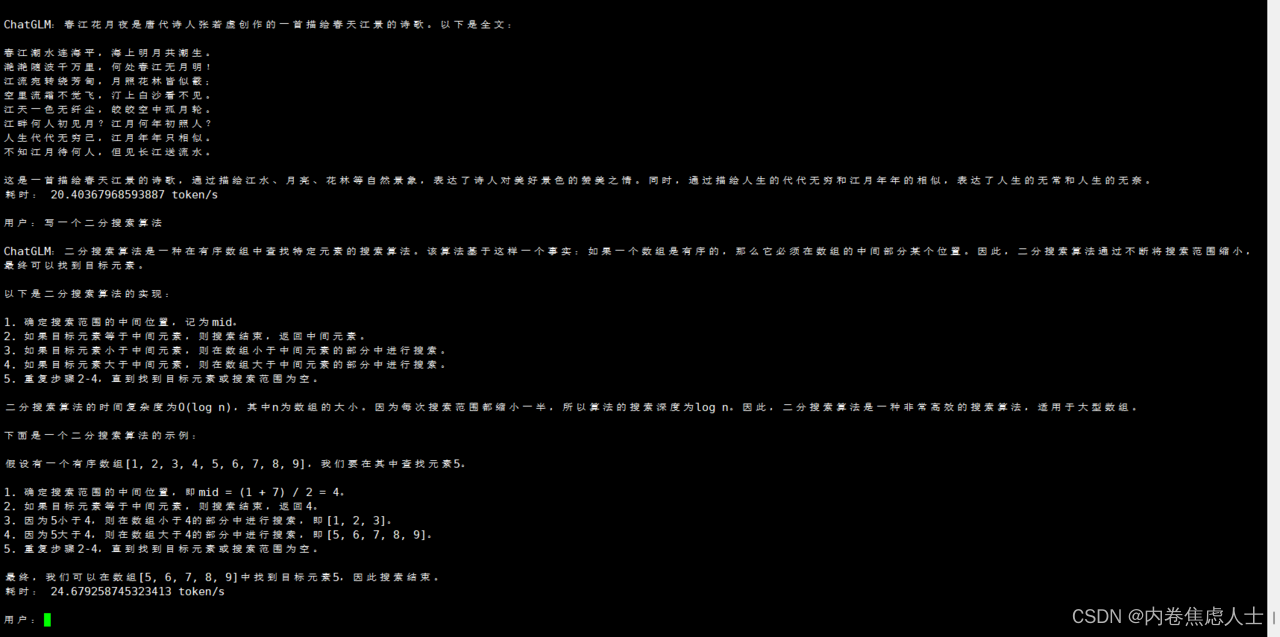
string的模拟实现
- msvc和g++下的string内存比较
- 成员变量
- 构造函数与析构函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值拷贝
- c_str、size和capacity函数以及重载[]、clear、expand_capacity
- 迭代器与遍历
- reserve
- push_back、append、+=
- insert
- 字符串比较运算符
- erase
- <<流提取 >>流插入
- resize
- find
- substr
- 源码地址
msvc和g++下的string内存比较
int main()
{std::string str1("HelloWorld");std::string str2("HelloWorldHelloWorld");cout << sizeof(str1) << " " << sizeof(str2) << endl;return 0;
}
在windows下使用vs2022 x64运行输出都为40字节:调试上面程序,在自动窗口中观察str1和str2的原始视图:

发现buf是包含16个字符的数组,里面存放了字符串,ptr为空,size和res分别为字符个数和容量。
而查看str2的字符串视图:发现buf数组为随机值,ptr指向实际的字符串,size和res分别为字符个数和容量。

MSVC编译器使用的string类内存模型可大概表示如下:
class string
{
private:char _buf[16];char* _ptr;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};
在64位下是40字节。
在g++11.4.0版本下运行结果为32字节。可以验证g++和vs2022的msvc都没有使用写拷贝:
int main() {string str1("hello world");string str2(str1);cout << (void *) str1.c_str() << endl; // 0xe8ce3ff7e0cout << (void *) str2.c_str() << endl; // 0xe8ce3ff7c0return 0;
}
现在我们来探索一下g++下的string内存结构:
int main() {std::string s1 = "HelloWorld";std::string s2 = "HelloWorldHelloWorld";std::string s3 = "HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld";cout << (void *) &s1 << " " << (void *) s1.c_str() << endl;cout << (void *) &s2 << " " << (void *) s2.c_str() << endl;cout << (void *) &s3 << " " << (void *) s3.c_str() << endl;return 0;
}
# 观察到s1的内存
0x00000000005ffe10 20 fe 5f 00 00 00 00 00 │ ·_····· │
0x00000000005ffe18 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │
0x00000000005ffe20 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 6f 72 │ HelloWor │
0x00000000005ffe28 6c 64 00 00 01 00 00 00 │ ld······ │
---------------------------------------------------------------------
# 观察到s2的内存
0x00000000005ffdf0 40 47 70 00 00 00 00 00 │ @Gp····· │
0x00000000005ffdf8 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │
0x00000000005ffe00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │
0x00000000005ffe08 45 15 8c be f7 7f 00 00 │ E······· │# s2指向的字符串
0x0000000000704740 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 6f 72 │ HelloWor │
0x0000000000704748 6c 64 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 │ ldHelloW │
0x0000000000704750 6f 72 6c 64 00 ab ab ab │ orld···· │
---------------------------------------------------------------------
# 观察到s3的内存
0x00000000005ffdd0 90 47 70 00 00 00 00 00 │ ·Gp····· │ # 指向字符数组
0x00000000005ffdd8 1e 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │ # size
0x00000000005ffde0 1e 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │ # capacity
0x00000000005ffdd8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ ········ │# s3指向的字符串
0x0000000000704790 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 6f 72 │ HelloWor │
0x0000000000704798 6c 64 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 │ ldHelloW │
0x00000000007047a0 6f 72 6c 64 48 65 6c 6c │ orldHell │
0x00000000007047a8 6f 57 6f 72 6c 64 00 ab │ oWorld·· │
观察上面3个string对象我们知道,第一个成员是char*的_str,指向保存的字符串地址。第二个成员是size。如果是小于等于15个字符,则后面16个字节保存短字符串。如果是大于15个字符的字符串,则第三个成员保存capacity容量,第四个成员则没有意义。
// 短字符串
class string {
private:char* _str;size_t _size;char _buf[16];
};// 长字符串
class string {
private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;size_t _reserve;
};
验证猜想:
int main() {std::string s1 = "HelloWorldHello";std::string s2 = "HelloWorldHelloWorld";std::string s3 = "HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld";cout << (void *) &s1 << " " << (void *) s1.c_str() << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << (void *) &s2 << " " << (void *) s2.c_str() << " " << s2.size() << " " << s2.capacity() << endl;cout << (void *) &s3 << " " << (void *) s3.c_str() << " " << s3.size() << " " << s3.capacity() << endl;s1.push_back('*'); // 插入数据扩容cout << (void *) &s1 << " " << (void *) s1.c_str() << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;s3.push_back('*'); // 插入数据扩容cout << (void *) &s3 << " " << (void *) s3.c_str() << " " << s3.size() << " " << s3.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}
/*
0xdd031ffde0 0xdd031ffdf0 15 15 # 扩容前s1
0xdd031ffdc0 0x2a486af25b0 20 20 # s2
0xdd031ffda0 0x2a486af6820 30 30 # s3
0xdd031ffde0 0x2a486af7860 16 30 # 扩容后s1
0xdd031ffda0 0x2a486af7890 31 60 # 扩容后s3
*/
成员变量
为了简单模拟字符串,我们不像g++和msvc一样保留对短字符串的处理,我们定义如下几个变量:
namespace my_std
{class string{private:char* _str; // 字符串数组size_t _size;size_t _capacity;static const size_t npos;};const size_t string::npos = -1;
}
// size:当前有效字符的个数
// capacity:最大能容纳的有效字符的个数,不包括\0
在自己的命名空间 my_std 中实现,防止与std冲突。
下面我们将模拟g++下的string,可以对照g++的string输出作为参考。
构造函数与析构函数
std标准库中string构造函数的使用:
int main() {std::string s1 = "HelloWorldHello";std::string s2 = "HelloWorldHelloWorld";std::string s3 = "HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld";cout << (void *) &s1 << " " << (void *) s1.c_str() << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << (void *) &s2 << " " << (void *) s2.c_str() << " " << s2.size() << " " << s2.capacity() << endl;cout << (void *) &s3 << " " << (void *) s3.c_str() << " " << s3.size() << " " << s3.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}
/*
0x84b4fff660 0x84b4fff670 15 15
0x84b4fff640 0x23a3caa25b0 20 20
0x84b4fff620 0x23a3caa6820 30 30
*/
我们模拟实现如下:这里的默认参数旨在一个string空对象的正确打印。
string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str))
{_capacity = (_size <= 15) ? 15 : _size;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);
}
如果是短字符串,我们将容量设置为15。如果是长字符串,容量设置为实际长度。
这里需要注意strcpy会拷贝 '\0' 。
下面是析构函数实现:因为构造函数中我们保证了容量至少是15,并且下面的实现resize中即使缩容也不会影响capacity实际容量,因此 _str不会为空。可以不加 _str 为空的判断。
~string()
{delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;_size = _capacity = 0;
}
拷贝构造函数
先看标准库中string的使用:
void test() {std::string str = "helloworldhelloworld";cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << " " << (void *) str.c_str() << endl; // 20 20 0x18ff84f25b0str.push_back('#');cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << " " << (void *) str.c_str() << endl; // 21 40 0x18ff84f7830std::string str1 = str;cout << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << " " << (void *) str1.c_str() << endl; // 21 21 0x18ff84f25b0}int main() {test();return 0;
}
可以观察到拷贝构造的str1的size和capacity都等于str的size,因此可以实现如下:
string(const string& s)
{// apply the new space_size = s._size;_capacity = s._size;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];// copy strstrcpy(_str, s.c_str());
}
赋值拷贝
先看g++下的赋值拷贝:
void test() {string str = "helloworldhelloworld";cout << "str:" << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << " " << (void *) str.c_str() << endl;str.push_back('#');cout << "str插入#:" << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << " " << (void *) str.c_str() << endl;string str1;cout << "str1扩容前:" << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << " " << (void *) str1.c_str() << endl;string str2 = "Hello";cout << str2.size() << " " << str2.capacity() << " " << (void *) str2.c_str() << endl;// 短字符串 原地复制str1 = str2;cout << "str1短字符串原地复制:" << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << " " << (void *) str1.c_str() << endl;// 长字符串 两倍扩容str1 = str;cout << "str1长字符串两倍扩容:" << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << " " << (void *) str1.c_str() << endl;str += "helloworldhelloworld";cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << " " << (void *) str.c_str() << endl;// 长字符串 两倍扩容不够 扩容到s.size()string str3;cout << "str3扩容前:" << str3.size() << " " << str3.capacity() << " " << (void *) str3.c_str() << endl;str3 = str;cout << "str3扩容后:" << str3.size() << " " << str3.capacity() << " " << (void *) str3.c_str() << endl;}int main() {test();return 0;
}
/*
str:20 20 0x17f061725b0
str插入#:21 40 0x17f06177830
str1扩容前:0 15 0x4dc55ffbc0
5 15 0x4dc55ffba0
str1短字符串原地复制:5 15 0x4dc55ffbc0
str1长字符串两倍扩容:21 30 0x17f061725b0
41 80 0x17f06177870
str3扩容前:0 15 0x4dc55ffb80
str3扩容后:41 41 0x17f06177830
*/
在等号赋值的过程中,如果赋值的字符串较短,则在原来的内存空间中直接复制。否则发生扩容,如果两倍扩容不够,则扩容到s._size。
string& operator=(const string& s)
{if (&s != this){if (s._size > _capacity){// 两倍扩容不够,则扩容到s._size_capacity = (s._size > 2 * _capacity) ? s._size : 2 * _capacity;delete[] _str;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];}strcpy(_str, s._str);_size = s._size;}return *this;
}
下面写了reserve函数之后可以修改为:代码上更简洁,但是多了一次拷贝。
string& operator=(const string& s)
{if (&s != this){reserve(s._size);strcpy(_str, s._str);_size = s._size;}return *this;
}
c_str、size和capacity函数以及重载[]、clear、expand_capacity
const char* c_str() const
{return _str;
}size_t size() const
{return _size;
}size_t capacity() const
{return _capacity;
}char& operator[](size_t pos)
{assert(pos < _size);return _str[pos];
}const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{assert(pos < _size);return _str[pos];
}
这里还专门针对const string对象写了重载[]的const成员函数。
void expand_capacity(std::string &str) {size_t old_capacity = str.capacity();cout << "init capacity: " << old_capacity << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {str.append("h");//str.push_back('h');if (old_capacity != str.capacity()) {old_capacity = str.capacity();cout << "expand capacity: " << old_capacity << endl;}}
}int main() {string str;expand_capacity(str);cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << endl;str.clear();cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}
/*
init capacity: 15
expand capacity: 30
expand capacity: 60
expand capacity: 120
100 120
0 120
*/
clear函数将size置0,容量保留:
void clear()
{_str[0] = '\0';_size = 0;
}
迭代器与遍历
class string
{
public:typedef char* iterator;iterator begin(){return _str;}iterator end(){return _str + _size;}
}
测试:
int main()
{// 遍历测试string str1("hello world");cout << str1.c_str() << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < str1.size(); ++i){cout << str1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;string::iterator it = str1.begin();while (it != str1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto ch : str1){cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
reserve
void test() {string s = "hello";cout << s.size() << " " << s.capacity() << " " << s << endl;s.reserve(5);cout << "(05)" << s.size() << " " << s.capacity() << " " << s << endl;s.reserve(18);cout << "(18)" << s.size() << " " << s.capacity() << " " << s << endl;s.reserve(61);cout << "(61)" << s.size() << " " << s.capacity() << " " << s << endl;
}int main() {test();return 0;
}
/*
5 15 hello
(05)5 15 hello
(18)5 30 hello
(61)5 61 hello
*/
标准库中的reserve函数的使用,reserve参数如果比capacity小,则没有变化。reserve参数比capacity大,发生扩容,如果两倍扩容不够,则扩容到输入的参数。
void reserve(size_t n)
{if (n > _capacity){// 两倍扩容不够,则扩容到n_capacity = (n > 2 * _capacity) ? n : 2 * _capacity;char* tmp = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(tmp, _str);delete[] _str;_str = tmp;}
}
push_back、append、+=
void push_back(char ch)
{/*if (_size == _capacity){reserve(_capacity * 2);}*/reserve(_size + 1);_str[_size++] = ch;_str[_size] = '\0';
}void append(const char* str)
{size_t len = strlen(str);reserve(_size + len);strcpy(_str + _size, str);_size += len;
}string& operator+=(const char* str)
{append(str);return *this;
}string& operator+=(char ch)
{push_back(ch);return *this;
}
值得说的是,有了上面的reserve,我们在扩容时,代码上就可以更简洁,不用进行 _size == _capacity 的判断:
void push_back(char ch)
{/*if (_size == _capacity){reserve(_capacity * 2);}*/reserve(_size + 1);_str[_size++] = ch;_str[_size] = '\0';
}
insert
要从 '\0' 开始向后移动,使用时注意while循环对size_t类型的判断,避免导致死循环:
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{assert(pos <= _size);reserve(_size + 1);/*size_t end = _size; // from '\0' startwhile (end >= pos) // when pos=0, while loop will not exit{_str[end + 1] = _str[end];--end;}*/size_t end = _size + 1; // from '\0' next pos startwhile (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end - 1];--end;}_str[pos] = ch;_size++;
}
下面是插入字符串str:
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{assert(pos <= _size);size_t len = strlen(str);reserve(_size + len);// 向后挪动数据size_t end = _size + 1; // from '\0' next pos startwhile (end > pos){_str[end - 1 + len] = _str[end - 1];--end;}// 拷贝数据/*for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){_str[i + pos] = str[i];}*/strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);_size += len;
}
这里使用 strncpy 指定拷贝的字节数。
字符串比较运算符
bool operator<(const string& s) const
{return strcmp(_str, s._str) < 0;
}bool operator==(const string& s) const
{return strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0;
}bool operator<=(const string& s) const
{return *this < s || *this == s;
}bool operator>(const string& s) const
{return !(*this <= s);
}bool operator>=(const string& s) const
{return !(*this < s);
}bool operator!=(const string& s) const
{return !(*this == s);
}
erase
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{assert(pos < _size);if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size){// 从pos删除到结尾_str[pos] = '\0';_size = pos;}else{// 从pos删除len长度个strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);_size -= len;}
}
验证:
int main()
{string str1("helloworld");cout << str1 << " " << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << endl;str1.erase(6);cout << str1 << " " << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << endl;str1.erase(0);cout << str1 << " " << str1.size() << " " << str1.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}/*
helloworld 10 15
hellow 6 150 15
*/
<<流提取 >>流插入
将<<和 >> 重载为全局函数,放在my_std命名空间中:
std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& out, const string& s)
{out << s.c_str();return out;
}
使用 istream::get() 方法,每次读取一个字符进行插入。
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, string& s)
{s.clear();char ch;// in >> ch;ch = in.get(); // istream::get()while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){s += ch;ch = in.get();}return in;
}
每次字符串执行+= s += ch; 效率太低,我们加入buf,提高插入的效率:
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, string& s)
{s.clear();char buf[128] = { '\0' };size_t i = 0;char ch;// in >> ch;ch = in.get(); // istream::get()while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){//s += ch;if (i == 127){s += buf;i = 0;}buf[i] = ch;i++;ch = in.get();}if (i >= 0){buf[i] = '\0';s += buf;}return in;
}
resize
cplusplus的resize
void resize (size_t n);
void resize (size_t n, char c);
int main()
{//test_main();string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(5);cout << s1 << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(50, 'x');cout << s1 << " " << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}
/*
hello world 11 15
hello 5 15
helloxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 50 50
*/
假设有字符串 str = "hello world" 的size为11,capacity为10。
针对以下三种参数调整空间:
1.当n=5时,也就是n<=size,可以直接令 str[5] = '\0',size变为5,容量不变。
2.当n=15时,也就是n>size,需要插入数据,直接调用reserve扩容为n个空间,然后将剩下的插入指定字符c。
我们自己实现的resize:
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{if (n <= _size){_str[n] = '\0';_size = n;}else{reserve(n);while (_size < n){_str[_size] = ch;++_size;}_str[_size] = '\0';}
}
find
find返回指定字符或者字符串从pos开始的下标:
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0)
{for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++){if (_str[i] == ch){return i;}}return npos;
}size_t find(const char* sub, size_t pos = 0)
{const char* p = strstr(_str + pos, sub);if (p){return p - _str;}else{return npos;}
}
substr
cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
实现如下:
string substr(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{string s;size_t end = pos + len;if (len == npos || end >= _size) // 取到结尾{// len为字串的sizelen = _size - pos; // end >=_sizeend = _size;}s.reserve(len);for (size_t i = pos; i < end; i++){s += _str[i];}return s;
}
值得说的是从pos开始指定取的len如果太长超过结尾,则需要修正取到的len的大小。
源码地址
https://github.com/shlyyy/stl/blob/main/my_string.h
https://gitee.com/shlyyy/stl/blob/master/my_string.h