1 多环境开发配置
问题导入
在实际开发中,项目的开发环境、测试环境、生产环境的配置信息是否会一致?如何快速切换?
1.1 多环境启动配置
- yaml文件多环境启动
不同环境使用—隔开
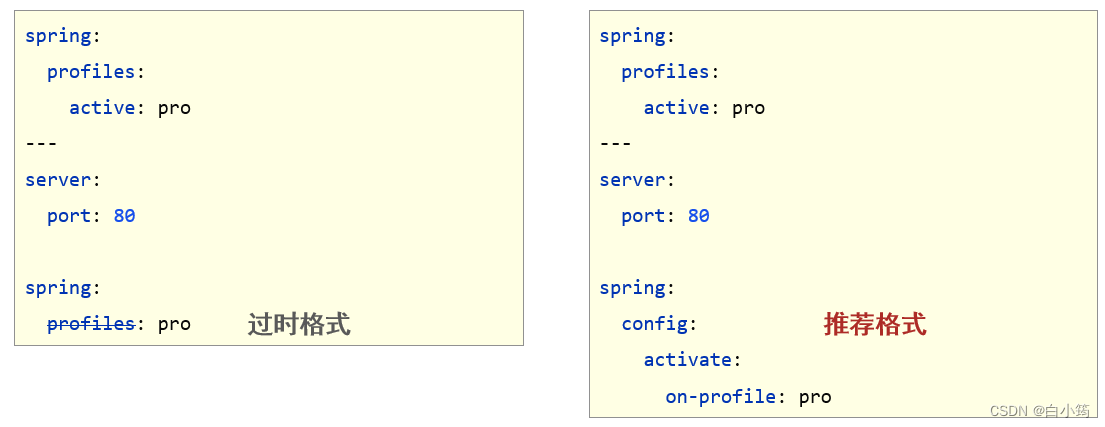
示例代码:
spring:profiles:active: dev#生产环境
---
spring:profiles: pro
server:port: 8081
#开发环境
---
spring:profiles: dev
server:port: 8082
#测试环境
---
spring:profiles: test
server:port: 8083
- properties文件多环境启动
不同环境使用文件名后缀区分
#主启动配置文件 application.properties
spring.profiles.active=pro
#环境分类配置文件 application-pro.properties
server.port=80
#环境分类配置文件 application-dev.properties
server.port=81
#环境分类配置文件application-test.properties
server.port=82
文件目录
1.2 多环境启动命令格式
- 带参数启动SpringBoot
java –jar springboot.jar --spring.profiles.active=test
java –jar springboot.jar --server.port=88
java –jar springboot.jar --server.port=88 --spring.profiles.active=test
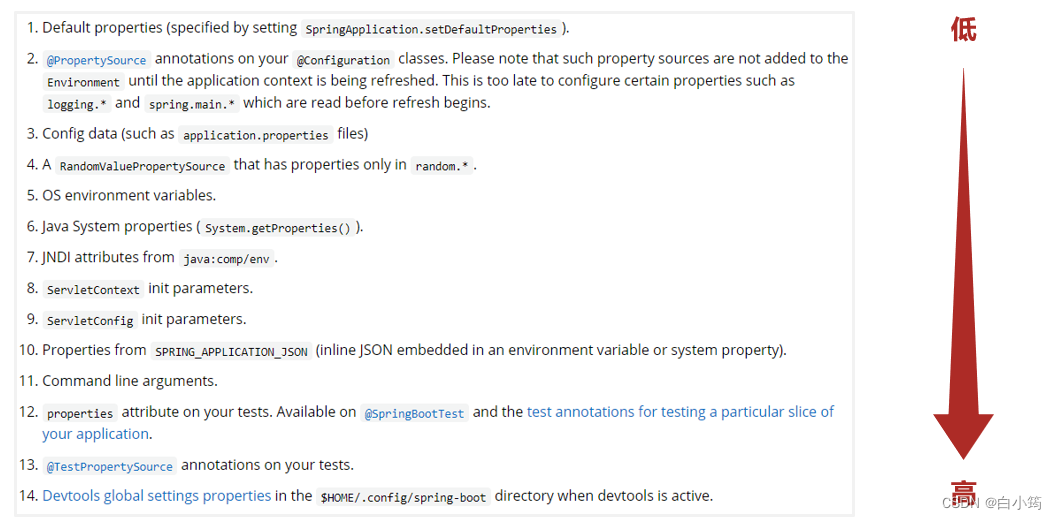
- 参数加载优先顺序
- 参看文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/spring-boot-features.html#boot-features-external-config
1.3 多环境开发控制
Maven与SpringBoot多环境兼容(步骤)
①:Maven中设置多环境属性
<profiles><profile><id>dev_env</id><properties><profile.active>dev</profile.active></properties><!--设置默认生效--><activation><activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault></activation></profile><profile><id>pro_env</id><properties><profile.active>pro</profile.active></properties></profile><profile><id>test_env</id><properties><profile.active>test</profile.active></properties></profile>
</profiles>
②:SpringBoot中引用Maven属性

③:执行Maven打包指令
- Maven指令执行完毕后,生成了对应的包,其中类参与编译,但是配置文件并没有编译,而是复制到包中

- 解决思路:对于源码中非java类的操作要求加载Maven对应的属性,解析${}占位符
④:对资源文件开启对默认占位符的解析
<build><plugins><plugin><artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId><configuration><encoding>utf-8</encoding><!--设置为true--> <useDefaultDelimiters>true</useDefaultDelimiters></configuration></plugin></plugins>
</build>
也可以将${profile.actice}改为@profile.active@
- Maven打包加载到属性,打包顺利通过

4. 配置文件分类
问题导入
SpringBoot的配置文件可以放在项目的哪些地方?

java –jar springboot.jar --spring.profiles.active=test --server.port=85 --server.servlet.context-path=/heima --server.tomcat.connection-timeout=-1 ... ...
-
SpringBoot中4级配置文件
1级: file :config/application.yml 【最高】
2级: file :application.yml
(jar包和application.yml在同一目录)
3级:classpath:config/application.yml
4级:classpath:application.yml 【最低】
(也就是resources下的application.yml)
-
作用:
1级与2级留做系统打包后设置通用属性
3级与4级用于系统开发阶段设置通用属性