1、排序算法
0、排序算法分类

1、直接插入排序
基本思想
直接插入排序的基本思想是:将数组中的所有元素依次跟前面已经排好的元素相比较,如果选择的元素比已排序的
元素小,则交换,直到全部元素都比较过为止。
算法描述
1、从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序
2、取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描
3、如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一位置
4、重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置
5、将新元素插入到该位置后
6、重复步骤2~5
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 直接插入排序*/
public class InsertionSort {public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j > 0; j--) {if (arr[j - 1] <= arr[j]) {break;}//交换操作int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j - 1];arr[j - 1] = temp;System.out.println("Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2};System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));insertionSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(n²) | O(n) | O(n²) | O(1) |
由于直接插入排序每次只移动一个元素的位, 并不会改变值相同的元素之间的排序, 因此它是一种稳定排序。
2、希尔排序
基本思想
将待排序数组按照步长gap进行分组,然后将每组的元素利用直接插入排序的方法进行排序;每次再将gap折半减
小,循环上述操作;当gap=1时,利用直接插入,完成排序。
算法描述
1、选择一个增量序列 t1,t2,…,tk,其中 ti>tj,tk=1(一般初次取数组半长,之后每次再减半,直到增量为1)。
2、按增量序列个数k,对序列进行k 趟排序。
3、每趟排序,根据对应的增量ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排
序。仅增量因子为1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 希尔排序*/
public class ShellSort {public static void shellSort(int[] arr){int gap = arr.length / 2;//不断缩小gap,直到1为止for (; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {System.out.println("Gap=" + gap);//使用当前gap进行组内插入排序for (int j = 0; (j+gap) < arr.length; j++){for(int k = 0; (k+gap)< arr.length; k += gap){System.out.println("Compare: arr[" + (k+gap)+ "]=" + arr[k+gap] + ", arr[" + k + "]=" + arr[k]);if(arr[k] > arr[k+gap]) {//交换操作int temp = arr[k+gap];arr[k+gap] = arr[k];arr[k] = temp;System.out.println(" Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = { 98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2 };System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));shellSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(nlog2 n) | O(nlog2 n) | O(nlog2 n) | O(1) |
希尔排序是稳定的排序算法
3、选择排序
基本思想
选择排序的基本思想:比较 + 交换。
在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到未排序序列的起始位置。在所有的完全依靠交换去移动元素的排序方法
中,选择排序属于非常好的一种。
算法描述
1、从待排序序列中,找到关键字最小的元素;
2、如果最小元素不是待排序序列的第一个元素,将其和第一个元素互换;
3、从余下的 N - 1 个元素中,找出关键字最小的元素,重复1、2步,直到排序结束。
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 简单选择排序*/
public class SelectionSort {public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){for(int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++){int min = i;//选出之后待排序中值最小的位置for(int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++){if(arr[j] < arr[min]){min = j;}}if(min != i){//交换操作int temp = arr[min];arr[min] = arr[i];arr[i] = temp;System.out.println("Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = { 98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2 };System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));selectionSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
选择排序是不稳定排序
4、堆排序
基本思想
此处以大顶堆为例,堆排序的过程就是将待排序的序列构造成一个堆,选出堆中最大的移走,再把剩余的元素调整
成堆,找出最大的再移走,重复直至有序。
算法描述
1、先将初始序列K[1…n]建成一个大顶堆, 那么此时第一个元素K1最大, 此堆为初始的无序区
2、再将关键字最大的记录K1 (即堆顶, 第一个元素)和无序区的最后一个记录 Kn 交换, 由此得到新的无序区
K[1…n-1]和有序区K[n], 且满足K[1…n-1].keys <= K[n].key
3、交换K1 和 Kn 后, 堆顶可能违反堆性质, 因此需将K[1…n-1]调整为堆. 然后重复步骤2, 直到无序区只有一个
元素时停止
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 堆排序*/
public class HeapSort {public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {for (int i = arr.length; i > 0; i--) {// 创建大订堆,将Kn置为最大元素max_heapify(arr, i);// 堆顶元素(第一个元素)与Kn交换int temp = arr[0];arr[0] = arr[i - 1];arr[i - 1] = temp;}}/*** arr为待排序的数组* limit为数组的长度*/private static void max_heapify(int[] arr, int limit) {if (arr.length <= 0 || arr.length < limit){return;}// 折半int parentIdx = limit / 2;for (; parentIdx >= 0; parentIdx--) {if (parentIdx * 2 >= limit) {continue;}// 左子节点位置int left = parentIdx * 2;// 右子节点位置,如果没有右节点,默认为左节点位置int right = (left + 1) >= limit ? left : (left + 1);int maxChildId = arr[left] >= arr[right] ? left : right;// 交换父节点与左右子节点中的最大值if (arr[maxChildId] > arr[parentIdx]) {int temp = arr[parentIdx];arr[parentIdx] = arr[maxChildId];arr[maxChildId] = temp;}}System.out.println("Max_Heapify: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = { 98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2 };System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));heapSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}}
堆排序是不稳定的排序算法
5、冒泡排序
基本思想
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们
的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完
成。这个算法的名字由来是因为越小的元素会经由交换慢慢“浮”到数列的顶端。
算法描述
冒泡排序算法的运作如下:
1、比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个。
2、对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对。这步做完后,最后的元素会是最大的
数。
3、针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个。
4、持续每次对越来越少的元素重复上面的步骤1~3,直到没有任何一对数字需要比较。
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 冒泡排序*/
public class BubbleSort {public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {//外层循环移动游标for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {//内层循环遍历游标及之后(或之前)的元素for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j + 1];arr[j + 1] = temp;System.out.println("Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2};System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));bubbleSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(n²) | O(n) | O(n²) | O(1) |
冒泡排序是稳定的排序算法
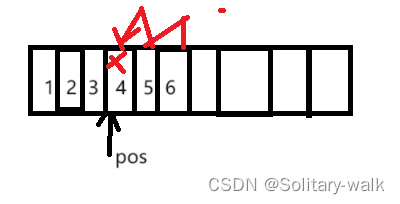
6、快速排序
基本思想
快速排序的基本思想:挖坑填数+分治法。
首先选一个轴值(pivot,也有叫基准的),通过一趟排序将待排记录分隔成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字
均比另一部分的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序。
算法描述
快速排序使用分治策略来把一个序列(list)分为两个子序列(sub-lists)。步骤为:
1、从数列中挑出一个元素,称为基准(pivot)。
2、重新排序数列,所有比基准值小的元素摆放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的元素摆在基准后面(相同的数可
以到任一边)。在这个分区结束之后,该基准就处于数列的中间位置。这个称为分区(partition)操作。
3、递归地(recursively)把小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列排序。
递归到最底部时,数列的大小是零或一,也就是已经排序好了。这个算法一定会结束,因为在每次的迭代
(iteration)中,它至少会把一个元素摆到它最后的位置去。
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 快速排序*/
public class QuickSort {public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {if (arr.length <= 0) {return;}if (low >= high) {return;}int left = low;int right = high;// 挖坑1:保存基准的值int temp = arr[left];while (left < right) {// 坑2:从后向前找到比基准小的元素,插入到基准位置坑1中while (left < right && arr[right] >= temp) {right--;}arr[left] = arr[right];// 坑3:从前往后找到比基准大的元素,放到刚才挖的坑2中while (left < right && arr[left] <= temp) {left++;}arr[right] = arr[left];}// 基准值填补到坑3中,准备分治递归快排arr[left] = temp;System.out.println("Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));quickSort(arr, low, left - 1);quickSort(arr, left + 1, high);}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2};System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(n²) | O(1)(原地分区递归版) |
快速排序是不稳定的排序算法
7、归并排序
基本思想
归并排序算法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子
序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。
算法描述
递归法(假设序列共有n个元素):
1、将序列每相邻两个数字进行归并操作,形成 floor(n/2)个序列,排序后每个序列包含两个元素;
2、将上述序列再次归并,形成 floor(n/4)个序列,每个序列包含四个元素;
3、重复步骤2,直到所有元素排序完毕。
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 归并排序*/
public class MergingSort {public static int[] mergingSort(int[] arr) {if (arr.length <= 1) {return arr;}int num = arr.length >> 1;int[] leftArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, num);int[] rightArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, num, arr.length);System.out.println("split two array: " + Arrays.toString(leftArr) + " And " + Arrays.toString(rightArr));//不断拆分为最小单元,再排序合并return mergeTwoArray(mergingSort(leftArr), mergingSort(rightArr));}private static int[] mergeTwoArray(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;//申请额外的空间存储合并之后的数组int[] result = new int[arr1.length + arr2.length];//选取两个序列中的较小值放入新数组while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) {if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {result[k++] = arr1[i++];} else {result[k++] = arr2[j++];}}//序列1中多余的元素移入新数组while (i < arr1.length) {result[k++] = arr1[i++];}//序列2中多余的元素移入新数组while (j < arr2.length) {result[k++] = arr2[j++];}System.out.println("Merging: " + Arrays.toString(result));return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, -5, -3, 4, 3, 6, -1, 99, 2};System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));mergingSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(n) |
归并排序是稳定的排序算法
8、基数排序
基本思想
它是这样实现的:将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位
开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。
基数排序按照优先从高位或低位来排序有两种实现方案:
-
MSD(Most significant digital) 从最左侧高位开始进行排序。先按k1排序分组, 同一组中记录, 关键码k1相
等, 再对各组按k2排序分成子组, 之后, 对后面的关键码继续这样的排序分组, 直到按最次位关键码kd对各子组
排序后. 再将各组连接起来, 便得到一个有序序列。MSD方式适用于位数多的序列。
-
LSD (Least significant digital)从最右侧低位开始进行排序。先从kd开始排序,再对kd-1进行排序,依次
重复,直到对k1排序后便得到一个有序序列。LSD方式适用于位数少的序列。
算法描述
我们以LSD为例,从最低位开始,具体算法描述如下:
1、取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数;
2、arr为原始数组,从最低位开始取每个位组成radix数组;
3、对radix进行计数排序(利用计数排序适用于小范围数的特点);
package com.example.number1;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 基数排序*/
public class RadixSort {public static void radixSort(int[] arr){if(arr.length <= 1) {return;}//取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数int max = 0;for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){if(max < arr[i]){max = arr[i];}}int maxDigit = 1;while(max / 10 > 0){maxDigit++;max = max / 10;}System.out.println("maxDigit: " + maxDigit);//申请一个桶空间int[][] buckets = new int[10][arr.length];int base = 10;//从低位到高位,对每一位遍历,将所有元素分配到桶中for(int i = 0; i < maxDigit; i++){//存储各个桶中存储元素的数量int[] bktLen = new int[10];//分配:将所有元素分配到桶中for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++){int whichBucket = (arr[j] % base) / (base / 10);buckets[whichBucket][bktLen[whichBucket]] = arr[j];bktLen[whichBucket]++;}//收集:将不同桶里数据挨个捞出来,为下一轮高位排序做准备,由于靠近桶底的元素排名靠前,因此从桶底先捞int k = 0;for(int b = 0; b < buckets.length; b++){for(int p = 0; p < bktLen[b]; p++){arr[k++] = buckets[b][p];}}System.out.println("Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));base *= 10;}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = { 98, 87, 200, 300, 150, 32, 4, 3, 6, 99, 2 };System.out.println("Array : " + Arrays.toString(arr));radixSort(arr);System.out.println("Array Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
| 平均时间复杂度 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(d*(n+r)) | O(d*(n+r)) | O(d*(n+r)) | O(n+r) |
其中,d 为位数,r 为基数,n 为原数组个数。
基数排序只有从最低位开始才是稳定的排序算法
9、总结
| 排序类型 | 平均情况 | 最好情况 | 最坏情况 | 辅助空间 | 稳定性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冒泡排序 | O(n²) | O(n) | O(n²) | O(1) | 稳定 |
| 选择排序 | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) | 不稳定 |
| 直接插入排序 | O(n²) | O(n) | O(n²) | O(1) | 稳定 |
| 折半插入排序 | O(n²) | O(n) | O(n²) | O(1) | 稳定 |
| 希尔排序 | O(n^1.3) | O(nlogn) | O(n²) | O(1) | 不稳定 |
| 归并排序 | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(n) | 稳定 |
| 快速排序 | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(n²) | O(nlog₂n) | 不稳定 |
| 堆排序 | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(nlog₂n) | O(1) | 不稳定 |
| 计数排序 | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | O(k) | 稳定 |
| 桶排序 | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | O(n²) | O(n+k) | (不)稳定 |
| 基数排序 | O(d(n+k)) | O(d(n+k)) | O(d(n+kd)) | O(n+kd) | 稳定 |


2、单例模式
总共有5种方法
(1)饿汉式(线程安全,调用效率高,但是不能延时加载)
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:19* Singleton模式的第一种实现方式* 饿汉式(线程安全,调用效率高,但是不能延时加载)*/
public class Singleton1 {private static Singleton1 instance = new Singleton1();private Singleton1() {}public static Singleton1 getInstance() {return instance;}public static void main(String[] args) {Singleton1 a1 = Singleton1.getInstance();Singleton1 a2 = Singleton1.getInstance();// trueSystem.out.println(a1 == a2);}
}
(2)懒汉式(线程不安全,调用效率不高,但是能延时加载)
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:21* Singleton模式的第二种实现方式* 懒汉式(线程不安全,调用效率不高,但是能延时加载)*/
public class Singleton2 {private static Singleton2 instance;private Singleton2() {}public static synchronized Singleton2 getInstance(){if (instance == null) {instance = new Singleton2();}return instance;}public static void main(String[] args) {Singleton2 a1 = Singleton2.getInstance();Singleton2 a2 = Singleton2.getInstance();// trueSystem.out.println(a1 == a2);}
}
(3)Double CheckLock实现单例:DCL也就是双重锁判断机制(由于JVM底层模型原因,偶尔会出问题,不建议使用)
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:28* Singleton模式的第三种实现方式* Double CheckLock实现单例:DCL也就是双重锁判断机制(由于JVM底层模型原因,偶尔会出问题,不建议使用)*/
public class Singleton3 {private volatile static Singleton3 instance;private Singleton3() {}public static Singleton3 getInstance() {if (instance == null) {synchronized (Singleton3.class) {if (instance == null) {instance = new Singleton3();}}}return instance;}public static void main(String[] args) {Singleton3 a1 = Singleton3.getInstance();Singleton3 a2 = Singleton3.getInstance();// trueSystem.out.println(a1 == a2);}
}
(4)静态内部类实现模式(线程安全,调用效率高,可以延时加载)
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:31* Singleton模式的第四种实现方式* 静态内部类实现模式(线程安全,调用效率高,可以延时加载)*/
public class Singleton4 {private static class SingletonClassInstance {private static final Singleton4 instance = new Singleton4();}private Singleton4() {}public static Singleton4 getInstance() {return SingletonClassInstance.instance;}public static void main(String[] args) {Singleton4 a1 = Singleton4.getInstance();Singleton4 a2 = Singleton4.getInstance();// trueSystem.out.println(a1 == a2);}
}
(5)枚举类(线程安全,调用效率高,不能延时加载,可以天然的防止反射和反序列化调用)
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:32* Singleton模式的第五种实现方式* 枚举类(线程安全,调用效率高,不能延时加载,可以天然的防止反射和反序列化调用)*/
public enum Singleton5 {//枚举元素本身就是单例INSTANCE;// 添加自己需要的操作public void singletonOperation() {}
}
package com.example.number2;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2021年12月31日 15:38*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Singleton5 singletona = Singleton5.INSTANCE;Singleton5 singletonb = Singleton5.INSTANCE;// trueSystem.out.println(singletona == singletonb);}
}
3、找出数组中重复的数字
题目一:找出数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0~n-1的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复
了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。例如,如果输入长度为7的数组
{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是重复的数字2或者3。
解法: 因为列表总共有n个元素,所有元素可能取到的元素有0~n-1,共n种。如果不存在重复的数字,那么排序后
数字i将会出现在下标为i的位置。现在让我们重新扫描数组,当扫描到下标为i的数字时,首先比较这个数字(记为
m)与i是否相等: 如果是,继续扫描下一个元素,如果不是,则再拿它与第m个数字比较: 如果它和第m个数字相
同,就找到了一个重复的元素;如果不同,就将m与第i个数字互换。接下来继续重头开始,重复换这个比较。
package com.example.number3;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:找出数组中重复的数字*/
public class Test1 {public void getDuplicate1(int[] num) {int NumChange;for (int index = 0; index < num.length; index++) {while (num[index] != index) {if (num[index] == num[num[index]]) {System.out.print("重复元素是:" + num[index]);break;} else {NumChange = num[num[index]];num[num[index]] = num[index];num[index] = NumChange;}}}}public void getDuplicate(int[] arr) {int i = 0;while (i < arr.length && arr != null) {int m = arr[i];if (m == i) {i += 1;} else {if (m == arr[m]) {System.out.println("重复元素是:" + m);break;} else {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[m];arr[m] = temp;i = 0;}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int arr[] = {4, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3};new Test1().getDuplicate1(arr);}
}
题目二:不修改数组找出重复的数字
在一个长度为n+1的数组里的所有数字都在1~n范围内,所以数字中至少有一个数字是重复的。请找出数组中任意
一个重复的数字,但不能修改输入的数组。例如,如果输入长度为8的数组{2,3,5,4,3,2,6,7},那么对应的输出是重
复的数字2或者3。
避免使用O(n)的辅助空间。我们把取值空间[1,n]从中间的数字m分为两部分,前面一部分为1~m,后面一部分为
m+1~n。如果数组中元素落在前面一部分的元素个数多于m个,那么数组中重复的元素一定落在前半区间;否
则,数组中重复的元素一定落在后半区间。然后,我们可以继续将包含重复元素的区间一分为二,直到找到一个重
复的元素。
package com.example.number3;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:不修改数组找出重复的数字*/
public class Test2 {public int findDuplicates(int arr[]) {int low = 1;int high = arr.length - 1;while (low <= high) {int mid = (low + high) / 2;int count_low = 0;for (int a : arr) {if (low <= a && a <= mid) {count_low += 1;}}if (high == low) {if (count_low > 1) {return low;} else {break;}}if (count_low > (mid - low + 1)) {high = mid;} else {low = mid + 1;}}return 0;}public static void main(String[] args) {int arr[] = {2, 3, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7};int reu = new Test2().findDuplicates(arr);System.out.println(reu);}
}
4、二维数组中的查找
题目:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完
成一个函数,输入这样一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
解法:从右上开始查找:如果数组中的数比这个整数大,向左移动一位,如果数组中的数比这个数小,向下移动一
位。
package com.example.number4;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二维数组中的查找*/
public class Test {public boolean search(int[][] arr, int value) {int a = arr[0].length;int b = arr.length;int i = 0;int j = a - 1;while (i <= b - 1 && j >= 0) {if (arr[i][j] == value) {return true;}if (arr[i][j] > value) {j--;} else {i++;}}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] arr = {{1, 2, 8, 9},{2, 4, 9, 12},{4, 7, 10, 13},{6, 8, 11, 15}};System.out.println(new Test().search(arr, 7));}}
5、替换空格
题目:请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,输入"We Are Happy.",则经过替换之后的
字符串为"We%20Are%20Happy." 先计算最终需要给出的长度,然后建立两个指针p1,p2,p1指向原始字符串的
末尾,p2指向替换后的字符串的末尾。同时移动p1,p2, 将p1指的内容逐个复制到p2, 当p1遇到空格时,在p2处插
入 %20, p1向前移动一个位置,p2向前移动3个位置,当p1和p2位置重合时,全部替换完成。
package com.example.number5;/*** @author zhangshixing* 替换空格*/
public class Test {public String change(char[] charArray) {int n = charArray.length;int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {if (charArray[i] == ' ') {count++;}}if (count == 0) {return null;}char[] temp = new char[n + 2 * count];int j = n + 2 * count - 1;int i = n - 1;while (i >= 0) {if (charArray[i] == ' ') {temp[j] = '0';temp[j - 1] = '2';temp[j - 2] = '%';j = j - 3;} else {temp[j] = charArray[i];j--;}i--;}return new String(temp);}public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "We are happy";char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();System.out.println(new Test().change(charArray));}
}
6、从尾到头打印链表
题目:输入一个链表的头结点,从尾到头反过来打印每个节点的值。
从头到尾遍历链表,并用一个栈存储每个节点的值,之后出栈输出。
package com.example.commnon;/*** @author zhangshixing* 链表结点*/public class Node {public String data;public Node next;public Node(String data) {super();this.data = data;}
}
package com.example.number6;import com.example.commnon.Node;import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 从尾到头打印链表*/
public class Test {public Node reverse1(Node head) {Node pre = head;Node cur = head.next;Node temp;while (cur != null) {temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}head.next = null;return pre;}/*** 采用栈** @param node*/public void reverse2(Node node) {Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();while (node != null) {stack.push(node);node = node.next;}while (!stack.empty()) {System.out.println(stack.pop().data);}}/*** 采用递归** @param node*/public void reverse3(Node node) {if (node != null) {reverse3(node.next);System.out.println(node.data);} else {return;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Node node1 = new Node("A");Node node2 = new Node("B");Node node3 = new Node("C");Node node4 = new Node("D");Node node5 = new Node("E");node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;Node newNode = new Test().reverse1(node1);while (newNode != null) {System.out.print(newNode.data + " ");newNode = newNode.next;}}
}
7、重建二叉树
题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中
都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返
回。
利用二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历的特点,前序遍历的第一个值一定为根节点,对应于中序遍历中间的一个点,在中
序遍历中,该点左侧的值为根节点的左子树,右侧的值为根节点的右子树。这时可以利用递归,取前序遍历的
[1:i+1]和中序遍历的[:i]作为对应的左子树继续上一个过程,取前序遍历的[i+1:]和中序遍历的[i+1:]对应与右子树继
续上一个过程,重建二叉树。
package com.example.commnon;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉树*/public class BinaryTreeNode {public int data;public BinaryTreeNode LchildNode;public BinaryTreeNode RchildNode;public BinaryTreeNode(int data) {super();this.data = data;}
}
package com.example.number7;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 重建二叉树*/
public class Test {public BinaryTreeNode findBinaryTree(int[] pre, int preStart,int preEnd, int[] in, int inStart, int inEnd) {if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd)return null;BinaryTreeNode root = new BinaryTreeNode(pre[preStart]);for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (in[i] == pre[preStart]) {root.LchildNode = findBinaryTree(pre, preStart + 1, i - inStart + preStart,in, inStart, i - 1);root.RchildNode = findBinaryTree(pre, i - inStart + preStart + 1, preEnd,in, i + 1, inEnd);}}return root;}public static void main(String[] args) {int preOrder[] = {1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8};int midOrder[] = {4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6};BinaryTreeNode root = new Test().findBinaryTree(preOrder, 0, preOrder.length - 1,midOrder, 0, midOrder.length - 1);System.out.println(root.data);}
}
8、二叉树的下一个结点
题目:给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包
含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
-
分析二叉树的下一个节点,一共有以下情况:
-
1.二叉树为空,则返回空;
-
2.节点右孩子存在,则设置一个指针从该节点的右孩子出发,一直沿着指向左子结点的指针找到的叶子节点即
为下一个节点;
-
3.节点右孩子不存在,节点是根节点,返回null。节点不是根节点,如果该节点是其父节点的左孩子,则返回
父节点;否则继续向上遍历其父节点的父节点,重复之前的判断,返回结果。
package com.example.commnon;/*** @author zhangshixing* TreeLinkNode*/
public class TreeLinkNode {public int val;public TreeLinkNode left = null;public TreeLinkNode right = null;public TreeLinkNode next = null;public TreeLinkNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}
package com.example.number8;import com.example.commnon.TreeLinkNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉树的下一个结点*/
public class Test {public TreeLinkNode getNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {if (pNode == null) {return null;}if (pNode.right != null) {pNode = pNode.right;while (pNode.left != null) {pNode = pNode.left;}return pNode;}while (pNode.next != null) {if (pNode.next.left == pNode) {return pNode.next;}pNode = pNode.next;}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeLinkNode pNode1 = new TreeLinkNode(8);TreeLinkNode pNode2 = new TreeLinkNode(6);TreeLinkNode pNode3 = new TreeLinkNode(10);TreeLinkNode pNode4 = new TreeLinkNode(5);TreeLinkNode pNode5 = new TreeLinkNode(7);TreeLinkNode pNode6 = new TreeLinkNode(9);TreeLinkNode pNode7 = new TreeLinkNode(11);pNode1.left = pNode2;pNode1.right = pNode3;pNode2.left = pNode4;pNode2.right = pNode5;pNode3.left = pNode6;pNode3.right = pNode7;System.out.println(new Test().getNext(pNode2).val);}}
9、用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
插入删除的过程:插入肯定是往一个栈stack1中一直插入;删除时,直接出栈无法实现队列的先进先出规则,这时
需要将元素从stack1出栈,压到另一个栈stack2中,然后再从stack2中出栈就OK了。需要稍微注意的是:当
stack2中还有元素,stack1中的元素不能压进来;当stack2中没元素时,stack1中的所有元素都必须压入stack2
中。否则顺序就会被打乱。
package com.example.number9;import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 用两个栈实现队列*/
public class Test {private Stack s1 = new Stack();private Stack s2 = new Stack();public void offer(Object x) {s1.push(x);}public void poll() {if (s1.size() == 0 && s2.size() == 0) {try {throw new Exception("empty queue");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}} else {if (s2.size() != 0) {System.out.println(s2.peek().toString());s2.pop();} else {while (s1.size() > 0) {s2.push(s1.pop());}System.out.println(s2.peek().toString());s2.pop();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {Test queue = new Test();queue.offer("a");queue.offer("b");queue.offer("c");queue.poll();= queue.poll();queue.poll();}
}
10、斐波那契数列
题目一:求斐波那契数列的第n项
package com.example.number10;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:求斐波那契数列的第n项*/
public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(new Test1().fibonacci(10));}public int fibonacci(int n) {int tempArray[] = {0, 1};if (n >= 2) {for (int i = 2; i < n + 1; i++) {tempArray[i % 2] = tempArray[0] + tempArray[1];}}return tempArray[n % 2];}
}
题目二:青蛙跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级台阶。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法?
package com.example.number10;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:青蛙跳台阶问题*/
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(new Test2().jumpFloor(10));}public int jumpFloor(int n) {int tempArray[] = {1, 2};if (n >= 3) {for (int i = 3; i < n + 1; i++) {tempArray[(i + 1) % 2] = tempArray[0] + tempArray[1];}}return tempArray[(n + 1) % 2];}
}
11、旋转数组的最小数字
题目:把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个递增排序的数组的一个
旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
package com.example.number11;/*** @author zhangshixing* 旋转数组的最小数字*/
public class Test {public int findMin(int[] arr) {int left = 0;int right = arr.length - 1;if (arr[right] > arr[left]) {try {throw new Exception("非旋转数组");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return -1;}}while (left < right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2;// 对于{1,0,1,1,1}之类的特殊处理if (arr[mid] == arr[left] && arr[left] == arr[right]) {return seachMin(arr, left, right);}if (right - left == 1) {break;}if (arr[mid] >= arr[left]) {left = mid;} else {right = mid;}}return arr[right];}private int seachMin(int[] arr, int left, int right) {int result = arr[left];for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; ++i) {if (arr[i] < result){result = arr[i];}}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};System.out.println(new Test().findMin(arr));}
}
12、矩阵中的路径
题目:请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的
任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某
一个格子,则之后不能再次进入这个格子。 例如 a b c e s f c s a d e e 这样的3 X 4 矩阵中包含一条字符串
”bcced”的路径,但是矩阵中不包含”abcb”路径,因为字符串的第一个字符b占据了矩阵中的第一行第二个格子
之后,路径不能再次进入该格子。
首先对整个矩阵遍历,找到第一个字符,然后向上下左右查找下一个字符,由于每个字符都是相同的判断方法(先
判断当前字符是否相等,再向四周查找),因此采用递归函数。由于字符查找过后不能重复进入,所以还要定义一
个与字符矩阵大小相同的布尔值矩阵,进入过的格子标记为true。如果不满足的情况下,需要进行回溯,此时,要
将当前位置的布尔值标记回false。(所谓的回溯无非就是对使用过的字符进行标记和处理后的去标记)。
package com.example.number12;/*** @author zhangshixing* 矩阵中的路径*/
public class Test {public boolean hasPath(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {if (matrix == null || rows < 1 || cols < 1 || str == null) {return false;}boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[rows * cols];for (@SuppressWarnings("unused") boolean v : isVisited) {v = false;}int pathLength = 0;for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {if (hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col, str, pathLength, isVisited)){return true;}}}return false;}private boolean hasPathCore(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, char[] str, int pathLength,boolean[] isVisited) {if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= rows || col >= cols || isVisited[row * cols + col] == true|| str[pathLength] != matrix[row * cols + col]) {return false;}if (pathLength == str.length - 1) {return true;}boolean hasPath = false;isVisited[row * cols + col] = true;hasPath = hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row - 1, col, str, pathLength + 1, isVisited)|| hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row + 1, col, str, pathLength + 1, isVisited)|| hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col - 1, str, pathLength + 1, isVisited)|| hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col + 1, str, pathLength + 1, isVisited);if (!hasPath) {isVisited[row * cols + col] = false;}return hasPath;}public static void main(String[] args) {String matrix = "abtgcfcsjdeh";String path = "bfce";System.out.println(new Test().hasPath(matrix.toCharArray(), 3, 4, path.toCharArray()));}
}
13、机器人的运动范围
题目:地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标(0,0)的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方
向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格
(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到
多少个格子?
也采用回溯法,先判断机器人能否进入(i,j),再判断周围4个格子。
package com.example.number13;/*** @author zhangshixing* 机器人的运动范围*/
public class Test {public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {if (rows <= 0 || cols <= 0 || threshold < 0){return 0;}boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[rows * cols];int count = movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, 0, 0, isVisited);return count;}private int movingCountCore(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, boolean[] isVisited) {if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= rows || col >= cols || isVisited[row * cols + col]|| cal(row) + cal(col) > threshold){return 0;}isVisited[row * cols + col] = true;return 1 + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row - 1, col, isVisited)+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row + 1, col, isVisited)+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col - 1, isVisited)+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col + 1, isVisited);}private int cal(int num) {int sum = 0;while (num > 0) {sum += num % 10;num /= 10;}return sum;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(new Test().movingCount(7,4,5));}
}
14、剪绳子
题目:给你一根长度为n的绳子,请把绳子剪成m段 (m和n都是整数,n>1并且m>1)每段绳子的长度记为k[0],k[1],
…,k[m].请问k[0]k[1]…*k[m]可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度为8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2,3,3
的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是18。
本题采用动态规划或者贪婪算法可以实现。一开始没有思路时,可以从简单的情况开始想,试着算以下比较短的
绳子是如何剪的。
当n=1时,最大乘积只能为0;
当n=2时,最大乘积只能为1;
当n=3时,最大乘积只能为2;
当n=4时,可以分为如下几种情况:1111,121,13,22,最大乘积为4;
往下推时,发现n≥4时,可以把问题变成几个小问题,即:如果把长度n绳子的最大乘积记为f(n),则有:
f(n)=max(f(i)*f(n-1)),0<i<n。所以思路就很容易出来了:从下往上推,先算小的问题,再算大的问题,大的
问题通过寻找小问题的最优组合得到。
其实这就是动态规划法,以下是动态规划法的几个特点
1.求一个问题的最优解
2.整体问题的最优解依赖各子问题的最优解
3.小问题之间还有相互重叠的更小的子问题
4.为了避免小问题的重复求解,采用从上往下分析和从下往上求解的方法求解问题
贪婪算法依赖于数学证明,当绳子大于5时,尽量多地剪出长度为3的绳子是最优解。
package com.example.number14;/*** @author zhangshixing* 剪绳子*/
public class Test {// ======动态规划======public static int maxProductAfterCutting_solution1(int length) {if (length <= 1)return 0;if (length == 2)return 1;if (length == 3)return 2;// 用于存放最大乘积值int[] product = new int[length + 1];// 下面几个不是乘积,因为其本身长度比乘积大product[0] = 0;product[1] = 1;product[2] = 2;product[3] = 3;// 开始从下到上计算长度为i绳子的最大乘积值product[i]for (int i = 4; i <= length; i++) {int max = 0;// 算不同子长度的乘积,找出最大的乘积for (int j = 1; j <= i / 2; j++) {if (max < product[j] * product[i - j])max = product[j] * product[i - j];}product[i] = max;}return product[length];}// =======贪婪算法========public static int maxProductAfterCutting_solution2(int length) {if (length <= 1)return 0;if (length == 2)return 1;if (length == 3)return 2;int timesOf3 = length / 3;int timesOf2 = 0;if (length - timesOf3 * 3 == 1) {timesOf3--;// timesOf2=2; //错误!}timesOf2 = (length - timesOf3 * 3) / 2;return (int) (Math.pow(3, timesOf3) * Math.pow(2, timesOf2));}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(maxProductAfterCutting_solution2(8));}
}
15、二进制中1的个数
题目:输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
方法一:通过与对应位上为1,其余位为0的数进行与运算。先把整数n与1做与运算,判断最低位是否为1;接着把
1左移一位,与n做与运算,可以判断次低位是否为1,反复左移,即可对每一个位置都进行判断,从而可以获得1的
个数。这种方法需要循环判断32次。
方法二:如果一个整数不为0,把这个整数减1,那么原来处在整数最右边的1就会变为0,原来在1后面的所有的0\
都会变成1。其余所有位将不会受到影响。再把原来的整数和减去1之后的结果做与运算,从原来整数最右边一个1
那一位开始所有位都会变成0。因此,把一个整数减1,再和原来的整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边的1变成0。
这种方法,整数中有几个1,就只需要循环判断几次。
package com.example.number15;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二进制中1的个数*/
public class Test {public static int NumberOf1_Solution1(int n) {int count = 0;int flag = 1;while (flag != 0) {if ((flag & n) != 0){count++;}flag = flag << 1;}return count;}public static int NumberOf1_Solution2(int n) {int count = 0;while (n != 0) {count++;n = (n - 1) & n;}return count;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(NumberOf1_Solution2(7));}
}
16、数值的整数次方
题目:给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。不考虑大数的情
况。
这道题很容易实现,但需要注意以下陷阱:
1)0的负数次方不存在;
2)0的0次方没有数学意义;
3)要考虑exponent为负数的情况。所以可以对exponent进行分类讨论,在对base是否为0进行讨论。
package com.example.number16;/*** @author zhangshixing* 数值的整数次方*/
public class Test {boolean IsInvalid = false;public double power(double base, int exponent) {IsInvalid = false;double result;if (exponent > 0) {result = powerCore(base, exponent);} else if (exponent < 0) {if (base == 0) {IsInvalid = true;return 0;}result = 1 / powerCore(base, -exponent);} else {return 1;}return result;}private double powerCore(double base, int exponent) {if (exponent == 1) {return base;}if (exponent == 0) {return 1;}double result = powerCore(base, exponent >> 1);result *= result;if ((exponent & 0x1) == 1) {result *= base;}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test demo = new Test();System.out.println(demo.power(2, 10));}
}
17、打印1到最大的n位数
题目:输入数字n,按顺序打印出从1最大的n位十进制数。比如输入3,则打印出1、2、3一直到最大的3位数即
999。
思路
陷阱:n过大时是大数问题,不能简单用int或者long数据输出,需要采用字符串或者数组表达大数。
解决方法:通过字符数组char[]来进行输出数字。
方法一:
1)在字符串表达的数字上模拟加法;
2)把字符串表达的数字打印出来。
方法二:
1)采用递归将每一位都从0到9排列出来;
2)把字符串表达的数字打印出来。
package com.example.number17;/*** @author zhangshixing* 打印1到最大的n位数*/
public class Test {public static void print1ToMaxOfNDights1s(int n) {if (n <= 0) {return;}char[] digit = new char[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {digit[i] = '0';}for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (digit[i] != '9') {int m = 0;digit[m]++;while (m < n - 1 && digit[m] > '9') {digit[m] = '0';digit[m + 1]++;m++;}printdigits(digit);}}}private static void printdigits(char[] digit) {int m = digit.length - 1;while (digit[m] == '0') {m--;}for (int i = m; i >= 0; i--) {System.out.print(digit[i]);}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {print1ToMaxOfNDights1s(3);}
}
18、删除链表的节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个结点指针,定义一个函数在O(1)时间删除该结点。
题目一:在O(1)时间内删除链表结点
如果要删除的节点后面有节点,则将该节点内容复制到要删除的节点,并删除该节点。
如果要删除的节点在链表头部,直接删除该节点。
如果要删除的节点在链尾,遍历至该节点删除。
package com.example.commnon;/*** @author zhangshixing* 列表结点*/
public class ListNode {public int data;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int data) {super();this.data = data;}
}
package com.example.number18;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:在O(1)时间内删除链表结点*/
public class Test1 {public static void deleteNode(ListNode head, ListNode deletedNode) {if (head == null || deletedNode == null){return;}// 要删除的节点不是尾节点if (deletedNode.next != null) {deletedNode.data = deletedNode.next.data;deletedNode.next = deletedNode.next.next;}// 链表只有一个节点,删除头结点else if (head == deletedNode) {head = null;}// 链表有多个节点,删除尾节点(需要从头到尾遍历找到要删除节点的前一个节点)else {ListNode temp = head;while (temp.next != deletedNode) {temp = temp.next;}temp.next = null;deletedNode = null;}}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode node1= new ListNode(1);ListNode node2= new ListNode(2);ListNode node3= new ListNode(3);ListNode node4= new ListNode(4);ListNode node5= new ListNode(5);ListNode node6= new ListNode(6);ListNode node7= new ListNode(7);node1.next=node2;node2.next=node3;node3.next=node4;node4.next=node5;node5.next=node6;node6.next=node7;deleteNode(node1,node3);while(node1!=null) {System.out.println(node1.data);node1=node1.next;}}}
题目二:删除链表中重复的结点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例
如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5。
思路
设置一个preNode,用于记录当前结点的前一个结点,再设置一个布尔变量needDelete,如果当前结点和后
一结点的值相同(记该值为dupVal),needDelete赋值为真。
当needDelete为真时,通过循环往后找到第一个不为dupVal的结点,把该结点设置为当前结点,并赋值给
preNode.next,即相当于完成了删除操作;而当needDelete为假时,把当前结点和preNode往后移一位即
可。
package com.example.number18;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2022年03月11日 17:42*/
public class Test2 {public static ListNode deleteDupliction(ListNode head){//只有0个或1个节点,直接returnif(head == null || head.next == null){return head;}//从头到尾开始遍历//如果当前节点是重复节点if(head.data == head.next.data){ListNode temp = head.next;//找到第一个与当前节点值不相等的节点while(temp != null && temp.data == head.data){temp = temp.next;}//从这个节点开始递归return deleteDupliction(temp);//当前节点不是重复节点}else{//从下一个节点开始递归head.next = deleteDupliction(head.next);//返回的是当前节点,因为它不是重复节点return head;}}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode node1= new ListNode(1);ListNode node2= new ListNode(2);ListNode node3= new ListNode(3);ListNode node4= new ListNode(3);ListNode node5= new ListNode(4);ListNode node6= new ListNode(4);ListNode node7= new ListNode(5);node1.next=node2;node2.next=node3;node3.next=node4;node4.next=node5;node5.next=node6;node6.next=node7;deleteDupliction(node1);while(node1!=null) {System.out.println(node1.data);node1=node1.next;}}
}
19、正则表达式匹配
题目:请实现一个函数用来匹配包括.和*的正则表达式。模式中的字符*表示任意一个字符,而.表示
它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次)。 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符
串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和ab*ac*a匹配,但是与"aa.a"和ab*a均不匹配。
思路
使用函数matchCore(char[] str, int indexOfStr, char[] pattern, int indexOfPattern) 来实现每一步的比较
(递归)。
(1)当模式中第二个字符不为
*时:若当前字符相等,则字符串和模式都后移一个字符,继续调用函数进行比较;若不相等,则返回false。
(2)当模式中第二个字符为
*时:若当前字符不相等,则模式后移两个字符,继续比较;若当前字符相等,则有三种情况:
1)字符串字符位置不变,模式后移两个字符,继续比较;
2)字符串后移一个字符,模式后移两个字符,继续比较;
3)字符串后移一个字符,模式字符位置不变,继续比较。
三种情况使用“||”进行并列比较。
package com.example.number19;/*** @author zhangshixing* 正则表达式匹配*/
public class Test {public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) {if (str == null || pattern == null) {return false;}return matchCore(str, 0, pattern, 0);}private boolean matchCore(char[] str, int indexOfStr, char[] pattern, int indexOfPattern) {if (indexOfStr == str.length && indexOfPattern == pattern.length) {return true;}if (indexOfStr < str.length && indexOfPattern == pattern.length) {return false;}if (indexOfPattern + 1 < pattern.length && pattern[indexOfPattern + 1] == '*') {if ((indexOfStr < str.length && pattern[indexOfPattern] == '.')|| (indexOfStr < str.length && pattern[indexOfPattern] == str[indexOfStr])) {return matchCore(str, indexOfStr, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2)|| matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern)|| matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2);} else {return matchCore(str, indexOfStr, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2);}}if (indexOfStr < str.length && (pattern[indexOfPattern] == str[indexOfStr] || pattern[indexOfPattern] == '.')) {return matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern + 1);}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test demo = new Test();System.out.println(demo.match("aaa".toCharArray(), "a.a".toCharArray()));}
}
20、表示数值的字符串
题目:请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符
串+100,5e2,-123,3.1416和-1E-16都表示数值。 但是12e,1a3.14,1.2.3,+-5和12e+4.3都不是。
package com.example.number20;/*** @author zhangshixing* 表示数值的字符串*/
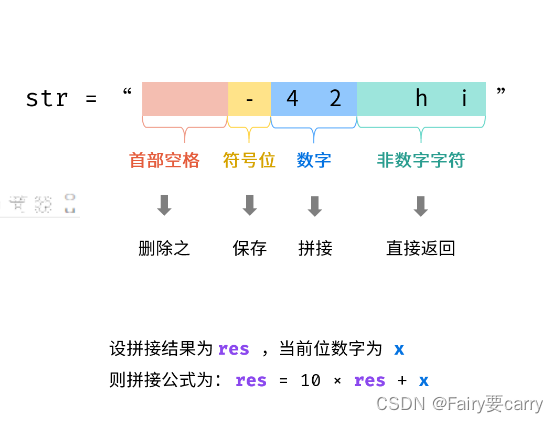
public class Test {public boolean isNumeric(char[] str) {if (str == null || str.length == 0)return false;int[] index = new int[1];index[0] = 0; // 用于记录当前字符位置// 先判断Aboolean isNumeric; //用于记录是否满足条件isNumeric = isInteger(str, index);// 判断Bif (index[0] < str.length && (str[index[0]] == '.')) {index[0]++;isNumeric = isUnsignedInteger(str, index) || isNumeric; // .B和A.和A.B形式均可以}// 判断e后面的Aif (index[0] < str.length && (str[index[0]] == 'e' || str[index[0]] == 'E')) {index[0]++;isNumeric = isInteger(str, index) && isNumeric;}if (isNumeric && index[0] == str.length)return true;elsereturn false;}private boolean isInteger(char[] str, int[] index) { // 用int[]才能传值,int的话需要定义index为全局变量if (index[0] < str.length && (str[index[0]] == '+' || str[index[0]] == '-'))index[0]++;return isUnsignedInteger(str, index);}private boolean isUnsignedInteger(char[] str, int[] index) {int start = index[0];while (index[0] < str.length && (str[index[0]] - '0' <= 9 && str[index[0]] - '0' >= 0))index[0]++;if (index[0] > start)return true;elsereturn false;}public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "+10e-6.23";System.out.println(new Test().isNumeric(str.toCharArray()));}}
21、调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目:输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有
的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分
对于任意一个整数数组,设置一个指针,从前往后走,如果遇到奇数则指针后移,遇到偶数时,希望把该偶
数放在数组后面;因此,再设置一个指针,从后往前走,遇到偶数时指针前移,遇到奇数时,则恰好可以与
前面的指针所指的偶数进行调换。
package com.example.number21;/*** @author zhangshixing* 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面*/
public class Test {public static void reOrderArray(int[] array) {if (array == null || array.length == 0)return;int length = array.length;int low = 0;int high = length - 1;int temp;while (low < high) {//向后移动low指针,直到它指向偶数while (low < length && (array[low] & 1) != 0)low++;//向前移动high指针,直到它指向奇数while (high >= 0 && (array[high] & 1) == 0)high--;if (low < high) {temp = array[low];array[low] = array[high];array[high] = temp;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};reOrderArray(a);for (int i : a) {System.out.println(i);}}}
22、链表中倒数第k个结点
题目:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
第一:从头开始遍历,计算链表个数n,然后重新遍历,第n-k+1个结点即为所需要的结点。
第二:采用了栈进行实现该方法,空间复杂度比较大。
第三:设置两个指针,第一个指针先遍历k-1步;从第k步开始,第二个指针指向头结点,两个结点同时往后遍
历,当第一个指针到达最后一个结点时,第二个指针指向的正好是倒数第k个结点。
package com.example.number22;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 链表中倒数第k个结点*/
public class Test {//方法1:利用栈,把结点入栈,然后输出第k个即可public static ListNode FindKthToTail1(ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || k <= 0)return null;int numbOfList = 1;Stack<ListNode> st = new Stack<ListNode>();st.push(head);ListNode node = head.next;while (node != null) {numbOfList++;st.push(node);node = node.next;}if (k > numbOfList)return null;else {for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {node = st.pop();}return node;}}//方法2:利用两个相距为k-1的指针,public static ListNode FindKthToTail2(ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || k <= 0)return null;ListNode pAhead = head;for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {pAhead = pAhead.next;if (pAhead == null)return null;}ListNode pBehind = head;while (pAhead.next != null) {pAhead = pAhead.next;pBehind = pBehind.next;}return pBehind;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode list1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode pnode1 = list1;for (int i = 2; i < 13; i++) {pnode1.next = new ListNode(i);pnode1 = pnode1.next;}System.out.println(FindKthToTail2(list1, 4).data);}}
23、链表中环的入口结点
题目:一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点。
1.确定链表是否有环:通过两个不同速度的指针确定,当两个指针指向同一个结点时,该结点为环中的一个
结点。快指针走两步,慢指针走一步。
2.确定环中结点的数目n:指针走一圈,边走边计数
3.找到环的入口:从头结点开始,通过两个相差为n的指针来得到(即寻找链表中倒数第n个结点)
package com.example.number23;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 链表中环的入口结点*/
public class Test {/** 确定链表是否有环,采用快慢指针确定* 返回值代表快慢指针相遇时的结点,返回null代表链表无环*/private static ListNode meetingNode(ListNode head) {if (head == null)return null;ListNode pSlow = head;ListNode pFast = head;while (pFast != null) {pSlow = pSlow.next;pFast = pFast.next;if (pFast != null)pFast = pFast.next;if (pSlow != null && pSlow == pFast)return pSlow;}return null;}/*** 计算环中入口结点*/public static ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {ListNode meetingNode = meetingNode(head);if (meetingNode == null)return null;//计算环中结点的数目int count = 1;ListNode pNode1 = meetingNode.next;while (pNode1 != meetingNode) {count++;pNode1 = pNode1.next;}//先移动pNode1,次数为countpNode1 = head;for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {pNode1 = pNode1.next;}ListNode pNode2 = head;while (pNode1 != pNode2) {pNode1 = pNode1.next;pNode2 = pNode2.next;}return pNode1;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5);node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;node5.next = node2;ListNode newNode = entryNodeOfLoop(node1);System.out.println(newNode.data);}}
24、反转链表
题目:输入一个链表,输出反转后的链表。
方法一:使用三个指针(pre,p,next)进行实现。令p指向pre,next则是用于防止链表断裂。
方法二:(递归):找到最后一个结点作为返回值,递归函数中,找到最后的头结点后,开始进行每个结点next
值的转换。
package com.example.number24;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 反转链表*/
public class Test {public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;while(cur!=null){ListNode next = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = next;}return pre;}public static ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {if(head == null || head.next==null)return head;ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return newHead;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode list1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode pnode1 = list1;for(int i=2;i<12;i++) {pnode1.next = new ListNode(i);pnode1 = pnode1.next;}ListNode newList = reverseList(list1);while(newList!=null) {System.out.println(newList.data);newList=newList.next;}}}
25、合并两个排序的链表
题目:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
思路:
递归实现:合并过程中,每次都是从两个链表中找出较小的一个来链接,因此可以采用递归来实现:当任意
一个链表为null时,直接链接另一个链表即可;其余情况只需要在两个链表中找出较小的一个结点进行链接,
该结点的next值继续通过递归函数来链接。
非递归实现:非递归实现比较容易想到,直接进行分情况讨论即可,要稍微注意下后面代码中头结点的赋值
过程。
package com.example.number25;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 合并两个排序的链表*/
public class Test {/** 递归版本*/public static ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if (list1 == null) return list2;if (list2 == null) return list1;if (list1.data < list2.data) {list1.next = merge(list1.next, list2);return list1;} else {list2.next = merge(list1, list2.next);return list2;}}/** 非递归*/public static ListNode merge2(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if (list1 == null) return list2;if (list2 == null) return list1;ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); //不能为nullListNode p = dummyHead;while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.data < list2.data) {p.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {p.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}p = p.next;}if (list1 == null)p.next = list2;elsep.next = list1;return dummyHead.next;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode list1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode pnode1 = list1;for (int i = 2; i < 12; i++) {pnode1.next = new ListNode(i);pnode1 = pnode1.next;}ListNode list2 = new ListNode(5);ListNode pnode2 = list2;for (int i = 12; i < 26; i++) {pnode2.next = new ListNode(i);pnode2 = pnode2.next;}ListNode head = merge2(list1, list2);while (head != null) {System.out.println(head.data);head = head.next;}}}
26、树的子结构
题目:输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思路
1)先对A树进行遍历,找到与B树的根结点值相同的结点R;
2)判断A树中以R为根结点的子树是否包含B树一样的结构;
package com.example.number26;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 树的子结构*/
public class Test {public static boolean hasSubtree(BinaryTreeNode root1, BinaryTreeNode root2) {if (root1 == null || root2 == null)return false;return doesTree1HasTree2(root1, root2) || hasSubtree(root1.LchildNode, root2)|| hasSubtree(root1.RchildNode, root2);}/** 判断root结点开始的子树中各个结点是否相同*/private static boolean doesTree1HasTree2(BinaryTreeNode root1, BinaryTreeNode root2) {if (root2 == null)return true;if (root1 == null)return false;return equal(root1.data, root2.data) && doesTree1HasTree2(root1.LchildNode, root2.LchildNode)&& doesTree1HasTree2(root1.RchildNode, root2.RchildNode);}/** 判断两个浮点数是否相等*/private static boolean equal(double num1, double num2) {if (num1 - num2 < 0.0000001 && num1 - num2 > -0.0000001)return true;return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);System.out.println(hasSubtree(Root, Root.RchildNode));}
}
27、二叉树的镜像
题目:操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
使用递归,先前序遍历,对每个结点交换左右子结点。
package com.example.number27;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;import java.util.LinkedList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉树的镜像*/
public class Test {public static void Mirror(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;//左右子结点交换BinaryTreeNode tempNode = root.LchildNode;root.LchildNode = root.RchildNode;root.RchildNode = tempNode;Mirror(root.LchildNode);Mirror(root.RchildNode);}public static void printTree2(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode>();queue.offer(root);BinaryTreeNode node = null;int pCount = 0; //当前层结点数目int nextCount = 1; //下一层结点数目while (!queue.isEmpty()) {pCount = nextCount;nextCount = 0;//打印当前层数字,并计算下一层结点数目for (int i = 1; i <= pCount; i++) {node = queue.poll();System.out.print(node.data + " ");if (node.LchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.LchildNode);nextCount++;}if (node.RchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.RchildNode);nextCount++;}}System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);printTree2(Root);Mirror(Root);printTree2(Root);}}
28、对称的二叉树
题目:请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,
定义其为对称的。
思路
不用分析根结点,只需要分析左右子树。可以看出,左右子树刚好是呈镜像的两颗二叉树,所以:对左子树
采用(父-左-右)的前序遍历,右子树采用(父-右-左)的前序遍历,遍历时判断两个结点位置的值是否相等
即可。(也可以这样理解:左树的左子树等于右树的右子树,左树的右子树等于右树的左子树,对应位置刚
好相反,判断两子树相反位置上的值是否相等即可)
package com.example.number28;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 对称的二叉树*/
public class Test {public boolean isSymmetrical(BinaryTreeNode pRoot) {if (pRoot == null)return true; //根结点为null时,认为是对称二叉树return isEqual(pRoot.LchildNode, pRoot.RchildNode);}private boolean isEqual(BinaryTreeNode pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode pRoot2) {if (pRoot1 == null && pRoot2 == null)return true;if (pRoot1 == null || pRoot2 == null)return false;return pRoot1.data == pRoot2.data&& isEqual(pRoot1.LchildNode, pRoot2.RchildNode)&& isEqual(pRoot1.RchildNode, pRoot2.LchildNode);}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Test demo = new Test();System.out.println(demo.isSymmetrical(Root));}}
29、顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 1 15 16
则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
package com.example.number29;/*** @author zhangshixing* 顺时针打印矩阵*/
public class Test {public void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {if (matrix == null || matrix.length <= 0)return;printMatrixInCircle(matrix, 0);}private void printMatrixInCircle(int[][] matrix, int start) {int row = matrix.length;int col = matrix[0].length;int endX = col - 1 - start;int endY = row - 1 - start;if (endX < start || endY < start)return;//仅一行if (endY == start) {for (int i = start; i <= endX; i++) {System.out.print(matrix[start][i] + " ");}return; //记得结束}//仅一列if (endX == start) {for (int i = start; i <= endY; i++) {System.out.print(matrix[i][start] + " ");}return; //记得结束}//打印边界for (int i = start; i <= endX; i++) {System.out.print(matrix[start][i] + " ");}for (int i = start + 1; i <= endY; i++) {System.out.print(matrix[i][endX] + " ");}for (int i = endX - 1; i >= start; i--) {System.out.print(matrix[endY][i] + " ");}for (int i = endY - 1; i >= start + 1; i--) {System.out.print(matrix[i][start] + " ");}//继续打印更内部的矩阵,令start+1printMatrixInCircle(matrix, start + 1);}public static void main(String[] args) {Test demo = new Test();int[][] a = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}};demo.printMatrix(a);}
}
30、包含main函数的栈
题目:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈最小元素的min函数。
思路:最初想法是定义一个成员变量min来存放最小元素,但是当最小元素弹出后,min就需要相应改变,所以
必须把每次的最小值都存储下来。考虑采用一个辅助栈来存放最小值:
栈:3,4,2,5,1
辅助栈:3,3,2,2,1
(压入时,把每次的最小元素(之前最小元素与新入栈元素的较小值)保存起来放到辅助栈中)
package com.example.number30;import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 包含main函数的栈*/
public class Test {Stack<Integer> stack_data = new Stack<Integer>();Stack<Integer> stack_min = new Stack<Integer>();public void push(int node) {stack_data.push(node);if (stack_min.empty() || stack_min.peek() > node) {stack_min.push(node);} else {stack_min.push(stack_min.peek());}}public void pop() {if (!stack_data.empty()) {stack_data.pop();stack_min.pop();}}public int min() {return stack_min.peek();}public static void main(String[] args) {Test demo = new Test();demo.push(5);System.out.println(demo.min());demo.push(6);System.out.println(demo.min());demo.push(3);System.out.println(demo.min());demo.push(1);System.out.println(demo.min());}}
31、栈的压入、弹出序列
题目:输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压
入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 是某栈的压入序列,序列 {4, 5, 3, 2, 1} 是该压栈序列对应的一
个弹出序列,但 {4, 3, 5, 1, 2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)。
建立一个栈,按照压栈序列依次进行入栈操作,按出栈序列的顺序依次弹出数字。在出栈时,若下一个要出
栈的数字与栈顶数字相同则弹出。如果压栈序列中的所有数字都入栈后没有完全出栈成功则代表两个序列不
匹配,返回false。
package com.example.number31;import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 栈的压入、弹出序列*/
public class Test {public static boolean isPopOrder(int[] pushA, int[] popA) {if (pushA == null || popA == null)return false;Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();//必须提前判断长度是否相等if (popA.length != pushA.length || pushA.length == 0)return false;int popIndex = 0;for (int pushIndex = 0; pushIndex < pushA.length; pushIndex++) {stack.push(pushA[pushIndex]);while (!stack.empty() && stack.peek() == popA[popIndex]) {stack.pop();popIndex++;}}return stack.empty();}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};int[] b = {4, 3, 5, 1, 2};System.out.println(isPopOrder(a, b));int[] c = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};int[] d = {4, 5, 3, 2, 1};System.out.println(isPopOrder(c, d));}}
32、从上往下打印二叉树
题目一:不分行从上到下打印二叉树
不分行从上往下打印二叉树:该题即为对二叉树的层序遍历,结点满足先进先出的原则,采用队列。每从队列中取
出头部结点并打印,若其有子结点,把子结点放入队列尾部,直到所有结点打印完毕。
package com.example.number32;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;import java.util.LinkedList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:不分行从上到下打印二叉树*/
public class Test1 {public static void printTree1(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode>();queue.offer(root);BinaryTreeNode node = null;while (queue.size() != 0) {node = queue.poll();System.out.print(node.data + " ");if (node.LchildNode != null)queue.offer(node.LchildNode);if (node.RchildNode != null)queue.offer(node.RchildNode);}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);printTree1(Root);}
}
题目二:分行上到下打印二叉树
分行从上到下打印二叉树:同样使用队列,但比第一题增加两个变量:当前层结点数目pCount,下一层结点数目
nextCount。根据当前层结点数目来打印当前层结点,同时计算下一层结点数目,之后令pCount等于
nextCount,重复循环,直到打印完毕。
package com.example.number32;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;import java.util.LinkedList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:分行上到下打印二叉树*/
public class Test2 {public static void printTree2(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode>();queue.offer(root);BinaryTreeNode node = null;int pCount = 0; //当前层结点数目int nextCount = 1; //下一层结点数目while (!queue.isEmpty()) {pCount = nextCount;nextCount = 0;//打印当前层数字,并计算下一层结点数目for (int i = 1; i <= pCount; i++) {node = queue.poll();System.out.print(node.data + " ");if (node.LchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.LchildNode);nextCount++;}if (node.RchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.RchildNode);nextCount++;}}System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);printTree2(Root);}}
题目三:按之字形顺序打印二叉树
自己开始想的方法:在(二)的基础上,多定义一个表示当前层数的变量level。每层结点不直接打印,放入一个
数组中,根据此时的层数level的奇偶来决定正向还是反向打印数组。
package com.example.number32;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目三:按之字形顺序打印二叉树*/
public class Test3 {public static void printTree3_1(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode>();queue.offer(root);BinaryTreeNode node = null;int pCount = 0; //当前层结点数目int nextCount = 1; //下一层结点数目int level = 1; //层数int[] pNums = null; //用于存储当前层的数字while (!queue.isEmpty()) {pCount = nextCount;nextCount = 0;pNums = new int[pCount];//存储当前层数字,并计算下一层结点数目for (int i = 0; i < pCount; i++) {node = queue.poll();pNums[i] = node.data;if (node.LchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.LchildNode);nextCount++;}if (node.RchildNode != null) {queue.offer(node.RchildNode);nextCount++;}}//根据当前层数确定正向或者反向打印数组if ((level & 1) != 0) {for (int i = 0; i < pCount; i++) {System.out.print(pNums[i] + " ");}} else {for (int i = pCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {System.out.print(pNums[i] + " ");}}level++;System.out.println();}}public static void printTree3_2(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<BinaryTreeNode>();Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<BinaryTreeNode>();BinaryTreeNode node = null;stack1.push(root);while (!stack1.empty() || !stack2.empty()) {while (!stack1.empty()) {node = stack1.pop();System.out.print(node.data + " ");if (node.LchildNode != null)stack2.push(node.LchildNode);if (node.RchildNode != null)stack2.push(node.RchildNode);}System.out.println();while (!stack2.empty()) {node = stack2.pop();System.out.print(node.data + " ");if (node.RchildNode != null)stack1.push(node.RchildNode);if (node.LchildNode != null)stack1.push(node.LchildNode);}System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);printTree3_2(Root);}}
33、二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目:输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。
假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
思路二叉树后序遍历数组的最后一个数为根结点,剩余数字中,小于根结点的数字(即左子树部分)都排在
前面,大于根结点的数字(即右子树部分)都排在后面。根据遍历数组的这个特性,可以编写出一个递归函
数,用于实现题目所要求的判断功能。
package com.example.number33;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列*/
public class Test {public static boolean verifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence) {if (sequence == null || sequence.length <= 0)return false;return verifyCore(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);}private static boolean verifyCore(int[] sequence, int start, int end) {if (start >= end)return false;//判断左子树int mid = start;while (sequence[mid] < sequence[end])mid++;//判断右子树for (int i = mid; i < end; i++) {if (sequence[i] < sequence[end])return false;}return verifyCore(sequence, start, mid - 1) && verifyCore(sequence, mid, end - 1);}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {5, 7, 6, 9, 11, 10, 8};System.out.println(verifySquenceOfBST(a));}}
34、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目:输入一颗二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点
开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
思路
1.假设找到了其中一条路径,达到叶结点后,由于没有指向父结点的指针,所以必须提前创建一个链表存储前
面经过的结点。
2.由于是从根结点出发,所以要想到使用前序遍历
3.利用链表存储结点,在该结点完成左右子树的路径搜索后(即递归函数结束,返回到其父结点之前),要删
除该结点,从而记录别的路径。
具体实现:通过前序遍历,从根结点出发,每次在链表中存储遍历到的结点,若到达叶子结点,则根据所有
结点的和是否等于输入的整数,判断是否打印输出。在当前结点访问结束后,递归函数将会返回到它的父结
点,所以在函数退出之前,要删除链表中的当前结点,以确保返回父结点时,储存的路径刚好是从根结点到
父结点。
改进:书中的代码是根据所有结点的和是否等于输入的整数,判断是否打印输出。其实没有这个必要,只需
要在每次遍历到一个结点时,令目标整数等于自己减去当前结点的值,若到达根结点时,最终的目标整数等
于0就可以打印输出。
package com.example.number34;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉树中和为某一值的路径*/
public class Test {public static void findPath(BinaryTreeNode root, int target) {if (root == null)return;ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();printPath(root, target, list);}private static void printPath(BinaryTreeNode node, int target, ArrayList<Integer> list) {if (node == null)return;list.add(node.data);target -= node.data; //每个结点的target不会受到方法的影响而改变if (target == 0 && node.LchildNode == null && node.RchildNode == null) { //叶子结点for (Integer integer : list)System.out.print(integer + " ");System.out.println();} else { //中间结点printPath(node.LchildNode, target, list);printPath(node.RchildNode, target, list);}list.remove(list.size() - 1);//删除当前结点,因为已经输出了}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);findPath(Root, 10);}}
35、复杂链表的复制
题目:输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意
一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题
程序会直接返回空)
package com.example.number35;/*** @author zhangshixing* 复杂链表的复制*/
public class Test {public class ComplexListNode {int val;ComplexListNode next = null;ComplexListNode sibling = null;ComplexListNode(int label) {this.val = label;}}/** 主程序(包含三步)*/public ComplexListNode cloneList(ComplexListNode head) {cloneNodes(head); //1.复制结点connectSiblingNodes(head); //2.设置siblingreturn reconnectNodes(head);//3.拆分长链表}/** 第一步:复制每个结点,并插入到原始节点的后面*/private void cloneNodes(ComplexListNode head) {ComplexListNode pNode=head;while(pNode!=null) {ComplexListNode clonedNode=new ComplexListNode(pNode.val);clonedNode.next=pNode.next;pNode.next=clonedNode;pNode=clonedNode.next;}}/** 第二步:根据原结点的sibling,设置复制结点的sibling*/private void connectSiblingNodes(ComplexListNode head) {ComplexListNode pNode=head;while(pNode!=null) {if(pNode.sibling!=null) //必须考虑到siblingNode==null的情况!pNode.next.sibling=pNode.sibling.next;pNode=pNode.next.next;}}/** 第三步:将长链表拆分成原始链表和复制链表(根据奇偶位置)*/private ComplexListNode reconnectNodes(ComplexListNode head) {ComplexListNode clonedHead=null;ComplexListNode clonedNode=null;ComplexListNode pNode=head;if(head!=null) {clonedHead=head.next;clonedNode=pNode.next;pNode.next=clonedNode.next;pNode=pNode.next; //提前将pNode指向下一个结点,方便判断是否为null}while(pNode!=null) {clonedNode.next=pNode.next;clonedNode=clonedNode.next;pNode.next=clonedNode.next;pNode=pNode.next;}return clonedHead;}
}
36、二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目:输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整
树中结点指针的指向。
package com.example.number36;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉搜索树与双向链表*/
public class Test {public static BinaryTreeNode convert(BinaryTreeNode head) {if (head == null)return head;BinaryTreeNode lastNodeInList = null;lastNodeInList = convertHelper(head, lastNodeInList);BinaryTreeNode firstNodeInList = lastNodeInList;while (firstNodeInList.LchildNode != null) {firstNodeInList = firstNodeInList.LchildNode;}return firstNodeInList;}//将以node为根结点的树转化为排序链表,链表头部与lastNode链接,并返回最后一个结点private static BinaryTreeNode convertHelper(BinaryTreeNode node,BinaryTreeNode lastNode) {//处理左子树,获得最大结点if (node.LchildNode != null)lastNode = convertHelper(node.LchildNode, lastNode);//链接最大结点和根结点node.LchildNode = lastNode;if (lastNode != null)lastNode.RchildNode = node;//处理右子树lastNode = node;if (node.RchildNode != null)lastNode = convertHelper(node.RchildNode, lastNode);return lastNode;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);BinaryTreeNode r = convert(Root);while (r != null) {System.out.println(r.data);r = r.RchildNode;}}}
37、序列化二叉树
题目:请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
序列化二叉树:把一棵二叉树按照某种遍历方式的结果以某种格式保存为字符串。需要注意的是,序列化二叉树的
过程中,如果遇到空节点,需要以某种符号(这里用#)表示。以下图二叉树为例,序列化二叉树时,需要将空节
点也存入字符串中。
反序列化二叉树:根据某种遍历顺序得到的序列化字符串,重构二叉树。具体思路是按前序遍历“根左右”的顺序,
根节点位于其左右子节点的前面,即非空(#)的第一个节点是某子树的根节点,左右子节点在该根节点后,以空
节点#为分隔符。
思路
一般情况下,需要采用前/后序遍历和中序遍历才能确定一个二叉树,但是其实可以只采用前序遍历(从根结
点开始),将空结点(null)输出为一个特殊符号(如“$”),就可以确定一个二叉树了。
将二叉树序列化为字符串,就是前序遍历的过程,遇见空结点时,序列化为“$”,每个结点间使用逗号分隔
开。
将字符串反序列化为二叉树,也使用前序遍历,遇见一个新数字(或者$)就建立一个新结点,不过需要注意的
是,数字可能不只是个位数字,因此创建了一个全局Int变量index(在字符串上的移动的指针),以便于截取
字符串中当前的结点值。
package com.example.number37;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 序列化二叉树*/
public class Test {String Serialize(BinaryTreeNode node) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();if (node == null) {sb.append("$,");} else {sb.append(node.data + ",");sb.append(Serialize(node.LchildNode));sb.append(Serialize(node.RchildNode));}return sb.toString();}int index = 0;BinaryTreeNode Deserialize(String str) {BinaryTreeNode node = null;if (str == null || str.length() == 0)return node;int start = index;while (str.charAt(index) != ',')index++;if (!str.substring(start, index).equals("$")) {node = new BinaryTreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str.substring(start, index)));index++; // 这条语句位置别放错了node.LchildNode = Deserialize(str);node.RchildNode = Deserialize(str);} else {index++;}return node;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);String result = new Test().Serialize(Root);System.out.println(result);BinaryTreeNode Root1 = new Test().Deserialize(result);System.out.println(Root1.data);}}
38、字符串的排列
题目:输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能
排列出来的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
将字符串看成两部分,一部分是第一个字符,另一部分是后面的所有字符。
首先确定第一个字符,该字符可以是字符串中的任意一个;固定第一个字符后,求出后面所有字符的排列
(相同步骤,采用递归)。
实现第一个字符的改变,只需要将第一个字符和后面所有字符进行交换即可(最早自己想的是从原始字符串
拿出第i个字符,然后合并剩下的字符到后面,其实就是个交换的过程,自己开始时想得太复杂了)。要记得
字符串输出后要将字符交换回来,变回原始的字符串。
package com.example.number38;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;/*** @author zhangshixing* 字符串的排列*/
public class Test {public static ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();if (str == null || str.length() == 0)return list;permutationCore(str.toCharArray(), 0, list);Collections.sort(list); //将list中的字符串排序return list;}private static void permutationCore(char[] strArray, int index, ArrayList<String> list) {if (index == strArray.length - 1) {if (!list.contains(String.valueOf(strArray))) //判断是否有重复字符串list.add(String.valueOf(strArray));} else {for (int i = index; i < strArray.length; i++) {char temp = strArray[index];strArray[index] = strArray[i];strArray[i] = temp;permutationCore(strArray, index + 1, list);strArray[i] = strArray[index];strArray[index] = temp;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Permutation("abc"));}}
39、数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目:数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组
{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
思路一:数字次数超过一半,则说明:排序之后数组中间的数字一定就是所求的数字。
利用partition()函数获得某一随机数字,其余数字按大小排在该数字的左右。若该数字下标刚好为n/2,则该
数字即为所求数字;若小于n/2,则在右边部分继续查找;反之,左边部分查找。
思路二:数字次数超过一半,则说明:该数字出现的次数比其他数字之和还多
遍历数组过程中保存两个值:一个是数组中某一数字,另一个是次数。遍历到下一个数字时,若与保存数字
相同,则次数加1,反之减1。若次数=0,则保存下一个数字,次数重新设置为1。由于要找的数字出现的次数
比其他数字之和还多,那么要找的数字肯定是最后一次把次数设置为1的数字。
package com.example.number39;/*** @author zhangshixing* 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字*/
public class Test {boolean isInputInvalid = true;//方法一:partition方法public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] array) {if (array == null || array.length <= 0)return 0;int low = 0;int high = array.length - 1;int index = partition(array, low, high);while (index != array.length >> 1) {if (index < array.length >> 1) {low = index + 1;index = partition(array, low, high);} else {high = index - 1;index = partition(array, low, high);}}//判断次数是否超过一半int num = array[index];int times = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {if (array[i] == num) {times++;}}if (times * 2 > array.length) {isInputInvalid = false;return num;}return 0;}private int partition(int[] array, int low, int high) {int pivotKey = array[low];while (low < high) {while (low < high && array[high] >= pivotKey)high--;int temp = array[low];array[low] = array[high];array[high] = temp;while (low < high && array[low] <= pivotKey)low++;temp = array[low];array[low] = array[high];array[high] = temp;}return low;}//方法二public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution2(int[] array) {if (array == null || array.length <= 0)return 0;int num = array[0];int count = 1;for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {if (count == 0) {num = array[i];count++;} else if (array[i] == num)count++;elsecount--;}if (count > 0) {int times = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {if (array[i] == num) {times++;}}if (times * 2 > array.length) {isInputInvalid = false;return num;}}return 0;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4, 2};System.out.println(new Test().MoreThanHalfNum_Solution2(a));}}
40、最小的k个数
题目:输入n个整数,找出其中最小的K个数。例如输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4。
思路
思路一:同剑指offer(39)数组中出现次数超过一半的数字中使用partition()方法,基于数组的第k个数字调
整,使得更小的k个数字都在数组左边即可。
思路二:依次遍历n个整数,用一个容器存放最小的k个数字,每遇到比容器中最大的数字还小的数字时,将
最大值替换为该数字。容器可以使用最大堆或者红黑树来实现。本文根据堆排序的原理来实现。
package com.example.number40;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 最小的k个数*/
public class Test {/** 方法一:采用partition()*/public static ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution1(int[] input, int k) {ArrayList<Integer> leastNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();while (input == null || k <= 0 || k > input.length)return leastNumbers;int start = 0;int end = input.length - 1;int index = partition(input, start, end);while (index != k - 1) {if (index < k - 1) {start = index + 1;index = partition(input, start, end);} else {end = index - 1;index = partition(input, start, end);}}for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {leastNumbers.add(input[i]);}return leastNumbers;}private static int partition(int[] arr, int start, int end) {int pivotKey = arr[start];while (start < end) {while (start < end && arr[end] >= pivotKey)end--;swap(arr, start, end);while (start < end && arr[start] <= pivotKey)start++;swap(arr, start, end);}return start;}private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}/** 方法二:基于堆的容器*/public static ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution2(int[] input, int k) {ArrayList<Integer> leastNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();while (input == null || k <= 0 || k > input.length)return leastNumbers;int[] numbers = new int[k]; //用于放最小的k个数for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)numbers[i] = input[i];//先放入前k个数for (int i = k / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {adjustHeap(numbers, i, k - 1);//将数组构造成最大堆形式}for (int i = k; i < input.length; i++) {if (input[i] < numbers[0]) { //存在更小的数字时numbers[0] = input[i];adjustHeap(numbers, 0, k - 1);//重新调整最大堆}}for (int n : numbers)leastNumbers.add(n);return leastNumbers;}//最大堆的调整方法,忘记时可以复习一下堆排序。private static void adjustHeap(int[] arr, int start, int end) {int temp = arr[start];int child = start * 2 + 1;while (child <= end) {if (child + 1 <= end && arr[child + 1] > arr[child])child++;if (arr[child] < temp)break;arr[start] = arr[child];start = child;child = child * 2 + 1;}arr[start] = temp;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8};System.out.println(GetLeastNumbers_Solution1(a, 4));}}
41、数据流中的中位数
题目:如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于
中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。我们使用
Insert()方法读取数据流,使用GetMedian()方法获取当前读取数据的中位数。
package com.example.number41;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;/*** @author zhangshixing* 数据流中的中位数*/
public class Test {//小顶堆,默认容量为11PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();//大顶堆,容量11PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(11,new Comparator<Integer>(){public int compare(Integer i1,Integer i2){return i2-i1;}});public void Insert(Integer num) {if(((minHeap.size()+maxHeap.size())&1)==0){//偶数时,下个数字加入小顶堆if(!maxHeap.isEmpty() && maxHeap.peek()>num){maxHeap.offer(num);num=maxHeap.poll();}minHeap.offer(num);}else{//奇数时,下一个数字放入大顶堆if(!minHeap.isEmpty() && minHeap.peek()<num){minHeap.offer(num);num=minHeap.poll();}maxHeap.offer(num);}}public Double GetMedian() {if((minHeap.size()+maxHeap.size())==0)throw new RuntimeException();double median;if((minHeap.size()+maxHeap.size()&1)==0){median=(maxHeap.peek()+minHeap.peek())/2.0;}else{median=minHeap.peek();}return median;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test demo = new Test();demo.Insert(1);demo.Insert(2);demo.Insert(3);demo.Insert(4);demo.Insert(5);System.out.println(demo.GetMedian());demo.Insert(6);System.out.println(demo.GetMedian());}}
42、连续子数组的最大和
题目:输入一个整型数组,数组里有正数也有负数。数组中一个或连续的多个整数组成一个子数组。求所有子数组
的和的最大值。要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
思路
分析规律,从第一个数字开始累加,若走到某一个数字时,前面的累加和为负数,说明不能继续累加了,要
从当前数字重新开始累加。在累加过程中,将每次累加和的最大值记录下来,遍历完成后,返回该数字。
package com.example.number42;/*** @author zhangshixing* 连续子数组的最大和*/
public class Test {static boolean InvalidInput = false;public static int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {if (array == null || array.length <= 0) {InvalidInput = true;return 0;}InvalidInput = false;int sum = array[0];int maxSum = array[0];for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {if (sum < 0)sum = array[i];elsesum += array[i];if (sum > maxSum)maxSum = sum;}return maxSum;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {1, -2, 3, 10, -4, 7, 2, -5};System.out.println(FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(a));}
}
43、1~n整数中1出现的次数
题目:输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。例如输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含
1的数字有1、10、11和12,1一共出现了5次。
思路:
如果是从头到尾遍历(n次),对每一个数字都计算其1的个数(logn次),则时间复杂度为O(nlogn),运
算效率太低。因此必须总结规律,提高效率。
总结规律如下:
对于整数n,我们将这个整数分为三部分:当前位数字cur,更高位数字high,更低位数字low,如:对于
n=21034,当位数是十位时,cur=3,high=210,low=4。
我们从个位到最高位 依次计算每个位置出现1的次数:
1)当前位的数字等于0时,例如n=21034,在百位上的数字cur=0,百位上是1的情况有:00100
~00199,01100
~01199,……,20100~20199。一共有21*100种情况,即high*100;2)当前位的数字等于1时,例如n=21034,在千位上的数字cur=1,千位上是1的情况有:01000
~01999,11000
~11999,21000~21034。一共有2*1000+(34+1)种情况,即high*1000+(low+1)。3)当前位的数字大于1时,例如n=21034,在十位上的数字cur=3,十位上是1的情况有:00010
~00019,……,21010
~21019。一共有(210+1)*10种情况,即(high+1)*10。这个方法只需要遍历每个位数,对于整数n,其位数一共有logn个,所以时间复杂度为O(logn)。
package com.example.number43;/*** @author zhangshixing* 1~n整数中1出现的次数*/
public class Test {public static int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {int count = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i *= 10) { //i代表位数int high = n / (i * 10); //更高位数字int low = (n % i); //更低位数字int cur = (n / i) % 10; //当前位数字if (cur == 0) {count += high * i;} else if (cur == 1) {count += high * i + (low + 1);} else {count += (high + 1) * i;}}return count;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(12));}}
44、数字序列中的某一位的数字
题目:数字以0123456789101112131415…的格式序列化到一个字符序列中。在这个序列中,第5位(从0开始计
数)是5,第13位是1,第19位是4,等等。请写一个函数,求任意第n位对应的数字。
思路:
逐一枚举数字,计算每个数字的位数相加,效率太低。
观察规律:
个位数的个数一共有10个,即0~9,共占了10
*1位数字;两位数的个数一共有90个,即10~99,每个数字占两位,共占了90
*2位数字;……
m位数的个数一共有9
*10(m-1)个,每个数字占m位,占了9`*`10(m-1)*m位数字。判断第n个对的数字是属于几位数,再从几位数中进行寻找。
package com.example.number44;/*** @author zhangshixing* 数字序列中的某一位的数字*/
public class Test {public static int digitAtIndex(int index) {if (index < 0)return -1;int m = 1; //m位数while (true) {int numbers = numbersOfIntegers(m); //m位数的个数if (index < numbers * m)return getDigit(index, m);index -= numbers * m;m++;}}/** 返回m位数的总个数* 例如,两位数一共有90个:10~99;三位数有900个:100~999*/private static int numbersOfIntegers(int m) {if (m == 1)return 10;return (int) (9 * Math.pow(10, m - 1));}/** 获取数字*/private static int getDigit(int index, int m) {int number = getFirstNumber(m) + index / m; //对应的m位数int indexFromRight = m - index % m; //在数字中的位置for (int i = 1; i < indexFromRight; i++)number /= 10;return number % 10;}/** 第一个m位数* 例如第一个两位数是10,第一个三位数是100*/private static int getFirstNumber(int m) {if (m == 1)return 0;return (int) Math.pow(10, m - 1);}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(digitAtIndex(0) == 0);System.out.println(digitAtIndex(1) == 1);System.out.println(digitAtIndex(19) == 4);System.out.println(digitAtIndex(1000) == 3);System.out.println(digitAtIndex(1001) == 7);System.out.println(digitAtIndex(1002) == 0);}}
45、把数组排成最小的数
题目:输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例
如输入数组{3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323。
思路
不好的方法:求出所有全排列(类似字符串的排列 ),将数字拼起来,最后求出所有的最小值。这效率太
低,且没有考虑到大数问题。
好的方法:观察规律,自行定义一种排序规则。
对于数字m和n,可以拼接成mn和nm,如果mn<nm,我们定义m小于n。反之则相反。利用这个排序规则,
从小排到大即可实现题目要求。
拼接m和n时,要考虑到大数问题,因此将m和n拼接起来的数字转换成字符串处理。因为mn和nm的字符串
位数相同,因此它们的大小只需要按照字符串大小的比较规则就可以了。
具体实现:将数字存入ArrayList中,通过利用Collections.sort(List list, Comparator<? super T> c)方法
进行排序。Comparator中重写compare()方法来规定比较规则。
package com.example.number45;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;/*** @author zhangshixing* 把数组排成最小的数*/
public class Test {public static String PrintMinNumber(int[] numbers) {if (numbers == null || numbers.length <= 0)return "";ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (int number : numbers)list.add(String.valueOf(number));Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String s1, String s2) {String a = s1 + s2;String b = s2 + s1;return a.compareTo(b);}});StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (String str : list)sb.append(str);return sb.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {3, 32, 321};System.out.println(PrintMinNumber(a));}}
46、把数字翻译成字符串
题目:给定一个数字,按照如下规则翻译成字符串:0翻译成"a",1翻译成"b"…25翻译成”z"。一个数字可能有多
个翻译。如12258有5种不同的翻译,分别是"bccfi", “bwfi”, “bczi”, “mcfi”, “mzi”。请实现一个函数,用来计算一个
数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
思路
看到题目,很容易想到使用递归:用f(i)来表示从第i位开始的不同翻译数目,可以得到有:
f(i)=f(i+1)+g(i,i+1)
*f(i+2)。i和i+1位数字拼起来在10~25范围内时g(i,i+1)的值为1,否则为0。但是存在重复的子问题,所以递归并非最佳方法,我们从数字的末尾开始计算f(i),自下而上解决问题,就可
以消除重复的子问题了。先算f(len-1),f(len-2),再根据公式f(i)=f(i+1)+g(i,i+1)*f(i+2)往前逐步推导到f(0),这
就是最终要求的结果。
package com.example.number46;/*** @author zhangshixing* 把数字翻译成字符串*/
public class Test {public static int getTranslationCount(int number) {if (number < 0)return 0;String sNumber = String.valueOf(number);int len = sNumber.length();int[] counts = new int[len];for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (i == len - 1) {counts[i] = 1;} else {counts[i] = counts[i + 1];if (canBeTrans(sNumber, i)) {if (i == len - 2)counts[i] += 1;elsecounts[i] += counts[i + 2];}}}return counts[0];}private static boolean canBeTrans(String sNumber, int i) {int a = sNumber.charAt(i) - '0';int b = sNumber.charAt(i + 1) - '0';int convert = a * 10 + b;if (convert >= 10 && convert <= 25)return true;return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(getTranslationCount(0) == 1);System.out.println(getTranslationCount(10) == 2);System.out.println(getTranslationCount(12258) == 5);System.out.println(getTranslationCount(-100) == 0);}}
47、礼物的最大价值
题目:在一个 m*n 的棋盘中的每一个格都放一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值(价值大于0).你可以从棋盘的左
上角开始拿各种里的礼物,并每次向右或者向下移动一格,直到到达棋盘的右下角。给定一个棋盘及上面个的礼
物,请计算你最多能拿走多少价值的礼物?
思路
动态规划:定义f(i,j)为到达(i,j)位置格子时能拿到的礼物总和的最大值,则有:
f(i,j)=max{f(i,j),f(i,j)}+values(i,j)。
同上道题一样,如果直接使用递归会产生大量的重复计算,因此,创建辅助的数组来保存中间计算结果。
辅助数组不用和m*n的二维数组一样大,只需要保存上一层的最大值就可以。代码中使用长度为列数n的一位
数组作为辅助数组,注释部分为二维辅助数组。
package com.example.number47;/*** @author zhangshixing* 礼物的最大价值*/
public class Test {public static int maxValueOfGifts(int[][] values) {if (values == null || values.length <= 0 || values[0].length <= 0)return 0;int rows = values.length;int cols = values[0].length;int[] maxValue = new int[cols];for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {int left = 0;int up = 0;if (i > 0)up = maxValue[j];if (j > 0)left = maxValue[j - 1];maxValue[j] = Math.max(up, left) + values[i][j];}}return maxValue[cols - 1];}public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] a = {{1, 10, 3, 8}, {12, 2, 9, 6}, {5, 7, 4, 11}, {3, 7, 16, 5}};System.out.println(maxValueOfGifts(a));}}
48、最长不含重复字符的子字符串
题目:请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。例如
在“arabcacfr”中,最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串是“acfr”,长度为4采用字典的方法,最后输出所有最长字符
的列表。
思路
动态规划法:定义函数f(i)为:以第i个字符为结尾的不含重复字符的子字符串的最大长度。
(1)当第i个字符之前未出现过,则有:f(i)=f(i-1)+1
(2)当第i个字符之前出现过,记该字符与上次出现的位置距离为d
1)如果d<=f(i-1),则有f(i)=d;
2)如果d>f(i-1),则有f(i)=f(i-1)+1;
我们从第一个字符开始遍历,定义两个int变量preLength和curLength来分别代表f(i-1)和f(i),再创建一个长
度为26的pos数组来存放26个字母上次出现的位置,即可根据上述说明进行求解。
注意:每次最大长度和字母出现位置要记得更新。
package com.example.number48;/*** @author zhangshixing* 最长不含重复字符的子字符串*/
public class Test {public static int maxLength(String str) {if (str == null || str.length() <= 0)return 0;int preLength = 0; //即f(i-1)int curLength = 0; //即f(i)int maxLength = 0;int[] pos = new int[26]; //用于存放字母上次出现的位置for (int i = 0; i < pos.length; i++)pos[i] = -1;for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {int letterNumber = str.charAt(i) - 'a';if (pos[letterNumber] < 0 || i - pos[letterNumber] > preLength) {curLength = preLength + 1;} else {curLength = i - pos[letterNumber];}pos[letterNumber] = i;if (curLength > maxLength)maxLength = curLength;preLength = curLength;}return maxLength;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(maxLength("arabcacfr") == 4);System.out.println(maxLength("a") == 1);System.out.println(maxLength("aaa") == 1);System.out.println(maxLength("abcdef") == 6);System.out.println(maxLength("") == 0);System.out.println(maxLength(null) == 0);}
}
49、丑数
题目:把只包含质因子2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14不是,因为它包含质因
子7。 习惯上我们把1当做是第一个丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第N个丑数。
解题思路:
如果被判断的数是1、2、3、5其中的一个,则这个数肯定是丑数。
如果被判断的数能被2整除,则将这个数除以2,再进行循环判断;
如果被判断的数能被3整除,则将这个数除以3,再进行循环判断;
如果被判断的数能被5整除,则将这个数除以5,再进行循环判断;
如果被判断的数不能被2、3、5这三个数其中的一个整除,则这个数肯定不是丑数。
package com.example.number49;/*** @author zhangshixing* 丑数*/
public class Test {public static boolean isUgly(int num) {if (num <= 0) {return false;}while (true) {if (num == 1 || num == 2 || num == 3 || num == 5) {return true;}if (num % 2 == 0) {num /= 2;} else if (num % 3 == 0) {num /= 3;} else if (num % 5 == 0) {num /= 5;} else {return false;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(isUgly(14));}
}
50、第一个只出现一次的字符
题目一:字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
在一个字符串(1<=字符串长度<=10000,全部由字母组成)中找到第一个只出现一次的字符,并返回它的位置
思路
创建哈希表,键值key为字符,值value为出现次数。第一遍扫描:对每个扫描到<的字符的次数加一;第二遍
扫描:对每个扫描到的字符通过哈希表查询次数,第一个次数为1的字符即为符合要求的输出。
由于字符(char)是长度为8的数据类型,共有256中可能,因此哈希表可以用一个长度为256的数组来代
替,数组的下标相当于键值key,对应字符的ASCII码值;数组的值相当于哈希表的值value,用于存放对应字
符出现的次数。
package com.example.number50;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符*/
public class Test1 {public static char firstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {if (str == null)return '\0';int[] repetitions = new int[256];for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)repetitions[i] = 0;for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {int loc = (int) str.charAt(i);repetitions[loc] += 1;}for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {int loc = (int) str.charAt(i);if (repetitions[loc] == 1)return (char) loc;}return '\0';}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println((firstNotRepeatingChar("google") == 'l'));System.out.println((firstNotRepeatingChar("aabccdbd") == '\0'));System.out.println((firstNotRepeatingChar("$abcdefg") == '$'));System.out.println((firstNotRepeatingChar(null) == '\0'));}
}
题目二:字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一
个只出现一次的字符是"g"。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。如
果当前字符流没有存在出现一次的字符,返回#字符。
package com.example.number50;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符*/
public class Test2 {private int index;private int[] occurence;// 在构造函数中初始化成员变量public Test2() {index = 0;occurence = new int[256];for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {occurence[i] = -1;}}public void insert(char ch) {if (occurence[(int) ch] == -1) {//第一次出现occurence[(int) ch] = index;} else if (occurence[(int) ch] >= 0) {//已经出现过了occurence[(int) ch] = -2;}index++;}public char getFirst() {//最大的integerint minIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE;char ch = '#';for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {if (occurence[i] >= 0 && occurence[i] < minIndex) {ch = (char) i;minIndex = occurence[i];}}return ch;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test2 so = new Test2();so.insert('g');so.insert('o');so.insert('o');so.insert('g');so.insert('l');so.insert('e');System.out.println(so.getFirst());}}
51、数组中的逆序对
题目:在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,
求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数P。
思路
如果遍历数组,对每个数字都和后面的数字比较大小,时间复杂度为O(n^2),效率太低。
利用归并排序的思想,先将数组分解成为n个长度为1的子数组,然后进行两两合并同时排好顺序。
在对两个子区域合并排序时,记左边区域(下标为start
~mid)的指针为i,右边区域(下标为mid+1~end)的指针为j,两个指针都指向该区域内最大的数字,排序时:
(1)如果i指向的数字大于j指向的数字,说明:逆序对有j-mid个,我们把i指向的数字放入临时创建的排序数
组中,然后令i-1,指向该区域前一个数字,继续进行排序;
(2)如果i指向的数字小于等于j指向的数字,说明暂时不存在逆序对,将j指向的数字放入临时创建的排序数
组中,然后令j-1,指向该区域前一个数字,继续进行排序;
(3)某一子区域数字都放入排序数组后,将另一个子区域剩下的数字放入排序数组中,完成排序;
package com.example.number51;/*** @author zhangshixing* 数组中的逆序对*/
public class Test {public static int inversePairs(int[] array) {if (array == null || array.length <= 0)return 0;int count = getCount(array, 0, array.length - 1);return count;}private static int getCount(int[] array, int start, int end) {if (start >= end)return 0;int mid = (end + start) >> 1;int left = getCount(array, start, mid);int right = getCount(array, mid + 1, end);//合并int count = 0;int i = mid; //左边区域的指针int j = end; //右边区域的指针int[] temp = new int[end - start + 1]; //临时区域int k = end - start; //临时区域的指针while (i >= start && j >= mid + 1) {if (array[i] > array[j]) {count += (j - mid);temp[k--] = array[i--];} else {temp[k--] = array[j--];}}while (i >= start)temp[k--] = array[i--];while (j >= mid + 1)temp[k--] = array[j--];for (k = 0; k < temp.length; k++)array[k + start] = temp[k];return count + left + right;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {7, 5, 6, 4};System.out.println(inversePairs(a));}}
52、两个链表的第一个公共节点
题目: 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
思路
蛮力法:遍历第一个链表的结点,每到一个结点,就在第二个链表上遍历每个结点,判断是否相等。时间复
杂度为O(m*n),效率低;
使用栈:由于公共结点出现在尾部,所以用两个栈分别放入两个链表中的结点,从尾结点开始出栈比较。时
间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m+n)。
利用长度关系:计算两个链表的长度之差,长链表先走相差的步数,之后长短链表同时遍历,找到的第一个
相同的结点就是第一个公共结点。
利用两个指针:一个指针顺序遍历list1和list2,另一个指针顺序遍历list2和list1,(这样两指针能够保证最终
同时走到尾结点),两个指针找到的第一个相同结点就是第一个公共结点。
package com.example.number52;import com.example.commnon.ListNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 两个链表的第一个公共节点*/
public class Test {//方法1:利用长度关系public static ListNode findFirstCommonNode1(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {int length1 = getLength(pHead1);int length2 = getLength(pHead2);int lengthDif = length1 - length2;ListNode longList = pHead1;ListNode shortList = pHead2;if (lengthDif < 0) {longList = pHead2;shortList = pHead1;lengthDif = -lengthDif;}for (int i = 0; i < lengthDif; i++)longList = longList.next;while (longList != null && longList != shortList) {longList = longList.next;shortList = shortList.next;}return longList; //没有公共结点刚好是null}private static int getLength(ListNode head) {int len = 0;while (head != null) {len++;head = head.next;}return len;}//方法2:两个指针,p1顺序遍历list1和list2;p2顺序遍历list2和list1;最终一定会相遇public static ListNode findFirstCommonNode2(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {ListNode p1 = pHead1;ListNode p2 = pHead2;while (p1 != p2) {p1 = p1 == null ? pHead2 : p1.next;p2 = p2 == null ? pHead1 : p2.next;}return p1;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode list1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode pnode1 = list1;for (int i = 2; i < 11; i++) {pnode1.next = new ListNode(i);pnode1 = pnode1.next;}ListNode resultNode = findFirstCommonNode1(list1, list1.next.next.next);System.out.println(resultNode.data);}
}
53、在排序数组中查找数字
题目一:数字在排序数组中出现的次数
统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数
思路
分析:对于例子来说,如果采用二分法找到某一个3后,再往前遍历和往后遍历到第一个和最后一个3,在长
度为n的数组中有可能出现O(n)个3,因此这样的扫描方法时间复杂度为O(n),效率与从头到尾扫描一样,速
度太慢。
这题关键是找到第一个和最后一个3,因此我们尝试改进二分法:中间数字比3大或者小的情况与之前类似,
关键是中间数字等于3的情况,这时可以分类讨论如下:
1)如果中间数字的前一个数字也等于3,说明第一个3在前面,继续在前半段查找第一个3;
2)如果中间数字的前一个数字不等于3,说明该位置是第一个3;
3)如果中间数字的后一个数字也等于3,说明最后一个3在后面,继续在后半段查找最后一个3;
4)如果中间数字的后一个数字不等于3,说明该位置是最后一个3;
package com.example.number53;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:数字在排序数组中出现的次数*/
public class Test1 {public static int GetNumberOfK(int [] array , int k) {if(array==null || array.length<=0)return 0;int firstK = getFirstK(array,0,array.length-1,k);if(firstK == -1)return 0;int lastK = getLastK(array,firstK,array.length-1,k);return lastK-firstK+1;}private static int getFirstK(int[] arr, int start, int end,int k){if(start>end)return -1;int mid = (start+end)>>1;if(arr[mid]==k){if( mid == 0 ||arr[mid-1]!=k )return mid;elseend = mid-1;}else if(arr[mid]<k){start = mid+1;}else{end = mid-1;}return getFirstK(arr,start,end,k);}private static int getLastK(int[] arr, int start, int end,int k){if(start>end)return -1;int mid = (start+end)>>1;if(arr[mid]==k){if(mid==arr.length-1 || arr[mid+1]!=k )return mid;elsestart = mid+1;}else if(arr[mid]<k){start = mid+1;}else{end = mid-1;}return getLastK(arr,start,end,k);}public static void main(String[] args) {int [] a = {1,2,3,3,3,3,4,5};System.out.println(GetNumberOfK(a, 3));}}
题目二:0~n-1中缺失的数字
一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0到n-1之内。
在范围0到n-1的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。
如果从头到尾依次比较值与小标是否相等,时间复杂度为O(n),效率低。
由于是排序数组,我们继续考虑使用二分查找算法,结合上图可知:
当中间数字等于其下标时,我们在后半部分查找;
当中间数字不等于其下标时,
1)如果中间数字的前一个数字也不等于其下标,则在前半部分查找;
2)如果中间数字的前一个数字等于其下标,则说明中间数字的下标即为我们所要找的数字。
package com.example.number53;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:0~n-1中缺失的数字*/
public class Test2 {public static int getMissingNumber(int[] arr) {if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)return -1;int low=0;int high=arr.length-1;while(low<=high) {int mid=(low+high)>>1;if(arr[mid]!=mid) {if(mid==0 || arr[mid-1]==mid-1)return mid;high=mid-1;}else {low=mid+1;}}if(low==arr.length)return low;return -1;}public static void main(String[] args) {int [] a = {0,1,2,4};System.out.println(getMissingNumber(a));}}
题目三:数组中数值和下标相等的元素
假设一个单调递增的数组里的每个元素都是整数并且是唯一的。 请编程实现一个函数找出数组中任意一个数值等
于其下标的元素。 例如,在数组{-3, -1, 1, 3, 5}中,数字3和它的下标相等。
package com.example.number53;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目三:数组中数值和下标相等的元素*/
public class Test3 {public static int getNumberSameAsIndex(int[] arr) {if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)return -1; //代表错误int low=0;int high=arr.length-1;while(low<=high) {int mid= (high+low)>>1;if(arr[mid]>mid)high=mid-1;else if(arr[mid]<mid)low=mid+1;elsereturn mid;}return -1;}public static void main(String[] args) {int [] a = {-3, -1, 1, 3, 5};System.out.println(getNumberSameAsIndex(a));}}
54、二叉搜索树的第K大结点
题目:给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。例如, (5,3,7,2,4,6,8) 中,按结点数值大
小顺序第三小结点的值为4。
设置全局变量index=0,对BST进行中序遍历,每遍历一个结点,index+1,当index=k时,该结点即为所求结点。
package com.example.number54;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 二叉搜索树的第K大结点*/
public class Test {static int index = 0;public static BinaryTreeNode KthNode(BinaryTreeNode pRoot, int k) {BinaryTreeNode pNode = null;if (pRoot == null || k <= 0)return pNode;pNode = getKthNode(pRoot, k);return pNode;}private static BinaryTreeNode getKthNode(BinaryTreeNode pRoot, int k) {BinaryTreeNode kthNode = null;if (pRoot.LchildNode != null)kthNode = getKthNode(pRoot.LchildNode, k);if (kthNode == null) {index++;if (k == index)kthNode = pRoot;}if (kthNode == null && pRoot.RchildNode != null)kthNode = getKthNode(pRoot.RchildNode, k);return kthNode;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);System.out.println(KthNode(Root, 3).data);}
}
55、二叉树的深度
题目一:二叉树的深度
输入一棵二叉树,求该树的深度。从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路
径的长度为树的深度。
package com.example.number55;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:二叉树的深度*/
public class Test1 {public static int TreeDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null)return 0;int left = TreeDepth(root.LchildNode);int right = TreeDepth(root.RchildNode);return Math.max(left + 1, right + 1);}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(10);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(12);System.out.println(TreeDepth(Root));}}
题目二:平衡二叉树
输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。
平衡二叉树的定义是任何节点的左右子树高度差都不超过1的二叉树。
package com.example.number55;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:平衡二叉树*/
public class Test2 {public static boolean IsBalanced_Solution(BinaryTreeNode root) {return getDepth(root) != -1;}public static int getDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int left = getDepth(root.LchildNode);if (left == -1) return -1;int right = getDepth(root.RchildNode);if (right == -1) return -1;return Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + Math.max(left, right);}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode Root = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(10);Root.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(12);System.out.println(IsBalanced_Solution(Root));BinaryTreeNode Root1 = new BinaryTreeNode(5);Root1.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(3);Root1.LchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(2);Root1.LchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(4);Root1.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(7);Root1.RchildNode.LchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(6);Root1.RchildNode.RchildNode = new BinaryTreeNode(8);System.out.println(IsBalanced_Solution(Root1));}}
56、数组中数字出现的次数
题目一:数组中只出现一次的两个数字
一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。要求时间
复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)。
思路
记住:两个相同的数字异或等于0.
如果数组中只有一个数字只出现一次,我们从头到尾异或每个数字,那么最终的结果刚好是那个只出现一次
的数字。
而本题里数组中有两个数字只出现一次,如果能够将数组分为两部分,两部分中都只有一个数字只出现一
次,那么就可以解决该问题了。
求解方法:
我们依旧从头到尾异或每个数字,那么最终的结果就是这两个只出现一次的数字的异或结果,由于两个数不
同,因此这个结果数字中一定有一位为1,把结果中第一个1的位置记为第n位。因为是两个只出现一次的数字
的异或结果,所以这两个数字在第n位上的数字一定是1和0。
接下来我们根据数组中每个数字的第n位上的数字是否为1来进行分组,恰好能将数组分为两个都只有一个数
字只出现一次的数组,对两个数组从头到尾异或,就可以得到这两个数了。
package com.example.number56;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:数组中只出现一次的两个数字*/
public class Test1 {public static void FindNumsAppearOnce(int[] array, int num1[], int num2[]) {if (array == null || array.length < 2)return;int resultExclusiveOR = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)resultExclusiveOR ^= array[i];int indexOf1 = 0;while (((resultExclusiveOR & 1) == 0) && (indexOf1 <= 4 * 8)) {//只有n>>1不完整,要n=n>>1resultExclusiveOR = resultExclusiveOR >> 1;indexOf1++;}num1[0] = 0;num2[0] = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {if (((array[i] >> indexOf1) & 1) == 1)num1[0] ^= array[i];elsenum2[0] ^= array[i];}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = {2, 4, 3, 6, 3, 2, 5, 5};int[] num1 = {0};int[] num2 = {0};FindNumsAppearOnce(array, num1, num2);System.out.println(num1[0] + " " + num2[0]);}}
题目二:数组中唯一只出现一次的数字
在一个数组中除了一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。
将所有数字的二进制表示的对应位都加起来,如果某一位能被三整除,那么只出<现一次的数字在该位为0;
反之,为1。
package com.example.number56;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:数组中唯一只出现一次的数字*/
public class Test2 {public static int findNumberAppearingOnce(int[] arr) {if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)throw new RuntimeException();int[] bitSum = new int[32];for(int i=0;i<32;i++)bitSum[i]=0;for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {int bitMask=1;for(int j=31;j>=0;j--) {//注意arr[i]&bitMask不一定等于1或者0,有可能等于00010000int bit=arr[i]&bitMask;if(bit!=0)bitSum[j]+=1;bitMask=bitMask<<1;}}int result=0;for(int i=0;i<32;i++) {result=result<<1;result+=(bitSum[i]%3);//result=result<<1; //不能放在后面,否则最前面一位就没了}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {int [] array = {4,3,4,3,2,3,4};System.out.println(findNumberAppearingOnce(array));}
}
57、和为s的数字
题目一:和为s的两个数字
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字S,在数组中查找两个数,是的他们的和正好是S,如果有多对数字的和等于
S,输出任意一对即可。
思路
从头开始遍历数字,确定一个数字后,对后面的数字遍历,判断和是否为s,这种方法复杂度为O(n^2),效率
太低。
我们考虑到,如果一个数字比较小,那么另一个数字一定比较大,同时数字为递增排列;所以,我们设置两
个指针,一个指针small从第一个数字(最小)出发,另一个指针big从最后一个数字(最大)出发:
当small加big的和小于s时,只需要将small指向后一个数字(更大),继续判断;
当small加big的和大于s时,只需要将big指向前一个数字(更小),继续判断;
当small加big的和等于s时,求解完成。
由于是从两边往中间移动,所以不会有跳过的情况,时间复杂度为O(n)。
package com.example.number57;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:和为s的两个数字*/
public class Test1 {public static ArrayList<Integer> FindNumbersWithSum(int[] array, int sum) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();if (array == null || array.length <= 0)return list;int low = 0;int high = array.length - 1;while (low < high) {if (array[low] + array[high] == sum) {list.add(array[low]);list.add(array[high]);break;} else if (array[low] + array[high] < sum)low++;elsehigh--;}return list;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {0, 1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 15};System.out.println(FindNumbersWithSum(a, 15));}}
题目二:和为s的连续整数序列
输出所有和为S的连续正数序列。序列内按照从小至大的顺序,序列间按照开始数字从小到大的顺序,例如:
15=1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8
指针法:
类似(57-1) 和为s的两个数字的方法,用两个指针small和big分别代表序列的最大值和最小值。令small从1开
始,big从2开始。
当从small到big的序列的和小于s时,增加big,使序列包含更多数字;(记得更新序列之和)
当从small到big的序列的和大于s时,增加small,使序列去掉较小的数字;(记得更新序列之和)
当从small到big的序列的和等于s时,此时得到一个满足题目要求的序列,输出,然后继续将small增大,往后
面找新的序列。
序列最少两个数字,因此,当small到了s/2时,就可以结束判断了。
package com.example.number57;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:和为s的连续整数序列*/
public class Test2 {public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> sequenceList = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();if (sum <= 0)return sequenceList;int small = 1;int big = 2;int curSum = small + big;while (small <= sum / 2) {if (curSum == sum) {ArrayList<Integer> sequence = new ArrayList<Integer>();for (int i = small; i <= big; i++)sequence.add(i);sequenceList.add(sequence);curSum -= small;small++; //这两行位置先后要注意}if (curSum < sum) {big++;curSum += big;}if (curSum > sum) {curSum -= small;small++;}}return sequenceList;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(FindContinuousSequence(15));}}
58、翻转字符串
题目一:翻转单词顺序
例如,“I am a student.”。翻转后的句子应该是“student. a am I”。
先每个单词翻转,最后再整体翻转。
package com.example.number58;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一:翻转单词顺序*/
public class Test1 {public static String ReverseSentence(char[] chars) {if (chars == null || chars.length <= 0)return String.valueOf(chars);//翻转整个句子reverseSb(chars, 0, chars.length - 1);//翻转单词(指针指向单词的第一个和最后一个)int start = 0;int end = 0;while (start < chars.length) {while (end < chars.length && chars[end] != ' ')end++;reverseSb(chars, start, end - 1);start = ++end;}/*翻转单词的另一种写法(指针指向blank位置)int blank = -1;for(int i = 0;i < chars.length;i++){if(chars[i] == ' '){int nextBlank = i;reverse(chars,blank + 1,nextBlank - 1);blank = nextBlank;}}reverse(chars,blank + 1,chars.length - 1);//最后一个单词单独进行反转*/return String.valueOf(chars);}private static void reverseSb(char[] chars, int start, int end) {while (start < end) {char temp = chars[start];chars[start] = chars[end];chars[end] = temp;start++;end--;}}public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "I am a student.";System.out.println(ReverseSentence(s.toCharArray()));}}
题目二:左旋转字符串
例如,字符序列S=”abcXYZdef”,要求输出循环左移3位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。
先每个单词翻转,最后再整体翻转。
package com.example.number58;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二:左旋转字符串*/
public class Test2 {public static String leftRotateString(char[] chars, int n) {if (chars == null || chars.length <= 0)return String.valueOf(chars);if (n <= 0 || n > chars.length)return String.valueOf(chars);reverse(chars, 0, n - 1);reverse(chars, n, chars.length - 1);reverse(chars, 0, chars.length - 1);return String.valueOf(chars);}private static void reverse(char[] chars, int start, int end) {while (start < end) {char temp = chars[start];chars[start] = chars[end];chars[end] = temp;start++;end--;}}public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "abcXYZdef";System.out.println(leftRotateString(s.toCharArray(), 3));}
}
59、队列的最大值
题目一: 滑动窗口的最大值。
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。例如,如果输入数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}及滑动
窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5}; 针对数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}的滑动窗
口有以下6个: {[2,3,4],2,6,2,5,1}, {2,[3,4,2],6,2,5,1}, {2,3,[4,2,6],2,5,1},{2,3,4,[2,6,2],5,1}, {2,3,4,2,
[6,2,5],1}, {2,3,4,2,6,[2,5,1]}。
package com.example.number59;import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目一: 滑动窗口的最大值*/
public class Test1 {public static ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size){ArrayList<Integer> max = new ArrayList<Integer>();if(num==null || num.length<=0 || size<=0 || size>num.length)return max;ArrayDeque<Integer> indexDeque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<size-1;i++){while(!indexDeque.isEmpty() && num[i]> num[indexDeque.getLast()])indexDeque.removeLast();indexDeque.addLast(i);}for(int i=size-1;i<num.length;i++){while(!indexDeque.isEmpty() && num[i]> num[indexDeque.getLast()])indexDeque.removeLast();if(!indexDeque.isEmpty() && (i-indexDeque.getFirst())>=size)indexDeque.removeFirst();indexDeque.addLast(i);max.add(num[indexDeque.getFirst()]);}return max;}public static void main(String[] args) {int [] a = {2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1};System.out.println(maxInWindows(a,3));}}
题目二: 队列的最大值
请定义一个队列并实现函数max得到队列里的最大值,要求函数max、push_back和pop_front的时间复杂度都是
O(1)。用队列先进先出的特点,可以免于考虑剔除最大值后,候补最大值不存在于队列的情况,大大减少了计算。
package com.example.number59;import java.util.ArrayDeque;/*** @author zhangshixing* 题目二: 队列的最大值*/
public class Test2 {private ArrayDeque<InternalData> data = new ArrayDeque<InternalData>();private ArrayDeque<InternalData> maximum = new ArrayDeque<InternalData>();private class InternalData {int number;int index;public InternalData(int number, int index) {this.number = number;this.index = index;}}private int curIndex;public void push_back(int number) {InternalData curData = new InternalData(number, curIndex);data.addLast(curData);while (!maximum.isEmpty() && maximum.getLast().number < number)maximum.removeLast();maximum.addLast(curData);curIndex++; //别漏了这句}public void pop_front() {if (data.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("队列为空,无法删除!");return;}InternalData curData = data.removeFirst();if (curData.index == maximum.getFirst().index)maximum.removeFirst();}public int max() {if (maximum == null) {System.out.println("队列为空,无法删除!");return 0;}return maximum.getFirst().number;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test2 testQueue = new Test2();// {2}testQueue.push_back(2);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 2);// {2, 3}testQueue.push_back(3);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 3);// {2, 3, 4}testQueue.push_back(4);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 4);// {2, 3, 4, 2}testQueue.push_back(2);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 4);// {3, 4, 2}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 4);// {4, 2}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 4);// {2}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 2);// {2, 6}testQueue.push_back(6);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 6);// {2, 6, 2}testQueue.push_back(2);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 6);// {2, 6, 2, 5}testQueue.push_back(5);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 6);// {6, 2, 5}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 6);// {2, 5}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 5);// {5}testQueue.pop_front();System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 5);// {5, 1}testQueue.push_back(1);System.out.println(testQueue.max() == 5);}}
60、n个骰子的点数
题目:把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为s。输入n,打印出s的所有可能的值的出现概率。
package com.example.number60;import java.text.NumberFormat;/*** @author zhangshixing* n个骰子的点数*/
public class Test {private static final int maxValue = 6;/*** 方法一:递归解法*/public static void printProbability1(int number) {if (number <= 0)return; //错误int[] probabilities = new int[maxValue * number - number + 1];//下标为i,对应的值代表点数之和为i+number总共出现的情况次数//点数从number~maxValue*number,所以数组大小为6*number-number+1for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.length; i++)probabilities[i] = 0;//计算不同点数出现的次数for (int i = 1; i <= maxValue; i++)calP(probabilities, number, number - 1, i); //第一次掷骰子,总点数只能是1~maxValue(即6)int totalP = (int) Math.pow(maxValue, number); //所有情况总共出现的次数for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.length; i++) {double ratio = (double) probabilities[i] / totalP;NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();format.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);//设置保留几位小数System.out.println("点数和为" + (i + number) + "的概率为:" + format.format(ratio));}}/*** 计算每种点数出现的次数** @param number:骰子总个数* @param curNumber:当前剩余骰子个数* @param sum:各个骰子加起来的总点数*/private static void calP(int[] probabilities, int number, int curNumber, int sum) {if (curNumber == 0) {probabilities[sum - number]++; //总数为sum的情况存放在sum-number下标中return;}for (int i = 1; i <= maxValue; i++)calP(probabilities, number, curNumber - 1, sum + i); //相当于剩余的骰子少一个,总点数增加。}//===========================================/*** 方法二:基于循环求骰子点数,时间性能好*/public static void printProbability2(int number) {if (number <= 0)return; //错误int[][] probabilities = new int[2][number * maxValue + 1];//[2]代表用两个数组交替保存,[number*maxValue+1]是指点数为所在下标时,该点数出现的总次数。//probabilities[*][0]是没用的,只是为了让下标对应点数for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < number * maxValue; j++) {probabilities[i][j] = 0;}}for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)probabilities[0][i] = 1; //第一个骰子出现的情况int flag = 0;for (int curNumber = 2; curNumber <= number; curNumber++) { //当前是第几个骰子for (int i = 0; i < curNumber; i++)probabilities[1 - flag][i] = 0; //前面的数据清零for (int i = curNumber; i <= curNumber * maxValue; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= 6 && j <= i; j++) {probabilities[1 - flag][i] += probabilities[flag][i - j];}}flag = 1 - flag;}int totalP = (int) Math.pow(maxValue, number); //所有情况总共出现的次数for (int i = number; i <= number * 6; i++) {double ratio = (double) probabilities[flag][i] / totalP;NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();format.setMaximumFractionDigits(8);//设置保留几位小数System.out.println("点数和为" + (i + number) + "的概率为:" + format.format(ratio));}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("=========方法一============");for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {System.out.println("-----骰子数为" + i + "时-----");printProbability1(i);}System.out.println("-----骰子数为" + 11 + "时-----");printProbability1(11);System.out.println("=========方法二============");for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {System.out.println("-----骰子数为" + i + "时-----");printProbability2(i);}System.out.println("-----骰子数为" + 11 + "时-----");printProbability1(11);}}
61、扑克牌中的顺子
题目:从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是⼀个顺⼦,即这5张牌是不是连续的。2~10为数字本身,A为1,J为
11,Q为12,K为13,⽽⼤、⼩王可以看成任意数字。
思路
输入为大小等于5的数组(大小王记为0),输出为布尔值。具体步骤如下:
1)进行对5张牌进行排序;
2)找出0的个数;
3)算出相邻数字的空缺总数;
4)如果0的个数大于等于空缺总数,说明连续,反之不连续;
5)记得判断相邻数字是否相等,如果有出现相等,说明不是顺子。
package com.example.number61;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author zhangshixing* 扑克牌中的顺子*/
public class Test {public static boolean isContinuous(int[] numbers) {if (numbers == null || numbers.length <= 0)return false;Arrays.sort(numbers);int numberOf0 = 0;int numberOfGap = 0;for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {if (numbers[i] == 0)numberOf0++;}int small = numberOf0;int big = numberOf0 + 1;while (big < numbers.length) {if (numbers[small] == numbers[big])return false;numberOfGap += numbers[big++] - numbers[small++] - 1;}if (numberOf0 >= numberOfGap) //大于等于,而不是等于!return true;return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a = {9, 10, 11, 12, 13};System.out.println(isContinuous(a));}}
62、圆圈中最后剩下的数字
题目:0, 1, …, n-1这n个数字排成一个圆圈,从数字0开始每次从这个圆圈里删除第m个数字。求出这个圆圈里剩
下的最后一个数字。
有一个不太容易发现的递推关系:
约瑟夫环的公式是:
f(n, m) = 0 (n = 1)
f(n, m) = [f(n-1, m) +m] % n (n > 1)
package com.example.number62;import java.util.LinkedList;/*** @author zhangshixing* 圆圈中最后剩下的数字*/
public class Test {public static int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {if (n < 1 || m < 1)return -1;int last = 0;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {//这里是i不是nlast = (last + m) % i;}return last;}public static int LastRemaining_Solution2(int n, int m) {if (n < 1 || m < 1)return -1;LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)list.add(i);int removeIndex = 0;while (list.size() > 1) {removeIndex = (removeIndex + m - 1) % list.size();list.remove(removeIndex);}return list.getFirst();}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(LastRemaining_Solution(5, 3));}}
63、股票的最大利润
题目: 假设把某股票的价格按照时间先后顺序存储在数组中,请问买卖该股票一次可获得的最大利润是多少?例
如,一只股票在某些时间节点的价格为{9,11,8,5,7,12,16,14}。如果我们能在价格为5的时候买入并在价格为16时
卖出,则能获得最大的利润为11。
思路: 动态规划,前i天的最大收益 = max{前i-1天的最大收益,第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格}
遍历每一个数字,并保存之前最小的数字,两者差最大即为最大利润。
值得注意的是,我自己一开始写的代码是默认不能亏本(即可以不买入卖出,利润不能为负数),所以比较简
单;
但如果可以亏本,最大利润指的是最小的亏损,那么要注意最小数字不能是最后一个。在下面的代码中可以
注意比较两种情况的差别。可以考虑的例子如 {16, 11, 7, 4, 2, 1}
package com.example.number63;/*** @author zhangshixing* 股票的最大利润*/
public class Test {public static int maxProfit(int[] prices) {int min_p = 9999, max_p = 0;for (int price : prices) {min_p = min_p < price ? min_p : price;max_p = max_p > (price - min_p) ? max_p : (price - min_p);}return max_p;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] prices = {9, 11, 8, 5, 7, 12, 16, 14};System.out.println(maxProfit(prices));}}
64、求1+2+3+…+n
题目:求1+2+3+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?
B:C)。
package com.example.number64;/*** @author zhangshixing* @date 2022年03月13日 9:46*/
public class Test {public static int getSum(int n) {int sum = n;boolean flag = (n > 1) && ((sum += getSum(n - 1)) > 0);// boolean flag = (n==1) || ((sum+=getSum(n-1))>0);return sum;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(getSum(10));}
}
65、不用加减乘除做加法
题目:写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、*、/四则运算符号。
对数字做运算,除了四则运算外,只剩下位运算了。根据一般情况下的加法步骤,设计如下:
1)不考虑进位对每一位相加:1加0,0加1都等于1,而0加0,1加1等于0,所以使用异或^操作;
2)计算进位:只有1加1产生进位,所以采用位与&操作,再左移1位;
3)将和与进位相加,即重复前两步操作。结束判断为进位为0。
a=a+b; => a=a^b;
b=a+b; => b=a^b;
a=a-b; => a=a^b;
package com.example.number65;/*** @author zhangshixing* 不用加减乘除做加法*/
public class Test {public static int add(int num1, int num2) {while (num2 != 0) {//只相加不进位int sum = num1 ^ num2;//进一位int carry = (num1 & num2) << 1;num1 = sum;num2 = carry;}return num1;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(add(1, 2));}}
66、构建乘积数组
题目:给定一个数组A[0,1,…,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,…,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*…*A[i-
1]*A[i+1]*…*A[n-1],不能使用除法。
package com.example.number66;/*** @author zhangshixing* 构建乘积数组*/
public class Test {public static int[] multiply(int[] A) {if (A == null || A.length < 2)return null;int[] B = new int[A.length];B[0] = 1;for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i++)B[i] = B[i - 1] * A[i - 1];int temp = 1;for (int i = A.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {temp *= A[i + 1];B[i] *= temp;}return B;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};for (int a : A) {System.out.println(a);}int[] B = multiply(A);for (int b : B) {System.out.println(b);}}
}
67、把字符串转换成整数
题目: 将一个字符串转换成一个整数,要求不能使用字符串转换整数的库函数。 数值为0或者字符串不是一个合法
的数值则返回0。
package com.example.number67;/*** @author zhangshixing* 把字符串转换成整数*/
public class Test {public static int parseString2Int(String str) {if (null == str || "" == str) {return 0;}// 数字的正负,默认是正数int symbol = 1;// 转换为字符数组char[] array = str.toCharArray();int sum = 0;// 如果第一位是'-',说明结果应该是个负数,'+'不需要处理symbol// 同时替换该位置上的字符为0,这样在下面的处理中,可以认为是跳过该字符// 因为0 * 10还是0if (array[0] == '-') {symbol = -1;array[0] = '0';} else if (array[0] == '+') {array[0] = '0';}for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {// 如果不是数字,而是其他字母符号一类非数字字符,则直接返回0if (array[i] < '0' || array[i] > '9') {return 0;}sum = sum * 10 + array[i] - '0';}return sum * symbol;}public static void main(String[] args) {int result = parseString2Int("-123");System.out.println(result);}
}
68、树中两个节点的最低公共祖先
题目: 输入两个树的结点,求两个结点的最低公共祖先,所谓的最低公共祖先是指距离两个节点最近的共同祖先。
1.当树为二叉搜索树
如果是二叉树,而且是二叉搜索树,那么是可以找到公共节点的。
二叉搜索树都是排序过的,位于左子树的节点都比父节点小,而位于右子树上面的节点都比父节点大。
如果当前节点的值比两个结点的值都大,那么最低的共同的父节点一定是在当前节点的左子树中,于是下一
步遍历当前节点的左子节点。
如果当前节点的值比两个结点的值都小,那么最低的共同的父节点一定是在当前节点的右子树中,于是下一
步遍历当前节点的右子节点。
这样从上到下,找到的第一个在两个输入结点的值之间的节点,就是最低的公共祖先。
package com.example.number68;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 当树为二叉搜索树*/
public class Test1 {public static BinaryTreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(BinaryTreeNode root,BinaryTreeNode a, BinaryTreeNode b) {if (root == null || a == null || b == null) {return null;}while (root != null) {if (root.data > a.data && root.data > b.data) {root = root.LchildNode;} else if (root.data < a.data && root.data < b.data) {root = root.RchildNode;} else {return root;}}return null;}public static void main(String args[]) {BinaryTreeNode n1 = new BinaryTreeNode(10);BinaryTreeNode n2 = new BinaryTreeNode(8);BinaryTreeNode n3 = new BinaryTreeNode(13);BinaryTreeNode n4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4);BinaryTreeNode n5 = new BinaryTreeNode(9);BinaryTreeNode n6 = new BinaryTreeNode(12);BinaryTreeNode n7 = new BinaryTreeNode(17);n1.LchildNode = n2;n1.RchildNode = n3;n2.LchildNode = n4;n2.RchildNode = n5;n3.LchildNode = n6;n3.RchildNode = n7;BinaryTreeNode parent = lowestCommonAncestor(n1, n6, n7);System.out.println(parent.data);}
}
2.当树为二叉树
可以用深度优先搜索,从叶子节点向上,标记子树中出现目标节点的情况。如果子树中有目标节点,标记为那个
目标节点,如果没有,标记为null。显然,如果左子树、右子树都有标记,说明就已经找到最小公共祖先了。如果
在根节点为p的左右子树中找p、q的公共祖先,则必定是p本身。
package com.example.number68;import com.example.commnon.BinaryTreeNode;/*** @author zhangshixing* 当树为二叉树*/
public class Test2 {public static BinaryTreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(BinaryTreeNode root, BinaryTreeNode a, BinaryTreeNode b) {// 发现目标节点则通过返回值标记该子树发现了某个目标结点// 如果在根节点为a的左右子树中找a、b的公共祖先,则必定是a本身。// 同理,如果在根节点为b的左右子树中找a、b的公共祖先,则必定是b本身。if (root == null || root == a || root == b) {return root;}// 查看左子树中是否有目标结点,没有为nullBinaryTreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.LchildNode, a, b);// 查看右子树是否有目标节点,没有为nullBinaryTreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.RchildNode, a, b);// 都不为空,说明左右子树都有目标结点,则公共祖先就是本身if (left != null && right != null) {return root;}// 如果发现了目标节点,则继续向上标记为该目标节点if (left == null) {return right;}if (right == null) {return left;}return null;}public static void main(String args[]) {BinaryTreeNode n1 = new BinaryTreeNode(1);BinaryTreeNode n2 = new BinaryTreeNode(2);BinaryTreeNode n3 = new BinaryTreeNode(3);BinaryTreeNode n4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4);BinaryTreeNode n5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5);BinaryTreeNode n6 = new BinaryTreeNode(6);BinaryTreeNode n7 = new BinaryTreeNode(7);n1.LchildNode = n2;n1.RchildNode = n3;n2.LchildNode = n4;n2.RchildNode = n5;n3.LchildNode = n6;n3.RchildNode = n7;BinaryTreeNode parent = lowestCommonAncestor(n1, n6, n7);System.out.println(parent.data);}
}