目录
一,顺序表表/ArrayList的缺陷
二,链表
三,链表的实现
四,与链表有关的题目练习(1)
1.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
2.反转一个单链表
3.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
4.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
5.将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
6.编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
7.链表的回文结构
一,顺序表表/ArrayList的缺陷
在上期我们已经熟悉了ArrayList的使用,并且进行了简单模拟实现。通过源码我们知道ArrayList底层使用数组来存储元素。
二,链表
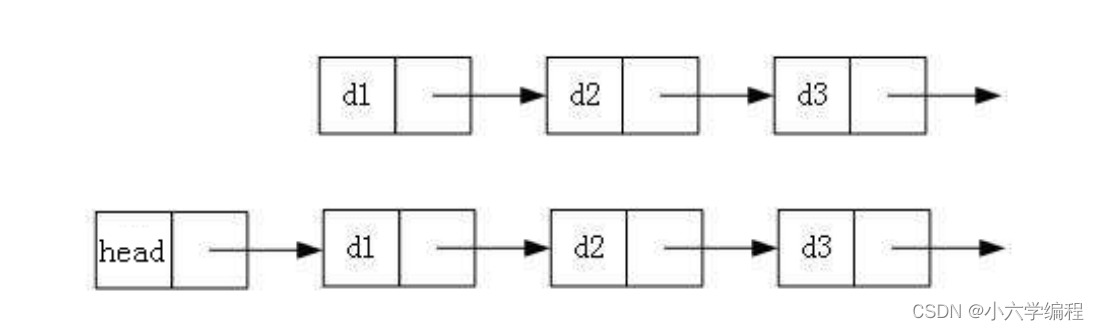
如果说顺序表其底层在物理意义上是一段连续的空间,那么链表便是是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
顺序表是一段连续不可分的空间:

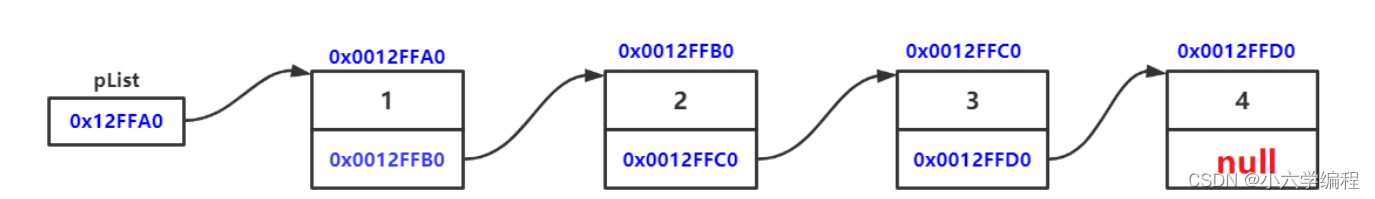
链表像一列火车一样,多个节点被串成一块具有连续性意义的结构,实际上各个节点都来自于不同的地址:




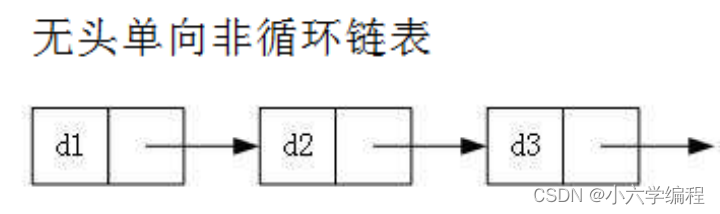
三,链表的实现
和上期顺序表一样,我们采用接口的方式实现:
接口部分:
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现
public interface IList {//头插法public void addFirst(int data);//尾插法public void addLast(int data);//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标public void addIndex(int index,int data);//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key);//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key);//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key);//得到单链表的长度public int size();//清空链表public void clear();//打印链表public void display();
}接口方法实现:
public class AchieveList implements IList{static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//创建一个链表public void crateList() {ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(34);ListNode node3 = new ListNode(56);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(78);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(99);node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;this.head = node1;}//头插法@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node =new ListNode(data);node.next = this.head;this.head = node;}//尾插法@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);cur.next = node;}//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = this.head;ListNode prev = this.head;if (index == 0) {node.next = cur;this.head = node;} else {int count = 0;while (count != index) {cur = cur.next;count++;}count = 0;while ((count+1) != index) {prev = prev.next;count++;}node.next = cur;prev.next = node;}}//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode cur = this.head;ListNode prev = this.head;int count = 1;while (cur.val != key) {if (count == size()) {return;}cur = cur.next;count++;}if (count == 1) {head = null;head = prev.next;} else {while (prev.next.val != key) {prev = prev.next;}prev.next = cur.next;}}//删除所有值为key的节点@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;int count = 1;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.val == key) {count++;}cur = cur.next;}for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {remove(key);}}//得到单链表的长度@Overridepublic int size() {int count = 1;ListNode cur = this.head;if (cur == null) {return 0;}while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;count++;}return count;}@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur.next != null) {head = null;head = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}head = null;}//打印链表@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;if (head == null) {System.out.println("[" + "]");} else {System.out.print("[");while (cur != null) {if (cur.next == null) {System.out.println(cur.val + "]");} else {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");}cur = cur.next;}}}四,与链表有关的题目练习(1)
1.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head,int val) {if (head == null) {return null;}ListNode cur = head.next;ListNode prev = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == val) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;} else {cur = cur.next;prev = prev.next;}}if (head.val == val) {head = head.next;}return head;}}2.反转一个单链表
思路:
现有如下链表:
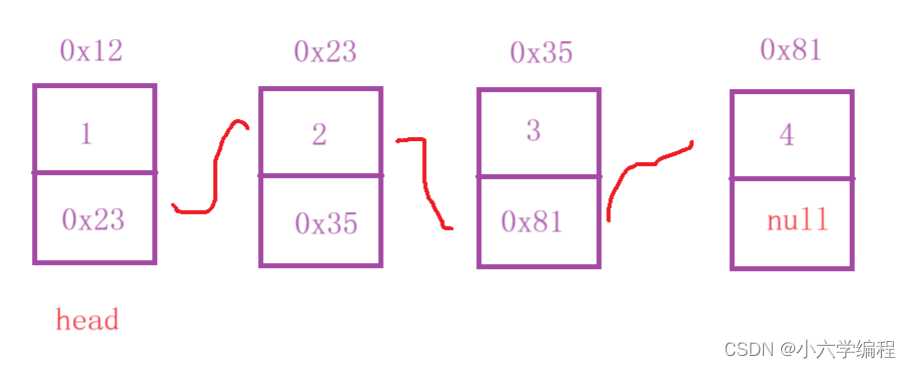
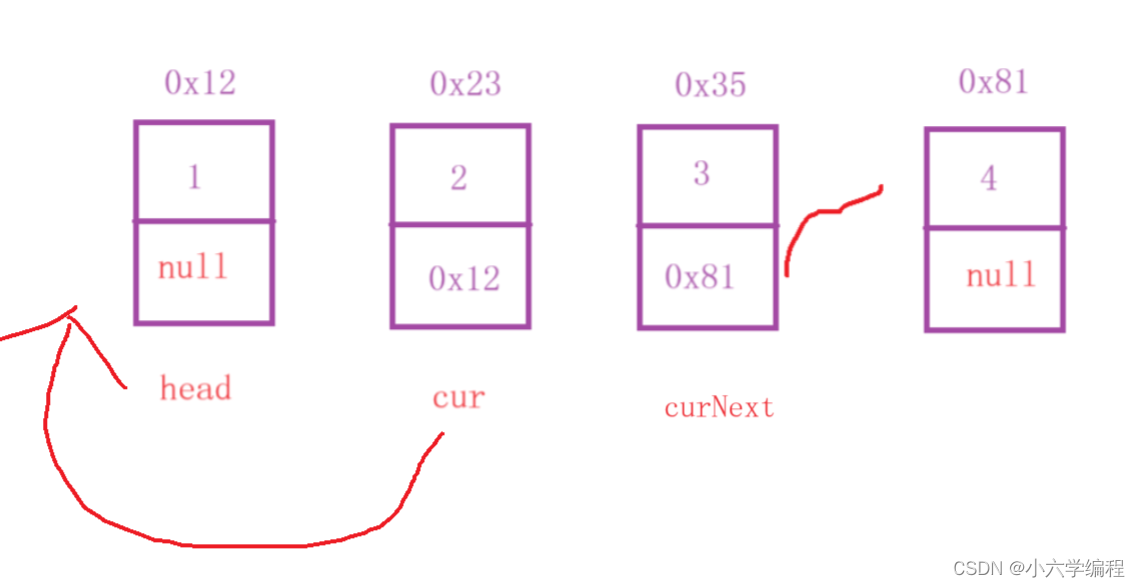
定义cur = head.next

将head.next指向null

定义变量curNext = cur.next

将cur的下一个节点设为head
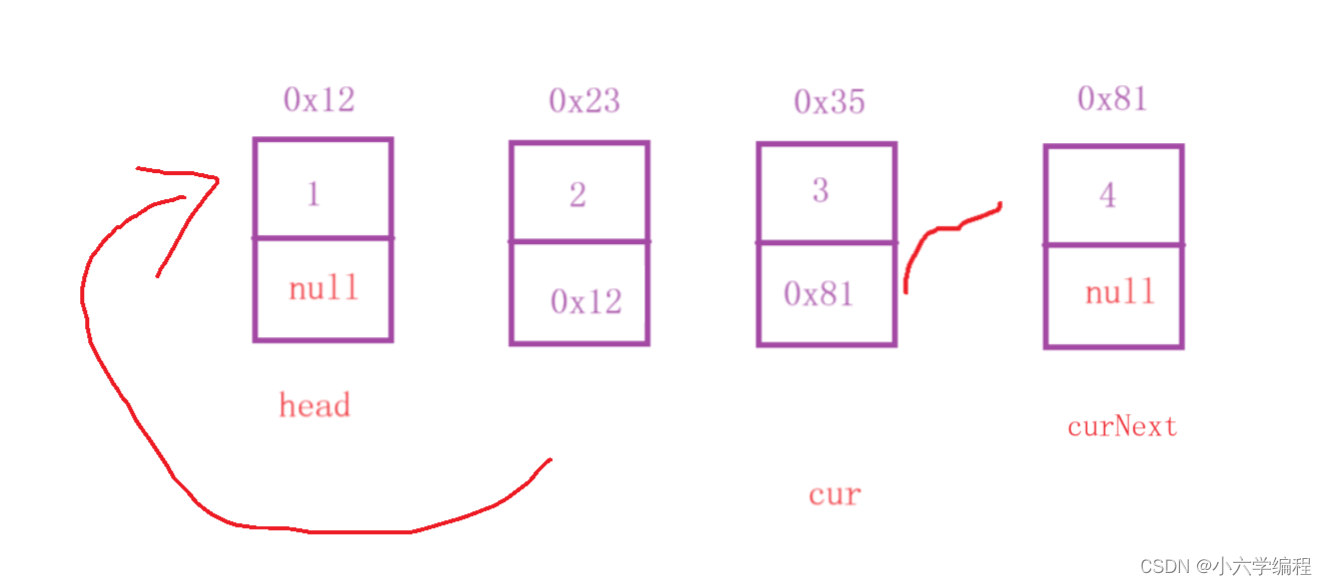
令cur = curNext;curNext = cur.next;
后以此思路循环
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}if (head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode cur = head.next;head.next = null;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = curNext;}return head;}}3.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
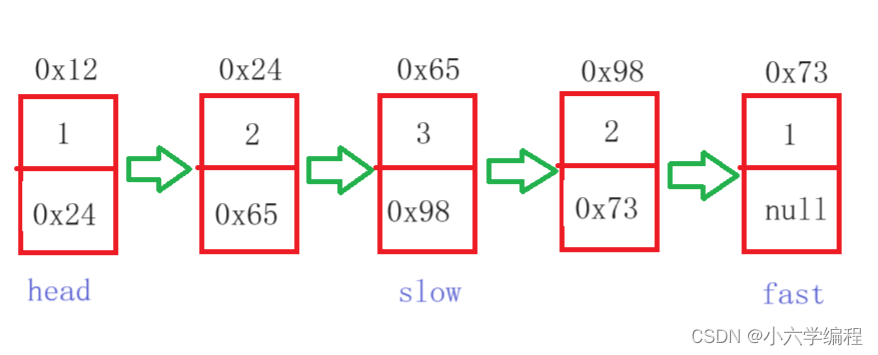
思路:
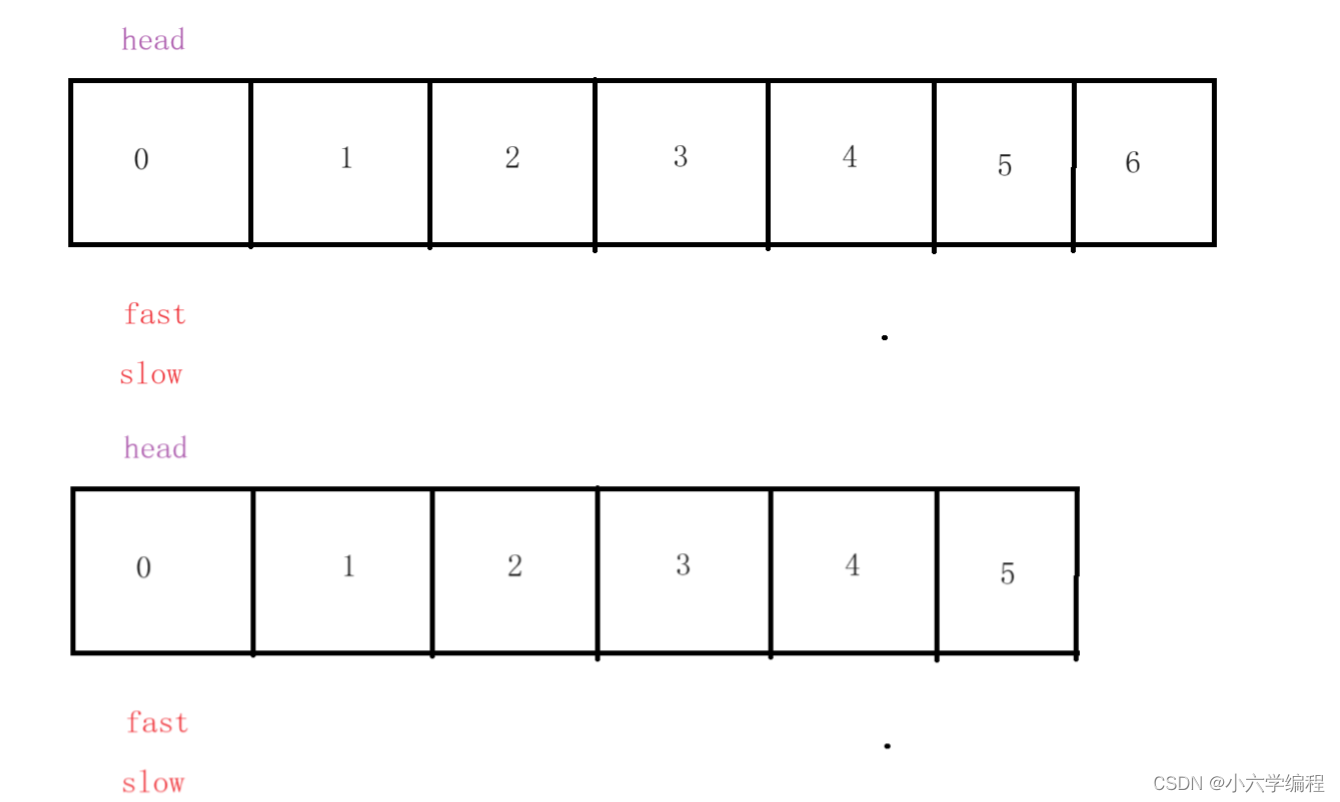
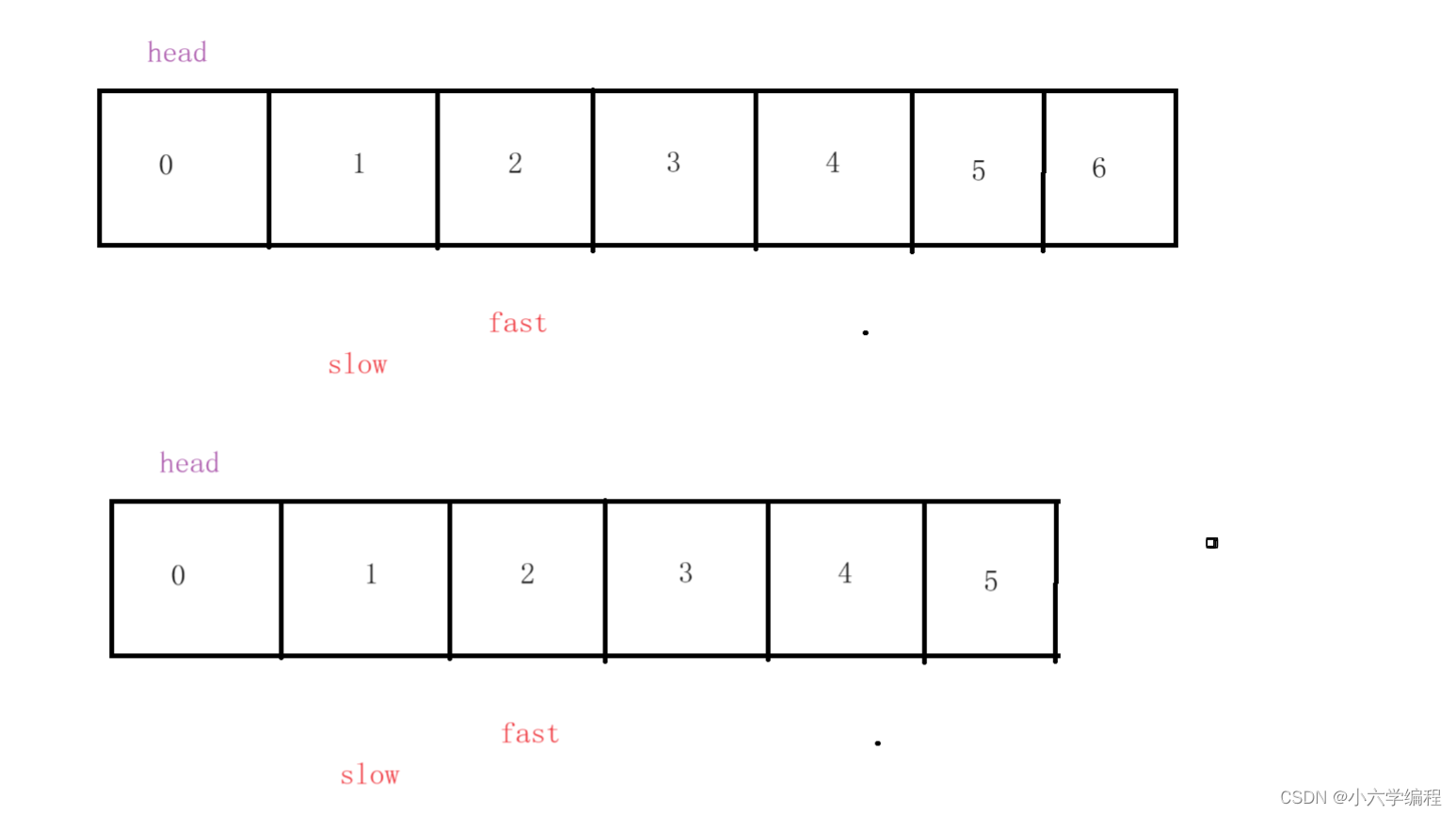
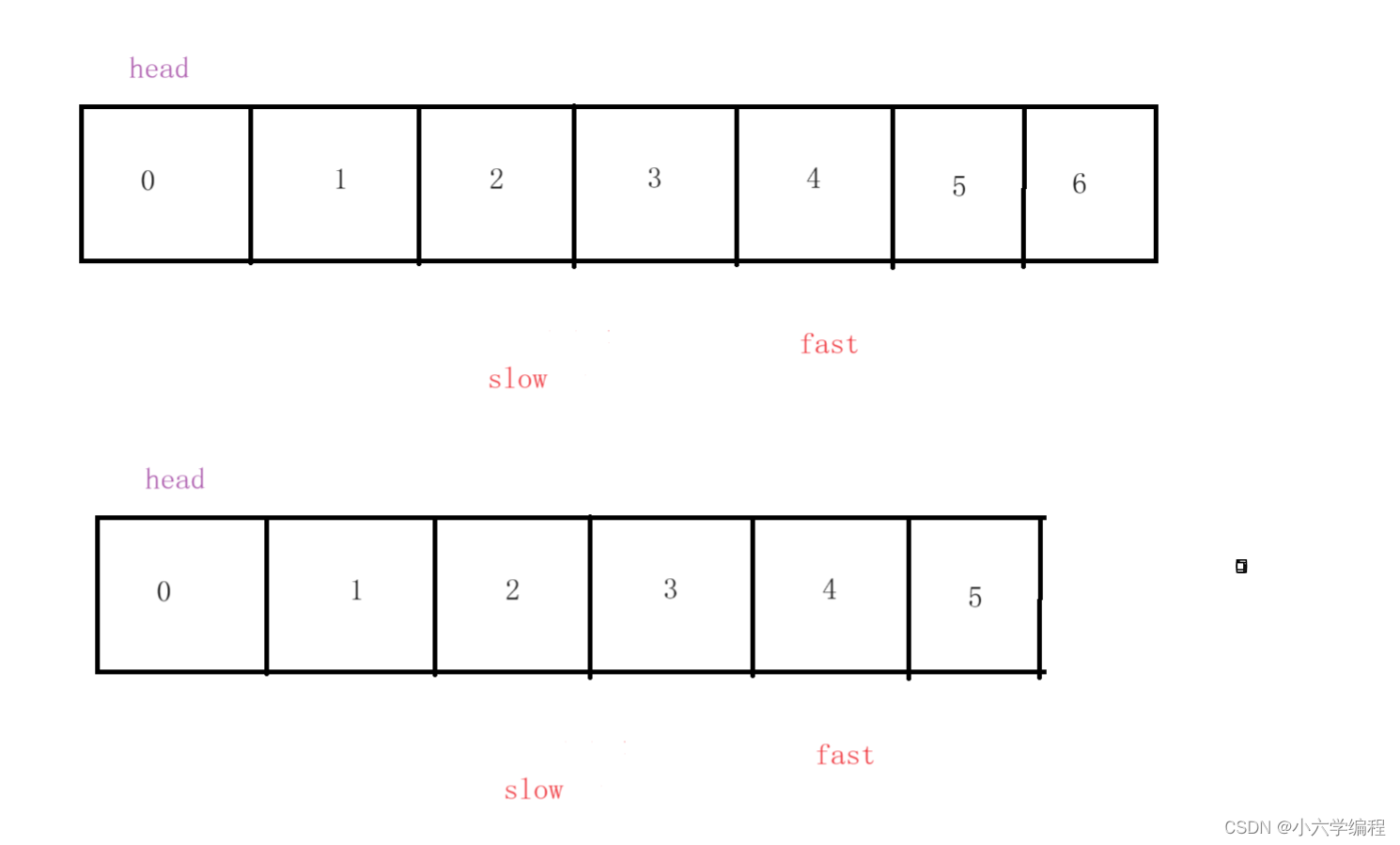
定义如图两个变量fast和slow,且都等于head
令fast每次走两步,slow每次走一步。当fast==null或者fast.next === null时
此时slow的位置必定是中间节点
初:
移动一次:
移动两次:
末:

class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}}
}4.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
假设有以下链表:
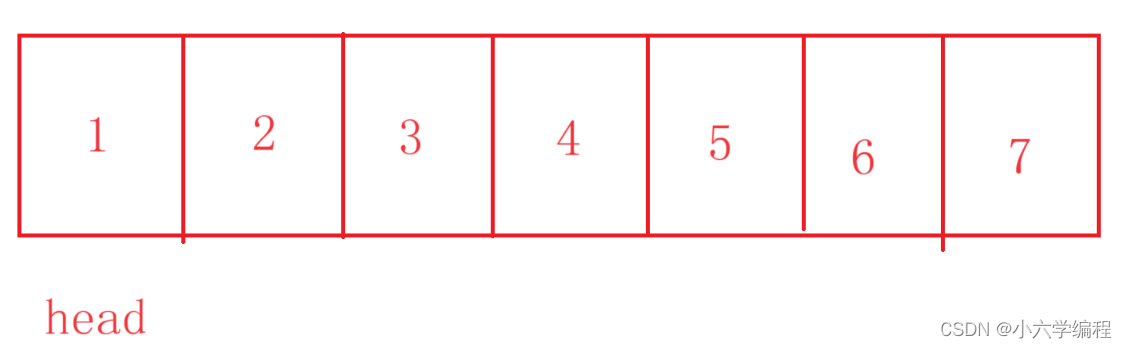
要求倒数第k个节点,我们可以先定义fast和slow两个位于头节点的变量
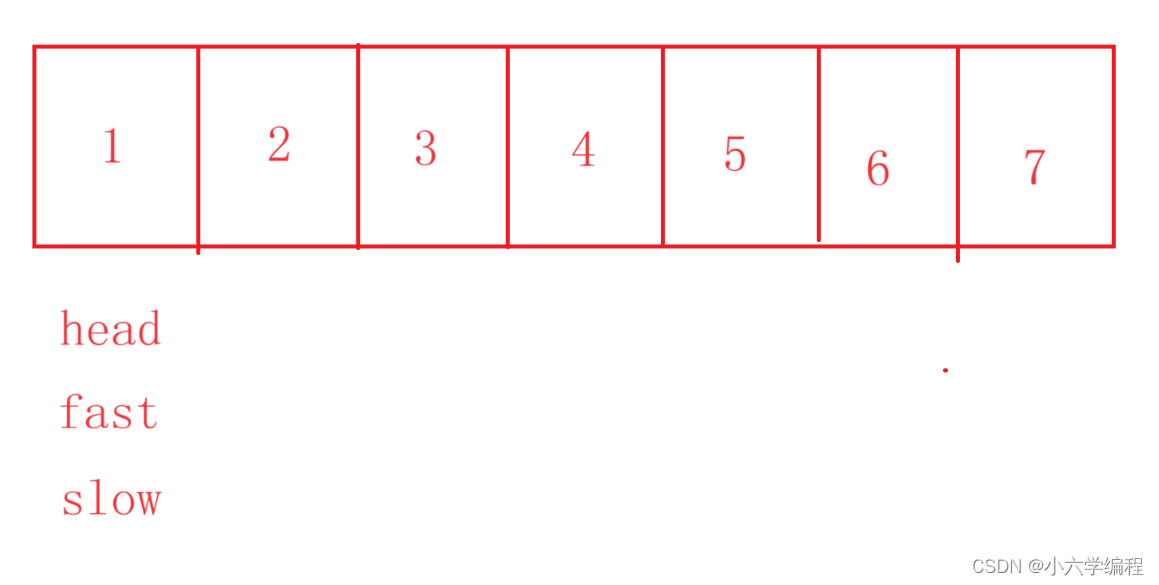
假如K为3,我们就先令fast先走K-1步

然后令fast和slow一起走同样的步数,直到fast.next为null
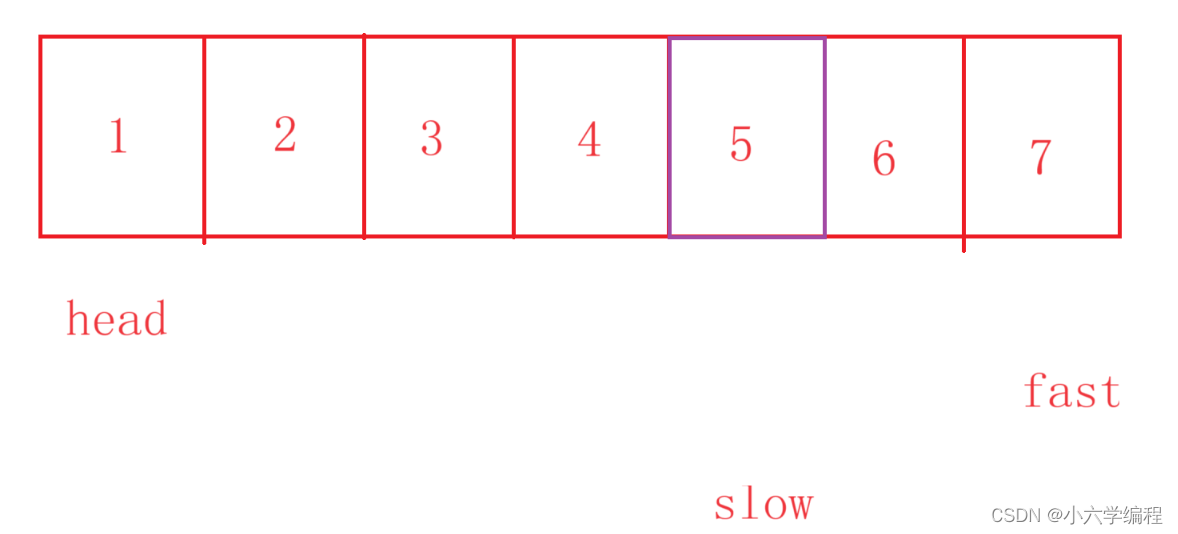
此时slow对应的位置就是所求的倒数第K个节点
public class Solution {public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {if (head == null) {return head;}if (k <= 0 && head != null ) {return null;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;for (int i = 0; i < k-1; i++) {fast = fast.next;//处理K太大的问题if (fast == null) {return null;}}while (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}}5.将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
思路:
先有以下两个有序链表需要被合并为一个有序链表

定义一个newH节点

将head1.val与head2.val进行比较,较小令它等于tmpH且令它等于它的下一个节点,tmpH为newH的下一个节点
如上图head1.val<head2.val,故发生以下变化
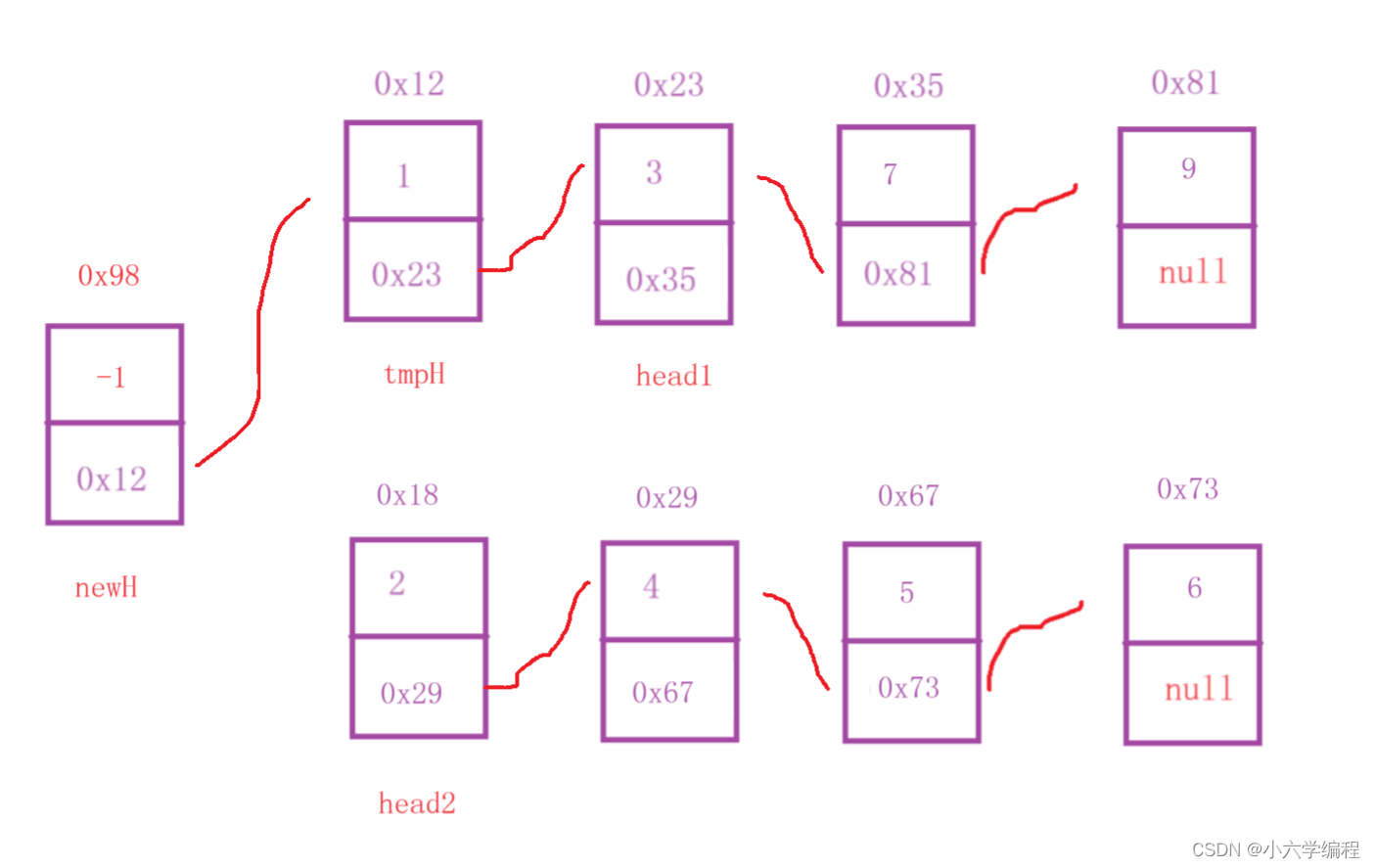
接着对head1.val与head2.val进行比较
head2.val更小
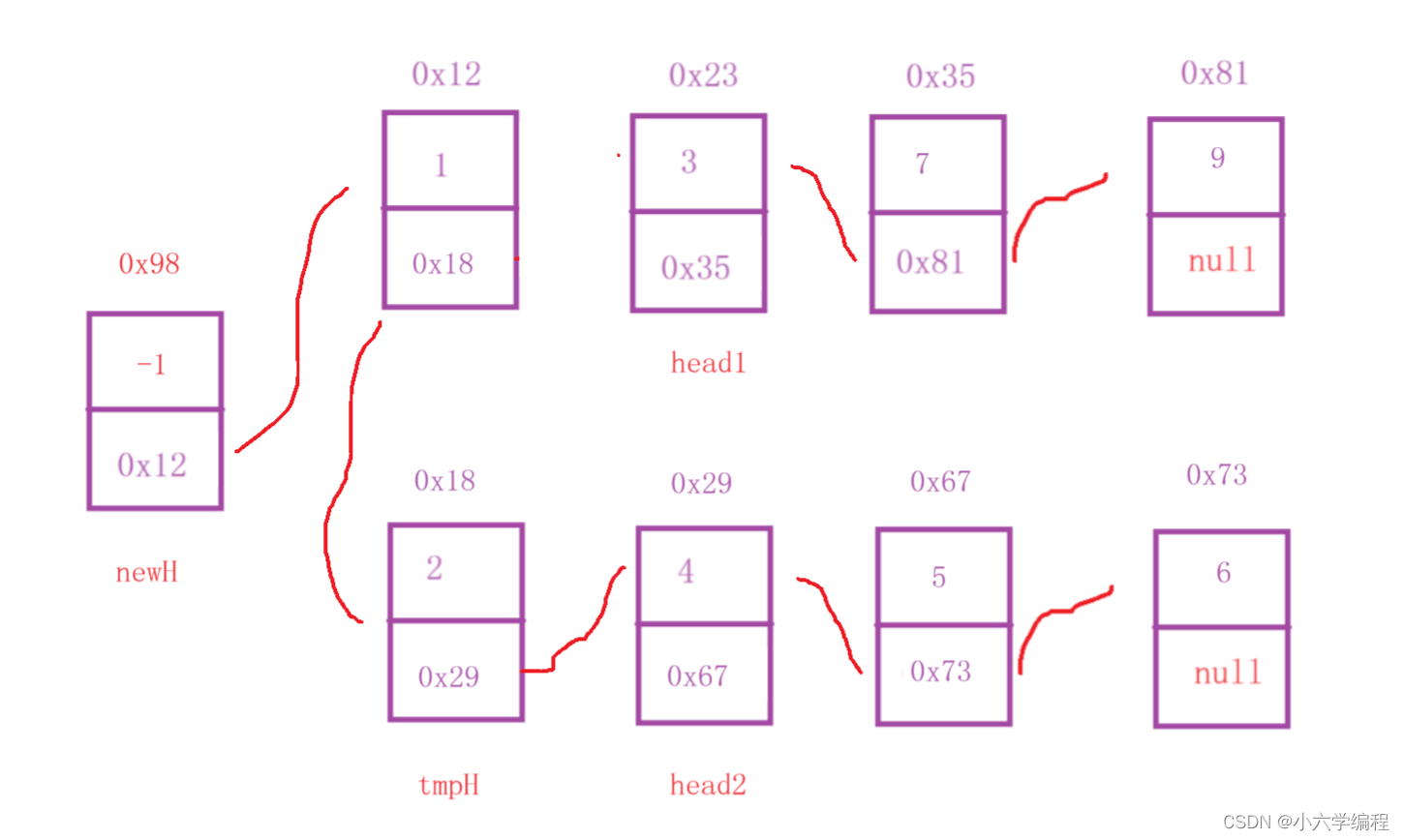
继续比较
head1.val更小
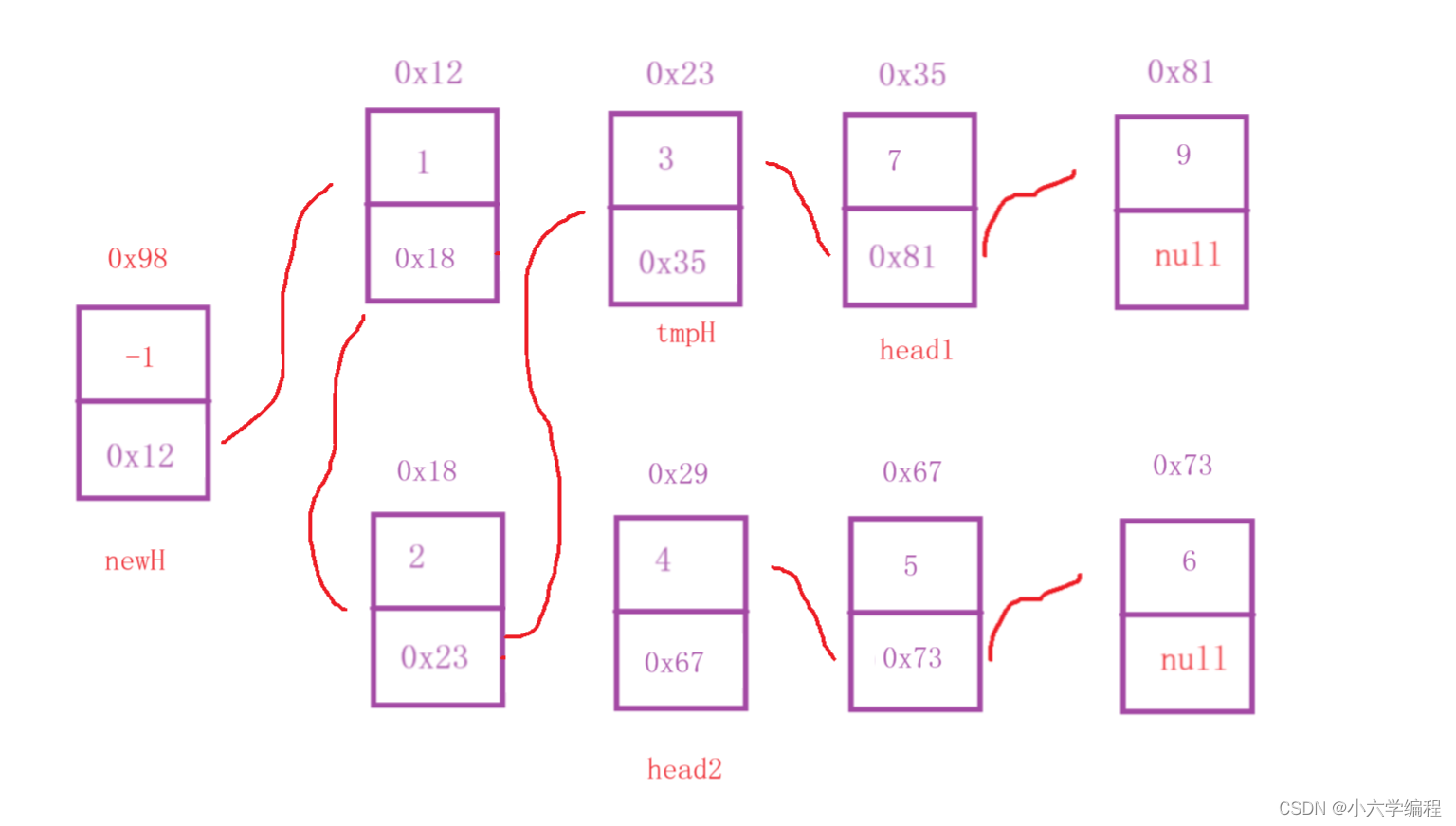
继续比较
head2.val更小

……
当其中有一个数组比较完了的时候,此时只需令tmpH.next为另一个head即可
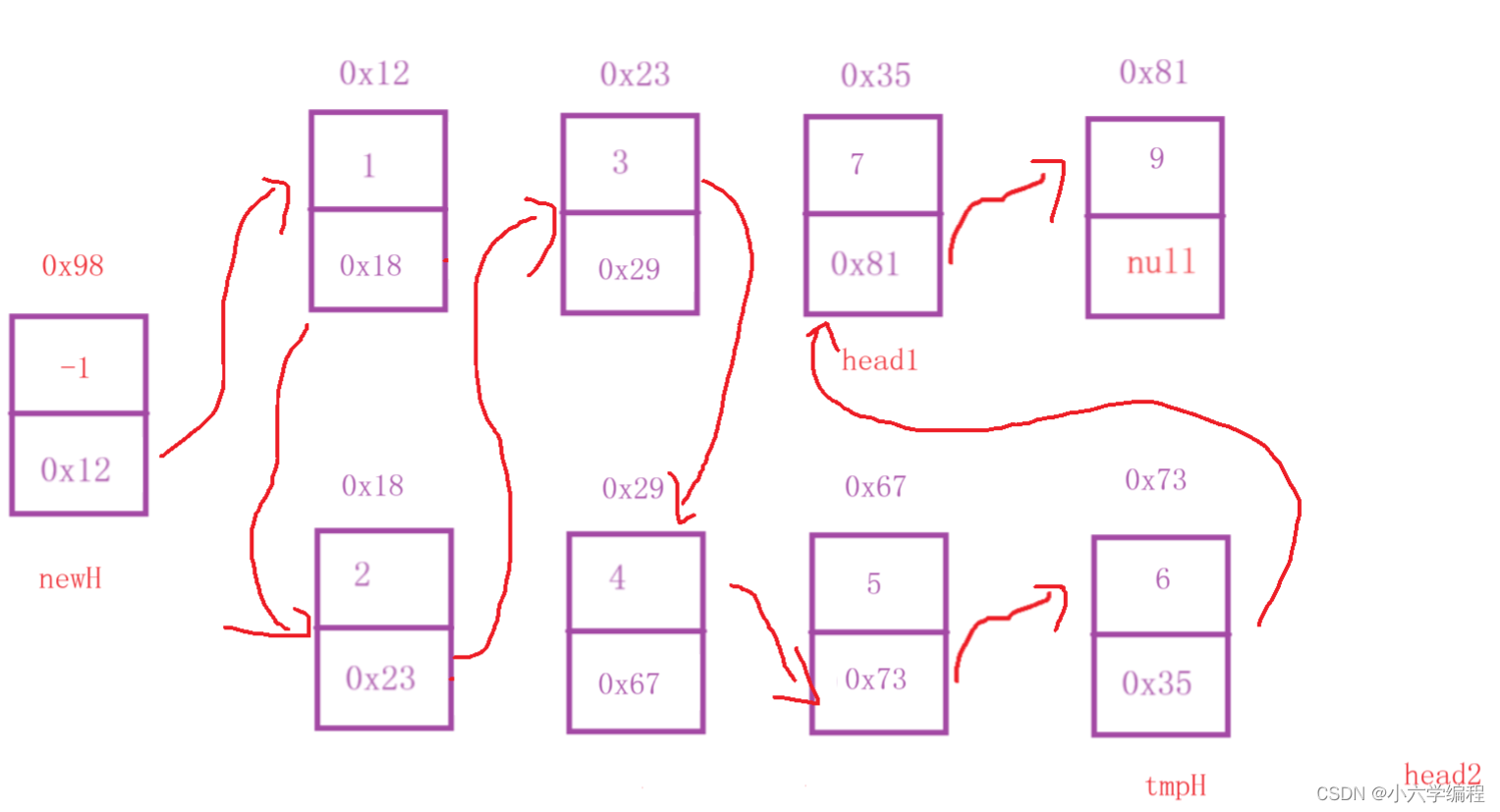
最后返回newH.next即可
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {ListNode newH = new ListNode(-1);ListNode tmpH = newH;while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {if (head1.val < head2.val) {tmpH.next = head1;tmpH = tmpH.next;head1 = head1.next;} else {tmpH.next = head2;tmpH = tmpH.next;head2 = head2.next;}}if (head1 != null) {tmpH.next = head1;}if (head2 != null) {tmpH.next = head2;}return newH.next;}}6.编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
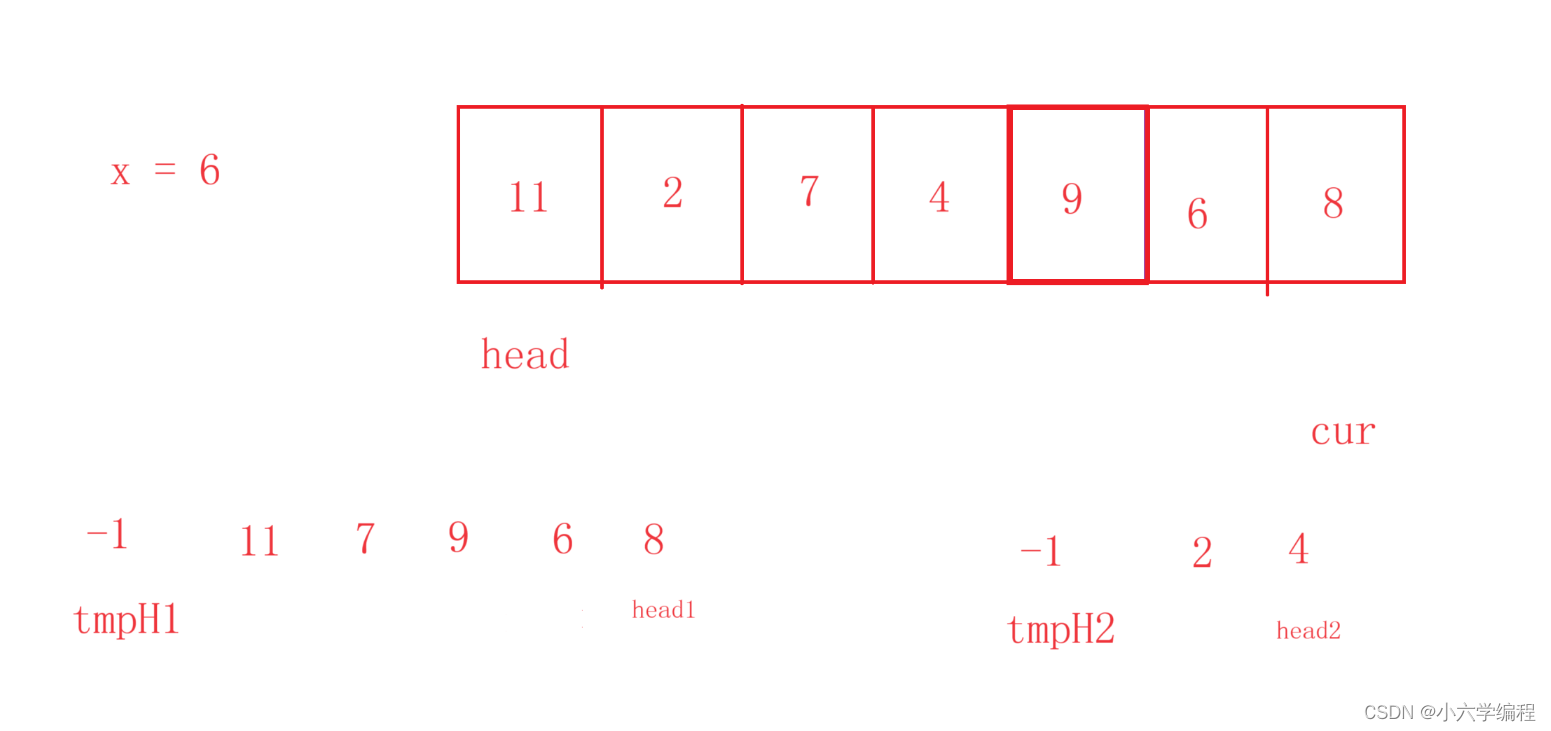
使用cur遍历顺序表
当cur.val<给定的值x时就让它进入链表1
当cur.val>=给定的值x时就让它进入链表2
最后将链表2的尾部插在链表1的头部,返回链表2
public class Partition {public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {ListNode cur = pHead;ListNode tmpH1 = new ListNode(-1);ListNode tmpH2 = new ListNode(-1);ListNode head1 = tmpH1;ListNode head2 = tmpH2;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val < x) {head2.next = cur;head2 = head2.next;} else {head1.next = cur;head1 = head1.next;}cur = cur.next;}tmpH2 = tmpH2.next;tmpH1 = tmpH1.next;head2.next = tmpH1;head1.next = null;if (tmpH2 == null) {return tmpH1;}if (tmpH1 == null) {return tmpH2;}return tmpH2;}}7.链表的回文结构
通过以上快慢指针的方式找到链表的中间节点
翻转
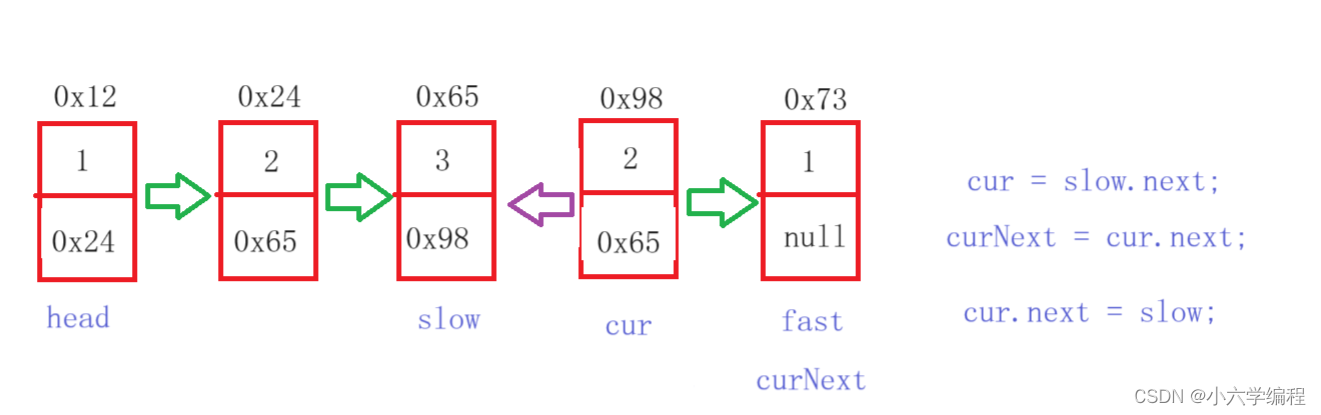
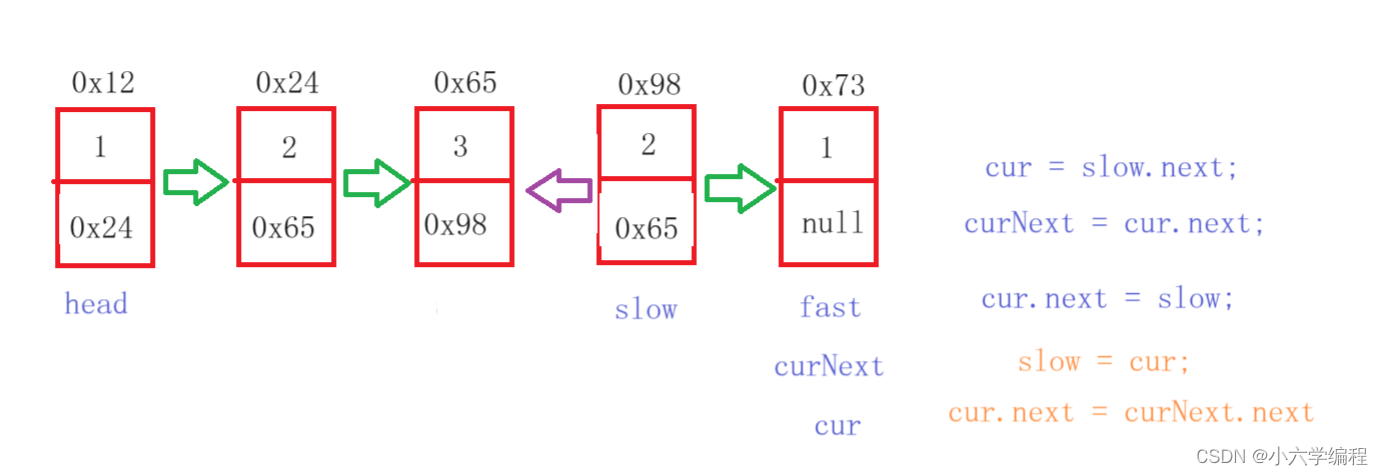
当slow和fast相遇时停止
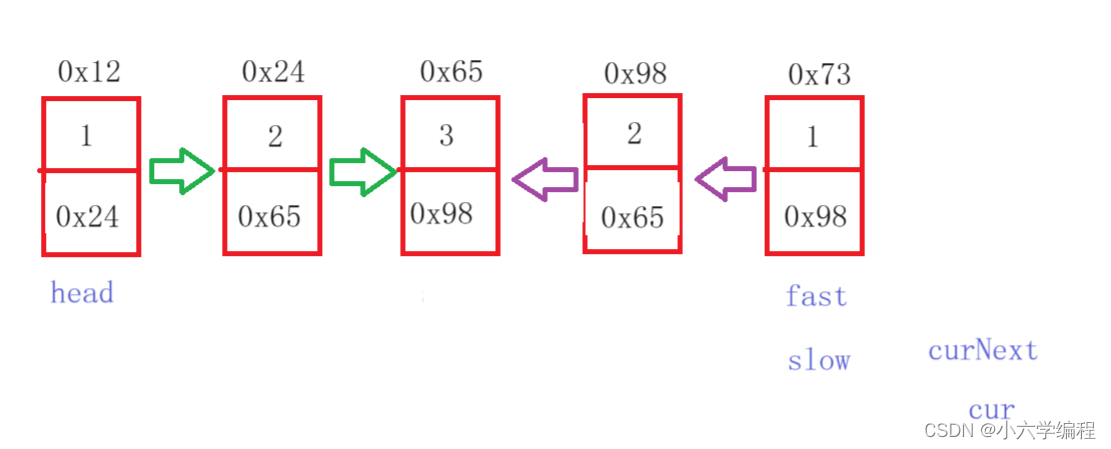
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {if (A == null || A.next == null) {return true;}ListNode fast = A;ListNode slow = A;//找中间位置while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}ListNode cur = slow.next;//翻转while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur = curNext;}ListNode right = slow;ListNode left = A;//从前到后 从后到前while (left.next != right.next ) {if (left.val != right.val) {return false;}if (left.next == right){return true;}left = left.next;right = right.next;}return true;}}




![[C#]利用opencvsharp实现深度学习caffe模型人脸检测](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9abd939faa5d437584fbbeff3a37e5e8.jpeg)