目录
- 前言
- 1. forEach()函数
- 2. demo
前言
在实战中学习新用法,特此记录下每个笔记,感兴趣也可收藏也可补充细节
代码例子:
import java.util.Arrays;
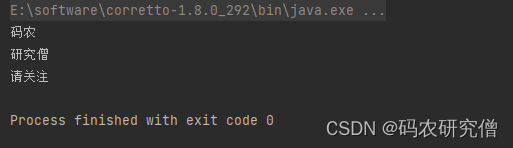
import java.util.List;public class ForEachExample {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> names = Arrays.asList("码农", "研究僧", "请关注");// 使用forEach打印每个名字,lambda用法names.forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));// 或者使用方法引用// names.forEach(System.out::println);}
}
输出结果如下:
1. forEach()函数
在Java 8中,引入了新的forEach方法,它是用于遍历集合元素的一种更便利的方式。
forEach方法被添加到Iterable接口中,因此所有实现了Iterable接口的集合类(如List、Set等)都可以使用forEach方法。
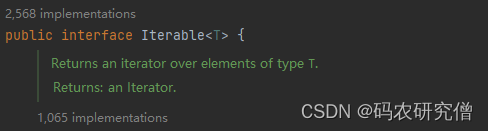
查看forEach()中的源代码,如下:
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}
}
参数action要对每个元素执行的操作,如果指定操作为null,抛出异常NullPointerException
2. demo
在前言中举例了一个list列表
但forEach也可用Map以及stram来表示
当遇到Map数组的时候,其demo如下:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Integer, String> studentMap = new HashMap<>();studentMap.put(1, "码农");studentMap.put(2, "研究僧");studentMap.put(3, "请关注我");// 使用forEach遍历哈希表的键值对studentMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value));}
}
截图如下:

当遇到数据流的时候,其demo如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
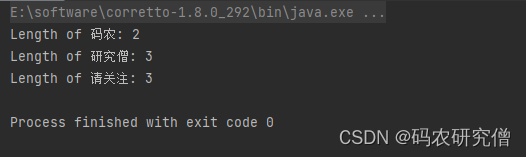
import java.util.List;public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> words = Arrays.asList("码农", "研究僧", "请关注");// 使用流和forEach打印每个单词的长度words.stream().forEach(word -> System.out.println("Length of " + word + ": " + word.length()));}
}
截图如下: