前言
前面的博客写了如何实现栈和队列,下来我们来看一下队列和栈的相关习题。
链接: 栈和队列的实现
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.用栈实现括号匹配
- 2.用队列实现栈
- 3.用栈实现队列
- 4.设计循环队列
1.用栈实现括号匹配

此题最重要的就是数量匹配和顺序匹配。
用栈可以完美的做到:
1.左括号入栈
2.有右括号,取栈顶左括号匹配

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef char STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top; // 标识栈顶位置的int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置pst->top = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素
//pst->top = -1;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);/*if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}*/return pst->top == 0;
}int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
//这里以上都是栈的代码
bool isValid(char* s)
{ST st;STInit(&st);while (*s){if (*s == '[' || *s == '(' || *s == '{'){STPush(&st, *s);}else{if (STEmpty(&st)!=NULL)//右括号比左括号多{STDestroy(&st);return false;}char top = STTop(&st);STPop(&st);if ((*s == ']' && top != '[')//控制顺序不匹配|| (*s == '}' && top != '{')|| (*s == ')' && top != '(')){STDestroy(&st);return false;}}++s;}bool ret = STEmpty(&st);//如果栈空了,那么就是都匹配走了STDestroy(&st); //只要不空,说明没匹配完,但只能解决左括号多,右括号少的问题return ret;
}
2.用队列实现栈



这样感觉没什么用,很低效,但是这题考的就是我们对于队列和栈性质的理解!
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{QDataType val;struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);// assert(pq->phead);QNode* del = pq->phead;pq->phead = pq->phead->next;free(del);del = NULL;if (pq->phead == NULL)pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size--;
}QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);// assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);// assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->phead == NULL;
}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
//这里之前都是队列的代码
typedef struct //匿名结构体
{Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate()
{MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&pst->q1);QueueInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) //插入,哪个不为空就往哪里插,都为空随便进一个都行
{if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);elseQueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{//假设q1为空,q2不为空Queue* emptyq=&obj->q1;Queue* nonemptyq=&obj->q2;if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))//如果假设错了,就交换{emptyq = &obj->q2;nonemptyq = &obj->q1; }//非空队列钱N-1个元素导入空队列,最后一个就是栈顶元素while (QueueSize(nonemptyq)>1){QueuePush(emptyq, QueueFront(nonemptyq));//将非空队列插入空队列QueuePop(nonemptyq);//删掉}//并返回栈顶元素int top=QueueFront(nonemptyq);QueuePop(nonemptyq);return top;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{//谁不为空就返回谁的队尾数据,队尾数据就是导数据之后栈顶的数据if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))return QueueBack(&obj->q1);elsereturn QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);//两个都为空才是空
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}
3.用栈实现队列



和队列实现栈的思路一样,主要考察栈和队列的性质
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top; // 标识栈顶位置的int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置pst->top = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素//pst->top = -1;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);/*if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}*/return pst->top == 0;
}int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
//以上为栈的代码
typedef struct
{ST pushst;//入数据栈ST popst;//出数据栈
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&obj->popst);STInit(&obj->pushst);return obj;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{STPush(&obj->pushst, x);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{int front = myQueuePeek(obj);//有数据不动,没数据导数据STPop(&obj->popst);return front;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) //返回队列开头的元素
{if (STEmpty(&obj->popst))//如果popst不为空,跳到最后返回栈顶元素{ while (!STEmpty(&obj->pushst)){//popst为空,那就导数据,把pushst的数据导入popst,再返回栈顶元素STPush(&obj->popst, STTop(&obj->pushst));STPop(&obj->pushst);}}return STTop(&obj->popst);//返回栈顶元素
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{return STEmpty(&obj->popst) && STEmpty(&obj->pushst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{STDestroy(&obj->popst);STDestroy(&obj->pushst);free(obj);
}
部分函数的结构如下:

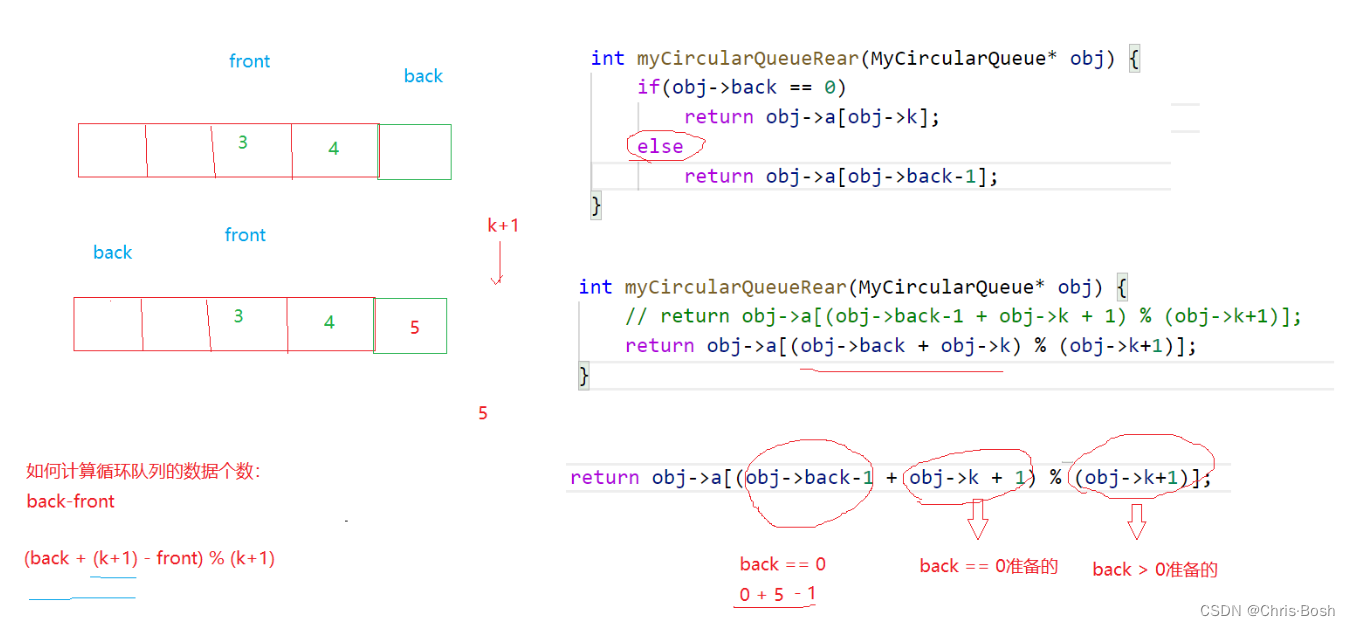
4.设计循环队列


①

②

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdbool.h>typedef struct
{int* a;//数组指针(一开始开的空间)int front;//头int back;//尾int k;//数据个数
} MyCircularQueue;MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));obj->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));obj->front = 0;obj->back = 0;obj->k = k;return obj;
}bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return obj->front == obj->back;//头等于尾是空
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return (obj->back + 1) % (obj->k + 1) == obj->front;//上述图片分析出的公式
}bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) //插入
{if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))return false; //如果满了就返回错obj->a[obj->back] = value;obj->back++;obj->back %= (obj->k + 1);//防止越界return true;
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) //删除
{if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return false;++obj->front;obj->front %= (obj->k + 1);return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) //从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
{if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;return obj->a[obj->front];
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) //获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
{if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;if (obj->back == 0)return obj->a[obj->k];elsereturn obj->a[obj->back - 1];
}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{free(obj->a);free(obj);
}
部分代码结构如下:
①

②

③