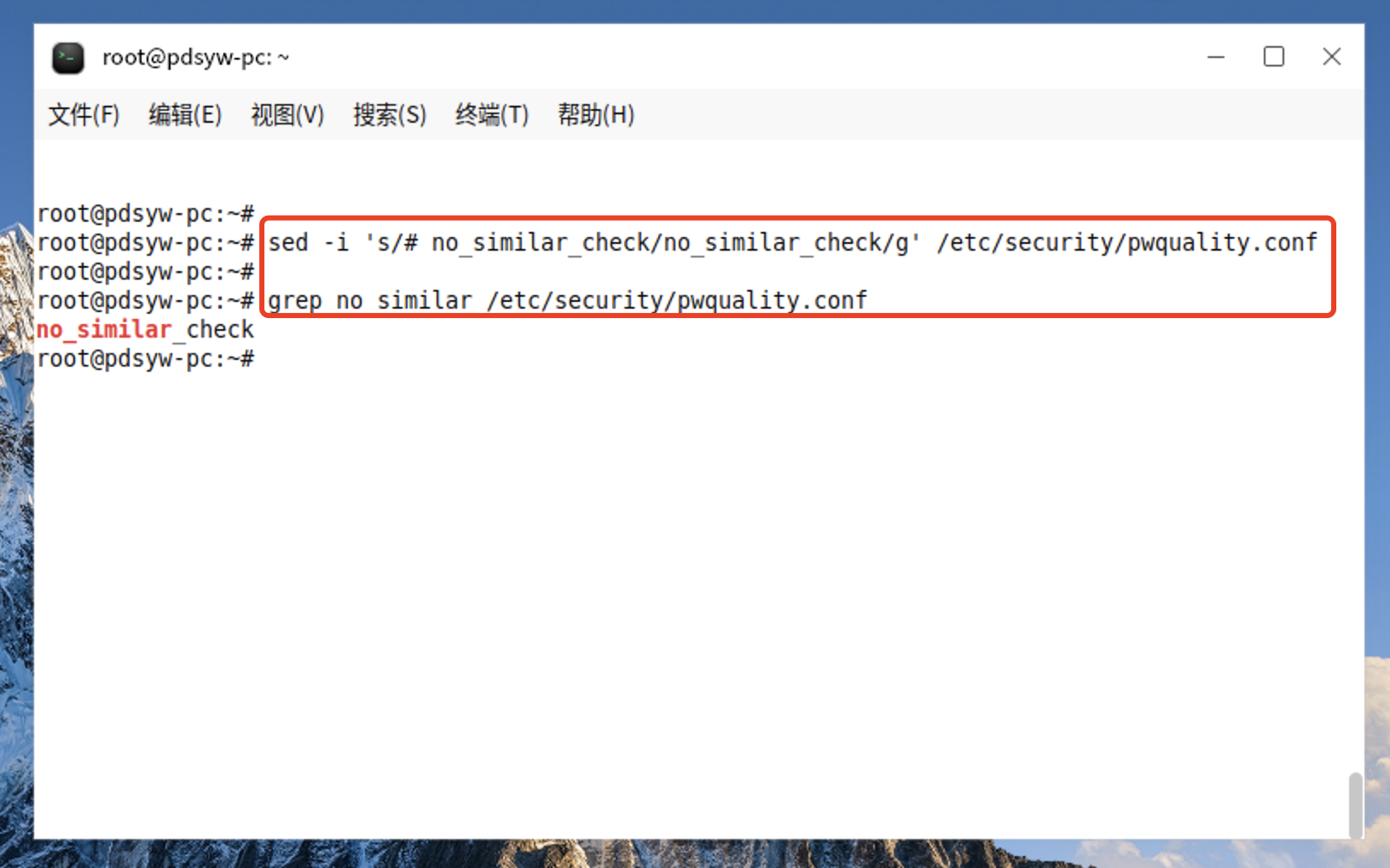
8.2、更改后的内容
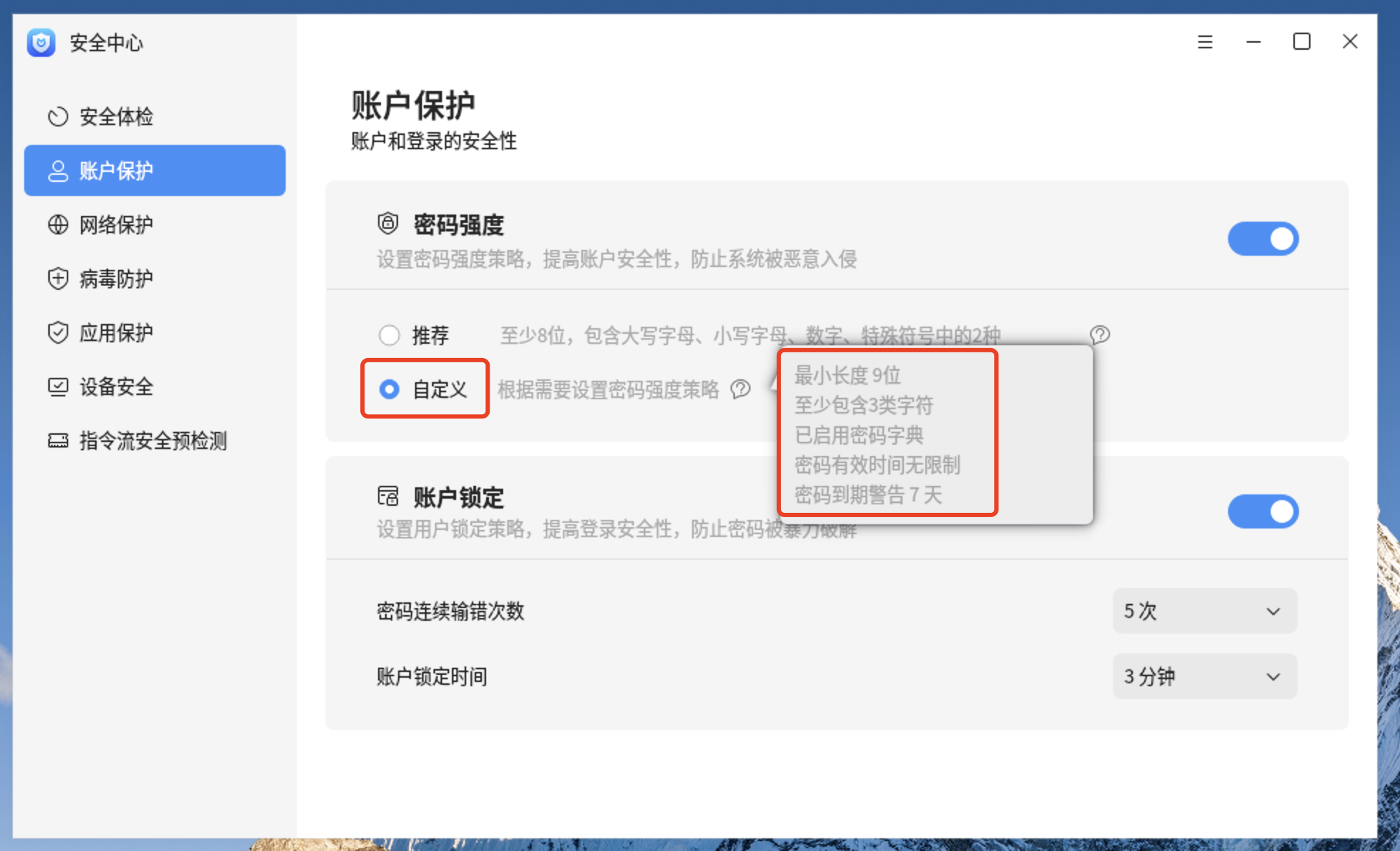
9.1、更改不启用密码字典检查
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i 's/# dictcheck = 0/dictcheck = 0/g' /etc/security/pwquality.conf
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep dictcheck /etc/security/pwquality.conf
dictcheck = 0
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
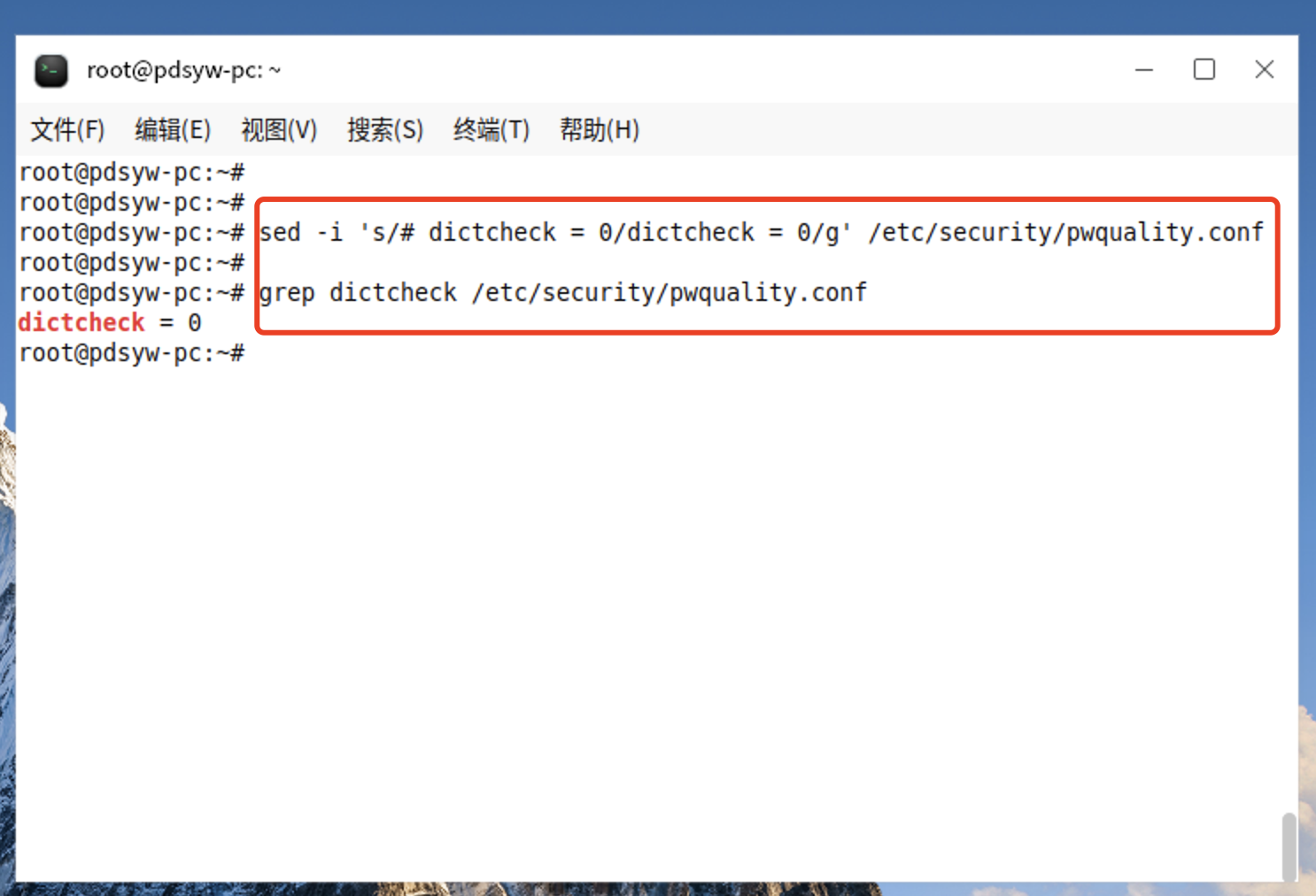
9.2、更改后的内容
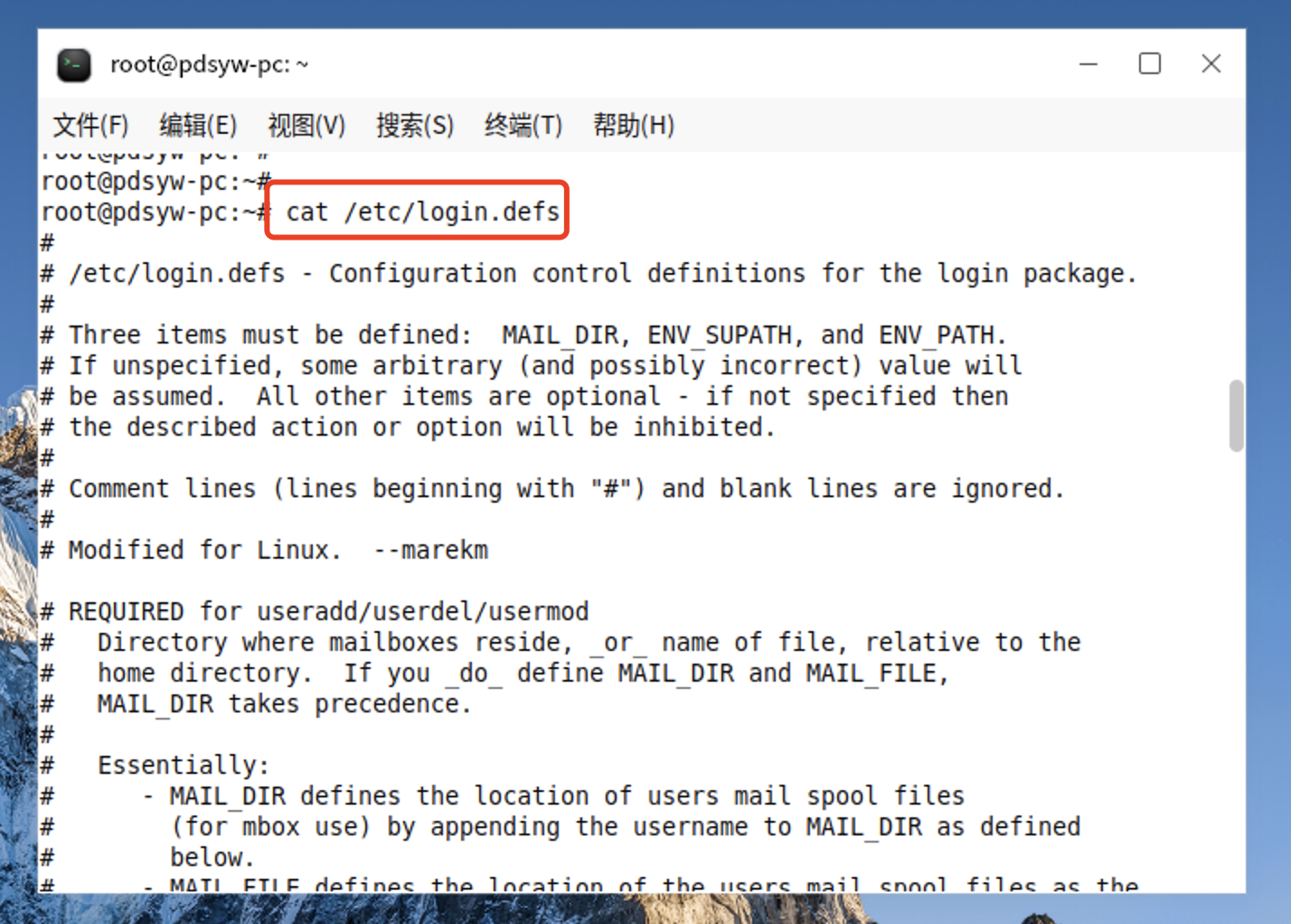
10、查看用户密码策略文件
root@pdsyw-pc:~# cat /etc/login.defs
#
# /etc/login.defs - Configuration control definitions for the login package.
#
# Three items must be defined: MAIL_DIR, ENV_SUPATH, and ENV_PATH.
# If unspecified, some arbitrary (and possibly incorrect) value will
# be assumed. All other items are optional - if not specified then
# the described action or option will be inhibited.
#
# Comment lines (lines beginning with "#") and blank lines are ignored.
#
# Modified for Linux. --marekm# REQUIRED for useradd/userdel/usermod
# Directory where mailboxes reside, _or_ name of file, relative to the
# home directory. If you _do_ define MAIL_DIR and MAIL_FILE,
# MAIL_DIR takes precedence.
#
# Essentially:
# - MAIL_DIR defines the location of users mail spool files
# (for mbox use) by appending the username to MAIL_DIR as defined
# below.
# - MAIL_FILE defines the location of the users mail spool files as the
# fully-qualified filename obtained by prepending the user home
# directory before $MAIL_FILE
#
# NOTE: This is no more used for setting up users MAIL environment variable
# which is, starting from shadow 4.0.12-1 in Debian, entirely the
# job of the pam_mail PAM modules
# See default PAM configuration files provided for
# login, su, etc.
#
# This is a temporary situation: setting these variables will soon
# move to /etc/default/useradd and the variables will then be
# no more supported
MAIL_DIR /var/mail
#MAIL_FILE .mail#
# Enable logging and display of /var/log/faillog login failure info.
# This option conflicts with the pam_tally PAM module.
#
FAILLOG_ENAB yes#
# Enable display of unknown usernames when login failures are recorded.
#
# WARNING: Unknown usernames may become world readable.
# See #290803 and #298773 for details about how this could become a security
# concern
LOG_UNKFAIL_ENAB no#
# Enable logging of successful logins
#
LOG_OK_LOGINS no#
# Enable "syslog" logging of su activity - in addition to sulog file logging.
# SYSLOG_SG_ENAB does the same for newgrp and sg.
#
SYSLOG_SU_ENAB yes
SYSLOG_SG_ENAB yes#
# If defined, all su activity is logged to this file.
#
#SULOG_FILE /var/log/sulog#
# If defined, file which maps tty line to TERM environment parameter.
# Each line of the file is in a format something like "vt100 tty01".
#
#TTYTYPE_FILE /etc/ttytype#
# If defined, login failures will be logged here in a utmp format
# last, when invoked as lastb, will read /var/log/btmp, so...
#
FTMP_FILE /var/log/btmp#
# If defined, the command name to display when running "su -". For
# example, if this is defined as "su" then a "ps" will display the
# command is "-su". If not defined, then "ps" would display the
# name of the shell actually being run, e.g. something like "-sh".
#
SU_NAME su#
# If defined, file which inhibits all the usual chatter during the login
# sequence. If a full pathname, then hushed mode will be enabled if the
# user's name or shell are found in the file. If not a full pathname, then
# hushed mode will be enabled if the file exists in the user's home directory.
#
HUSHLOGIN_FILE .hushlogin
#HUSHLOGIN_FILE /etc/hushlogins#
# *REQUIRED* The default PATH settings, for superuser and normal users.
#
# (they are minimal, add the rest in the shell startup files)
ENV_SUPATH PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
ENV_PATH PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games#
# Terminal permissions
#
# TTYGROUP Login tty will be assigned this group ownership.
# TTYPERM Login tty will be set to this permission.
#
# If you have a "write" program which is "setgid" to a special group
# which owns the terminals, define TTYGROUP to the group number and
# TTYPERM to 0620. Otherwise leave TTYGROUP commented out and assign
# TTYPERM to either 622 or 600.
#
# In Debian /usr/bin/bsd-write or similar programs are setgid tty
# However, the default and recommended value for TTYPERM is still 0600
# to not allow anyone to write to anyone else console or terminal# Users can still allow other people to write them by issuing
# the "mesg y" command.TTYGROUP tty
TTYPERM 0600#
# Login configuration initializations:
#
# ERASECHAR Terminal ERASE character ('\010' = backspace).
# KILLCHAR Terminal KILL character ('\025' = CTRL/U).
# UMASK Default "umask" value.
#
# The ERASECHAR and KILLCHAR are used only on System V machines.
#
# UMASK is the default umask value for pam_umask and is used by
# useradd and newusers to set the mode of the new home directories.
# 022 is the "historical" value in Debian for UMASK
# 027, or even 077, could be considered better for privacy
# There is no One True Answer here : each sysadmin must make up his/her
# mind.
#
# If USERGROUPS_ENAB is set to "yes", that will modify this UMASK default value
# for private user groups, i. e. the uid is the same as gid, and username is
# the same as the primary group name: for these, the user permissions will be
# used as group permissions, e. g. 022 will become 002.
#
# Prefix these values with "0" to get octal, "0x" to get hexadecimal.
#
ERASECHAR 0177
KILLCHAR 025
UMASK 022#
# Password aging controls:
#
# PASS_MAX_DAYS Maximum number of days a password may be used.
# PASS_MIN_DAYS Minimum number of days allowed between password changes.
# PASS_WARN_AGE Number of days warning given before a password expires.
#
PASS_MAX_DAYS 99999
PASS_MIN_DAYS 0
PASS_WARN_AGE 7#
# Min/max values for automatic uid selection in useradd
#
UID_MIN 1000
UID_MAX 60000
# System accounts
#SYS_UID_MIN 100
#SYS_UID_MAX 999#
# Min/max values for automatic gid selection in groupadd
#
GID_MIN 1000
GID_MAX 60000
# System accounts
#SYS_GID_MIN 100
#SYS_GID_MAX 999#
# Max number of login retries if password is bad. This will most likely be
# overriden by PAM, since the default pam_unix module has it's own built
# in of 3 retries. However, this is a safe fallback in case you are using
# an authentication module that does not enforce PAM_MAXTRIES.
#
LOGIN_RETRIES 5#
# Max time in seconds for login
#
LOGIN_TIMEOUT 60#
# Which fields may be changed by regular users using chfn - use
# any combination of letters "frwh" (full name, room number, work
# phone, home phone). If not defined, no changes are allowed.
# For backward compatibility, "yes" = "rwh" and "no" = "frwh".
#
CHFN_RESTRICT rwh#
# Should login be allowed if we can't cd to the home directory?
# Default in no.
#
DEFAULT_HOME yes#
# If defined, this command is run when removing a user.
# It should remove any at/cron/print jobs etc. owned by
# the user to be removed (passed as the first argument).
#
#USERDEL_CMD /usr/sbin/userdel_local#
# Enable setting of the umask group bits to be the same as owner bits
# (examples: 022 -> 002, 077 -> 007) for non-root users, if the uid is
# the same as gid, and username is the same as the primary group name.
#
# If set to yes, userdel will remove the user's group if it contains no
# more members, and useradd will create by default a group with the name
# of the user.
#
USERGROUPS_ENAB yes#
# Instead of the real user shell, the program specified by this parameter
# will be launched, although its visible name (argv[0]) will be the shell's.
# The program may do whatever it wants (logging, additional authentification,
# banner, ...) before running the actual shell.
#
# FAKE_SHELL /bin/fakeshell#
# If defined, either full pathname of a file containing device names or
# a ":" delimited list of device names. Root logins will be allowed only
# upon these devices.
#
# This variable is used by login and su.
#
#CONSOLE /etc/consoles
#CONSOLE console:tty01:tty02:tty03:tty04#
# List of groups to add to the user's supplementary group set
# when logging in on the console (as determined by the CONSOLE
# setting). Default is none.
#
# Use with caution - it is possible for users to gain permanent
# access to these groups, even when not logged in on the console.
# How to do it is left as an exercise for the reader...
#
# This variable is used by login and su.
#
#CONSOLE_GROUPS floppy:audio:cdrom#
# If set to "yes", new passwords will be encrypted using the MD5-based
# algorithm compatible with the one used by recent releases of FreeBSD.
# It supports passwords of unlimited length and longer salt strings.
# Set to "no" if you need to copy encrypted passwords to other systems
# which don't understand the new algorithm. Default is "no".
#
# This variable is deprecated. You should use ENCRYPT_METHOD.
#
#MD5_CRYPT_ENAB no#
# If set to MD5 , MD5-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to SHA256, SHA256-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to SHA512, SHA512-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to DES, DES-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password (default)
# Overrides the MD5_CRYPT_ENAB option
#
# Note: It is recommended to use a value consistent with
# the PAM modules configuration.
#
ENCRYPT_METHOD SHA512#
# Only used if ENCRYPT_METHOD is set to SHA256 or SHA512.
#
# Define the number of SHA rounds.
# With a lot of rounds, it is more difficult to brute forcing the password.
# But note also that it more CPU resources will be needed to authenticate
# users.
#
# If not specified, the libc will choose the default number of rounds (5000).
# The values must be inside the 1000-999999999 range.
# If only one of the MIN or MAX values is set, then this value will be used.
# If MIN > MAX, the highest value will be used.
#
# SHA_CRYPT_MIN_ROUNDS 5000
# SHA_CRYPT_MAX_ROUNDS 5000################# OBSOLETED BY PAM ##############
# #
# These options are now handled by PAM. Please #
# edit the appropriate file in /etc/pam.d/ to #
# enable the equivelants of them.
#
################MOTD_FILE
#DIALUPS_CHECK_ENAB
#LASTLOG_ENAB
#MAIL_CHECK_ENAB
#OBSCURE_CHECKS_ENAB
#PORTTIME_CHECKS_ENAB
#SU_WHEEL_ONLY
#CRACKLIB_DICTPATH
#PASS_CHANGE_TRIES
#PASS_ALWAYS_WARN
#ENVIRON_FILE
#NOLOGINS_FILE
#ISSUE_FILE
#PASS_MIN_LEN
#PASS_MAX_LEN
#ULIMIT
#ENV_HZ
#CHFN_AUTH
#CHSH_AUTH
#FAIL_DELAY################# OBSOLETED #######################
# #
# These options are no more handled by shadow. #
# #
# Shadow utilities will display a warning if they #
# still appear. #
# #
#################################################### CLOSE_SESSIONS
# LOGIN_STRING
# NO_PASSWORD_CONSOLE
# QMAIL_DIRroot@pdsyw-pc:~#
11.1、更改密码有效时间为90天
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i '/^PASS_MAX_DAYS/c\PASS_MAX_DAYS 90' /etc/login.defs
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep PASS_MAX_DAYS /etc/login.defs
# PASS_MAX_DAYS Maximum number of days a password may be used.
PASS_MAX_DAYS 90
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
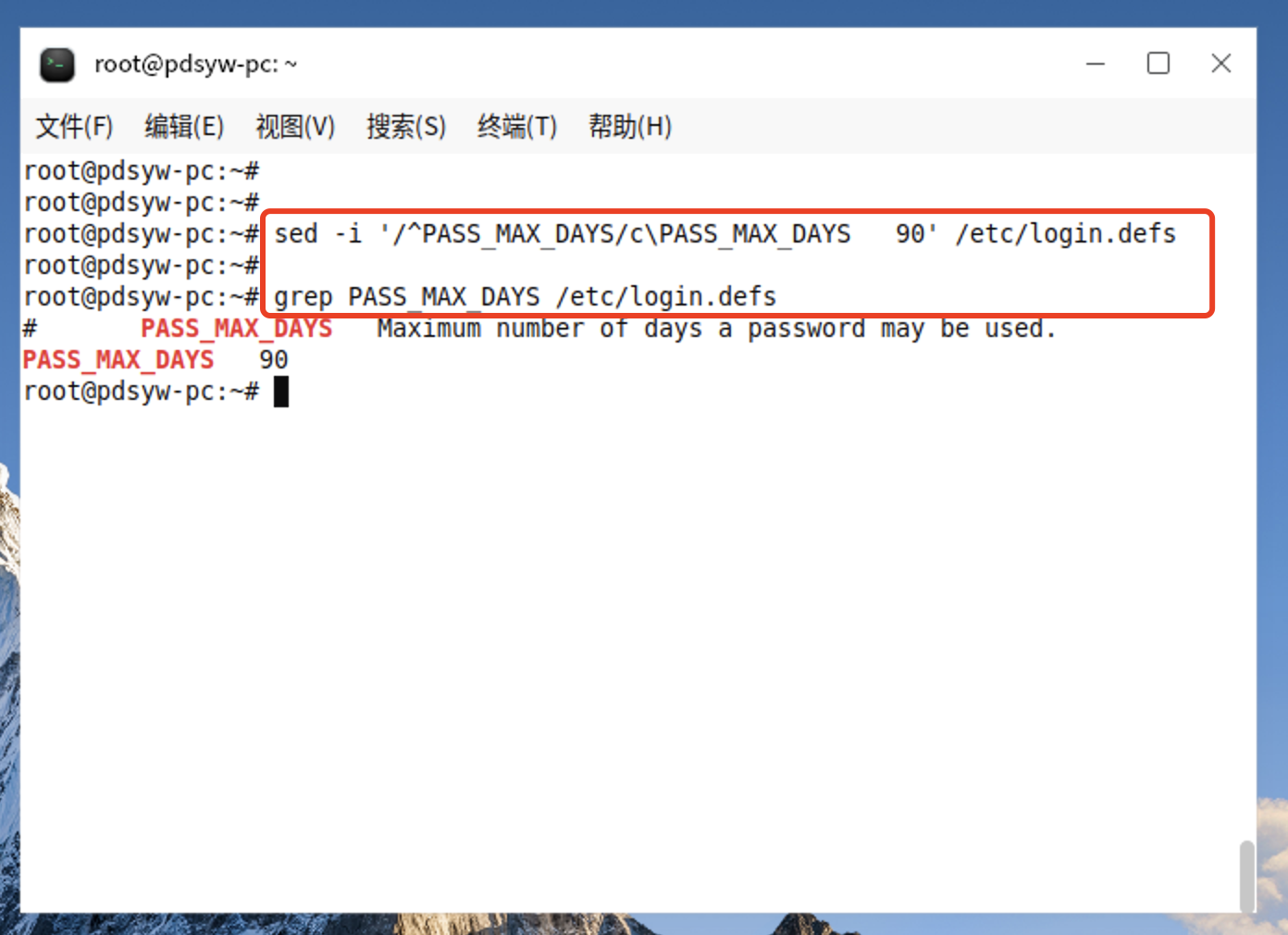
11.2、更改后的内容
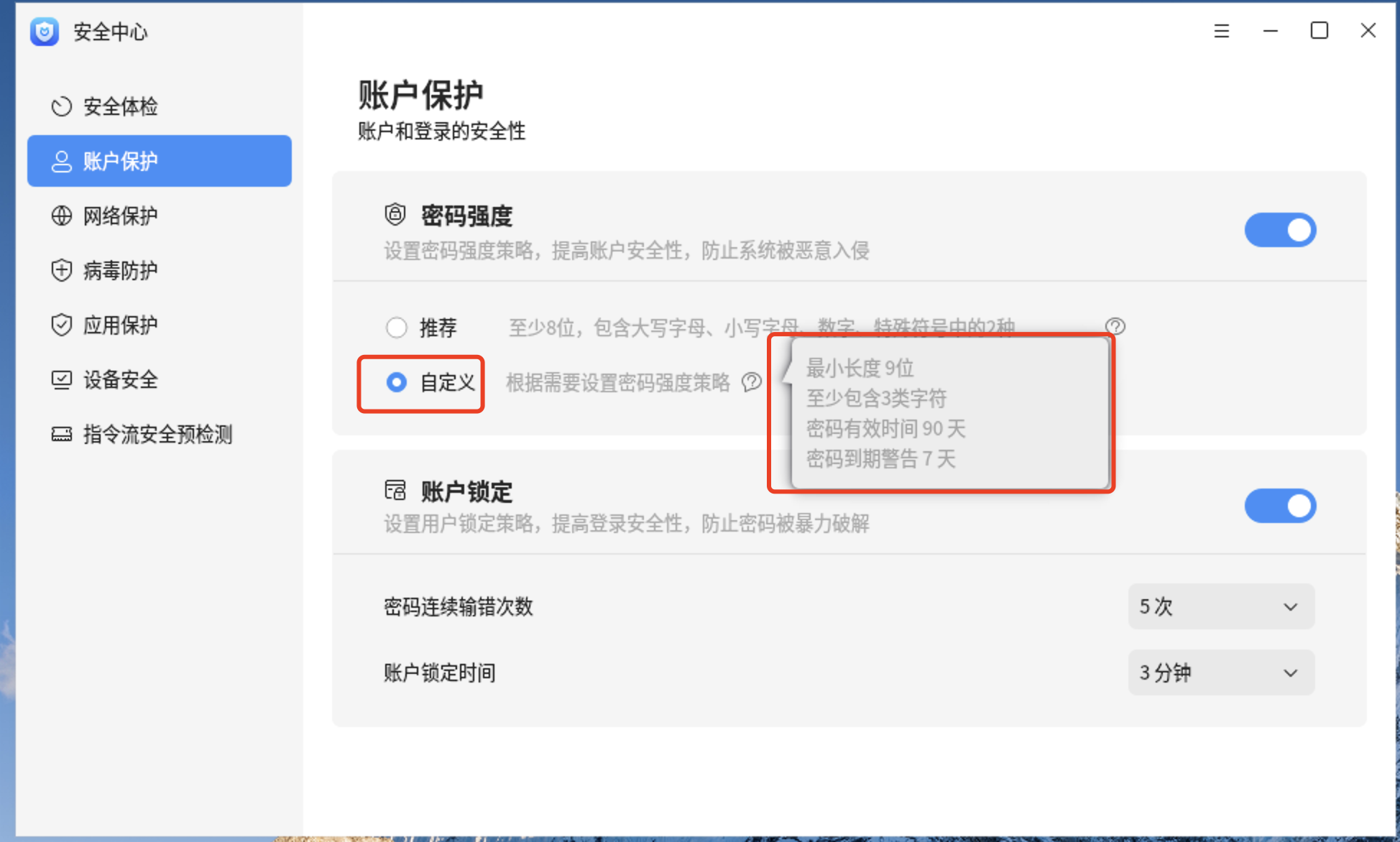
12.1、更改密码到期警告为15天
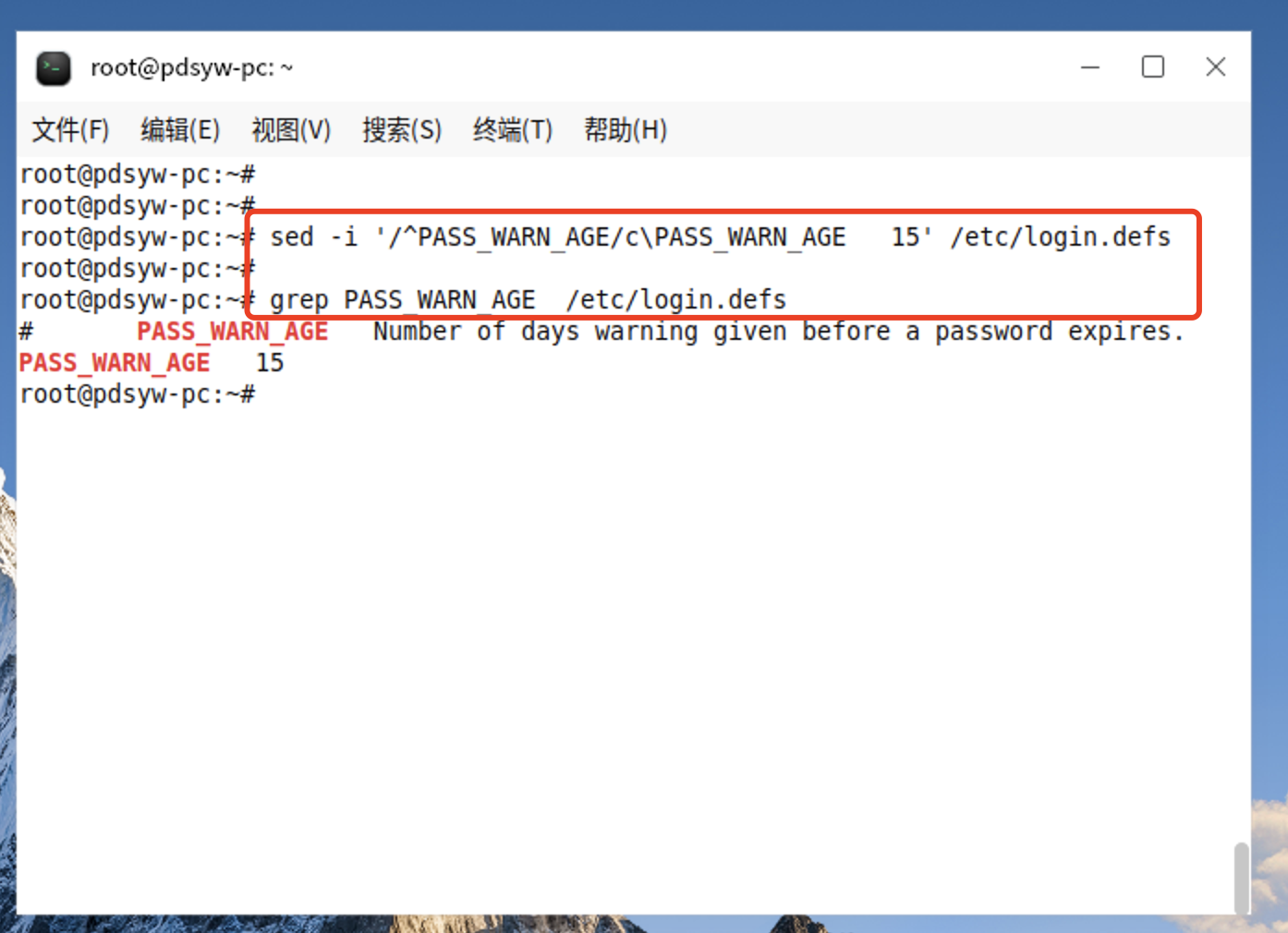
root@pdsyw-pc:~# sed -i '/^PASS_WARN_AGE/c\PASS_WARN_AGE 15' /etc/login.defs
root@pdsyw-pc:~#
root@pdsyw-pc:~# grep PASS_WARN_AGE /etc/login.defs
# PASS_WARN_AGE Number of days warning given before a password expires.
PASS_WARN_AGE 15
root@pdsyw-pc:~#