SpringBoot3核心原理
事件和监听器
生命周期监听
场景:监听应用的生命周期
可以通过下面步骤自定义SpringApplicationRunListener来监听事件。
①、编写SpringApplicationRunListener实现类
②、在META-INF/spring.factories中配置org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=自己的Listener,还可以指定一个有参构造器,接收两个参数SpringApplication application, String[] args
③、springboot在spring-boot.jar中配置了默认的Listener,如下:
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener

场景实现
创建监听器
MyApplicationListener
package com.louis.listener;import org.springframework.boot.ConfigurableBootstrapContext;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;import java.time.Duration;/*** springboot应用生命周期监听* @author XRY* @date 2023年07月14日14:51*/
public class MyApplicationListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {@Overridepublic void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {System.out.println("===========starting==========正在启动=======");}@Overridepublic void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {System.out.println("===========environmentPrepared==========环境准备完成=======");}@Overridepublic void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {//相当与IOC容器System.out.println("===========contextPrepared==========ioc容器准备完成=======");}@Overridepublic void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {System.out.println("===========contextLoaded==========ioc容器加载完成=======");}@Overridepublic void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {System.out.println("===========started==========启动完成=======");}@Overridepublic void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {System.out.println("===========ready==========准备就绪=======");}@Overridepublic void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {System.out.println("===========failed==========应用启动失败=======");}
}
提示:
想要让配置的监听器生效,需要在根目录下创建一个META-INF文件夹并添加文件spring.factories(它是一个key,value写法:key为接口全类名, value为我们创建类的全类名)
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=com.louis.listener.MyApplicationListener
springboot应用生命周期监听
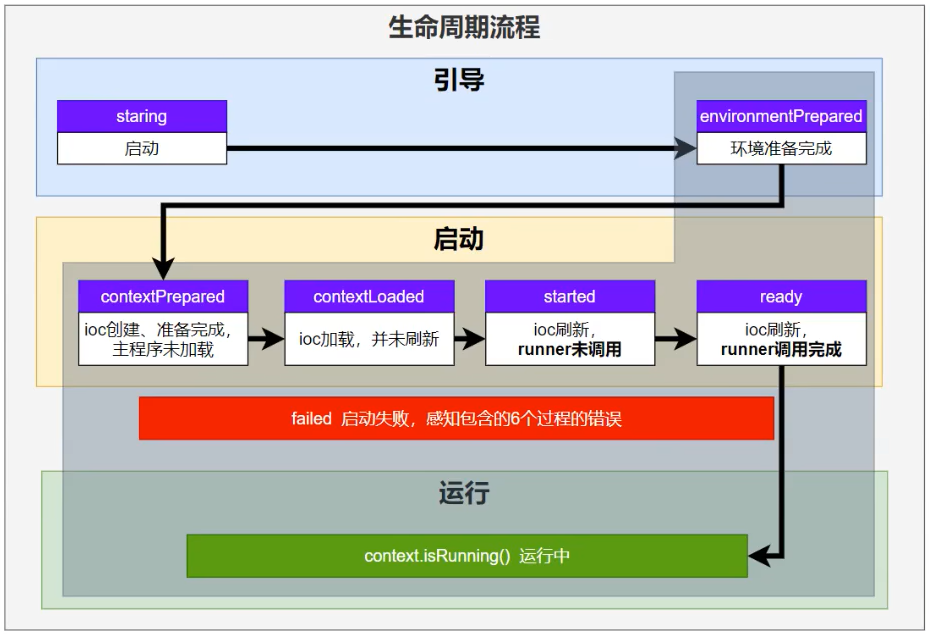
Listener先要从BootStrapContext引导整个项目启动,主要分为下面的几个步骤:
-
引导:利用BootstrapContext引导整个项目启动
starting:应用开始,调用SpringApplication的run方法,只要有了BootStrapContext就执行 environmentPrepared:环境准备好(把启动参数等绑定到环境变量中),但是ioc容器还没有创建。(调一次) -
启动:
contextPrepared: ioc容器创建并准备好,但是sources(主配置类)没加载,并关闭上下文,组件还没有创建(调一次)
contextLoaded: ioc容器加载。著配置类加载进去,但是ioc容器还没有刷新。(Bean都没创建)
started: ioc容器刷新了(容器中加入了Bean),但是runner没调用。
ready: ioc容器刷新了(容器中加入了Bean),所有runner调用完。 -
运行
以前的步骤都正确执行,代表容器running
事件触发时机
1、各种回调监听器介绍
| 监听器 | 监听阶段 | 作用 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BootstrapRegistryInitializer | 感知特定阶段 | 感知引导初始化META-INF/spring.factories 创建引导上下文bootstrapContext的时候触发可以在主程序调用:application.add.BootstrapRegistryInitializer() | 进行密钥校对授权 |
| ApplicationContextInitializer | 感知特定阶段 | 感知ioc容器初始化META-INF/spring.factories | |
| ApplicationListener | 感知全阶段 | 基于事件机制,感知事件。@Bean或EventListener、SpringApplication.addListeners(…)或SpringApplicationBuilder.listeners(…)、META-INF/spring.factories | |
| SpringApplicationRunListener | 感知全阶段生命周期+各种阶段 | 自定义操作META-INF/spring.factories | |
| ApplicationRunner | 感知特定阶段 | 感知应用就绪Ready的@Bean | |
| CommandLineRunner | 感知特定阶段 | 感知应用就绪Ready的@Bean |
总结:
如果项目启动前做事:BootstrapRegistryInitializer和ApplicationContextInitializer
如果想要在项目启动完成后做事:ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
如果想要干涉生命周期:SpringApplicationRunListener
如果想要用事件机制:ApplicationListener
2、事件完整触发流程(9种事件)
- ApplicationStartingEvent:应用启动但未做任何事情,
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent:Environment准备好,但context未创建
- ApplicationContextInitializedEvent:ApplicationContext准备好,ApplicationContextInitializers调用,到那时任何bean未加载
- ApplicationPreparedEvent:容器刷新之前,bean定义信息加载
- ApplicationStartedEvent:容器刷新完成,runner未调用
- AvailabilityChangeEvent:LivenessState.CORRECT应用存活,存活探针
- ApplicationReadyEvent:任何runner被调用
- AvailabilityChangeEvent:ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC应用就绪,可以接收请求,就绪探针
- ApplicationFailedEvent:启动出错
事件发送顺序

**两个探针的作用是感知应用是否存货和就绪。 **
3、SpringBoot事件驱动开发
应用启动过程生命周期事件感知(9大事件)、应用运行中事件感知(无数种)
- 事件发布:ApplicationEventPublisherAware或注入:ApplicationEventMulticaser
- 事件监听:组件 + @EventListener
示例

创建service
AccountService
@Service
public class AccountService {public void addAccountScore(String username){System.out.println(username + "加了1分");}
}
CouponService
@Service
public class CouponService {public void sendCoupon(String username){System.out.println(username + "随机得到了一张优惠券");}
}
SystemService
@Service
public class SystemService {public void recordLog(String username, String password){System.out.println(username + " ,密码为" + password + "登录信息已被记录");}
}
不使用事件
LoginController
@RestController
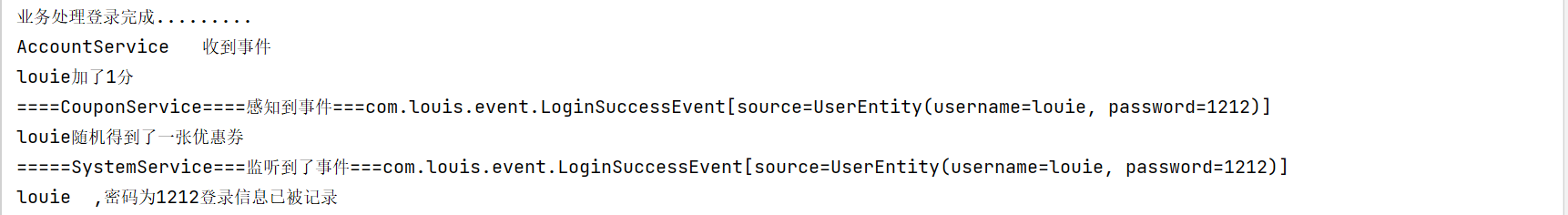
public class LoginController {@AutowiredAccountService accountService;@AutowiredCouponService couponService;@AutowiredSystemService systemService;@GetMapping("login")public String login(@RequestParam String username,@RequestParam String password){//业务处理登录System.out.println("业务处理登录完成.........");//1、账户服务自动签到加积分accountService.addAccountScore(username);//2、优惠服务随机发放优惠券couponService.sendCoupon(username);//3、系统服务登记用户登录信息systemService.recordLog(username, password);return username + "登录成功";}
}


使用事件机制
创建实体类UserEntity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserEntity {private String username;private String password;
}
创建事件LoginSuccessEvent,继承ApplicationEvent
package com.louis.event;import com.louis.entity.UserEntity;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;import java.awt.desktop.AppEvent;/*** @author XRY 登录成功事件, 所有事件都推荐继承ApplicationEvent* @date 2023年07月14日19:19*///登录成功事件
public class LoginSuccessEvent extends ApplicationEvent {/*** @param source 代表谁登录成功了*/public LoginSuccessEvent(UserEntity source) {super(source);}
}
创建事件发送类 EventPublisher
package com.louis.event;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年07月14日19:18*/
@Service
public class EventPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {/*** 底层发送事件的组件,SpringBoot会通过ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口自动注入给我们*/ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;/*** 所有事件都可以发* @param event*/public void sendEvent(ApplicationEvent event){//用底层API发送事件applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);}/*** 会被自动调用,把真正发事件的底层组件注入进来* @param applicationEventPublisher*/@Overridepublic void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;}
}
控制器LoginController
@RestController
public class LoginController {//事件@AutowiredEventPublisher eventPublisher;@GetMapping("login")public String login(@RequestParam String username,@RequestParam String password){//业务处理登录System.out.println("业务处理登录完成.........");//发送事件//1、创建事件信息LoginSuccessEvent event = new LoginSuccessEvent(new UserEntity(username, password));//2、发送事件eventPublisher.sendEvent(event);return username + "登录成功";}
}

自动配置原理
入门理解
应用关注的三大核心:场景、配置、组件
1、 自动配置流程
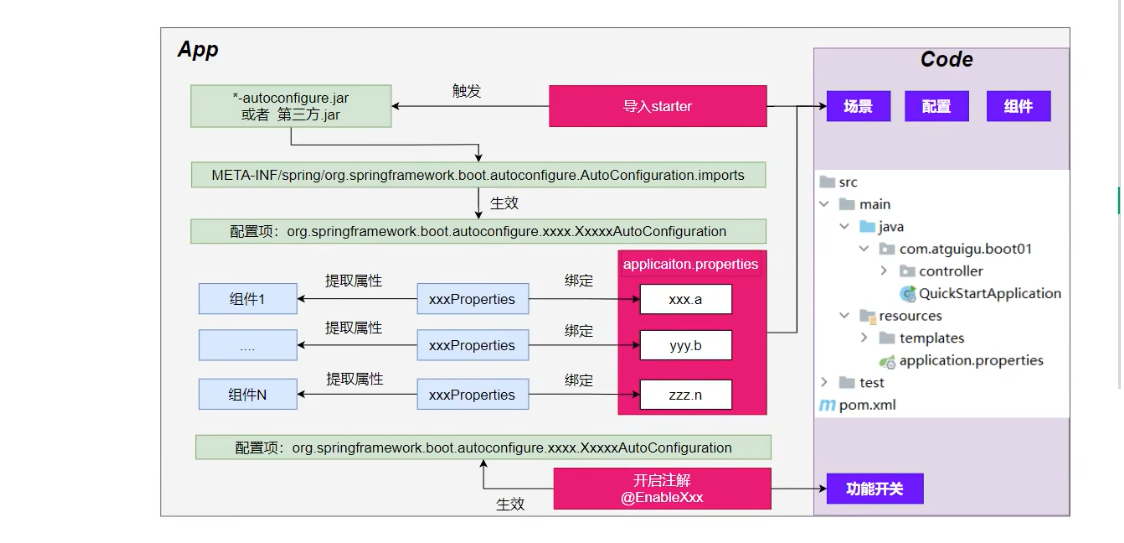
①、导入starter
②、依赖导入autoconfigure
③、寻找类路径下META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.import文件
④、启动,加载所有自动配置类-xxxAutoConfiguration
i、给容器种配置功能组件
ii、组件参数绑定到属性类中。xxxProperties
iii、属性类和配置文件前缀项绑定
iV、@Conditional派生的条件注解进行判断是否组件生效
⑤、效果:
i、修改配置文件、修改底层参数
ii、所有场景自动配置好直接使用
iii、可以注入SpringBoot配置好的组件随时使用。
2、SPI机制
SPI 全称是 Service Provider Interface,是一种 JDK 内置的动态加载实现扩展点的机制,通过 SPI 技术我们可以动态获取接口的实现类,不用自己来创建。这个不是什么特别的技术,只是 一种设计理念。它实际上是基于接口的编程+策略模式+配置文件组合实现的动态加载机制。

系统设计的各个抽象,往往有很多不同的实现方案,在面向对象的设计里,一般推荐模块之间基于接口编程,模块之间不对实现类进行硬编码。一旦代码里涉及具体的实现类,就违反了可拔插的原则,如果需要替换一种实现,就需要修改代码。为了实现在模块装配的时候能不在程序里动态指明,这就需要一种服务发现机制。Java SPI就是提供这样的一个机制:为某个接口寻找服务实现的机制。有点类似IOC的思想,就是将装配的控制权移到程序之外,在模块化设计中这个机制尤其重要。所以SPI的核心思想就是解耦。
3、功能开关
-
自动配置:全部都配置好,什么都不用管,自动批量导入。
项目启动,spi文件中指定的所有都加载
-
@Enablexxx:手动控制哪些功能的开启,手动导入。
开启xxx功能,都是利用@Import把此功能要用的组件导入进去。
进阶理解
@SpringBootApplication是以下三个注解的复合注解:
①、@SpringBootConfiguration:就是@Configuration,容器中的组件,配置类。Spring ioc启动就会加载创建这个类对象。
②、@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置,由如下两注解复合:
- @AutoConfigurationPackage
扫描主程序包。利用@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)加载自己想要给容器中导入的组件。把主程序所在包的所有组件导入进来。即只扫描主程序及主程序所在的包及其子包。
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
加载所有自动配置类,加载starter导入组件List configurations = ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class,getBeanClassLoader()).getCandidates();
扫描SPI文件:“META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.Autoconfiguration.imports”
③、@ComponentScan
组件扫描,排除一些组件,排除前面已经扫描进来的配置类和自动配置类。
自定义starter
场景:抽取聊天机器人场景,它可以打招呼。
效果:任何项目导入此starter都具有打招呼功能,并且问候语中的人名需要可以在配置文件中修改。
实现步骤
①、创建自定义starter项目,引入spring-boot-starter基础依赖
②、编写模块功能,引入模块所有需要的依赖,编写xxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类
③、编写配置文件META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports指定启动需要加载的自动配置。
④、其他下项目引入即可使用。
通用业务代码
小技巧:可以导入如下依赖重启项目,再写配置文件会有提示。
<!--导入配置处理器,自定义的properties配置文件会有提示-->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
配置类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "robot")
@Component
@Data
public class RobotProperties {private String name;private String email;private Integer age;
}
配置文件
robot.name=张三
robot.age=23
robot.email=louis@qq.com
通用功能
@Service
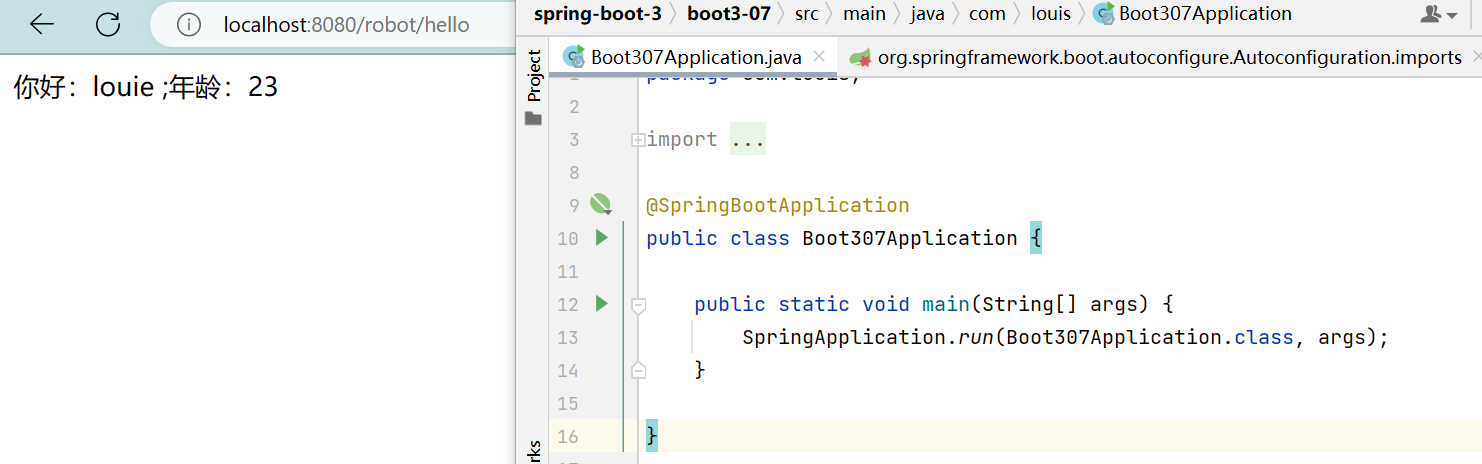
public class RobotService {@AutowiredRobotProperties robotProperties;public String sayHello(){return "你好:" + robotProperties.getName() + " ;年龄:" + robotProperties.getAge();}
}
控制器
@RestController
public class RobotController {@AutowiredRobotService robotService;@GetMapping("/robot/hello")public String sayHello(){return robotService.sayHello();}
}

基本抽取(新建模块)
新建模块时不需要选择任何场景。
复制公共功能

根据公共功能,添加场景
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--导入配置处理器,自定义的properties配置文件会有提示-->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
删除主类

在需要引用项目下导入该starter
<!--自定义的starter-->
<dependency><groupId>com.louis</groupId><artifactId>boot3-robot-starter</artifactId><version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
在starter下编写配置类
原因:SpringBoot项目只能扫描主程序以及主程序所在的子包,当导入自定义的starter时,不属于这一层级。
@Configuration
@Import({RobotController.class, RobotService.class, RobotProperties.class})
public class RobotAutoConfiguration {}
在主程序导入配置类

@SpringBootApplication
@Import(RobotAutoConfiguration.class)
public class Boot307Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Boot307Application.class, args);}}
引入starter不会读取starter本身的配置。
编写application.properties
robot.name=louie
robot.age=23
robot.email=louis@qq.com
测试

总结:
a、创建starter,将公共代码所需的所有依赖导入
b、将公共代码复制到starter
c、自己写一个RobotAutoConfiguration,该容器中导入需要组件(主程序扫描规则)
d、测试功能
使用Enable机制
原因:在导入starter的时候,使用者可能不知道需要导入哪些相关的文件。
在我们的starter编写注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import({RobotAutoConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableRobot {
}在主程序中使用@EnableRobot注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableRobot
public class Boot307Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Boot307Application.class, args);}}
测试

总结:
别人引入starter需要使用@EnableRobot开启功能
完全自动
依赖SpringBoot的SPI机制"META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.Autoconfiguration.imports"在其中放置RobotAutoConfiguration配置类的全类名。如:com.louis.starter.robot.config.RobotAutoConfiguration
 只需要导入starter,不用加任何注解。
只需要导入starter,不用加任何注解。
测试