简介
前两节我们介绍串口驱动的框架和tty core部分。这节我们介绍和硬件紧密相关的串口驱动部分。
UART驱动部分依赖于硬件平台,而TTY驱动和具体的平台无关。虽然UART部分依赖于平台,但是不管是哪个硬件平台,驱动的思路都是一致的,下面分模块来分别介绍。
关键数据结构
struct uart_driver
struct uart_driver结构体本身并不包含底层UART硬件的操作方法,其是所有串口设备驱动的抽象和封装。起到了连接硬件设备驱动和TTY驱动的作用。注册了struct uart_driver后还不能使用UART设备,还需要关联具体的UART设备。
uart_driver 结构体表示 UART 驱动, 它定义在include/linux/serial_core.h文件中,内容如下:
struct uart_driver {struct module *owner;const char *driver_name;const char *dev_name;int major;int minor;int nr;struct console *cons;/** these are private; the low level driver should not* touch these; they should be initialised to NULL*/struct uart_state *state;struct tty_driver *tty_driver;
};
owner:指向该驱动程序的拥有者模块的指针,即加载该驱动程序的内核模块。driver_name:字符串,表示驱动程序的名称。dev_name:字符串,表示设备名称,即驱动程序控制的设备文件的名称,比如ttyS。major:表示设备文件的主设备号。minor:表示设备文件的次设备号。nr:整数,表示该驱动程序控制的设备数量。cons:指向struct console类型的指针,表示该串口设备所绑定的控制台。
此外,结构体中还包含了两个私有的指针字段:
state:指向struct uart_state类型的指针,表示该驱动程序内部的状态信息。tty_driver:指向struct tty_driver类型的指针,表示该驱动程序所对应的 tty 驱动程序。
struct uart_port
一个串口芯片上往往有多个串行端口(serial ports,对应于一个物理上的串口),这些串行端口具备相同的操作机制。Linux内核将这些串行端口用struct uart_port结构体描述。struct uart_port用于描述一个UART端口的中断、I/O内存地址、FIFO大小、端口类型等信息。
在 Linux 内核中,每个串口设备都会对应一个 struct uart_port 数据结构,并且这个数据结构会作为串口设备的一个属性被保存在相应的设备节点中。
当应用程序通过打开设备节点来访问串口设备时,内核会通过设备节点获取对应的 struct uart_port 数据结构,然后通过这个数据结构来进行串口的读写等操作。
struct uart_port {spinlock_t lock; /* port lock */unsigned long iobase; /* in/out[bwl] */unsigned char __iomem *membase; /* read/write[bwl] */unsigned int (*serial_in)(struct uart_port *, int);void (*serial_out)(struct uart_port *, int, int);void (*set_termios)(struct uart_port *,struct ktermios *new,struct ktermios *old);void (*set_mctrl)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int);int (*startup)(struct uart_port *port);void (*shutdown)(struct uart_port *port);void (*throttle)(struct uart_port *port);void (*unthrottle)(struct uart_port *port);int (*handle_irq)(struct uart_port *);void (*pm)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int state,unsigned int old);void (*handle_break)(struct uart_port *);int (*rs485_config)(struct uart_port *,struct serial_rs485 *rs485);unsigned int irq; /* irq number */unsigned long irqflags; /* irq flags */unsigned int uartclk; /* base uart clock */unsigned int fifosize; /* tx fifo size */unsigned char x_char; /* xon/xoff char */unsigned char regshift; /* reg offset shift */unsigned char iotype; /* io access style */unsigned char unused1;unsigned int read_status_mask; /* driver specific */unsigned int ignore_status_mask; /* driver specific */struct uart_state *state; /* pointer to parent state */struct uart_icount icount; /* statistics */struct console *cons; /* struct console, if any *//* flags must be updated while holding port mutex */upf_t flags;/** Must hold termios_rwsem, port mutex and port lock to change;* can hold any one lock to read.*/upstat_t status;int hw_stopped; /* sw-assisted CTS flow state */unsigned int mctrl; /* current modem ctrl settings */unsigned int timeout; /* character-based timeout */unsigned int type; /* port type */const struct uart_ops *ops;unsigned int custom_divisor;unsigned int line; /* port index */unsigned int minor;resource_size_t mapbase; /* for ioremap */resource_size_t mapsize;struct device *dev; /* parent device */unsigned char hub6; /* this should be in the 8250 driver */unsigned char suspended;unsigned char irq_wake;unsigned char unused[2];struct attribute_group *attr_group; /* port specific attributes */const struct attribute_group **tty_groups; /* all attributes (serial core use only) */struct serial_rs485 rs485;void *private_data; /* generic platform data pointer */
};
unsigned long iobase: 指定了该串口设备在I/O空间中的基地址。unsigned char __iomem *membase: 指向该串口设备在内存中映射的地址。unsigned int (*serial_in)(struct uart_port *, int): 函数指针,用于从串口设备中读取数据。void (*serial_out)(struct uart_port *, int, int): 函数指针,用于向串口设备中写入数据。void (*set_termios)(struct uart_port *, struct ktermios *new, struct ktermios *old): 函数指针,用于设置串口设备的终端参数。void (*set_mctrl)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int): 函数指针,用于设置串口设备的 modem 控制信号。int (*startup)(struct uart_port *port): 函数指针,用于初始化串口设备并启动传输。void (*shutdown)(struct uart_port *port): 函数指针,用于关闭串口设备。void (*throttle)(struct uart_port *port): 函数指针,用于将串口设备的传输流控制为停止状态。void (*unthrottle)(struct uart_port *port): 函数指针,用于取消串口设备的传输流控制停止状态。int (*handle_irq)(struct uart_port *): 函数指针,用于处理串口设备的中断。void (*pm)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int state, unsigned int old): 函数指针,用于处理串口设备的电源管理。void (*handle_break)(struct uart_port *): 函数指针,用于处理串口设备的中断信号中断符。int (*rs485_config)(struct uart_port *, struct serial_rs485 *rs485): 函数指针,用于配置 RS485 串行通信参数。unsigned int irq: 该串口设备所使用的中断号。unsigned long irqflags: 该串口设备的中断标志。unsigned int uartclk: 该串口设备的时钟频率。unsigned int fifosize: 该串口设备的 FIFO 大小。unsigned char x_char: XON/XOFF 字符。unsigned char regshift: 寄存器偏移量。unsigned char iotype: I/O 访问类型。unsigned char unused1: 未使用的成员变量。unsigned int read_status_mask: 用于指定读取状态的屏蔽位。unsigned int ignore_status_mask: 用于指定忽略状态的屏蔽位。struct uart_state *state: 指向该串口设备所在状态结构体的指针。struct uart_icount icount: 用于存储串口设备的统计信息。struct console *cons: 指向该串口设备所属控制台设备的指针。unsigned int mctrl:当前调制解调器控制(Modem Control)的设置。这个值包含了当前控制信号(如DTR、RTS、DSR、CTS等)的状态。通常由硬件控制。unsigned int timeout:基于字符的超时时间。当字符被传输到UART端口时,如果在规定的时间内没有收到下一个字符,则会超时并发送通知。通常由驱动程序设置。unsigned int type:端口类型。这个值通常用于标识UART硬件的特殊性质(如芯片类型、波特率范围等)。const struct uart_ops *ops:一个指向struct uart_ops结构体的指针。这个结构体包含了与UART驱动程序相关的函数指针,如UART读、写、启动、停止等等。unsigned int custom_divisor:自定义除数,用于实现非标准波特率。这个值通常由驱动程序设置。unsigned int line:端口索引,用于标识该UART端口的编号。unsigned int minor:端口的次设备号,用于标识该UART端口在系统中的位置。resource_size_t mapbase、resource_size_t mapsize:映射区域的起始地址和大小。这些值通常由驱动程序设置,用于将UART端口的物理地址映射到虚拟地址。struct device *dev:指向父设备的指针。通常是该UART设备所连接的总线控制器设备。unsigned char hub6:用于指示Hub6电路板的状态。这个变量应该是在8250驱动程序中定义的。unsigned char suspended:用于指示该端口是否被挂起。unsigned char irq_wake:用于指示该端口是否支持唤醒中断。unsigned char unused[2]:未使用的字节。struct attribute_group *attr_group:指向属性组的指针。属性组包含了UART设备的属性和操作,如设备状态、波特率设置等等。const struct attribute_group **tty_groups:指向指针数组的指针,该数组包含了所有属性组的指针,供串行核心使用。struct serial_rs485 rs485:RS485配置结构体,用于RS485通信。void *private_data:指向私有数据的指针。这个指针通常由驱动程序使用,用于保存驱动程序特定的数据。
struct uart_ops
Linux 系统收发数据最终调用的都是 ops 中的函数。 ops 是 uart_ops类型的结构体指针变量。uart硬件操作函数集合,底层硬件驱动必须实现这个结构体。
uart_ops结构体 用于定义一个串口驱动程序的接口,让上层调用这些接口实现串口的读写等操作。它包含了很多函数指针,每个函数指针对应了一个特定的串口操作。
在Linux内核中,串口的驱动程序是分为两层实现的:串口芯片驱动程序和 serial core 层。其中,serial core 层提供了大量的函数接口,供上层的串口芯片驱动程序使用,这些函数接口的定义就包含在了 struct uart_ops 结构体中。
当编写串口芯片驱动程序时,需要实现 struct uart_ops 结构体中定义的各个函数接口,以便 serial core 层调用。
例如,在芯片驱动程序中实现的 uart_start() 函数就对应了 struct uart_ops 结构体中的 startup 函数指针。
因此,struct uart_ops 结构体是串口驱动程序实现的关键,其定义了驱动程序需要实现的所有函数接口,并与 serial core 层进行了对接。
struct uart_ops {unsigned int (*tx_empty)(struct uart_port *);void (*set_mctrl)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int mctrl);unsigned int (*get_mctrl)(struct uart_port *);void (*stop_tx)(struct uart_port *);void (*start_tx)(struct uart_port *);void (*throttle)(struct uart_port *);void (*unthrottle)(struct uart_port *);void (*send_xchar)(struct uart_port *, char ch);void (*stop_rx)(struct uart_port *);void (*enable_ms)(struct uart_port *);void (*break_ctl)(struct uart_port *, int ctl);int (*startup)(struct uart_port *);void (*shutdown)(struct uart_port *);void (*flush_buffer)(struct uart_port *);void (*set_termios)(struct uart_port *, struct ktermios *new,struct ktermios *old);void (*set_ldisc)(struct uart_port *, struct ktermios *);void (*pm)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int state,unsigned int oldstate);void (*wake_peer)(struct uart_port *);/** Return a string describing the type of the port*/const char *(*type)(struct uart_port *);/** Release IO and memory resources used by the port.* This includes iounmap if necessary.*/void (*release_port)(struct uart_port *);/** Request IO and memory resources used by the port.* This includes iomapping the port if necessary.*/int (*request_port)(struct uart_port *);void (*config_port)(struct uart_port *, int);int (*verify_port)(struct uart_port *, struct serial_struct *);int (*ioctl)(struct uart_port *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLLint (*poll_init)(struct uart_port *);void (*poll_put_char)(struct uart_port *, unsigned char);int (*poll_get_char)(struct uart_port *);
#endif
};
tx_empty():检查串口的发送缓冲区是否为空,用于判断是否可以发送数据。set_mctrl():设置串口的 modem 控制信号,如 RTS、DTR 等。get_mctrl():获取串口的 modem 控制信号。stop_tx():停止当前正在发送的数据。start_tx():开始发送数据。throttle():限制发送速率,减少发送的数据量。unthrottle():取消限制发送速率。send_xchar():发送一个 XON 或 XOFF 字符,用于流控。stop_rx():停止接收数据。enable_ms():启用串口的 modem 状态检测功能。break_ctl():发送一个 break 信号。startup():初始化串口硬件。shutdown():关闭串口硬件。flush_buffer():清空串口的缓冲区。set_termios():设置串口的终端参数。set_ldisc():设置串口的行规则。pm():实现串口的 power management。wake_peer():用于唤醒其他休眠状态的串口。
另外,还包含了一些函数指针用于处理串口的 IO 资源:
type():返回描述串口类型的字符串。release_port():释放串口的 IO 和内存资源,包括解除 IO 映射等。request_port():请求串口的 IO 和内存资源,包括 IO 映射等。config_port():配置串口的参数。verify_port():验证串口的参数是否正确。ioctl():实现串口设备的 ioctl 接口。
struct uart_state
uart_state 表示 UART 状态,并与 struct uart_port 结构体配合使用来管理 UART 端口。
struct uart_port 结构体表示 UART 端口的硬件信息和操作,而 struct uart_state 结构体则表示与该端口相关的软件状态。
由于 UART 状态可以包含多个,因此可以在同一时刻使用多个 UART 状态来管理多个 UART 端口的操作。
struct uart_state {struct tty_port port;enum uart_pm_state pm_state;struct circ_buf xmit;struct uart_port *uart_port;
};
struct tty_port port:表示 tty 端口的状态信息,包括接受和发送缓冲区,控制信息和流控信息等等。enum uart_pm_state pm_state:表示串口设备的电源管理状态,可以是UART_PM_STATE_ON、UART_PM_STATE_OFF或UART_PM_STATE_UNDEFINED。struct circ_buf xmit:表示串口设备的发送缓冲区,用于存储待发送的数据。struct uart_port *uart_port:表示该串口设备对应的struct uart_port结构体。
当应用程序向串口设备写入数据时,数据将被存储到 xmit 缓冲区中,并且将触发串口驱动程序的数据发送处理函数。这个函数会从 xmit 缓冲区中取出数据,并通过 uart_port 中的函数指针将数据发送到物理串口。在发送数据时,驱动程序还会根据串口的流控状态进行数据流控制。
当收到数据时,数据将被存储到 port 的接受缓冲区中,并且将触发串口驱动程序的数据接收处理函数。处理函数将从接受缓冲区中取出数据并将其传递给应用程序。
数据结构抽象完毕后,serial core向下层的driver提供了方便的编程API,主要包括以下函数。
关键API
uart_register_driver
uart_register_driver将定义并填充好的uart driver注册到kernel中,一般在驱动模块的init接口中被调用。
int uart_register_driver(struct uart_driver *drv)
{struct tty_driver *normal;int i, retval;BUG_ON(drv->state);drv->state = kzalloc(sizeof(struct uart_state) * drv->nr, GFP_KERNEL);if (!drv->state)goto out;normal = alloc_tty_driver(drv->nr);if (!normal)goto out_kfree;drv->tty_driver = normal;normal->driver_name = drv->driver_name;normal->name = drv->dev_name;normal->major = drv->major;normal->minor_start = drv->minor;normal->type = TTY_DRIVER_TYPE_SERIAL;normal->subtype = SERIAL_TYPE_NORMAL;normal->init_termios = tty_std_termios;normal->init_termios.c_cflag = B9600 | CS8 | CREAD | HUPCL | CLOCAL;normal->init_termios.c_ispeed = normal->init_termios.c_ospeed = 9600;normal->flags = TTY_DRIVER_REAL_RAW | TTY_DRIVER_DYNAMIC_DEV;normal->driver_state = drv;tty_set_operations(normal, &uart_ops);/** Initialise the UART state(s).*/for (i = 0; i < drv->nr; i++) {struct uart_state *state = drv->state + i;struct tty_port *port = &state->port;tty_port_init(port);port->ops = &uart_port_ops;}retval = tty_register_driver(normal);if (retval >= 0)return retval;for (i = 0; i < drv->nr; i++)tty_port_destroy(&drv->state[i].port);put_tty_driver(normal);
out_kfree:kfree(drv->state);
out:return -ENOMEM;
}
uart_register_driver()注册所做工作如下:
-
根据driver支持的最大设备数,申请n个
uart_state空间,每一个uart_state都有一个 uart_port 。 -
接着它会分配一个
tty_driver对象,并初始化它的各个属性,如driver_name,name,major,minor_start等等。这些属性是用于在 TTY 子系统中创建 tty 设备的,它们的值来自于uart_driver对象中指定的值。 -
接下来,它会在
tty_driver中设置 tty 操作,其中tty_ops是一个结构体,定义了 UART 串行接口所需要的函数。这些函数在串口设备注册后,当有数据进出串口时,TTY 子系统会调用这些函数。tty_set_operations()函数用于在tty_driver中设置 tty 操作。 -
在初始化完
tty_driver后,函数会遍历所有的 UART 设备状态对象,并初始化它们。这些状态对象被存储在uart_driver对象的state字段中。每个 UART 设备状态对象包含一个tty_port对象,其中存储了关于该串口设备的信息,例如流控、字长、奇偶校验等等。在此处,tty_port的操作被设置为uart_port_ops,它包含了具体实现 UART 串行接口所需的函数。 -
最后会调用
tty_register_driver()函数来向内核注册 tty 驱动程序,并将驱动程序的tty_driver结构体与uart_driver结构体相关联。 -
如果注册失败,该函数将释放之前分配的内存。如果注册成功,该函数将返回 0,否则将返回一个负的错误码。
总结一句话:tty serial core底层驱动层和tty层之间的联系需要从uart_register_driver()中连接,tty_driver是在uart_driver注册过程中构建的。
uart_unregister_driver
uart_unregister_driver是一个Linux内核中的串口驱动反注册函数,用于将之前注册的驱动程序与系统中的串口设备取消关联。
/*** uart_unregister_driver - remove a driver from the uart core layer* @drv: low level driver structure** Remove all references to a driver from the core driver. The low* level driver must have removed all its ports via the* uart_remove_one_port() if it registered them with uart_add_one_port().* (ie, drv->port == NULL)*/
void uart_unregister_driver(struct uart_driver *drv)
{struct tty_driver *p = drv->tty_driver;unsigned int i;/*获取与该驱动程序关联的 tty_driver 实例*/tty_unregister_driver(p);/*取消注册驱动程序,将它与系统中的 tty 设备断开关联*/put_tty_driver(p);/*释放该 tty_driver 实例,如果此时该实例的使用计数为零,即没有其他模块在使用该实例,那么它将会被完全卸载并释放所有内存资源*/for (i = 0; i < drv->nr; i++)tty_port_destroy(&drv->state[i].port);kfree(drv->state);drv->state = NULL;drv->tty_driver = NULL;
}uart_add_one_port
uart_add_one_port用于将一个UART端口添加到UART驱动程序的状态表中,并注册TTY端口设备,让用户空间能够通过该设备与UART通信。
/*** uart_add_one_port - attach a driver-defined port structure* @drv: pointer to the uart low level driver structure for this port* @uport: uart port structure to use for this port.** This allows the driver to register its own uart_port structure* with the core driver. The main purpose is to allow the low* level uart drivers to expand uart_port, rather than having yet* more levels of structures.*/
int uart_add_one_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport)
{struct uart_state *state;struct tty_port *port;int ret = 0;struct device *tty_dev;int num_groups;/*检查是否在中断上下文中,如果是则直接返回错误*/BUG_ON(in_interrupt());/*检查所添加的端口是否超出驱动程序支持的范围,如果是则返回EINVAL*/if (uport->line >= drv->nr)return -EINVAL;/*获取该端口所对应的状态信息(uart_state)以及端口(tty_port)*/state = drv->state + uport->line;port = &state->port;mutex_lock(&port_mutex);mutex_lock(&port->mutex);/*检查端口是否已经被其他设备占用,如果是则返回EINVAL*/if (state->uart_port) {ret = -EINVAL;goto out;}/* 链接端口和驱动程序状态表,并进行相应的初始化工作,包括PM状态、控制台、spinlock等 */state->uart_port = uport;uport->state = state;state->pm_state = UART_PM_STATE_UNDEFINED;uport->cons = drv->cons;uport->minor = drv->tty_driver->minor_start + uport->line;/** If this port is a console, then the spinlock is already* initialised.*/if (!(uart_console(uport) && (uport->cons->flags & CON_ENABLED))) {spin_lock_init(&uport->lock);lockdep_set_class(&uport->lock, &port_lock_key);}if (uport->cons && uport->dev)of_console_check(uport->dev->of_node, uport->cons->name, uport->line);/*配置端口的属性,例如波特率、数据位、停止位等*/uart_configure_port(drv, state, uport);num_groups = 2;if (uport->attr_group)num_groups++;/*分配并设置TTY设备属性组,这些属性组包括TTY设备通用属性组和用户自定义属性组*/uport->tty_groups = kcalloc(num_groups, sizeof(*uport->tty_groups),GFP_KERNEL);if (!uport->tty_groups) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}uport->tty_groups[0] = &tty_dev_attr_group;if (uport->attr_group)uport->tty_groups[1] = uport->attr_group;/*注册TTY端口设备,并将其与tty_driver和tty_port关联起来*/tty_dev = tty_port_register_device_attr(port, drv->tty_driver,uport->line, uport->dev, port, uport->tty_groups);/*如果注册成功,将该设备标记为可唤醒*/if (likely(!IS_ERR(tty_dev))) {device_set_wakeup_capable(tty_dev, 1);} else {dev_err(uport->dev, "Cannot register tty device on line %d\n",uport->line);}/** Ensure UPF_DEAD is not set.*/uport->flags &= ~UPF_DEAD;out:mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);mutex_unlock(&port_mutex);return ret;
}
uart_remove_one_port
uart_remove_one_port用于从核心驱动程序中分离(断开)一个指定的端口结构。
/*** uart_remove_one_port - detach a driver defined port structure* @drv: pointer to the uart low level driver structure for this port* @uport: uart port structure for this port** This unhooks (and hangs up) the specified port structure from the* core driver. No further calls will be made to the low-level code* for this port.*/
int uart_remove_one_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport)
{struct uart_state *state = drv->state + uport->line;struct tty_port *port = &state->port;struct tty_struct *tty;int ret = 0;/*检查当前是否处于中断上下文中*/BUG_ON(in_interrupt());/*检查uart状态结构中的uart端口指针是否等于传递给该函数的uart端口指针,如果不是则打印一条错误消息*/if (state->uart_port != uport)dev_alert(uport->dev, "Removing wrong port: %p != %p\n",state->uart_port, uport);/*获取tty端口结构的互斥锁,该锁用于防止并发修改端口状态*/mutex_lock(&port_mutex);/*获取tty端口结构的互斥锁,然后检查uart端口指针是否为空。如果为空,则表示当前端口已被删除。在这种情况下,将返回-EINVAL并解锁互斥锁 */mutex_lock(&port->mutex);if (!state->uart_port) {mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);ret = -EINVAL;goto out;}/*锁定 port->mutex 互斥锁,并将 uport->flags 设置为 UPF_DEAD,表示该端口已经被关闭。之后解锁 port->mutex。*/uport->flags |= UPF_DEAD;mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);/*从tty层中删除设备*/tty_unregister_device(drv->tty_driver, uport->line);/*获取 tty 设备对应的 tty 结构体,并使用 tty_vhangup() 函数关闭该 tty 设备的控制终端。最后,使用 tty_kref_put() 函数释放 tty 结构体的引用计数。*/tty = tty_port_tty_get(port);if (tty) {tty_vhangup(port->tty);tty_kref_put(tty);}/*如果该端口用作控制台,则使用 unregister_console() 函数取消该端口的控制台注册*/if (uart_console(uport))unregister_console(uport->cons);/*根据 uport->type 的值来释放端口的 IO 和内存资源,如果 uport->type 的值为 PORT_UNKNOWN,则表示没有对应的资源需要释放*/if (uport->type != PORT_UNKNOWN)uport->ops->release_port(uport);kfree(uport->tty_groups);/*将 uport->type 的值设置为 PORT_UNKNOWN,表示该端口不再存在。同时将 state->uart_port 设置为 NULL,表示 state 对应的端口不再与 uport 相关联。*/uport->type = PORT_UNKNOWN;state->uart_port = NULL;
out:mutex_unlock(&port_mutex);return ret;
}
uart_write_wakeup
uart_write_wakeupuart_write_wakeup唤醒上层因向串口端口写数据而阻塞的进程,通常在串口发送中断处理函数中调用该函数。
/** This routine is used by the interrupt handler to schedule processing in* the software interrupt portion of the driver.*/
void uart_write_wakeup(struct uart_port *port)
{struct uart_state *state = port->state;/** This means you called this function _after_ the port was* closed. No cookie for you.*/BUG_ON(!state);/*函数唤醒与state->port相关联的终端。*/tty_wakeup(state->port.tty);
}
uart_suspend_port
uart_suspend_port函数用于将端口挂起以进行电源管理。它执行一系列操作,包括检查子设备是否可以唤醒系统,停止发送和接收数据,等待发送缓冲区为空,关闭端口,停止控制台,并更改端口的电源管理状态。
int uart_suspend_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport)
{struct uart_state *state = drv->state + uport->line;struct tty_port *port = &state->port;struct device *tty_dev;struct uart_match match = {uport, drv};/*给port加锁,以确保在执行其他操作时不会发生竞争条件*/mutex_lock(&port->mutex);/*查找与uport->dev相关联的子设备。它使用match结构体和serial_match_port函数来匹配子设备*/tty_dev = device_find_child(uport->dev, &match, serial_match_port);/*如果找到了子设备并且该设备可以唤醒系统,则将uport->irq设置为唤醒中断,并将uport->irq_wake设置为1。然后,释放tty_dev并解锁port的互斥锁,并返回0*/if (device_may_wakeup(tty_dev)) {if (!enable_irq_wake(uport->irq))uport->irq_wake = 1;put_device(tty_dev);mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);return 0;}/*如果找到了子设备但该设备不能唤醒系统,则释放tty_dev*/put_device(tty_dev);/* Nothing to do if the console is not suspending *//*如果控制台未启用挂起并且uport是控制台,则跳转到unlock解锁*/if (!console_suspend_enabled && uart_console(uport))goto unlock;/*将uport->suspended设置为1,表示端口已挂起。*/uport->suspended = 1;/*如果端口已初始化,则执行一些操作以停止传输并关闭端口。这些操作包括设置ASYNCB_SUSPENDED和清除ASYNCB_INITIALIZED标志,停止发送和接收数据,等待发送缓冲区为空,关闭端口*/if (port->flags & ASYNC_INITIALIZED) {const struct uart_ops *ops = uport->ops;int tries;set_bit(ASYNCB_SUSPENDED, &port->flags);clear_bit(ASYNCB_INITIALIZED, &port->flags);spin_lock_irq(&uport->lock);ops->stop_tx(uport);ops->set_mctrl(uport, 0);ops->stop_rx(uport);spin_unlock_irq(&uport->lock);/** Wait for the transmitter to empty.*/for (tries = 3; !ops->tx_empty(uport) && tries; tries--)msleep(10);if (!tries)dev_err(uport->dev, "%s%d: Unable to drain transmitter\n",drv->dev_name,drv->tty_driver->name_base + uport->line);ops->shutdown(uport);}/** Disable the console device before suspending.*//* *//*如果uport是控制台,则停止控制台*/if (uart_console(uport))console_stop(uport->cons);/*调用uart_change_pm函数以更改端口的电源管理状态为UART_PM_STATE_OFF*/uart_change_pm(state, UART_PM_STATE_OFF);
unlock:mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);return 0;
}
uart_resume_port
uart_resume_port作用是恢复一个已经挂起的UART端口。
int uart_resume_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport)
{struct uart_state *state = drv->state + uport->line;struct tty_port *port = &state->port;struct device *tty_dev;struct uart_match match = {uport, drv};struct ktermios termios;mutex_lock(&port->mutex);/*使用device_find_child搜索与名为match的struct uart_match匹配的uport->dev的子设备*/tty_dev = device_find_child(uport->dev, &match, serial_match_port);/*如果找到设备并且端口未挂起并且设备可以唤醒,则函数禁用IRQ唤醒并返回0*/if (!uport->suspended && device_may_wakeup(tty_dev)) {if (uport->irq_wake) {disable_irq_wake(uport->irq);uport->irq_wake = 0;}put_device(tty_dev);mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);return 0;}/*函数将uport->suspended设置为0*/put_device(tty_dev);uport->suspended = 0;/** Re-enable the console device after suspending.*//*如果端口是控制台端口,则函数将termios结构设置为控制台cflag设置*/if (uart_console(uport)) {/** First try to use the console cflag setting.*/memset(&termios, 0, sizeof(struct ktermios));termios.c_cflag = uport->cons->cflag;/** If that's unset, use the tty termios setting.*/if (port->tty && termios.c_cflag == 0)termios = port->tty->termios;/*如果启用了控制台挂起,则函数使用uart_change_pm将电源管理状态更改为打开状态,使用uport->ops->set_termios设置termios,并使用console_start启动控制台*/if (console_suspend_enabled)uart_change_pm(state, UART_PM_STATE_ON);uport->ops->set_termios(uport, &termios, NULL);if (console_suspend_enabled)console_start(uport->cons);}if (port->flags & ASYNC_SUSPENDED) {const struct uart_ops *ops = uport->ops;int ret;/*如果端口已挂起,则函数使用uart_change_pm将电源管理状态更改为打开状态*/uart_change_pm(state, UART_PM_STATE_ON);spin_lock_irq(&uport->lock);/*使用ops->set_mctrl将调制解调器控制线设置为0*/ops->set_mctrl(uport, 0);spin_unlock_irq(&uport->lock);if (console_suspend_enabled || !uart_console(uport)) {/* Protected by port mutex for now */struct tty_struct *tty = port->tty;/*使用ops->startup启动端口*/ret = ops->startup(uport);if (ret == 0) {/*如果端口成功启动,则使用uart_change_speed更改端口速度,使用ops->start_tx启动传输,并在port->flags中设置ASYNCB_INITIALIZED位*/if (tty)uart_change_speed(tty, state, NULL);spin_lock_irq(&uport->lock);ops->set_mctrl(uport, uport->mctrl);ops->start_tx(uport);spin_unlock_irq(&uport->lock);set_bit(ASYNCB_INITIALIZED, &port->flags);} else {/** Failed to resume - maybe hardware went away?* Clear the "initialized" flag so we won't try* to call the low level drivers shutdown method.*//*如果端口无法恢复,则函数清除ASYNCB_INITIALIZED位并调用uart_shutdown*/uart_shutdown(tty, state);}}clear_bit(ASYNCB_SUSPENDED, &port->flags);}mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);return 0;
}
uart_get_baud_rate
uart_get_baud_rate,该函数的作用是根据给定的终端设置和范围,获取一个可用的波特率。如果无法获取满足要求的波特率,则会尽可能地使用最接近的波特率。
/*** uart_get_baud_rate - return baud rate for a particular port* @port: uart_port structure describing the port in question.* @termios: desired termios settings.* @old: old termios (or NULL)* @min: minimum acceptable baud rate* @max: maximum acceptable baud rate** Decode the termios structure into a numeric baud rate,* taking account of the magic 38400 baud rate (with spd_** flags), and mapping the %B0 rate to 9600 baud.** If the new baud rate is invalid, try the old termios setting.* If it's still invalid, we try 9600 baud.** Update the @termios structure to reflect the baud rate* we're actually going to be using. Don't do this for the case* where B0 is requested ("hang up").*/
unsigned int
uart_get_baud_rate(struct uart_port *port, struct ktermios *termios,struct ktermios *old, unsigned int min, unsigned int max)
{unsigned int try;unsigned int baud;unsigned int altbaud;int hung_up = 0;upf_t flags = port->flags & UPF_SPD_MASK;switch (flags) {case UPF_SPD_HI:altbaud = 57600;break;case UPF_SPD_VHI:altbaud = 115200;break;case UPF_SPD_SHI:altbaud = 230400;break;case UPF_SPD_WARP:altbaud = 460800;break;default:altbaud = 38400;break;}for (try = 0; try < 2; try++) {baud = tty_termios_baud_rate(termios);/** The spd_hi, spd_vhi, spd_shi, spd_warp kludge...* Die! Die! Die!*/if (try == 0 && baud == 38400)baud = altbaud;/** Special case: B0 rate.*/if (baud == 0) {hung_up = 1;baud = 9600;}if (baud >= min && baud <= max)return baud;/** Oops, the quotient was zero. Try again with* the old baud rate if possible.*/termios->c_cflag &= ~CBAUD;if (old) {baud = tty_termios_baud_rate(old);if (!hung_up)tty_termios_encode_baud_rate(termios,baud, baud);old = NULL;continue;}/** As a last resort, if the range cannot be met then clip to* the nearest chip supported rate.*/if (!hung_up) {if (baud <= min)tty_termios_encode_baud_rate(termios,min + 1, min + 1);elsetty_termios_encode_baud_rate(termios,max - 1, max - 1);}}/* Should never happen */WARN_ON(1);return 0;
}
该函数所作工作如下
- 根据
UPF_SPD_MASK标志位解析出一个备用波特率altbaud。 - 函数会尝试两次获取波特率。第一次,函数会从
termios中解析出当前波特率,如果它等于38400,则将波特率设置为备用波特率altbaud。如果波特率等于0(即请求“挂起”),则设置波特率为9600。如果波特率在min和max范围内,则返回该波特率。 - 如果第一次获取的波特率为
0,则函数会尝试使用旧的终端设置。 - 如果仍然无法满足要求,函数会将波特率剪裁到最接近的支持的波特率。剪裁的方式是,如果波特率小于等于最小值
min,则设置波特率为min + 1,否则设置波特率为max - 1。
uart_get_divisor
uart_get_divisor,用于计算给定端口的 UART 时钟分频器值,以实现指定的波特率 。主要是通过一些基本的数学运算来计算出 UART 时钟分频器值。这个值是用来配置 UART 硬件的,以实现指定的波特率。
在串口通信中,时钟分频器值对应着波特率,即时钟分频器值越小,波特率越高,传输速度越快。
/*** uart_get_divisor - return uart clock divisor* @port: uart_port structure describing the port.* @baud: desired baud rate** Calculate the uart clock divisor for the port.*/
unsigned int
uart_get_divisor(struct uart_port *port, unsigned int baud)
{unsigned int quot;/** Old custom speed handling.*/if (baud == 38400 && (port->flags & UPF_SPD_MASK) == UPF_SPD_CUST)quot = port->custom_divisor;elsequot = DIV_ROUND_CLOSEST(port->uartclk, 16 * baud);return quot;
}该函数所作工作如下
-
首先根据给定的波特率计算出 UART 时钟周期的长度
period,这个周期的长度是通过16 * baud计算得到的。然后,将端口的 UART 时钟频率除以period,得到的商值quot就是需要的 UART 时钟分频器值。这里使用了DIV_ROUND_CLOSEST宏,它的作用是将浮点数四舍五入为最接近的整数值。 -
在计算时钟分频器值时,还有一个特殊的情况需要处理。如果给定的波特率为
38400,并且端口的标志位值为UPF_SPD_CUST,则需要使用端口的自定义分频器值,而不是根据公式计算出来的值。这是因为在一些老的串口驱动中,可能会使用自定义分频器值来支持一些特殊的波特率。
uart_update_timeout
uart_update_timeout用于设置串口的 FIFO 超时时间。FIFO(First-In-First-Out)是串口硬件中用于缓存数据的一种常见结构,它可以提高串口传输的效率。而超时时间则是指在 FIFO 中没有数据传输时,等待多长时间后自动清空 FIFO。超时时间的设置可以影响串口传输的稳定性和效率。
/*** uart_update_timeout - update per-port FIFO timeout.* @port: uart_port structure describing the port* @cflag: termios cflag value* @baud: speed of the port** Set the port FIFO timeout value. The @cflag value should* reflect the actual hardware settings.*/
void
uart_update_timeout(struct uart_port *port, unsigned int cflag,unsigned int baud)
{unsigned int bits;/* byte size and parity */switch (cflag & CSIZE) {case CS5:bits = 7;break;case CS6:bits = 8;break;case CS7:bits = 9;break;default:bits = 10;break; /* CS8 */}if (cflag & CSTOPB)bits++;if (cflag & PARENB)bits++;/** The total number of bits to be transmitted in the fifo.*/bits = bits * port->fifosize;/** Figure the timeout to send the above number of bits.* Add .02 seconds of slop*/port->timeout = (HZ * bits) / baud + HZ/50;
}
- 根据终端设置中的 cflag 值,计算出每个字节需要传输的位数
bits。根据 cflag 中的 CSIZE 标志位,确定每个字节的位数(5、6、7 或 8 位),并根据 CSTOPB 和 PARENB 标志位,增加停止位和奇偶校验位的位数。 - 将每个字节需要传输的位数
bits乘以 FIFO 的大小,得到总共需要传输的位数。 - 根据波特率和总共需要传输的位数,计算出超时时间。将总共需要传输的位数除以波特率,得到传输这些数据所需要的时间,再加上一些额外的时间(0.02 秒)作为缓冲,得到超时时间。
- 最后,将计算出来的超时时间赋值给端口结构体中的 timeout 成员变量,从而完成 FIFO 超时时间的设置。
uart_match_port
uart_match_port根据两个端口的属性比较两个串口端口是否相等。
/** Are the two ports equivalent?*/
int uart_match_port(struct uart_port *port1, struct uart_port *port2)
{if (port1->iotype != port2->iotype)return 0;switch (port1->iotype) {case UPIO_PORT:return (port1->iobase == port2->iobase);case UPIO_HUB6:return (port1->iobase == port2->iobase) &&(port1->hub6 == port2->hub6);case UPIO_MEM:case UPIO_MEM32:case UPIO_MEM32BE:case UPIO_AU:case UPIO_TSI:return (port1->mapbase == port2->mapbase);}return 0;
}
- 根据两个串口端口的 iotype 属性进行比较,如果不相等,则两个端口不相等,函数返回 0。
- 根据 iotype 属性的不同,比较两个端口的其他属性。对于 UPIO_PORT 和 UPIO_HUB6 类型的端口,比较它们的 iobase 和 hub6 属性是否相等;对于其他类型的端口,比较它们的 mapbase 属性是否相等。如果所有属性都相等,则两个端口相等,函数返回 1,否则返回 0。
uart_console_write
uart_console_write用于将控制台消息写入串口。
在嵌入式系统中,通常需要将控制台输出重定向到串口,以便进行调试和日志记录。该函数实现了将一个字符串写入串口的操作,其中需要将字符串中的换行符转换为回车换行符。
/*** uart_console_write - write a console message to a serial port* @port: the port to write the message* @s: array of characters* @count: number of characters in string to write* @putchar: function to write character to port*/
void uart_console_write(struct uart_port *port, const char *s,unsigned int count,void (*putchar)(struct uart_port *, int))
{unsigned int i;for (i = 0; i < count; i++, s++) {if (*s == '\n')putchar(port, '\r');putchar(port, *s);}
}
该函数的实现主要是遍历字符串中的所有字符,并将每个字符写入串口。在写入字符之前,需要判断该字符是否为换行符。如果是换行符,则需要先将其转换为回车换行符,再写入串口。
总结
对接底层的部分,Kernel 主要是提供了两个接口:
1、uart_register_driver (一次调用)
2、uart_add_one_port (多次调用)
通过这两个接口,实现了芯片将自己的 UART 对接到 Linux Kernel UART Driver 中。
芯片厂商需要自行设计并实现的部分有:
1、uart_drvier 结构(一个)
2、uart_port 结构(多个)
3、uart_ops 对串口的操作集(可能一个,可能多个)
所以从结构上来看,整个对接过程为:
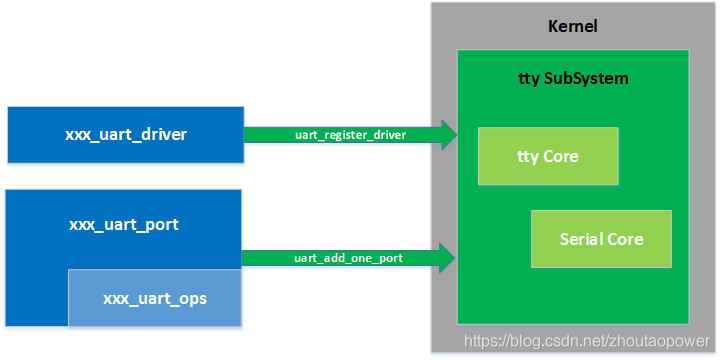
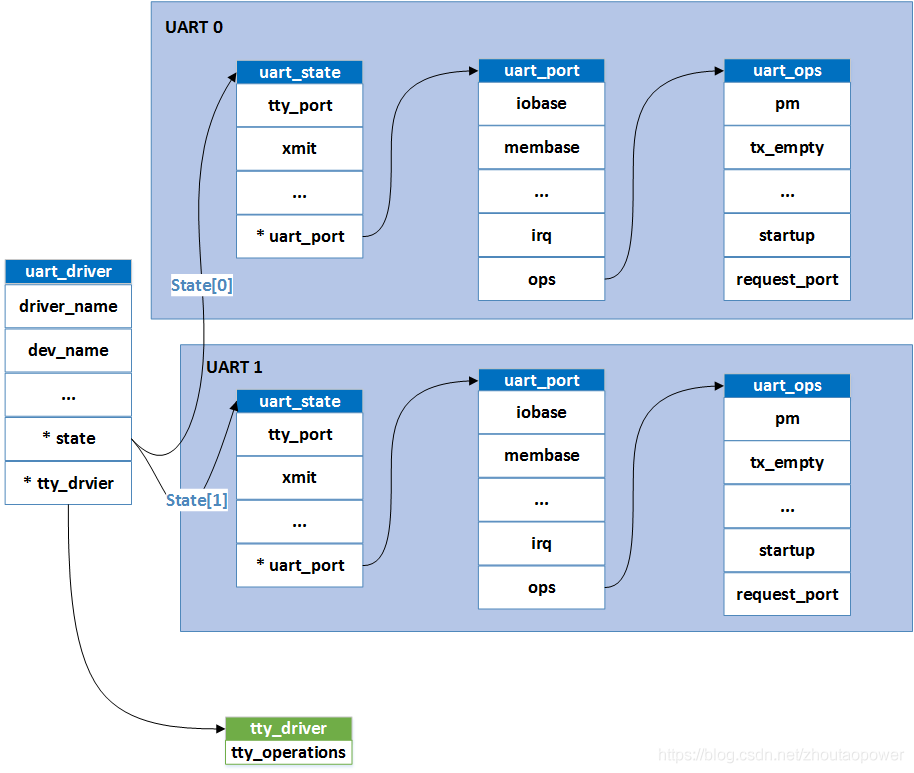
这里有一点需要特别注意,在对接底层的部分中,Kernel 定义了一个结构体叫:struct uart_ops
在 tty 层,对 tty_driver 初始化的时候(serial_core.c),调用到:
tty_set_operations(normal, &uart_ops);
而他的实现是:
void tty_set_operations(struct tty_driver *driver,const struct tty_operations *op){driver->ops = op;
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL(tty_set_operations);
看到了么,传进去的是 **tty_operations *op**,所以,在 tty_driver 挂接的 uart_ops 并非那个 struct uart_ops,而是这个 serial_core.c 文件内定义的:
static const struct tty_operations uart_ops = {.open = uart_open,.close = uart_close,.write = uart_write,.put_char = uart_put_char,.flush_chars = uart_flush_chars,.write_room = uart_write_room,.chars_in_buffer= uart_chars_in_buffer,.flush_buffer = uart_flush_buffer,.ioctl = uart_ioctl,.throttle = uart_throttle,.unthrottle = uart_unthrottle,.send_xchar = uart_send_xchar,.set_termios = uart_set_termios,.set_ldisc = uart_set_ldisc,.stop = uart_stop,.start = uart_start,.hangup = uart_hangup,.break_ctl = uart_break_ctl,.wait_until_sent= uart_wait_until_sent,
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS.proc_show = uart_proc_show,
#endif.tiocmget = uart_tiocmget,.tiocmset = uart_tiocmset,.set_serial = uart_set_info_user,.get_serial = uart_get_info_user,.get_icount = uart_get_icount,
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL.poll_init = uart_poll_init,.poll_get_char = uart_poll_get_char,.poll_put_char = uart_poll_put_char,
#endif
};
名字一样,但是不是同一个结构,容易让人眼花~~
本文参考
https://blog.csdn.net/zhoutaopower/article/details/99289550
https://www.cnblogs.com/timemachine213/p/14317462.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u011728480/article/details/105676239