集合框架概述
1.1 生活中的容器

1.2 数组的特点与弊端
- 一方面,面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,为了方便对多个对象的操作,就要对对象进行存储。
- 另一方面,使用数组存储对象方面具有
一些弊端,而Java 集合就像一种容器,可以动态地把多个对象的引用放入容器中。 - 数组在内存存储方面的
特点:- 数组初始化以后,长度就确定了。
- 数组中的添加的元素是依次紧密排列的,有序的,可以重复的。
- 数组声明的类型,就决定了进行元素初始化时的类型。不是此类型的变量,就不能添加。
- 可以存储基本数据类型值,也可以存储引用数据类型的变量
- 数组在存储数据方面的
弊端:- 数组初始化以后,长度就不可变了,不便于扩展
- 数组中提供的属性和方法少,不便于进行添加、删除、插入、获取元素个数等操作,且效率不高。
- 数组存储数据的特点单一,只能存储有序的、可以重复的数据
- Java 集合框架中的类可以用于存储多个
对象,还可用于保存具有映射关系的关联数组。
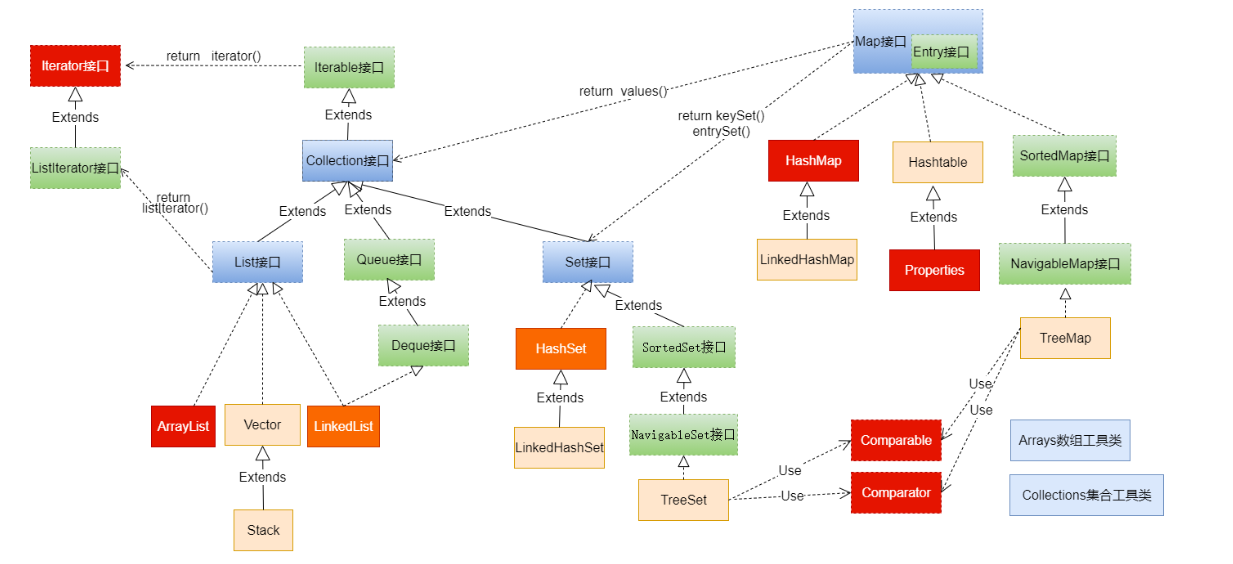
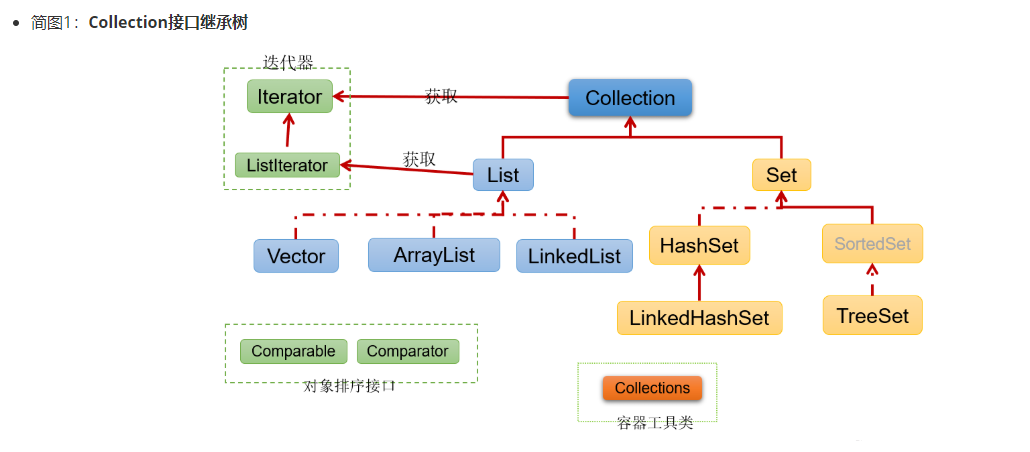
1.3 Java集合框架体系
Java 集合可分为 Collection 和 Map 两大体系:
-
Collection接口:用于存储一个一个的数据,也称
单列数据集合。- List子接口:用来存储有序的、可以重复的数据(主要用来替换数组,"动态"数组)
- 实现类:ArrayList(主要实现类)、LinkedList、Vector
- List子接口:用来存储有序的、可以重复的数据(主要用来替换数组,"动态"数组)
-
Set子接口:用来存储无序的、不可重复的数据(类似于高中讲的"集合")
- 实现类:HashSet(主要实现类)、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
-
Map接口:用于存储具有映射关系“key-value对”的集合,即一对一对的数据,也称
双列数据集合。(类似于高中的函数、映射。(x1,y1),(x2,y2) —> y = f(x) )- HashMap(主要实现类)、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties
-
JDK提供的集合API位于java.util包内
-
图示:集合框架全图

1.4 集合的使用场景
Collection接口及方法
- JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)去实现。
- Collection 接口是 List和Set接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 集合。方法如下:
2.1 添加
(1)add(E obj):添加元素对象到当前集合中
(2)addAll(Collection other):添加other集合中的所有元素对象到当前集合中,即this = this ∪ other
注意:add和addAll的区别
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;public class TestCollectionAdd {@Testpublic void testAdd(){//ArrayList是Collection的子接口List的实现类之一。Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");System.out.println(coll);}@Testpublic void testAddAll(){Collection c1 = new ArrayList();c1.add(1);c1.add(2);System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//2System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);Collection c2 = new ArrayList();c2.add(1);c2.add(2);System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//2System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);Collection other = new ArrayList();other.add(1);other.add(2);other.add(3);System.out.println("other集合元素的个数:" + other.size());//3System.out.println("other = " + other);System.out.println();c1.addAll(other);System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//5System.out.println("c1.addAll(other) = " + c1);c2.add(other);System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//3System.out.println("c2.add(other) = " + c2);}@Testpublic void arrays(){// TODO: 2024/1/5 一次添加多个元素 Collection array = new ArrayList();array.addAll(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));System.out.println(array.size());}}
2.2 判断
(3)int size():获取当前集合中实际存储的元素个数
(4)boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空集合
(5)boolean contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否存在一个与obj对象equals返回true的元素
(6)boolean containsAll(Collection coll):判断coll集合中的元素是否在当前集合中都存在。即coll集合是否是当前集合的“子集”
(7)boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前集合与obj是否相等
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;public class TestCollectionContains {@Testpublic void test01() {Collection coll = new ArrayList();System.out.println("coll在添加元素之前,isEmpty = " + coll.isEmpty());coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll的元素个数" + coll.size());System.out.println("coll在添加元素之后,isEmpty = " + coll.isEmpty());}@Testpublic void test02() {Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll = " + coll);System.out.println("coll是否包含“小李广” = " + coll.contains("小李广"));System.out.println("coll是否包含“宋红康” = " + coll.contains("宋红康"));Collection other = new ArrayList();other.add("小李广");other.add("扫地僧");other.add("尚硅谷");System.out.println("other = " + other);System.out.println("coll.containsAll(other) = " + coll.containsAll(other));}@Testpublic void test03(){Collection c1 = new ArrayList();c1.add(1);c1.add(2);System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//2System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);Collection c2 = new ArrayList();c2.add(1);c2.add(2);System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//2System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);Collection other = new ArrayList();other.add(1);other.add(2);other.add(3);System.out.println("other集合元素的个数:" + other.size());//3System.out.println("other = " + other);System.out.println();c1.addAll(other);System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//5System.out.println("c1.addAll(other) = " + c1);System.out.println("c1.contains(other) = " + c1.contains(other));System.out.println("c1.containsAll(other) = " + c1.containsAll(other));System.out.println();c2.add(other);System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());System.out.println("c2.add(other) = " + c2);System.out.println("c2.contains(other) = " + c2.contains(other));System.out.println("c2.containsAll(other) = " + c2.containsAll(other));}}
2.3 删除
(8)void clear():清空集合元素
(9) boolean remove(Object obj) :从当前集合中删除第一个找到的与obj对象equals返回true的元素。
(10)boolean removeAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中删除所有与coll集合中相同的元素。即this = this - this ∩ coll
(11)boolean retainAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中删除两个集合中不同的元素,使得当前集合仅保留与coll集合中的元素相同的元素,即当前集合中仅保留两个集合的交集,即this = this ∩ coll;
注意几种删除方法的区别
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;public class TestCollectionRemove {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll = " + coll);coll.remove("小李广");System.out.println("删除元素\"小李广\"之后coll = " + coll);coll.clear();System.out.println("coll清空之后,coll = " + coll);}@Testpublic void test02() {Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll = " + coll);Collection other = new ArrayList();other.add("小李广");other.add("扫地僧");other.add("尚硅谷");System.out.println("other = " + other);coll.removeAll(other);System.out.println("coll.removeAll(other)之后,coll = " + coll);System.out.println("coll.removeAll(other)之后,other = " + other);}@Testpublic void test03() {Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll = " + coll);Collection other = new ArrayList();other.add("小李广");other.add("扫地僧");other.add("尚硅谷");System.out.println("other = " + other);coll.retainAll(other);System.out.println("coll.retainAll(other)之后,coll = " + coll);System.out.println("coll.retainAll(other)之后,other = " + other);}}
2.4 其它
(12)Object[] toArray():返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组
(13)hashCode():获取集合对象的哈希值
(14)iterator():返回迭代器对象,用于集合遍历
Iterator(迭代器)接口
3.1 Iterator接口
-
在程序开发中,经常需要遍历集合中的所有元素。针对这种需求,JDK专门提供了一个接口
java.util.Iterator。Iterator接口也是Java集合中的一员,但它与Collection、Map接口有所不同。- Collection接口与Map接口主要用于
存储元素 Iterator,被称为迭代器接口,本身并不提供存储对象的能力,主要用于遍历Collection中的元素
- Collection接口与Map接口主要用于
-
Collection接口继承了java.lang.Iterable接口,该接口有一个iterator()方法,那么所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象。
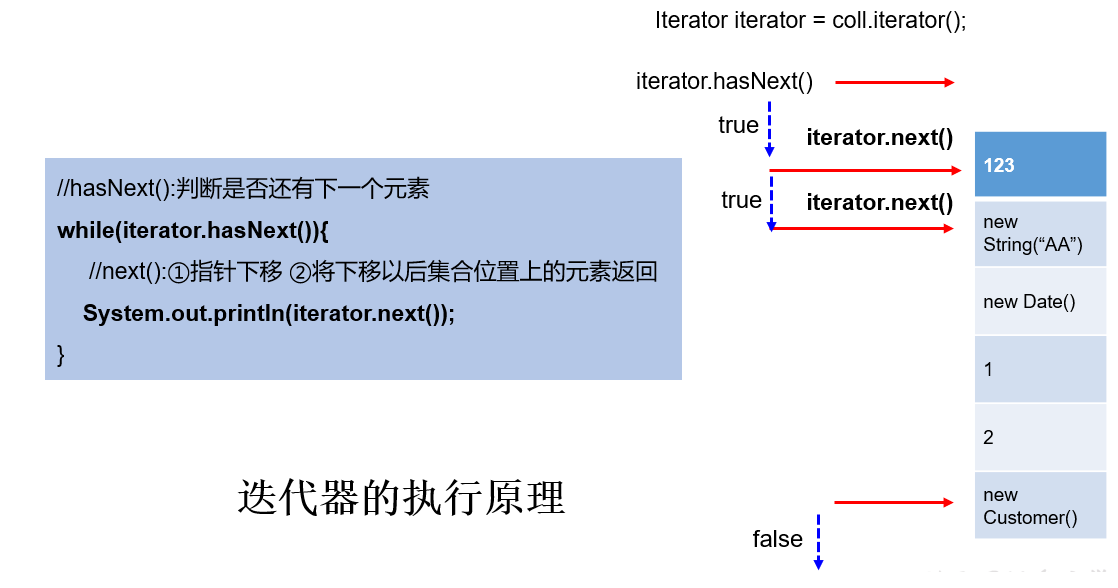
public Iterator iterator(): 获取集合对应的迭代器,用来遍历集合中的元素的。- 集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。
-
Iterator接口的常用方法如下:
public E next():返回迭代的下一个元素。public boolean hasNext():如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。
-
注意:在调用it.next()方法之前必须要调用it.hasNext()进行检测。若不调用,且下一条记录无效,直接调用it.next()会抛出
NoSuchElementException异常。
举例:
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class TestIterator {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next()); //报NoSuchElementException异常}@Testpublic void test02(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();//获取迭代器对象while(iterator.hasNext()) {//判断是否还有元素可迭代System.out.println(iterator.next());//取出下一个元素}}
}
3.2 迭代器的执行原理
Iterator迭代器对象在遍历集合时,内部采用指针的方式来跟踪集合中的元素,接下来通过一个图例来演示Iterator对象迭代元素的过程:
使用Iterator迭代器删除元素:java.util.Iterator迭代器中有一个方法:void remove()
Iterator iter = coll.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){Object obj = iter.next();if(obj.equals("Tom")){iter.remove();}
}
注意:
-
Iterator可以删除集合的元素,但是遍历过程中通过迭代器对象的remove方法,不是集合对象的remove方法。
-
如果还未调用next()或在上一次调用 next() 方法之后已经调用了 remove() 方法,再调用remove()都会报IllegalStateException。
-
Collection已经有remove(xx)方法了,为什么Iterator迭代器还要提供删除方法呢?
-
因为迭代器的remove()可以按指定的条件进行删除。
例如:要删除以下集合元素中的偶数
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class TestIteratorRemove {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(1);coll.add(2);coll.add(3);coll.add(4);coll.add(5);coll.add(6);Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()){Integer element = (Integer) iterator.next();if(element % 2 == 0){iterator.remove();}}System.out.println(coll);}
}
在JDK8.0时,Collection接口有了removeIf 方法,即可以根据条件删除
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.function.Predicate;public class TestCollectionRemoveIf {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");coll.add("佛地魔");System.out.println("coll = " + coll);coll.removeIf(new Predicate() {@Overridepublic boolean test(Object o) {String str = (String) o;return str.contains("地");}});System.out.println("删除包含\"地\"字的元素之后coll = " + coll);}
}
3.3 foreach循环
-
foreach循环(也称增强for循环)是 JDK5.0 中定义的一个高级for循环,专门用来
遍历数组和集合的。 -
foreach循环的语法格式:
for(元素的数据类型 局部变量 : Collection集合或数组){ //操作局部变量的输出操作
}
//这里局部变量就是一个临时变量,自己命名就可以
举例:
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;public class TestForeach {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");//foreach循环其实就是使用Iterator迭代器来完成元素的遍历的。for (Object o : coll) {System.out.println(o);}}@Testpublic void test02(){int[] nums = {1,2,3,4,5};for (int num : nums) {System.out.println(num);}System.out.println("-----------------");String[] names = {"张三","李四","王五"};for (String name : names) {System.out.println(name);}}
}
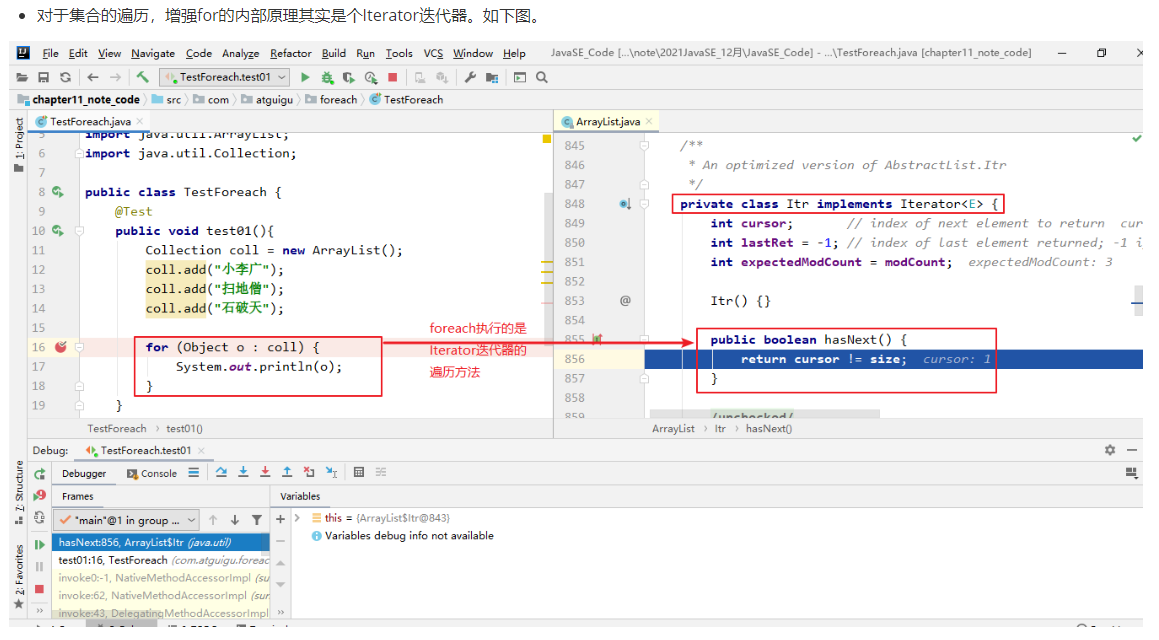
它用于遍历Collection和数组。通常只进行遍历元素,不要在遍历的过程中对集合元素进行增删操作。
- 练习:判断输出结果为何?
public class ForTest {public static void main(String[] args) {String[] str = new String[5];for (String myStr : str) {myStr = "atguigu";System.out.println(myStr);}for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {System.out.println(str[i]);}}
}
Collection子接口1:List
4.1 List接口特点
- 鉴于Java中数组用来存储数据的局限性,我们通常使用
java.util.List替代数组 - List集合类中
元素有序、且可重复,集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引。
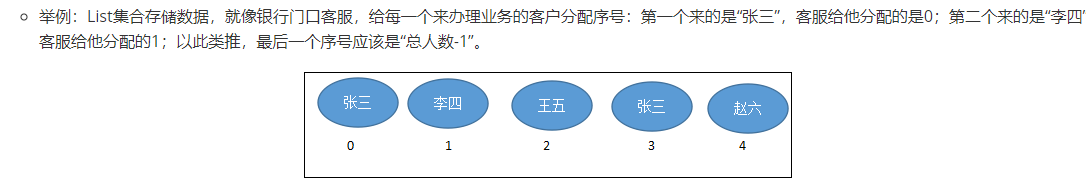
JDK API中List接口的实现类常用的有:ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector。
4.2 List接口方法
List除了从Collection集合继承的方法外,List 集合里添加了一些根据索引来操作集合元素的方法。
- 插入元素
void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素- boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
- 获取元素
Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素- List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合
- 获取元素索引
- int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
- int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
- 删除和替换元素
-
Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素 -
Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele
-
注意:在JavaSE中List名称的类型有两个,一个是java.util.List集合接口,一个是java.awt.List图形界面的组件,别导错包了。
4.3 List接口主要实现类:ArrayList
- ArrayList 是 List 接口的
主要实现类 - 本质上,ArrayList是对象引用的一个”变长”数组
- Arrays.asList(…) 方法返回的 List 集合,既不是 ArrayList 实例,也不是 Vector 实例。 Arrays.asList(…) 返回值是一个固定长度的 List 集合
4.4 List的实现类之二:LinkedList
对于频繁的插入或删除元素的操作,建议使用LinkedList类,效率较高。这是由底层采用链表(双向链表)结构存储数据决定的。

特有方法:
- void addFirst(Object obj)
- void addLast(Object obj)
- Object getFirst()
- Object getLast()
- Object removeFirst()
- Object removeLast()
4.5 List的实现类之三:Vector
- Vector 是一个
古老的集合,JDK1.0就有了。大多数操作与ArrayList相同,区别之处在于Vector是线程安全的。 - 在各种List中,最好把
ArrayList作为默认选择。当插入、删除频繁时,使用LinkedList;Vector总是比ArrayList慢,所以尽量避免使用。 - 特有方法:
- void addElement(Object obj)
- void insertElementAt(Object obj,int index)
- void setElementAt(Object obj,int index)
- void removeElement(Object obj)
- void removeAllElements()
4.6 练习
- 定义学生类,属性为姓名、年龄,提供必要的getter、setter方法,构造器,toString(),equals()方法。
- 使用ArrayList集合,保存录入的多个学生对象。
- 循环录入的方式,1:继续录入,0:结束录入。
- 录入结束后,用foreach遍历集合。
- 代码实现,效果如图所示:
public class Student {private Integer age;private String name;public Student(Integer age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}public Student() {}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;public class StudentTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);ArrayList stuList = new ArrayList();while (true) {System.out.println("选择(录入 1 ;结束 0)");int x = scanner.nextInt();//根据x的值,判断是否需要继续循环if (x == 1) {System.out.println("姓名");String name = scanner.next();System.out.println("年龄");int age = scanner.nextInt();Student stu = new Student(age, name);stuList.add(stu);} else if (x == 0) {break;} else {System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入");}}for (Object stu : stuList) {System.out.println(stu);}}
}
Collection子接口2:Set
5.1 Set接口概述
- Set接口是Collection的子接口,Set接口相较于Collection接口没有提供额外的方法
- Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试把两个相同的元素加入同一个 Set 集合中,则添加操作失败。
- Set集合支持的遍历方式和Collection集合一样:foreach和Iterator。
- Set的常用实现类有:HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet。
5.2 Set主要实现类:HashSet
5.2.1 HashSet概述
-
HashSet 是 Set 接口的主要实现类,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用这个实现类。
-
HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存储、查找、删除性能。
-
HashSet 具有以下
特点:- 不能保证元素的排列顺序
- HashSet 不是线程安全的
- 集合元素可以是 null
-
HashSet 集合
判断两个元素相等的标准:两个对象通过hashCode()方法得到的哈希值相等,并且两个对象的equals()方法返回值为true。 -
对于存放在Set容器中的对象,对应的类一定要重写hashCode()和equals(Object obj)方法,以实现对象相等规则。即:“相等的对象必须具有相等的散列码”。
-
HashSet集合中元素的无序性,不等同于随机性。这里的无序性与元素的添加位置有关。具体来说:我们在添加每一个元素到数组中时,具体的存储位置是由元素的hashCode()调用后返回的hash值决定的。导致在数组中每个元素不是依次紧密存放的,表现出一定的无序性。
5.2.2 HashSet中添加元素的过程:
-
第1步:当向 HashSet 集合中存入一个元素时,HashSet 会调用该对象的 hashCode() 方法得到该对象的 hashCode值,然后根据 hashCode值,通过某个散列函数决定该对象在 HashSet 底层数组中的存储位置。
-
第2步:如果要在数组中存储的位置上没有元素,则直接添加成功。
-
第3步:如果要在数组中存储的位置上有元素,则继续比较:
- 如果两个元素的hashCode值不相等,则添加成功;
- 如果两个元素的hashCode()值相等,则会继续调用equals()方法:
- 如果equals()方法结果为false,则添加成功。
- 如果equals()方法结果为true,则添加失败。
第2步添加成功,元素会保存在底层数组中。
第3步两种添加成功的操作,由于该底层数组的位置已经有元素了,则会通过
链表的方式继续链接,存储。
举例:
import java.util.Objects;public class MyDate {private int year;private int month;private int day;public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;MyDate myDate = (MyDate) o;return year == myDate.year &&month == myDate.month &&day == myDate.day;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(year, month, day);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyDate{" +"year=" + year +", month=" + month +", day=" + day +'}';}
}
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.HashSet;public class TestHashSet {@Testpublic void test01(){HashSet set = new HashSet();set.add("张三");set.add("张三");set.add("李四");set.add("王五");set.add("王五");set.add("赵六");System.out.println("set = " + set);//不允许重复,无序}@Testpublic void test02(){HashSet set = new HashSet();set.add(new MyDate(2021,1,1));set.add(new MyDate(2021,1,1));set.add(new MyDate(2022,2,4));set.add(new MyDate(2022,2,4));System.out.println("set = " + set);//不允许重复,无序}
}
5.2.3 重写 hashCode() 方法的基本原则
- 在程序运行时,同一个对象多次调用 hashCode() 方法应该返回相同的值。
- 当两个对象的 equals() 方法比较返回 true 时,这两个对象的 hashCode() 方法的返回值也应相等。
- 对象中用作 equals() 方法比较的 Field,都应该用来计算 hashCode 值。
注意:如果两个元素的 equals() 方法返回 true,但它们的 hashCode() 返回值不相等,hashSet 将会把它们存储在不同的位置,但依然可以添加成功。
5.2.4 重写equals()方法的基本原则
-
重写equals方法的时候一般都需要同时复写hashCode方法。通常参与计算hashCode的对象的属性也应该参与到equals()中进行计算。
-
推荐:开发中直接调用Eclipse/IDEA里的快捷键自动重写equals()和hashCode()方法即可。
- 为什么用Eclipse/IDEA复写hashCode方法,有31这个数字?
首先,选择系数的时候要选择尽量大的系数。因为如果计算出来的hash地址越大,所谓的“冲突”就越少,查找起来效率也会提高。(减少冲突)
其次,31只占用5bits,相乘造成数据溢出的概率较小。
再次,31可以 由i*31== (i<<5)-1来表示,现在很多虚拟机里面都有做相关优化。(提高算法效率)
最后,31是一个素数,素数作用就是如果我用一个数字来乘以这个素数,那么最终出来的结果只能被素数本身和被乘数还有1来整除!(减少冲突)
5.2.5 练习
**练习:**在List内去除重复数字值,要求尽量简单
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;public class TestHashSet {@Testpublic void test01(){HashSet set = new HashSet();set.add("张三");set.add("张三");set.add("李四");set.add("王五");set.add("王五");set.add("赵六");System.out.println("set = " + set);//不允许重复,无序}}
5.3 Set实现类之二:LinkedHashSet
-
LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet 的子类,不允许集合元素重复。
-
LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,但它同时使用
双向链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以添加顺序保存的。 -
LinkedHashSet
插入性能略低于 HashSet,但在迭代访问Set 里的全部元素时有很好的性能。
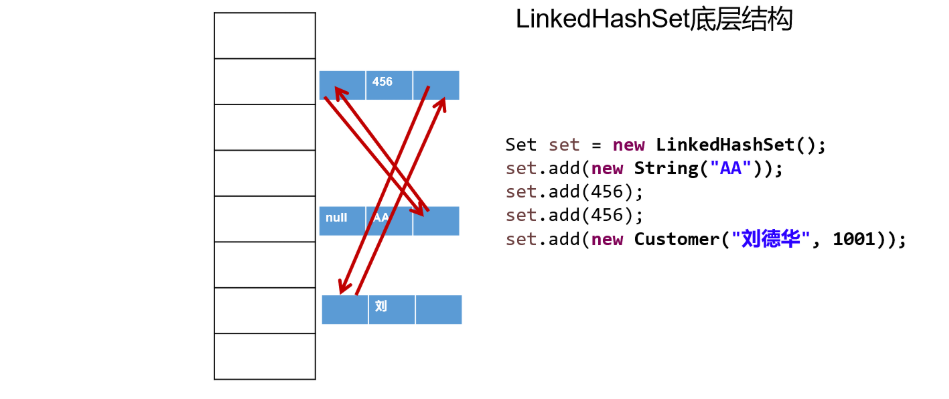
举例:
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;public class TestHashSet {@Testpublic void test01(){LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet();set.add("张三");set.add("张三");set.add("李四");set.add("王五");set.add("王五");set.add("赵六");System.out.println("set = " + set);//不允许重复,体现添加顺序}}
5.4 Set实现类之三:TreeSet
5.4.1 TreeSet概述
- TreeSet 是 SortedSet 接口的实现类,TreeSet 可以按照添加的元素的指定的属性的大小顺序进行遍历。
- TreeSet底层使用
红黑树结构存储数据 - 新增的方法如下: (了解)
- Comparator comparator()
- Object first()
- Object last()
- Object lower(Object e)
- Object higher(Object e)
- SortedSet subSet(fromElement, toElement)
- SortedSet headSet(toElement)
- SortedSet tailSet(fromElement)
- TreeSet特点:不允许重复、实现排序(自然排序或定制排序)
- TreeSet 两种排序方法:
自然排序和定制排序。默认情况下,TreeSet 采用自然排序。自然排序:TreeSet 会调用集合元素的 compareTo(Object obj) 方法来比较元素之间的大小关系,然后将集合元素按升序(默认情况)排列。- 如果试图把一个对象添加到 TreeSet 时,则该对象的类必须实现 Comparable 接口。
- 实现 Comparable 的类必须实现 compareTo(Object obj) 方法,两个对象即通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小。
定制排序:如果元素所属的类没有实现Comparable接口,或不希望按照升序(默认情况)的方式排列元素或希望按照其它属性大小进行排序,则考虑使用定制排序。定制排序,通过Comparator接口来实现。需要重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法。- 利用int compare(T o1,T o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。
- 要实现定制排序,需要将实现Comparator接口的实例作为形参传递给TreeSet的构造器。
- 因为只有相同类的两个实例才会比较大小,所以向 TreeSet 中添加的应该是
同一个类的对象。 - 对于 TreeSet 集合而言,它判断
两个对象是否相等的唯一标准是:两个对象通过compareTo(Object obj) 或compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法比较返回值。返回值为0,则认为两个对象相等。
5.4.2 举例
举例1:
Map接口
现实生活与开发中,我们常会看到这样的一类集合:用户ID与账户信息、学生姓名与考试成绩、IP地址与主机名等,这种一一对应的关系,就称作映射。Java提供了专门的集合框架用来存储这种映射关系的对象,即java.util.Map接口。
6.1 Map接口概述
-
Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有
映射关系的数据:key-valueCollection集合称为单列集合,元素是孤立存在的(理解为单身)。Map集合称为双列集合,元素是成对存在的(理解为夫妻)。
-
Map 中的 key 和 value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据。但常用String类作为Map的“键”。
-
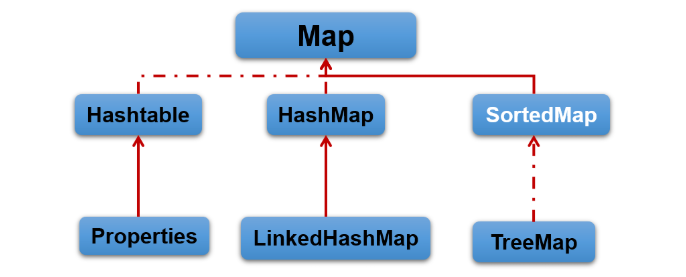
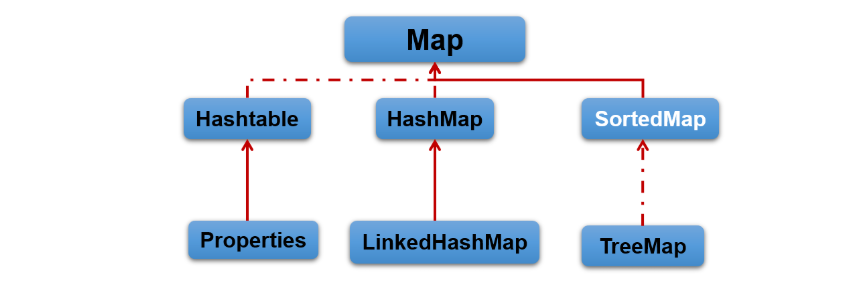
Map接口的常用实现类:
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap和``Properties。其中,HashMap是 Map 接口使用频率最高`的实现类。
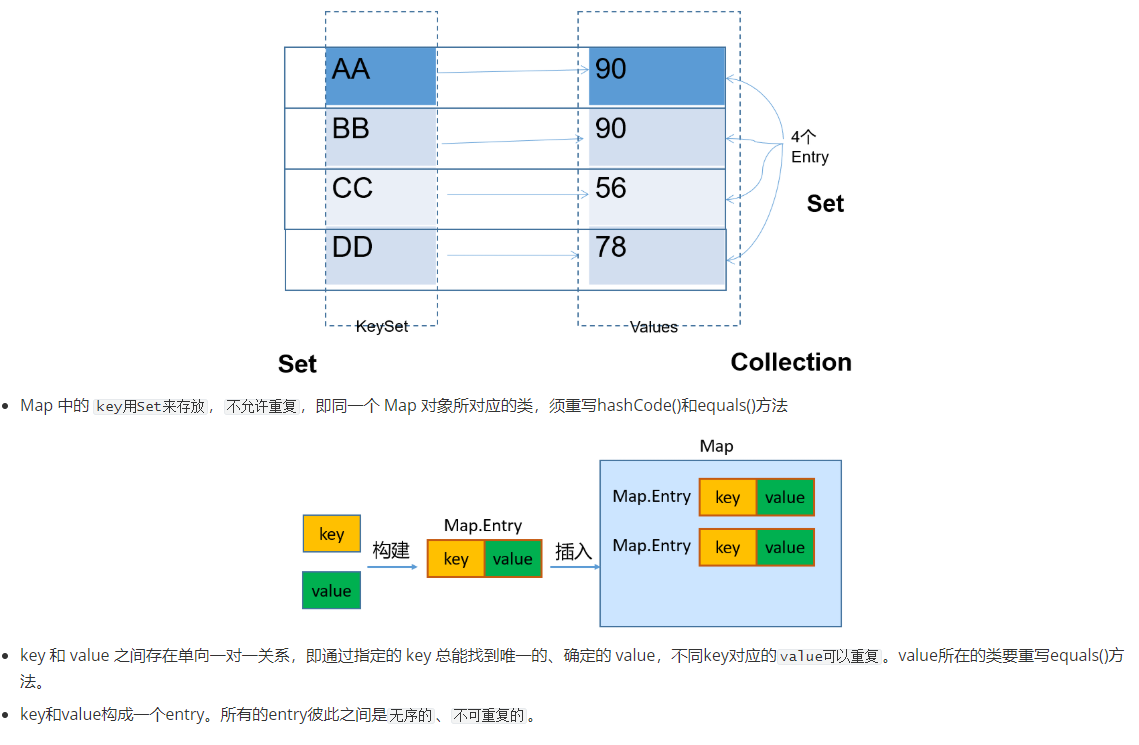
6.2 Map中key-value特点
这里主要以HashMap为例说明。HashMap中存储的key、value的特点如下:
6.2 Map接口的常用方法
- 添加、修改操作:
- Object put(Object key,Object value):将指定key-value添加到(或修改)当前map对象中
- void putAll(Map m):将m中的所有key-value对存放到当前map中
- 删除操作:
- Object remove(Object key):移除指定key的key-value对,并返回value
- void clear():清空当前map中的所有数据
- 元素查询的操作:
- Object get(Object key):获取指定key对应的value
- boolean containsKey(Object key):是否包含指定的key
- boolean containsValue(Object value):是否包含指定的value
- int size():返回map中key-value对的个数
- boolean isEmpty():判断当前map是否为空
- boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前map和参数对象obj是否相等
- 元视图操作的方法:
- Set keySet():返回所有key构成的Set集合
- Collection values():返回所有value构成的Collection集合
- Set entrySet():返回所有key-value对构成的Set集合
举例:
import java.util.HashMap;public class TestMapMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建 map对象HashMap map = new HashMap();//添加元素到集合map.put("黄晓明", "杨颖");map.put("李晨", "李小璐");map.put("李晨", "范冰冰");map.put("邓超", "孙俪");System.out.println(map);//删除指定的key-valueSystem.out.println(map.remove("黄晓明"));System.out.println(map);//查询指定key对应的valueSystem.out.println(map.get("邓超"));System.out.println(map.get("黄晓明"));}
}
6.3 Map的主要实现类:HashMap
6.3.1 HashMap概述
- HashMap是 Map 接口
使用频率最高的实现类。 - HashMap是线程不安全的。允许添加 null 键和 null 值。
- 存储数据采用的哈希表结构,底层使用
一维数组+单向链表+红黑树进行key-value数据的存储。与HashSet一样,元素的存取顺序不能保证一致。 - HashMap
判断两个key相等的标准是:两个 key 的hashCode值相等,通过 equals() 方法返回 true。 - HashMap
判断两个value相等的标准是:两个 value 通过 equals() 方法返回 true。
6.3.2 练习
**练习1:**添加你喜欢的歌手以及你喜欢他唱过的歌曲
例如:
import java.util.*;public class TestMapMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个HashMap用于保存歌手和其歌曲集HashMap singers = new HashMap();//声明一组key,valueString singer1 = "周杰伦";ArrayList songs1 = new ArrayList();songs1.add("双节棍");songs1.add("本草纲目");songs1.add("夜曲");songs1.add("稻香");//添加到map中singers.put(singer1,songs1);//声明一组key,valueString singer2 = "陈奕迅";List songs2 = Arrays.asList("浮夸", "十年", "红玫瑰", "好久不见", "孤勇者");//添加到map中singers.put(singer2,songs2);//遍历mapSet entrySet = singers.entrySet();for(Object obj : entrySet){Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)obj;String singer = (String) entry.getKey();List songs = (List) entry.getValue();System.out.println("歌手:" + singer);System.out.println("歌曲有:" + songs);}}
}
练习2:二级联动
将省份和城市的名称保存在集合中,当用户选择省份以后,二级联动,显示对应省份的地级市供用户选择。

import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;class CityMap{public static Map model = new HashMap();static {model.put("北京", new String[] {"北京"});model.put("上海", new String[] {"上海"});model.put("天津", new String[] {"天津"});model.put("重庆", new String[] {"重庆"});model.put("黑龙江", new String[] {"哈尔滨","齐齐哈尔","牡丹江","大庆","伊春","双鸭山","绥化"});model.put("吉林", new String[] {"长春","延边","吉林","白山","白城","四平","松原"});model.put("河北", new String[] {"石家庄","张家口","邯郸","邢台","唐山","保定","秦皇岛"});}}public class ProvinceTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Set keySet = CityMap.model.keySet();for(Object s : keySet) {System.out.print(s + "\t");}System.out.println();System.out.println("请选择你所在的省份:");Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);String province = scan.next();String[] citys = (String[])CityMap.model.get(province);for(String city : citys) {System.out.print(city + "\t");}System.out.println();System.out.println("请选择你所在的城市:");String city = scan.next();System.out.println("信息登记完毕");}}
6.4 Map实现类之二:LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类
- 存储数据采用的哈希表结构+链表结构,在HashMap存储结构的基础上,使用了一对
双向链表来记录添加元素的先后顺序,可以保证遍历元素时,与添加的顺序一致。 - 通过哈希表结构可以保证键的唯一、不重复,需要键所在类重写hashCode()方法、equals()方法。
public class TestLinkedHashMap {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap();map.put("王五", 13000.0);map.put("张三", 10000.0);//key相同,新的value会覆盖原来的value//因为String重写了hashCode和equals方法map.put("张三", 12000.0);map.put("李四", 14000.0);//HashMap支持key和value为null值String name = null;Double salary = null;map.put(name, salary);Set entrySet = map.entrySet();for (Object obj : entrySet) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)obj;System.out.println(entry);}}
}
6.5 Map实现类之三:TreeMap
- TreeMap存储 key-value 对时,需要根据 key-value 对进行排序。TreeMap 可以保证所有的 key-value 对处于
有序状态。 - TreeSet底层使用
红黑树结构存储数据 - TreeMap 的 Key 的排序:
自然排序:TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,而且所有的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛出 ClasssCastException定制排序:创建 TreeMap 时,构造器传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
- TreeMap判断
两个key相等的标准:两个key通过compareTo()方法或者compare()方法返回0。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class TestIterator {@Testpublic void test01(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next());System.out.println(iterator.next()); //报NoSuchElementException异常}@Testpublic void test02(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add("小李广");coll.add("扫地僧");coll.add("石破天");Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();//获取迭代器对象while(iterator.hasNext()) {//判断是否还有元素可迭代System.out.println(iterator.next());//取出下一个元素}}
}
6.6 Map实现类之四:Hashtable
- Hashtable是Map接口的
古老实现类,JDK1.0就提供了。不同于HashMap,Hashtable是线程安全的。 - Hashtable实现原理和HashMap相同,功能相同。底层都使用哈希表结构(数组+单向链表),查询速度快。
- 与HashMap一样,Hashtable 也不能保证其中 Key-Value 对的顺序
- Hashtable判断两个key相等、两个value相等的标准,与HashMap一致。
- 与HashMap不同,Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 或 value。
面试题:Hashtable和HashMap的区别
HashMap:底层是一个哈希表(jdk7:数组+链表;jdk8:数组+链表+红黑树),是一个线程不安全的集合,执行效率高
Hashtable:底层也是一个哈希表(数组+链表),是一个线程安全的集合,执行效率低HashMap集合:可以存储null的键、null的值 Hashtable集合,不能存储null的键、null的值
Hashtable和Vector集合一样,在jdk1.2版本之后被更先进的集合(HashMap,ArrayList)取代了。所以HashMap是Map的主要实现类,Hashtable是Map的古老实现类。
Hashtable的子类Properties(配置文件)依然活跃在历史舞台 Properties集合是一个唯一和IO流相结合的集合
6.7 Map实现类之五:Properties
-
Properties 类是 Hashtable 的子类,该对象用于处理属性文件
-
由于属性文件里的 key、value 都是字符串类型,所以 Properties 中要求 key 和 value 都是字符串类型(在配置文件里面比较常见)
-
存取数据时,建议使用setProperty(String key,String value)方法和getProperty(String key)方法
@Test
public void test01() {Properties properties = System.getProperties();String fileEncoding = properties.getProperty("file.encoding");//当前源文件字符编码System.out.println("fileEncoding = " + fileEncoding);
}
@Test
public void test02() {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.setProperty("user","songhk");properties.setProperty("password","123456");System.out.println(properties);
}@Test
public void test03() throws IOException {Properties pros = new Properties();pros.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));String user = pros.getProperty("user");System.out.println(user);
}
Collections工具类
参考操作数组的工具类:Arrays,Collections 是一个操作 Set、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类。
7.1 常用方法
Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法(均为static方法):
排序操作:
- reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
- swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
查找
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
- Object min(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
- int binarySearch(List list,T key)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且必须是可比较大小的,即支持自然排序的。而且集合也事先必须是有序的,否则结果不确定。
- int binarySearch(List list,T key,Comparator c)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且集合也事先必须是按照c比较器规则进行排序过的,否则结果不确定。
- int frequency(Collection c,Object o):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
复制、替换
- void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中
- boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
- 提供了多个unmodifiableXxx()方法,该方法返回指定 Xxx的不可修改的视图。
添加
- boolean addAll(Collection c,T... elements)将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。
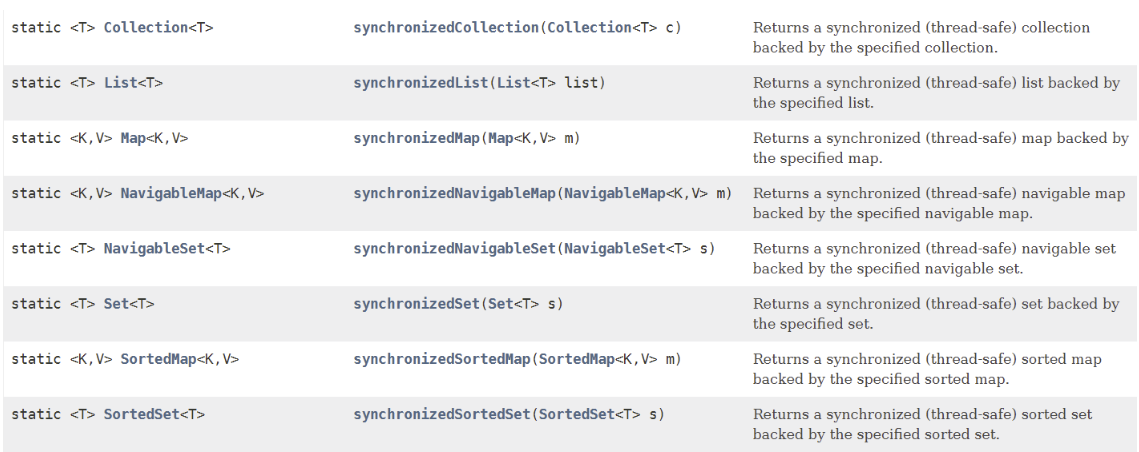
同步
- Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题:
7.2 举例
```bash
package com.zxl.maps;import org.junit.Test;import java.text.Collator;
import java.util.*;public class TestCollections {/*创建内部类Man* */class Man {private String name;private Integer age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public Man(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Man{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}@Testpublic void test01(){/*public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c,T... elements)将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。Collection的集合的元素类型必须>=T类型*/Collection<Object> coll = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(coll, "hello","java");Collections.addAll(coll, 1,2,3,4);Collection<String> coll2 = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(coll2, "hello","java");//Collections.addAll(coll2, 1,2,3,4);//String和Integer之间没有父子类关系}@Testpublic void test02(){/** public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll)* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,而且支持自然排序** public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp)* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,按照比较器comp找出最大者**/List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Man("张三",23));list.add(new Man("李四",28));list.add(new Man("王五",25));/** Man max = Collections.max(list);//要求Man实现Comparable接口,或者父类实现* System.out.println(max);*/Man max = Collections.max(list, new Comparator<Man>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();}});System.out.println(max);}@Testpublic void test03(){/** public static void reverse(List<?> list)* 反转指定列表List中元素的顺序。*/List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");System.out.println(list);Collections.reverse(list);System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test04(){/** public static void shuffle(List<?> list)* List 集合元素进行随机排序,类似洗牌,打乱顺序*/List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");Collections.shuffle(list);System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test05() {/** public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)* 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序** public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> c)* 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序*/List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Man("张三",23));list.add(new Man("李四",24));list.add(new Man("王五",25));System.out.println(list);Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Man>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {return Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA).compare(o1.getName(),o2.getName());}});System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test06(){/** public static void swap(List<?> list,int i,int j)* 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换*/List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");Collections.swap(list,0,2);System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test07(){/** public static int frequency(Collection<?> c,Object o)* 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数*/List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");int count = Collections.frequency(list, "hello");System.out.println("count = " + count);}@Testpublic void test08(){/** public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest,List<? extends T> src)* 将src中的内容复制到dest中*/List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){//1-5list.add(i);}List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=11; i<=13; i++){//11-13list2.add(i);}Collections.copy(list, list2);System.out.println(list);List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=11; i<=20; i++){//11-20list3.add(i);}//java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Source does not fit in dest//Collections.copy(list, list3);//System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test09(){/** public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list,T oldVal,T newVal)* 使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值*/List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");Collections.replaceAll(list, "hello","song");System.out.println(list);}
}