从今天起,我们开始学习状态模式。在实际的软件开发中,状态模式并不是很常用,但是在能够用到的场景里,它可以发挥很大的作用。从这一点上来看,它有点像我们之前讲到的组合模式。
可以简短的回顾一下组合模式:适合处理树型结构的场景。
状态模式一般用来实现状态机,而状态机常用在游戏、工作流引擎等系统开发中。不过,状态机的实现方式有多种,除了状态模式,比较常用的还有分支逻辑法和查表法。今天,我们就详细讲讲这几种实现方式,并且对比一下它们的优劣和应用场景。
什么是有限状态机?
有限状态机,英文翻译是Finite State Machine,缩写为FSM,简称为状态机。状态机有3个组成部分:状态(State)、事件(Event)、动作(Action)。其中,事件也称为转移条件(Transition Condition)。事件触发状态的转移及动作的执行。不过,动作不是必须的,也可能只转移状态,不执行任何动作。
马里奥形态的转变就是一个状态机。其中,马里奥的不同形态就是状态机中的“状态”,游戏情节(比如吃了蘑菇)就是状态机中的“事件”,加减积分就是状态机中的“动作”。比如,吃蘑菇这个事件,会触发状态的转移:从小马里奥转移到超级马里奥,以及触发动作的执行(增加100积分)。
为了方便接下来的讲解,我对游戏背景做了简化,只保留了部分状态和事件。简化之后的状态转移如下图所示:

public enum State {SMALL(0),SUPER(1),FIRE(2),CAPE(3);private int value;private State(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return this.value;}
}public class MarioStateMachine {private int score;private State currentState;public MarioStateMachine() {this.score = 0;this.currentState = State.SMALL;}public void obtainMushRoom() {//TODO}public void obtainCape() {//TODO}public void obtainFireFlower() {//TODO}public void meetMonster() {//TODO}public int getScore() {return this.score;}public State getCurrentState() {return this.currentState;}
}public class ApplicationDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {MarioStateMachine mario = new MarioStateMachine();mario.obtainMushRoom();int score = mario.getScore();State state = mario.getCurrentState();System.out.println("mario score: " + score + "; state: " + state);}
}状态机实现方式一:分支逻辑法
对于如何实现状态机,我总结了三种方式。其中,最简单直接的实现方式是,参照状态转移图,将每一个状态转移,原模原样地直译成代码。这样编写的代码会包含大量的if-else或switch-case分支判断逻辑,甚至是嵌套的分支判断逻辑,所以,我把这种方法暂且命名为分支逻辑法。如果状态转移极其复杂很容易出现if-else条件错误的情况。
状态机实现方式二:查表法
实际上,上面这种实现方法有点类似hard code,对于复杂的状态机来说不适用,而状态机的第二种实现方式查表法,就更加合适了。接下来,我们就一块儿来看下,如何利用查表法来补全骨架代码。
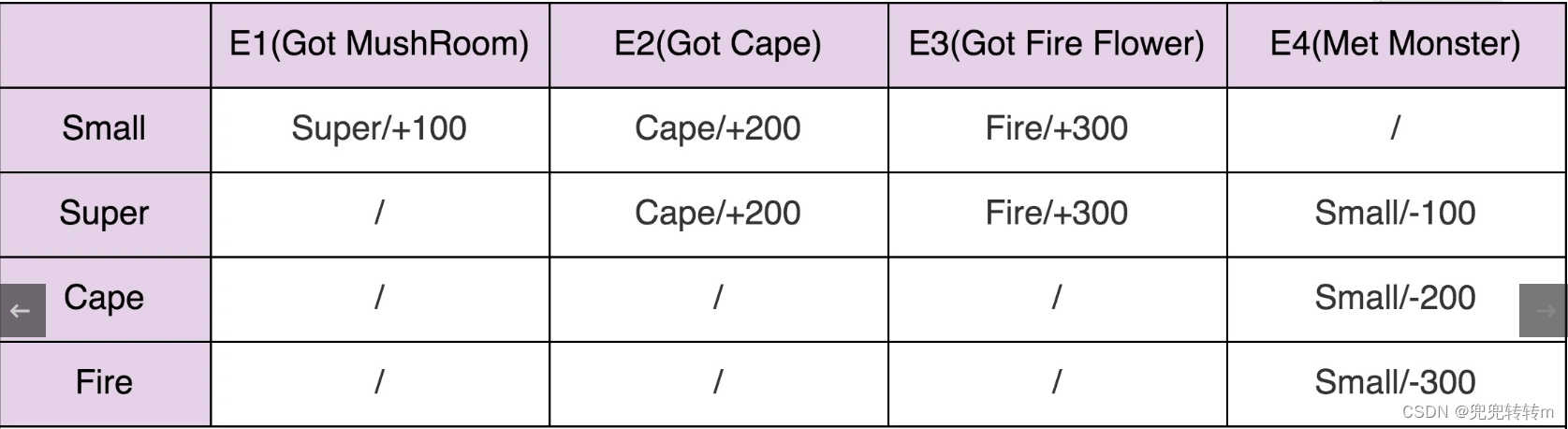
public enum Event {GOT_MUSHROOM(0),GOT_CAPE(1),GOT_FIRE(2),MET_MONSTER(3);private int value;private Event(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return this.value;}
}public class MarioStateMachine {private int score;private State currentState;private static final State[][] transitionTable = {{SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL},{SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL},{CAPE, CAPE, CAPE, SMALL},{FIRE, FIRE, FIRE, SMALL}};private static final int[][] actionTable = {{+100, +200, +300, +0},{+0, +200, +300, -100},{+0, +0, +0, -200},{+0, +0, +0, -300}};public MarioStateMachine() {this.score = 0;this.currentState = State.SMALL;}public void obtainMushRoom() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_MUSHROOM);}public void obtainCape() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_CAPE);}public void obtainFireFlower() {executeEvent(Event.GOT_FIRE);}public void meetMonster() {executeEvent(Event.MET_MONSTER);}private void executeEvent(Event event) {int stateValue = currentState.getValue();int eventValue = event.getValue();this.currentState = transitionTable[stateValue][eventValue];this.score += actionTable[stateValue][eventValue];}public int getScore() {return this.score;}public State getCurrentState() {return this.currentState;}}状态机实现方式三:状态模式
对于简单的加减积分可以使用查表法进行实现,但是如果设计复杂的业务呢?比如操作数据库,发送消息通知等等,就没办法使用如此简单的二维数组来表示了。这也就是说,查表法的实现方式有一定局限性。
状态模式通过将事件触发的状态转移和动作执行,拆分到不同的状态类中,来避免分支判断逻辑。我们还是结合代码来理解这句话。
public interface IMario { //所有状态类的接口State getName();//以下是定义的事件void obtainMushRoom();void obtainCape();void obtainFireFlower();void meetMonster();
}public class SmallMario implements IMario {private MarioStateMachine stateMachine;public SmallMario(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {this.stateMachine = stateMachine;}@Overridepublic State getName() {return State.SMALL;}@Overridepublic void obtainMushRoom() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new SuperMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 100);}@Overridepublic void obtainCape() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new CapeMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 200);}@Overridepublic void obtainFireFlower() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new FireMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 300);}@Overridepublic void meetMonster() {// do nothing...}
}public class SuperMario implements IMario {private MarioStateMachine stateMachine;public SuperMario(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {this.stateMachine = stateMachine;}@Overridepublic State getName() {return State.SUPER;}@Overridepublic void obtainMushRoom() {// do nothing...}@Overridepublic void obtainCape() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new CapeMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 200);}@Overridepublic void obtainFireFlower() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new FireMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 300);}@Overridepublic void meetMonster() {stateMachine.setCurrentState(new SmallMario(stateMachine));stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() - 100);}
}// 省略CapeMario、FireMario类...public class MarioStateMachine {private int score;private IMario currentState; // 不再使用枚举来表示状态public MarioStateMachine() {this.score = 0;this.currentState = new SmallMario(this);}public void obtainMushRoom() {this.currentState.obtainMushRoom();}public void obtainCape() {this.currentState.obtainCape();}public void obtainFireFlower() {this.currentState.obtainFireFlower();}public void meetMonster() {this.currentState.meetMonster();}public int getScore() {return this.score;}public State getCurrentState() {return this.currentState.getName();}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;}public void setCurrentState(IMario currentState) {this.currentState = currentState;}
}上面的代码实现不难看懂,我只强调其中的一点,即MarioStateMachine和各个状态类之间是双向依赖关系。MarioStateMachine依赖各个状态类是理所当然的,但是,反过来,各个状态类为什么要依赖MarioStateMachine呢?这是因为,各个状态类需要更新MarioStateMachine中的两个变量,score和currentState。
public interface IMario {State getName();void obtainMushRoom(MarioStateMachine stateMachine);void obtainCape(MarioStateMachine stateMachine);void obtainFireFlower(MarioStateMachine stateMachine);void meetMonster(MarioStateMachine stateMachine);
}public class SmallMario implements IMario {private static final SmallMario instance = new SmallMario();private SmallMario() {}public static SmallMario getInstance() {return instance;}@Overridepublic State getName() {return State.SMALL;}@Overridepublic void obtainMushRoom(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {stateMachine.setCurrentState(SuperMario.getInstance());stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 100);}@Overridepublic void obtainCape(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {stateMachine.setCurrentState(CapeMario.getInstance());stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 200);}@Overridepublic void obtainFireFlower(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {stateMachine.setCurrentState(FireMario.getInstance());stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 300);}@Overridepublic void meetMonster(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) {// do nothing...}
}// 省略SuperMario、CapeMario、FireMario类...public class MarioStateMachine {private int score;private IMario currentState;public MarioStateMachine() {this.score = 0;this.currentState = SmallMario.getInstance();}public void obtainMushRoom() {this.currentState.obtainMushRoom(this);}public void obtainCape() {this.currentState.obtainCape(this);}public void obtainFireFlower() {this.currentState.obtainFireFlower(this);}public void meetMonster() {this.currentState.meetMonster(this);}public int getScore() {return this.score;}public State getCurrentState() {return this.currentState.getName();}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;}public void setCurrentState(IMario currentState) {this.currentState = currentState;}
}反思和总结:
实际上,像游戏这种比较复杂的状态机,包含的状态比较多,我优先推荐使用查表法,而状态模式会引入非常多的状态类,会导致代码比较难维护。相反,像电商下单、外卖下单这种类型的状态机,它们的状态并不多,状态转移也比较简单,但事件触发执行的动作包含的业务逻辑可能会比较复杂,所以,更加推荐使用状态模式来实现。