0x00 前言
演示使用的Linux版本(#cat /etc/issue):Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS \n \l
最后更新日期:2023.7.17
0x01 fseek函数使用小结
1.函数描述
设置stream文件的位置指针偏移到指定位置1。
2.声明
#include <stdio.h>
int fseek( FILE *stream, long offset, int origin );
参数:
stream:这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了流。
offset:相对 origin 偏移的字节数。
origin:起始位置 。它为指定的下列值之一: SEEK_SET 、 SEEK_CUR 、 SEEK_END
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
SEEK_SET | 当前位置为文件的开头 |
SEEK_CUR | 当前位置为文件指针的位置 |
SEEK_END | 当前位置为文件的末尾 |
返回值:
成功时为 0 ,否则为非零。
3.实例
该例实现功能为:从a文件复制其全部内容,然后覆写到b文中,最后再将一个字符串"hello word!"内容追加到b文件中。
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{int num = 0;int count = 0;char buffer[1024] = {0};char str[1024] = "hello word!";FILE* source_fd;FILE* target_fd;if(argc != 3){printf("Usage:copy Sourcefile Targetfile\n");return -1;}if(!(source_fd = fopen(*(argv + 1), "rb"))){//二进制读取文件内容printf("Source file open error!\n");return -2;}if(!(target_fd = fopen(*(argv + 2), "wb"))){ //文件清空,再二进制写入新的数据,若不想清空文件,第二参数写"ab"变为追加方式printf("Target file open error!\n");return -3;}num = fread(buffer, sizeof(char), sizeof(buffer), source_fd);fseek(target_fd, 0, SEEK_SET);if(fwrite(buffer, sizeof(char), strlen(buffer), target_fd) != num){printf("Target file write buffer error!\n");return -4;}fseek(target_fd, strlen(buffer), SEEK_SET);if(fwrite(str, sizeof(char), strlen(str), target_fd) != strlen(str)){printf("Target file write str error!\n");return -5;}fclose(source_fd);fclose(target_fd);return 0;
}当前目录下有a、b两个文件,其中a文件有内容如下,b文件内容为空:
a:
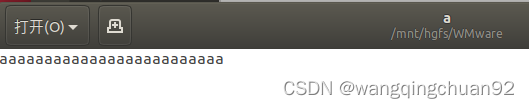
b:

gcc编译程序并运行:

此时查看b文件:
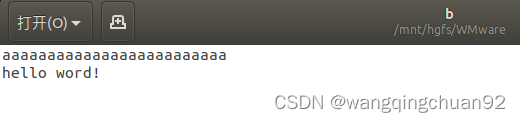
可以看到覆写成功。此时若我们将代码中的第二个fseek(target_fd, strlen(buffer), SEEK_SET);改成fseek(target_fd, 4, SEEK_SET);也就是将文件位置指针偏移4个字节(小于a内容长度),再编译运行则b文件内容如下:
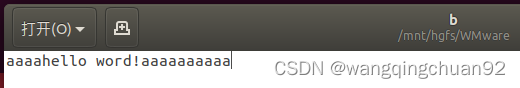
可以看到这次的修改将从第4个字节后开始覆写字符串"hello word!"内容。
以上。
https://www.apiref.com/cpp-zh/c/io/fseek.html ↩︎