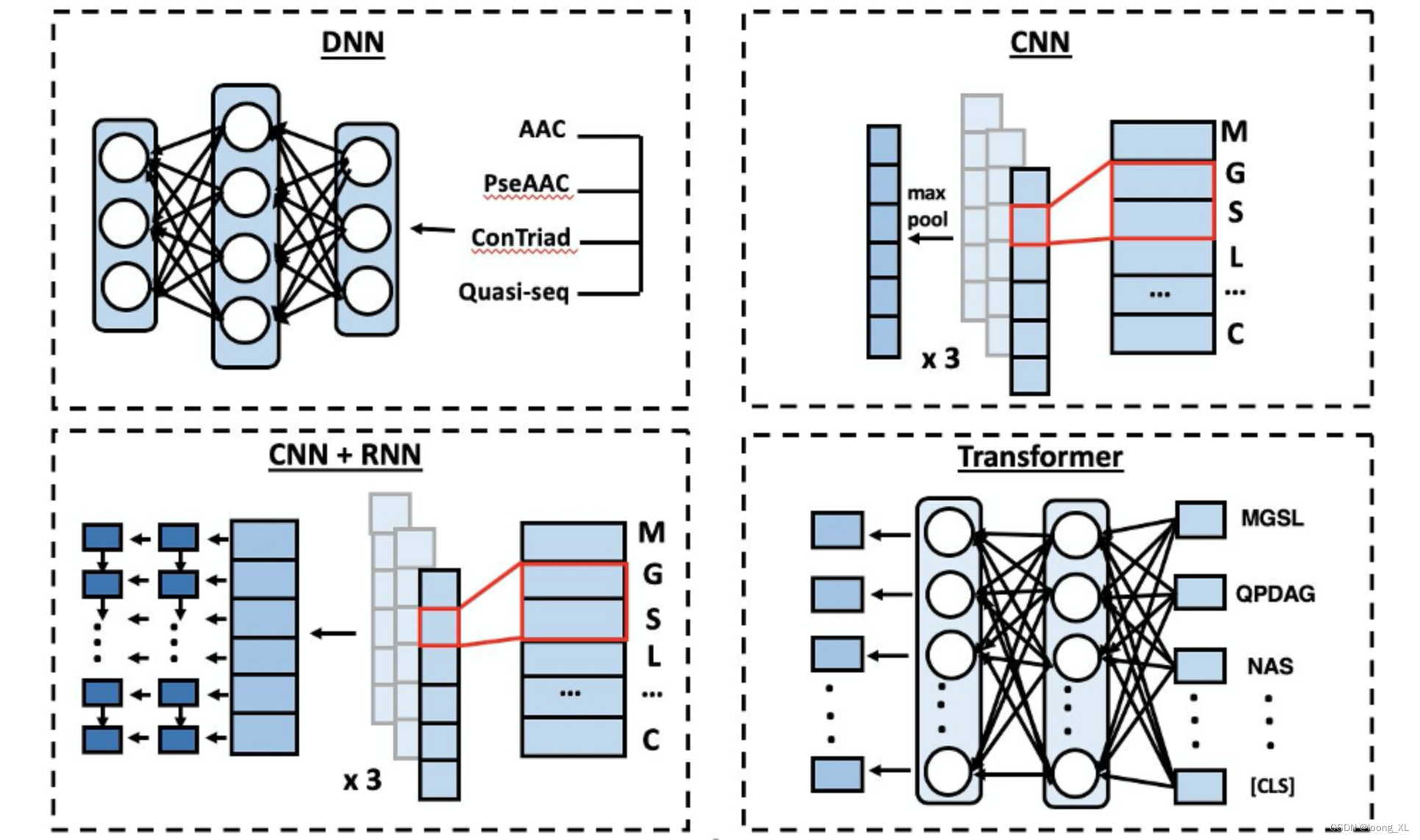
B 样条曲线的定义
p ( t ) = ∑ i = 0 n P i F i , k ( t ) p(t) = \sum_{i=0}{n} P_i F_{i, k}(t) p(t)=i=0∑nPiFi,k(t)
方程中 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个控制点, P i P_i Pi, i = 0 , 1 , ⋯ n i=0, 1, \cdots n i=0,1,⋯n 要用到 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个 k k k 次 B 样条基函数 F i , k F_{i, k} Fi,k, i = 0 , 1 , ⋯ , n i=0, 1, \cdots, n i=0,1,⋯,n, 节点矢量为 T = [ t 0 , t 1 , ⋯ , t n + k + 1 ] T = [t_0, t_1, \cdots, t_{n+k+1}] T=[t0,t1,⋯,tn+k+1]。 F i , k ( t ) F_{i, k}(t) Fi,k(t) 是由一个称为节点矢量的非递减的参数 t t t 的序列, t 0 ≤ t 1 ≤ ⋯ ≤ t n + k + 1 t_0 \leq t_1 \leq \cdots \leq t_{n+k+1} t0≤t1≤⋯≤tn+k+1所决定的 k k k 次分段多项式。
B 样条曲线划分为四种类型,均匀 B 样条曲线,准均匀B 样条曲线,分段 Bezier 曲线和非均匀 B 样条曲线。
定义域
给定 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个控制点, P i P_i Pi, i = 0 , 1 , ⋯ n i=0, 1, \cdots n i=0,1,⋯n, 相应地要求 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个 B 样条基函数 F i , k ( t ) F_{i, k}(t) Fi,k(t) 定义一个 k k k 次 B 样条曲线,这 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个 k k k 次 B 样条由节点矢量 T = [ t 0 , t 1 , ⋯ t n + k + 1 ] T = [t_0, t_1, \cdots t_{n+k+1}] T=[t0,t1,⋯tn+k+1] 所决定。
并非这个些节点矢量所包含的 n + k + 1 n+k +1 n+k+1 个区间都在该曲线的定义域,其中两端的各 k k k 个几点区间,不能作为 B 样条曲线的定义区间。
这是因为 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个控制点中最前的 n + 1 n+1 n+1 个顶点 P i P_i Pi, i = 0 , 1 , ⋯ k i=0,1, \cdots k i=0,1,⋯k 定义了 B 样条曲线的首段,其定义区间为 t ∈ [ t k , t k + 1 ] t\in [t_k, t_{k+1}] t∈[tk,tk+1] 往后移动一个顶点 P i P_i Pi, i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ k + 1 i=1, 2, \cdots k+1 i=1,2,⋯k+1 定义第二段,其定义区间为 t ∈ [ t k + , t k + 2 ] t \in [t_{k+}, t_{k+2}] t∈[tk+,tk+2] 依次类推,最后 k + 1 k+1 k+1 个顶点, P i P_i Pi, i = n − k , b − k − 1 , ⋯ n i=n-k, b-k-1, \cdots n i=n−k,b−k−1,⋯n 定义最后一段,其定义区间为 t ∈ [ t n , t n + 1 ] t\in[t_n, t_{n+1}] t∈[tn,tn+1], 因此,高于零次的 k k k 次B 样条曲线的定义域为
t ∈ [ t k , t n + 1 ] t \in [t_k, t_{n+1}] t∈[tk,tn+1]
三次均匀 B 样条曲线
{ F 0 , 3 ( t ) = 1 6 ( 1 − t ) 3 = ( − t 3 + 3 t 2 − 3 t + 1 ) F 1 , 3 ( t ) = 1 6 ( 3 t 3 − 6 t 2 + 4 ) F 2 , 3 ( t ) = 1 6 ( − 3 t 3 + 3 t 2 + 3 t + 1 ) F 3 , 3 ( t ) = 1 6 t 3 \begin{cases} F_{0,3}(t) = \frac{1}{6} (1-t)^3 = (-t^3 + 3t^2 -3t+1)\\ F_{1,3}(t) = \frac{1}{6} (3t^3 - 6t^2 +4)\\ F_{2,3}(t) = \frac{1}{6} (-3t^3 + 3t^2 + 3t +1) \\ F_{3,3}(t) = \frac{1}{6} t^3\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧F0,3(t)=61(1−t)3=(−t3+3t2−3t+1)F1,3(t)=61(3t3−6t2+4)F2,3(t)=61(−3t3+3t2+3t+1)F3,3(t)=61t3


三次 B 样条的几何性质
{ p ( 0 ) = 1 6 ( p 0 + 4 p 1 + p 2 ) = 1 3 ( p 0 + p 2 2 ) + 2 3 p 1 = 1 3 p m + 2 3 p 1 p ( 1 ) = 1 6 ( p 1 + 4 p 2 + p 3 ) = 1 3 ( p 1 + p 3 2 ) + 2 3 p 2 = 1 3 p n + 2 3 p 2 \begin{cases} p(0) = \frac{1}{6}(p_0 + 4 p_1 + p_2) = \frac{1}{3} (\frac{p_0 + p_2}{2}) + \frac{2}{3}p_1 = \frac{1}{3}p_m + \frac{2}{3}p_1\\ p(1) = \frac{1}{6}(p_1 + 4 p_2 + p_3) = \frac{1}{3} (\frac{p_1 + p_3}{2}) + \frac{2}{3}p_2 = \frac{1}{3}p_n + \frac{2}{3}p_2\\ \end{cases} {p(0)=61(p0+4p1+p2)=31(2p0+p2)+32p1=31pm+32p1p(1)=61(p1+4p2+p3)=31(2p1+p3)+32p2=31pn+32p2
{ p ′ ( 0 ) = 1 2 ( p 2 − p 0 ) p ′ ( 1 ) = 1 2 ( p 3 + p 1 ) \begin{cases} p'(0) = \frac{1}{2}(p_2 - p_0) \\ p'(1) = \frac{1}{2}(p_3 + p_1) \\ \end{cases} {p′(0)=21(p2−p0)p′(1)=21(p3+p1)
{ p ′ ′ ( 0 ) = p 0 − 2 p 1 + p 2 = 2 ( p 0 + p 2 2 − p ) = 2 ( p m − p 1 ) p ′ ′ ( 1 ) = p 1 − 2 p 2 + p 3 = 2 ( p 1 + p 3 2 − p 2 ) = 2 ( p n − p 2 ) \begin{cases} p''(0) = p_0 - 2p_1 + p_2 = 2(\frac{p_0 + p_2}{2} -p)= 2(p_m - p_1) \\ p''(1) = p_1 - 2p_2 + p_3 = 2(\frac{p_1 + p_3}{2} -p_2)= 2(p_n - p_2) \\ \end{cases} {p′′(0)=p0−2p1+p2=2(2p0+p2−p)=2(pm−p1)p′′(1)=p1−2p2+p3=2(2p1+p3−p2)=2(pn−p2)

#include <QWidget>
#include <QApplication>
#include <QPainter>
#include <QPointF>
#include <QPainterPath>const double knot[13] = {-3/6.0, -2/6.0, -1/6.0, 0.0, 1 / 6.0, 2 / 6.0, 3 / 6.0, 4 / 6.0, 5 / 6.0, 1.0, 7/ 6.0, 8/ 6.0, 9/6.0};double BasisFunctionValue(double t, int i, int k)
{double val1, val2, val;if (k == 0){if ((t >= knot[i]) && t < knot[i + 1]){return 1.0;}else{ // 其它return 0.0;}}if (k > 0){if (t < knot[i] || t > knot[i + k + 1]) {return 0.0; // 其它}else{double coffcient1, coffcient2; // 凸组合系数1 凸组合系数 2double denominator = 0.0; // 分母denominator = knot[i + k] - knot[i];if (denominator == 0.0){// 约定 0/0 = 0coffcient1 = 0.0;}else{coffcient1 = (t - knot[i]) / denominator; // 计算的第一项}denominator = knot[i + k + 1] - knot[i + 1]; // 递推公式第二项分母if (denominator == 0.0){// 约定 0/0 = 0coffcient2 = 0.0;}else{coffcient2 = (knot[i + k + 1] - t) / denominator; // 递推公式第二项}val1 = coffcient1 * BasisFunctionValue(t, i, k - 1); // 递推公式第一项的只val2 = coffcient2 * BasisFunctionValue(t, i+1, k - 1); // 递推公式第二项的只val = val1 + val2; // 基函数的值}}return val;
}void drawBSplineCure(QPainter* painter, const std::vector<QPointF>& P)
{// Set line colorQColor lineColor(0, 0, 255);// Set point colorQColor pointColor(255, 0, 0);QPainterPath bezierPath;QPen pen(lineColor);pen.setWidth(2); // Set the line width as neededpainter->setPen(pen);QPointF center(900, 600); // Center coordinatesint k = 3; // Degree of the B-spline curvefor (int i = k; i <= P.size() - k; ++i){double tStep = 0.01;for (double t = 0.0; t <= 1.0; t += tStep){QPointF p(0, 0); // Discrete pointfor (int j = 0; j < P.size(); ++j){double BValue = BasisFunctionValue(t, j, k);p += P[j] * BValue;}if (t == 0.0){bezierPath.moveTo(p + center);}else{bezierPath.lineTo(p + center);}painter->setPen(pointColor);painter->setBrush(Qt::NoBrush);painter->drawEllipse(p + center, 5, 5);}}painter->drawPath(bezierPath);
}void drawControlPolygon(QPainter* painter, std::vector<QPointF> P)
{QColor lineColor(0, 0, 0);QColor pointColor(0, 0, 255); // Blue color for pointsQPen polyLinePen(lineColor);painter->setPen(polyLinePen);QBrush pointBrush(pointColor);painter->setBrush(pointBrush);QPointF center(900, 600);QVector<QPointF> shiftedPoints;std::transform(P.begin(), P.end(), std::back_inserter(shiftedPoints),[center](const QPointF& point) { return point + center; });painter->drawPolyline(shiftedPoints.data(), shiftedPoints.size());for (const QPointF& point : shiftedPoints){painter->drawEllipse(point, 5, 5);}}std::vector<QPointF> getControlPoints(){std::vector<QPointF> controlPoints = {QPointF(-600, -50),QPointF(-500, 200), // 控制点QPointF(-160, 250),QPointF(-250, -300),QPointF(160, -200), // 控制点QPointF(200, 200),QPointF(600, 180),QPointF(700, -60), // 控制点QPointF(500, -200)};return controlPoints;
}class MyWidget : public QWidget {
public:MyWidget(QWidget* parent = nullptr) : QWidget(parent) {setFixedSize(1800, 1200);}protected:void paintEvent(QPaintEvent* event) override {Q_UNUSED(event);QPainter painter(this);painter.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing, true);std::vector<QPointF> controlPoints = getControlPoints();drawBSplineCure(&painter, controlPoints);drawControlPolygon(&painter, controlPoints);}public:int n = 8;int k = 3;};int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {QApplication app(argc, argv);MyWidget widget;widget.show();return app.exec();
}