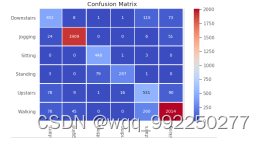
1、单链表的定义
由于顺序表的插入删除操作需要移动大量的元素,影响了运行效率,因此引入了线性表的链式存储——单链表。单链表通过一组任意的存储单元来存储线性表中的数据元素,不需要使用地址连续的存储单元,因此它不要求在逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻。
单链表的特点:
- 单链表不要求逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻,因此不需要连续的存储空间。
- 单链表是非随机的存储结构,即不能直接找到表中某个特定的结点。查找某个特定的结点时,需要从表头开始遍历,依次查找。
优点:
- 支持动态内存分配。由于单链表不需要预先分配一段连续的空间,因此可以根据实际需求动态地申请、释放节点空间,避免浪费内存。
- 支持高效的插入、删除操作。由于单链表中的节点是通过指针相连的,因此在插入、删除一个节点时,只需要修改其前驱节点或后继节点的指针即可,时间复杂度为O ( 1 ) 。
缺点:
- 不支持随机访问。由于单链表中的节点不是连续存储的,因此不能像数组一样通过下标来直接访问一个元素,需要从头节点开始遍历整个链表才能访问任意位置的元素。
创建一个类
template <class T> // T为单链表存储的元素类型
class linkList
{
private:struct Node{public:T data; // 结点的数据域 Node* next; // 结点的指针域,指向后继结点 Node(const T value, Node* p = NULL) // 具有两个参数的Node构造函数 { data = value;next = p;}Node(Node* p = NULL) // 具有一个参数的Node构造函数 { next = p;}};Node* head; // 单链表的头指针 Node* tail; // 单链表的尾int curLength; // 单链表的当前长度Node* getPosition(int i)const; // 返回指向单链表中第i个元素的指针 public:linkList(); // 构造函数 ~linkList(); // 析构函数 void clear(); // 将单链表清空,使之成为空表bool empty()const; // 判空int size(); // 返回单链表的当前实际长度 void insert(int i, const T& value); // 在位置i上插入一个元素value,表的长度增1void remove(int i); // 删除位置i上的元素value,若删除位置合法,表的长度减1 int search(const T& value)const; // 查找值为value的元素第一次出现的位序T visit(int i)const; // 访问位序为i的元素值,“位序”0表示第一个元素,类似于数组下标void traverse()const; // 遍历单链表 void headCreate(); // “头插法”void tailCreate(); // “尾插法”void inverse(); // 逆置单链表int prior(const T& value)const; // 查找值为value的元素的前驱};2、单链表的初始化
- 通常会用头指针来标识一个单链表,头指针为nullptr时表示一个空表。
- 但是,为了操作方便,会在单链表的第一个结点之前附加一个结点,称为头结点。
- 头结点的数据域可以不设任何信息,也可以记录表长等信息。
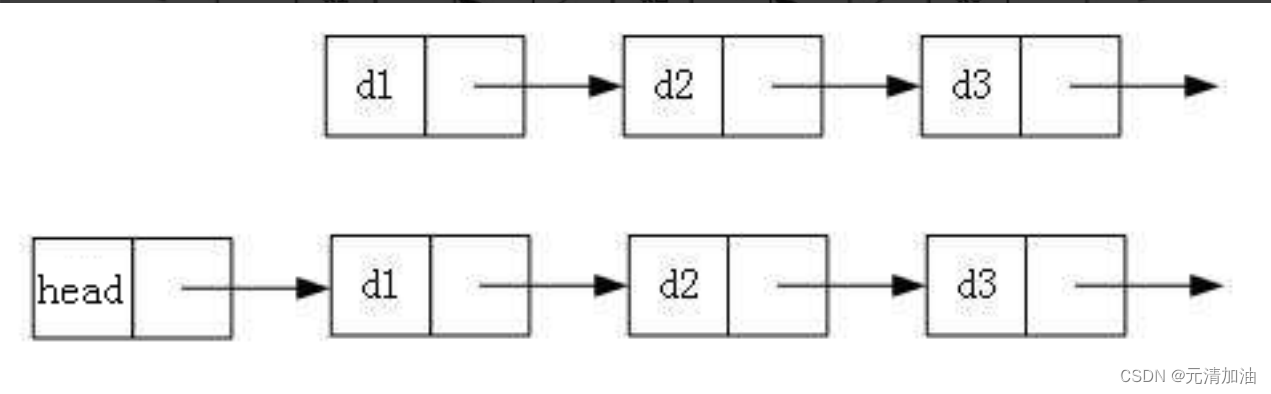
代码实现:
template <class T>
linkList<T>::linkList()
{head = tail = new Node(); // 创建带有头结点的空表curLength = 0;
}
3、单链表的建立
3.1、头插法建立单链表
头插法建立单链表是说将新结点插入到当前链表的表头,即头结点之后。
思路:输入一个结束标志flag,使用一个while循环,判断条件是 value != flag
代码实现:
template <class T> // 头插法创建
void linkList<T>::headCreate()
{Node* p;T value, flag;cin >> flag; // 输入结束标志cin >> value;while (value != flag){p = new Node(value);p->next = head->next;head->next = p;curLength++;cin >> value;}
}3.2、尾插法建立单链表
尾插法建立单链表,就是将新结点插入到当前链表的表尾。
代码实现:
template <class T> // 尾插法创建链表
void linkList<T> ::tailCreate()
{Node* p;T value, flag;cin >> flag; // 输入结束标志cin >> value;while (value != flag){p = new Node(value);tail->next = p;tail = p;curLength++;cin >> value;}}4、单链表的遍历
代码实现:
template <class T>
void linkList<T> ::traverse()const
{Node* p = head->next;while (p != nullptr){cout << p->data << " ";p = p->next;}cout << endl;}5、单链表的长度
代码实现:
template <class T>
int linkList<T>::size()
{ return curLength;
}6、单链表的查找
6.1、按值查找
代码实现:
template <class T>
int linkList<T> ::search(const T& value)const
{Node* current = head->next;int i = 0;while (current != nullptr){if (current->data == value){break;}else{current = current->next;i++;}}if (current != nullptr){return i;}return -1;}6.2、按位查找
代码实现:
template <class T> // 访问位序为i的元素返回其数据域
T linkList<T> ::visit(int i)const
{if (i < 0 || i>(curLength - 1)){T a = 0;return a;}Node* current = head->next;while (i--){current = current->next;}return current->data;}
7、单链表的插入
返回指向单链表中第i个元素的指针
template <class T>
typename linkList<T> ::Node* linkList<T> ::getPosition(int i)const
{Node* ptemp = head;int k = 0;while (k < i){ptemp = ptemp->next;k++;}return ptemp;
}代码实现:
template <class T>
void linkList<T> ::insert(int i, const T& value)
{Node* current = getPosition(i);Node* newNode = new Node(value);newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;curLength++;}8、单链表的删除
代码实现:
template <class T>
void linkList<T>::remove(int i)
{Node* current = getPosition(i);Node* del = current->next;current->next = del->next;delete del;curLength--;}9、单链表的判空
代码实现:
template <class T>
bool linkList<T>::empty()const
{return head->next == nullptr;
}总代码实现:
#include<stack>template <class T> // T为单链表存储的元素类型
class linkList
{
private:struct Node{public:T data; // 结点的数据域 Node* next; // 结点的指针域,指向后继结点 Node(const T value, Node* p = NULL) // 具有两个参数的Node构造函数 { data = value;next = p;}Node(Node* p = NULL) // 具有一个参数的Node构造函数 { next = p;}};Node* head; // 单链表的头指针 Node* tail; // 单链表的尾int curLength; // 单链表的当前长度Node* getPosition(int i)const; // 返回指向单链表中第i个元素的指针 public:linkList(); // 构造函数 ~linkList(); // 析构函数 void clear(); // 将单链表清空,使之成为空表bool empty()const; // 判空int size(); // 返回单链表的当前实际长度 void insert(int i, const T& value); // 在位置i上插入一个元素value,表的长度增1void remove(int i); // 删除位置i上的元素value,若删除位置合法,表的长度减1 int search(const T& value)const; // 查找值为value的元素第一次出现的位序T visit(int i)const; // 访问位序为i的元素值,“位序”0表示第一个元素,类似于数组下标void traverse()const; // 遍历单链表 void headCreate(); // “头插法”void tailCreate(); // “尾插法”void inverse(); // 逆置单链表int prior(const T& value)const; // 查找值为value的元素的前驱};template <class T>
linkList<T>::linkList()
{head = tail = new Node(); // 创建带有头结点的空表curLength = 0;
}template <class T>
linkList<T>::~linkList()
{clear();delete head; // 删除头结点
}template <class T>
bool linkList<T>::empty()const
{return head->next == nullptr;
}template <class T>
int linkList<T>::size()
{ return curLength;
}template <class T>
void linkList<T>::clear()
{Node* p = head->next;while (p){head = head->next;delete p;p = head;}}template <class T>
typename linkList<T> ::Node* linkList<T> ::getPosition(int i)const
{Node* ptemp = head;int k = 0;while (k < i){ptemp = ptemp->next;k++;}return ptemp;
}template <class T>
void linkList<T> ::insert(int i, const T& value)
{Node* current = getPosition(i);Node* newNode = new Node(value);newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;curLength++;}template <class T>
void linkList<T>::remove(int i)
{Node* current = getPosition(i);Node* del = current->next;current->next = del->next;delete del;curLength--;}template <class T>
void linkList<T> ::traverse()const
{Node* p = head->next;while (p != nullptr){cout << p->data << " ";p = p->next;}cout << endl;}template <class T>
int linkList<T> ::search(const T& value)const
{Node* current = head->next;int i = 0;while (current != nullptr){if (current->data == value){break;}else{current = current->next;i++;}}if (current != nullptr){return i;}return -1;}template <class T> // 访问位序为i的元素返回其数据域
T linkList<T> ::visit(int i)const
{if (i < 0 || i>(curLength - 1)){T a = 0;return a;}Node* current = head->next;while (i--){current = current->next;}return current->data;}template <class T> // 头插法创建
void linkList<T>::headCreate()
{Node* p;T value, flag;cin >> flag; // 输入结束标志cin >> value;while (value != flag){p = new Node(value);p->next = head->next;head->next = p;curLength++;cin >> value;}
}template <class T> // 尾插法创建链表
void linkList<T> ::tailCreate()
{Node* p;T value, flag;cin >> flag; // 输入结束标志cin >> value;while (value != flag){p = new Node(value);tail->next = p;tail = p;curLength++;cin >> value;}}
template <class T> // 头插法逆置
void linkList<T> ::inverse()
{Node* temp = nullptr;Node* p = head->next;head->next = nullptr;while (p != nullptr){temp = p;p = p->next;temp->next = head->next;head->next = temp;}}template <class T>
int linkList<T> ::prior(const T& value)const
{Node* current = head->next;int a = 0;Node* p = nullptr;while (current != nullptr){if (current->data == value){break;}else{current = current->next;a++;}}if (current != nullptr){return a - 1;}return -1;}
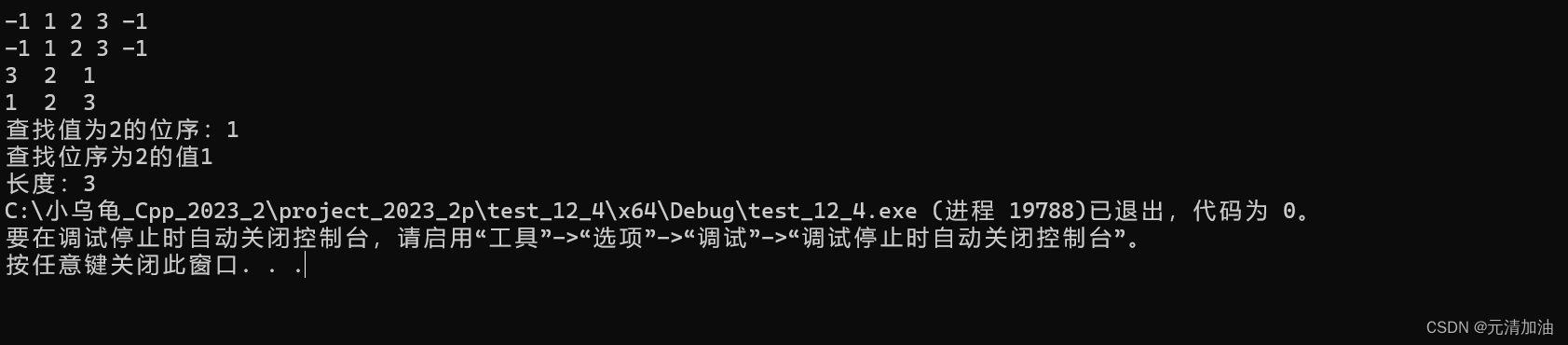
执行
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;#include"SList.h"int main()
{linkList<int>* lk1, * lk2;lk1 = new linkList<int>();lk2 = new linkList<int>();int i;int val;lk1->headCreate(); // 测试头插法创建单链表lk2->tailCreate(); // 测试尾插法创建单链表 lk1->traverse(); // 测试遍历lk2->traverse(); // 测试遍历cout << "查找值为2的位序:" << lk1->search(2) << endl;cout << "查找位序为2的值" << lk1->visit(2) << endl;cout << "长度:" << lk1->size();return 0;
}执行结果