在Java技术体系中,如果想要在不改变已有代码逻辑的情况下,对已有的函数进行功能增强,一般可以使用两种方式,如AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),即面向切面编程,以及代理模式,如使用JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 动态代理。例如Mybatis的源码中同时使用了JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 动态代理,但是对于Mapper接口是使用JDK动态代理模式。在JetCache则使用AOP的方式,在spring环境下,使用@Cached注解可以为一个方法添加缓存,@CacheUpdate用于更新缓存,@CacheInvalidate用于移除缓存元素。注解可以加在接口上也可以加在类上,加注解的类必须是一个spring bean,例如:
public interface UserService {@Cached(name="userCache.", key="#userId", expire = 3600)User getUserById(long userId);@CacheUpdate(name="userCache.", key="#user.userId", value="#user")void updateUser(User user);@CacheInvalidate(name="userCache.", key="#userId")void deleteUser(long userId);
}Spring中AOP代理由Spring的IOC容器负责生成、管理,其依赖关系也由IOC容器负责管理。因此,AOP代理可以直接使用容器中的其它bean实例作为目标,这种关系可由IOC容器的依赖注入提供。Spring创建代理的规则为:
- 默认使用Java动态代理来创建AOP代理,这样就可以为任何接口实例创建代理了
- 当需要代理的类不是代理接口的时候,Spring会切换为使用CGLIB代理,也可强制使用CGLIB
CacheAdvisor类

切面选择AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor实现,切点是通过StaticMethodMatcherPointcut匹配包含Cached、CacheUpdate和CacheInvalidate注解的方法。通过实现MethodInterceptor接口实现操作相应函数的增强逻辑。CacheAdvisor是AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor的子类,源码如下:
/*** 缓存顾问类,继承自AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor。*/
public class CacheAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {/*** 缓存顾问的bean名称。*/public static final String CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME = "jetcache2.internalCacheAdvisor";@Autowiredprivate ConfigMap cacheConfigMap; // 注入缓存配置映射private String[] basePackages; // 基础包路径/*** 获取Pointcut对象。** @return Pointcut对象*/@Overridepublic Pointcut getPointcut() {CachePointcut pointcut = new CachePointcut(basePackages); // 创建CachePointcut对象pointcut.setCacheConfigMap(cacheConfigMap); // 设置CachePointcut的缓存配置映射return pointcut;}/*** 设置缓存配置映射。** @param cacheConfigMap 缓存配置映射*/public void setCacheConfigMap(ConfigMap cacheConfigMap) {this.cacheConfigMap = cacheConfigMap;}/*** 设置基础包路径。** @param basePackages 基础包路径*/public void setBasePackages(String[] basePackages) {this.basePackages = basePackages;}
}
在上面的类中会设置JetCache扫描的基础包路径,缓存配置信息。并实现了PointcutAdvisor接口的getPointcut()函数,PointcutAdvisor接口是Advisor的子接口,Advisor是Spring AOP的顶层抽象,用来管理Advice和Pointcut,所以毫无疑问PointcutAdvisor接口也是用来管理Advice和Pointcut的。PointcutAdvisor源码如下:
/*** 所有由切点驱动的Advisor的超接口。* 这涵盖了几乎所有除了引入Advisor之外的Advisor,* 对于方法级别的匹配不适用。** @author Rod Johnson*/
public interface PointcutAdvisor extends Advisor {/*** 获取驱动该顾问的Pointcut。*/Pointcut getPointcut();}
CachePointcut类
在上面的CacheAdvisor类中实现了PointcutAdvisor接口的getPointcut()函数,并创建了CachePointcut类的实例。接下来,我们需要先看一下CachePointcut的类图。
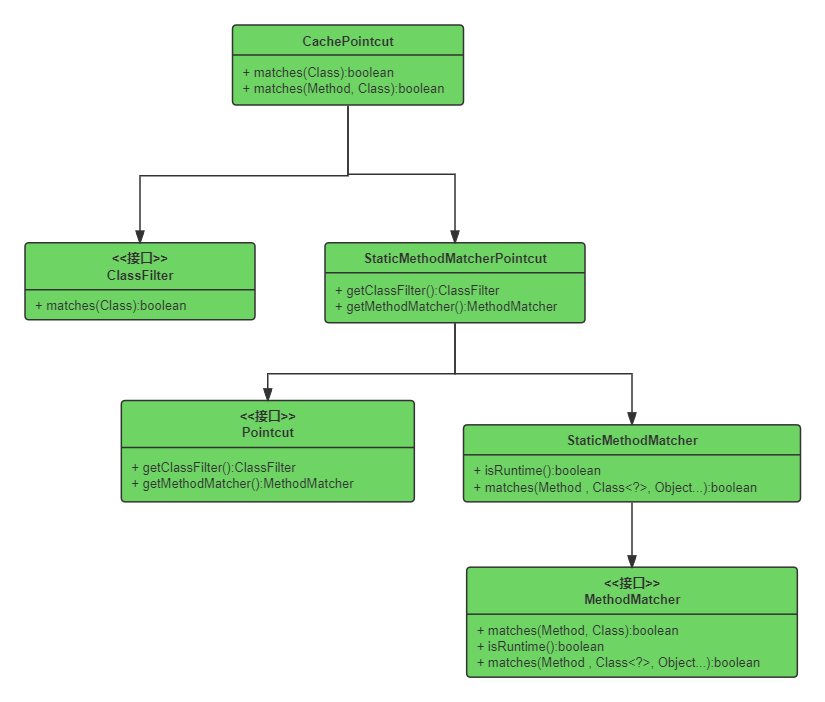
Pointcut接口
Pointcut接口有两个接口方法,分别用于加载ClassFilter和MethodMatcher接口实例,并通过这两个实例实现切入点的逻辑功能。
/*** 核心Spring切点抽象类。** <p>切点由{@link ClassFilter}和{@link MethodMatcher}组成。* 这些基本概念和一个Pointcut可以通过{@link org.springframework.aop.support.ComposablePointcut}组合起来。** @author Rod Johnson* @see ClassFilter* @see MethodMatcher* @see org.springframework.aop.support.Pointcuts* @see org.springframework.aop.support.ClassFilters* @see org.springframework.aop.support.MethodMatchers*/
public interface Pointcut {/*** 返回该点切的ClassFilter。* @return ClassFilter(永远不会为null)*/ClassFilter getClassFilter();/*** 返回该点切的MethodMatcher。* @return MethodMatcher(永远不会为null)*/MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();/*** 常规Pointcut实例,始终匹配。*/Pointcut TRUE = TruePointcut.INSTANCE;}
ClassFilter接口
ClassFilter的matches方法定义判断某个类是否需要被纳入切面,源码如下:
/*** 过滤器,用于限制目标类集中对切点或引入的匹配。** <p>可用于作为{@link Pointcut}的一部分或针对整个{@link IntroductionAdvisor}的目标。** <p>此类的具体实现通常应提供适当的{@link Object#equals(Object)}和{@link Object#hashCode()}* 的实现,以便允许在缓存场景中使用过滤器 - 例如,在由CGLIB生成的代理中。** @author 罗德·约翰逊* @see Pointcut* @see MethodMatcher*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ClassFilter {/*** 是否应应用切点到给定的接口或目标类?* @param clazz 候选目标类* @return 是否应应用给定的目标类*/boolean matches(Class<?> clazz);/*** 匹配所有类的类过滤器的规范实例。*/ClassFilter TRUE = TrueClassFilter.INSTANCE;
}
MethodMatcher接口
MethodMatcher的matches方法则是定义判断某个方法是否需要被纳入切面。MethodMatcher源码如下:
/*** 是`Pointcut`的一部分:用于检查目标方法是否有资格应用建议。** <p>MethodMatcher可以静态地(`statically`)或动态地(`dynamically`)进行评估(`evaluated`)。* 静态匹配涉及方法和(可能)方法属性。动态匹配还提供了特定调用的参数,并且在运行Pointcut上的先前建议时产生的任何效果。** <p>如果实现从其`#isRuntime()`方法返回`false`,则可以进行静态评估,并且此方法的所有调用的参数将相同,无论其参数如何。这意味着如果`#isRuntime()`方法返回`false`,则3个参数的`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class, Object[])`方法将永远不会被调用。** <p>如果实现从其2个参数的`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class)`方法返回`true`并且`#isRuntime()`方法返回`true`,则会在每个相关建议的潜在执行之前立即调用3个参数的`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class, Object[])`方法,以决定是否应运行建议。之前运行的所有建议,例如拦截器链中的早期拦截器,都已经运行,因此他们在参数或线程局部状态中产生的任何状态更改都将可用。** <p>此接口的 concrete 实现通常应适当地提供`Object#equals(Object)`和`Object#hashCode()`,以便允许matcher用作缓存场景中的matcher——例如,在由CGLIB生成的代理中。** @author Rod Johnson* @since 11.11.2003* @see Pointcut* @see ClassFilter*/
public interface MethodMatcher {/*** 执行静态检查,以确定给定方法是否匹配。* <p>如果此方法返回`false`或`#isRuntime()`方法返回`false`,则不会进行运行时检查(即不会调用`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class, Object[])`)。* @param method 候选方法* @param targetClass 目标类* @return 如果此方法静态匹配,则返回true*/boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass);/*** 是否为MethodMatcher动态,即必须在2个参数的matches方法返回true的情况下,最终调用`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class, Object[])`方法进行运行时检查?* <p>可以在创建AOP代理时调用,无需在每次方法调用之前再次调用。* @return 如果静态匹配通过,则在3个参数的`#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class, Object[])`方法上的运行时匹配是否需要*/boolean isRuntime();/*** 检查此方法是否有运行时(动态)匹配,该方法必须静态匹配。* <p>仅在2个参数的matches方法针对给定方法和目标类返回true,并且`#isRuntime()`方法返回true时调用该方法。在建议运行之前立即调用,之前在建议链中的任何早期建议已经运行。* @param method 候选方法* @param targetClass 目标类* @param args 方法的方法* @return 是否存在运行时匹配* @see MethodMatcher#matches(Method, Class)*/boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, Object... args);/*** 与所有方法都匹配的规范实例。*/MethodMatcher TRUE = TrueMethodMatcher.INSTANCE;}
在上面的接口中分别支持对类的匹配和函数的匹配,那我们先看一下CachePointcut中对于类的匹配,源码如下:
public class CachePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements ClassFilter {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CachePointcut.class);private ConfigMap cacheConfigMap;private String[] basePackages;/*** 构造函数** @param basePackages 基础包名数组*/public CachePointcut(String[] basePackages) {setClassFilter(this);this.basePackages = basePackages;}/*** 判断类是否匹配** @param clazz 类对象* @return 是否匹配*/@Overridepublic boolean matches(Class clazz) {boolean b = matchesImpl(clazz);logger.trace("check class match {}: {}", b, clazz);return b;}/*** 实现类是否匹配** @param clazz 类对象* @return 是否匹配*/private boolean matchesImpl(Class clazz) {if (matchesThis(clazz)) {return true;}Class[] cs = clazz.getInterfaces();if (cs != null) {for (Class c : cs) {if (matchesImpl(c)) {return true;}}}if (!clazz.isInterface()) {Class sp = clazz.getSuperclass();if (sp != null && matchesImpl(sp)) {return true;}}return false;}/*** 判断类是否匹配** @param clazz 类对象* @return 是否匹配*/public boolean matchesThis(Class clazz) {String name = clazz.getName();if (exclude(name)) {return false;}return include(name);}/*** 判断类是否包含在基础包名数组中** @param name 类名* @return 是否包含*/private boolean include(String name) {if (basePackages != null) {for (String p : basePackages) {if (name.startsWith(p)) {return true;}}}return false;}/*** 判断类是否排除** @param name 类名* @return 是否排除*/private boolean exclude(String name) {if (name.startsWith("java")) {return true;}if (name.startsWith("org.springframework")) {return true;}if (name.indexOf("$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$") >= 0) {return true;}if (name.indexOf("$$FastClassBySpringCGLIB$$") >= 0) {return true;}return false;}}
上面的代码逻辑还是比较简单的,主要是判断类的包名是否以配置的JetCache扫描的包路径开头,如果以配置的JetCache扫描的包路径开头就匹配上了。
接下来的matches(Method, Class)函数用于匹配对应类的相应函数,主要是带有注解Cached、CacheUpdate和CacheInvalidate的方法,源码如下:
/*** 判断给定的方法是否与目标类匹配** @param method 待判断的方法* @param targetClass 目标类* @return 如果匹配则返回true,否则返回false*/@Overridepublic boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) {boolean b = matchesImpl(method, targetClass);if (b) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("check method match true: method={}, declaringClass={}, targetClass={}",method.getName(),ClassUtil.getShortClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName()),targetClass == null ? null : ClassUtil.getShortClassName(targetClass.getName()));}} else {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("check method match false: method={}, declaringClass={}, targetClass={}",method.getName(),ClassUtil.getShortClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName()),targetClass == null ? null : ClassUtil.getShortClassName(targetClass.getName()));}}return b;}/*** 实现方法匹配的逻辑** @param method 待判断的方法* @param targetClass 目标类* @return 如果匹配则返回true,否则返回false*/private boolean matchesImpl(Method method, Class targetClass) {if (!matchesThis(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return false;}if (exclude(targetClass.getName())) {return false;}String key = getKey(method, targetClass);CacheInvokeConfig cac = cacheConfigMap.getByMethodInfo(key);if (cac == CacheInvokeConfig.getNoCacheInvokeConfigInstance()) {return false;} else if (cac != null) {return true;} else {cac = new CacheInvokeConfig();CacheConfigUtil.parse(cac, method);String name = method.getName();Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();parseByTargetClass(cac, targetClass, name, paramTypes);if (!cac.isEnableCacheContext() && cac.getCachedAnnoConfig() == null &&cac.getInvalidateAnnoConfigs() == null && cac.getUpdateAnnoConfig() == null) {cacheConfigMap.putByMethodInfo(key, CacheInvokeConfig.getNoCacheInvokeConfigInstance());return false;} else {cacheConfigMap.putByMethodInfo(key, cac);return true;}}}
在上面的matchesImpl函数中会执行如下几个步骤:
1、调用matchesThis函数判断指定的类的包名是否以配置的JetCache扫描的包路径开头,这是为了排除没有JetCache不会扫描的类。
2、调用exclude函数用于排除Java和Spring自带的类名,以及使用CGLIB动态代理生成的类。
3、根据类和函数信息生成唯一键Key,然后查询缓存cacheConfigMap中对应的缓存调用配置信息。
4、如果cacheConfigMap缺少指定类的指定函数的缓存调用配置信息,则构建CacheInvokeConfig实例,并解析函数的注解信息。
CacheConfigUtil.parse函数会解析函数上的Cached、CacheUpdate和CacheInvalidate注解上的信息。其源码如下:
/*** 解析方法上的注解,并将解析结果存入CacheInvokeConfig对象* @param cac CacheInvokeConfig对象,用于存储解析结果* @param method 待解析的方法* @return 是否存在有效的注解*/public static boolean parse(CacheInvokeConfig cac, Method method) {boolean hasAnnotation = false;CachedAnnoConfig cachedConfig = parseCached(method);if (cachedConfig != null) {cac.setCachedAnnoConfig(cachedConfig);hasAnnotation = true;}boolean enable = parseEnableCache(method);if (enable) {cac.setEnableCacheContext(true);hasAnnotation = true;}List<CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig> invalidateAnnoConfigs = parseCacheInvalidates(method);if (invalidateAnnoConfigs != null) {cac.setInvalidateAnnoConfigs(invalidateAnnoConfigs);hasAnnotation = true;}CacheUpdateAnnoConfig updateAnnoConfig = parseCacheUpdate(method);if (updateAnnoConfig != null) {cac.setUpdateAnnoConfig(updateAnnoConfig);hasAnnotation = true;}if (cachedConfig != null && (invalidateAnnoConfigs != null || updateAnnoConfig != null)) {throw new CacheConfigException("@Cached不能同时存在@CacheInvalidate或@CacheUpdate: " + method);}return hasAnnotation;}
在上面的方法中,第一步会调用函数parseCached来解析注解@Cached中的信息,源码如下:
private static CachedAnnoConfig parseCached(Method m) {Cached anno = m.getAnnotation(Cached.class);if (anno == null) {return null;}CachedAnnoConfig cc = new CachedAnnoConfig();cc.setArea(anno.area());cc.setName(anno.name());cc.setCacheType(anno.cacheType());cc.setSyncLocal(anno.syncLocal());cc.setEnabled(anno.enabled());cc.setTimeUnit(anno.timeUnit());cc.setExpire(anno.expire());cc.setLocalExpire(anno.localExpire());cc.setLocalLimit(anno.localLimit());cc.setCacheNullValue(anno.cacheNullValue());cc.setCondition(anno.condition());cc.setPostCondition(anno.postCondition());cc.setSerialPolicy(anno.serialPolicy());cc.setKeyConvertor(anno.keyConvertor());cc.setKey(anno.key());cc.setDefineMethod(m);CacheRefresh cacheRefresh = m.getAnnotation(CacheRefresh.class);if (cacheRefresh != null) {RefreshPolicy policy = parseRefreshPolicy(cacheRefresh);cc.setRefreshPolicy(policy);}CachePenetrationProtect protectAnno = m.getAnnotation(CachePenetrationProtect.class);if (protectAnno != null) {PenetrationProtectConfig protectConfig = parsePenetrationProtectConfig(protectAnno);cc.setPenetrationProtectConfig(protectConfig);}return cc;}异步调用缓存保护注解@CachePenetrationProtect和缓存刷新注解@CacheRefresh仅支持使用@Cached的函数上可用,所以JetCache就将其在一个函数中实现了,不过分开实现可能会更合理。
第二步就会调用parseEnableCache函数解析@EnableCache注解,如果相应的函数存在@EnableCache注解,则CacheInvokeConfig实例的enableCacheContext字段为true。如果在需要使用缓存的函数上加了@Cached注解后再加@EnableCache注解可能会嫌麻烦,实际上不在函数上加注解@EnableCache也能启用缓存,后面再详细介绍。
第三步开始调用parseCacheInvalidates函数解析@CacheInvalidate注解和@CacheInvalidateContainer注解,@CacheInvalidateContainer注解中可以定义多个@CacheInvalidate。而一个函数只能有一个@CacheInvalidate注解,当一个函数的修改需要将多种缓存数据清除时就可以选择@CacheInvalidateContainer注解,当然@CacheInvalidate注解中的multi可以支持清空多个key的缓存,但需要在key字段中指定获取多个删除key的表达式。源码如下:
public static List<CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig> parseCacheInvalidates(Method m) {List<CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig> annoList = null;CacheInvalidate ci = m.getAnnotation(CacheInvalidate.class);if (ci != null) {annoList = new ArrayList<>(1);annoList.add(createCacheInvalidateAnnoConfig(ci, m));} else {CacheInvalidateContainer cic = m.getAnnotation(CacheInvalidateContainer.class);if (cic != null) {CacheInvalidate[] cacheInvalidates = cic.value();annoList = new ArrayList<>(cacheInvalidates.length);for (CacheInvalidate cacheInvalidate : cacheInvalidates) {annoList.add(createCacheInvalidateAnnoConfig(cacheInvalidate, m));}}}return annoList;}第四步就是调用parseCacheUpdate函数解析@CacheUpdate注解,源码如下:
private static CacheUpdateAnnoConfig parseCacheUpdate(Method m) {CacheUpdate anno = m.getAnnotation(CacheUpdate.class);if (anno == null) {return null;}CacheUpdateAnnoConfig cc = new CacheUpdateAnnoConfig();cc.setArea(anno.area());cc.setName(anno.name());if (cc.getName() == null || cc.getName().trim().equals("")) {throw new CacheConfigException("name is required for @CacheUpdate: " + m.getClass().getName() + "." + m.getName());}cc.setKey(anno.key());cc.setValue(anno.value());if (cc.getValue() == null || cc.getValue().trim().equals("")) {throw new CacheConfigException("value is required for @CacheUpdate: " + m.getClass().getName() + "." + m.getName());}cc.setCondition(anno.condition());cc.setMulti(anno.multi());cc.setDefineMethod(m);return cc;}
5、调用parseByTargetClass函数获取指定类的父类或接口上的缓存配置信息。源码如下:
private void parseByTargetClass(CacheInvokeConfig cac, Class<?> clazz, String name, Class<?>[] paramTypes) {if (!clazz.isInterface() && clazz.getSuperclass() != null) {parseByTargetClass(cac, clazz.getSuperclass(), name, paramTypes);}Class<?>[] intfs = clazz.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> it : intfs) {parseByTargetClass(cac, it, name, paramTypes);}boolean matchThis = matchesThis(clazz);if (matchThis) {Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method method : methods) {if (methodMatch(name, method, paramTypes)) {CacheConfigUtil.parse(cac, method);break;}}}}6、将上面解析到缓存函数配置信息保存到缓存cacheConfigMap中。如果函数带有Cached、CacheUpdate和CacheInvalidate等注解时matchesImpl函数就返回true,否则返回false。
至此,针对带有Cached、CacheUpdate和CacheInvalidate等注解的函数就可以纳入到Spring的切面,当对应的函数被调用时就会调用CacheAdvisor类的getAdvice()函数获取对应的切面Advice,接下来就是要定义一个Advice增强器用于提供加载缓存、更新缓存和删除缓存数据的能力。
JetCacheInterceptor类
MethodInterceptor是AOP项目中的拦截器,它拦截的目标是方法。实现MethodInterceptor拦截器大致也分为两种,一种是实现MethodInterceptor接口,另一种利用AspectJ的注解或配置。JetCache采用的是使用JetCacheInterceptor类来实现MethodInterceptor接口。源码如下:
/*** @author huangli*/
public class JetCacheInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, ApplicationContextAware {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JetCacheInterceptor.class);@Autowiredprivate ConfigMap cacheConfigMap; // 缓存配置映射private ApplicationContext applicationContext; // 上下文对象private GlobalCacheConfig globalCacheConfig; // 全局缓存配置ConfigProvider configProvider; // 配置提供者CacheManager cacheManager; // 缓存管理器@Overridepublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {this.applicationContext = applicationContext; // 设置上下文对象}@Overridepublic Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {if (configProvider == null) {configProvider = applicationContext.getBean(ConfigProvider.class); // 获取配置提供者}if (configProvider != null && globalCacheConfig == null) {globalCacheConfig = configProvider.getGlobalCacheConfig(); // 获取全局缓存配置}if (globalCacheConfig == null || !globalCacheConfig.isEnableMethodCache()) {return invocation.proceed(); // 执行目标方法}if (cacheManager == null) {cacheManager = applicationContext.getBean(CacheManager.class); // 获取缓存管理器if (cacheManager == null) {logger.error("There is no cache manager instance in spring context"); // 输出错误日志return invocation.proceed(); // 执行目标方法}}Method method = invocation.getMethod(); // 获取目标方法Object obj = invocation.getThis(); // 获取目标对象CacheInvokeConfig cac = null; // 缓存调用配置if (obj != null) {String key = CachePointcut.getKey(method, obj.getClass()); // 获取缓存键cac = cacheConfigMap.getByMethodInfo(key); // 获取对应的缓存配置}/*if(logger.isTraceEnabled()){logger.trace("JetCacheInterceptor invoke. foundJetCacheConfig={}, method={}.{}(), targetClass={}",cac != null,method.getDeclaringClass().getName(),method.getName(),invocation.getThis() == null ? null : invocation.getThis().getClass().getName());}*/if (cac == null || cac == CacheInvokeConfig.getNoCacheInvokeConfigInstance()) {return invocation.proceed(); // 执行目标方法}CacheInvokeContext context = configProvider.newContext(cacheManager).createCacheInvokeContext(cacheConfigMap); // 创建缓存调用上下文context.setTargetObject(invocation.getThis()); // 设置目标对象context.setInvoker(invocation::proceed); // 设置调用者context.setMethod(method); // 设置目标方法context.setArgs(invocation.getArguments()); // 设置参数context.setCacheInvokeConfig(cac); // 设置缓存调用配置context.setHiddenPackages(globalCacheConfig.getHiddenPackages()); // 设置隐藏包return CacheHandler.invoke(context); // 执行缓存处理}public void setCacheConfigMap(ConfigMap cacheConfigMap) {this.cacheConfigMap = cacheConfigMap; // 设置缓存配置映射}}
在上面的JetCacheInterceptor类中,cacheConfigMap会缓存每个缓存实例的配置信息,就是是通过上面解析函数中带有的@Cached、@CacheUpdate和@CacheInvalidate等注解中定义的配置信息。JetCacheInterceptor类的invoke函数主要实现如下几个步骤:
1、获取全局缓存配置实例globalCacheConfig,如果全局配置中配置了不启用缓存,就执行目标方法。启用缓存的全局配置就是在例如Application类上加一个@EnableMethodCache注解,设置一下JetCache扫描的包名前缀。
2、获取MethodInvocation类型参数的目标方法和目标对象信息,然后根据目标类和目标方法获取目标方法的缓存配置信息。如果目标方法不存在缓存配置信息,即没有@Cached、@CacheUpdate或@CacheInvalidate注解,则执行执行目标方法。源码如下:
Method method = invocation.getMethod(); // 获取目标方法Object obj = invocation.getThis(); // 获取目标对象CacheInvokeConfig cac = null; // 缓存调用配置if (obj != null) {String key = CachePointcut.getKey(method, obj.getClass()); // 获取缓存键cac = cacheConfigMap.getByMethodInfo(key); // 获取对应的缓存配置}if (cac == null || cac == CacheInvokeConfig.getNoCacheInvokeConfigInstance()) {return invocation.proceed(); // 执行目标方法}3、构建缓存执行上下文,执行CacheHandler类的静态方法invoke(CacheInvokeContext),源码如下:
CacheInvokeContext context = configProvider.newContext(cacheManager).createCacheInvokeContext(cacheConfigMap); // 创建缓存调用上下文context.setTargetObject(invocation.getThis()); // 设置目标对象context.setInvoker(invocation::proceed); // 设置调用者context.setMethod(method); // 设置目标方法context.setArgs(invocation.getArguments()); // 设置参数context.setCacheInvokeConfig(cac); // 设置缓存调用配置context.setHiddenPackages(globalCacheConfig.getHiddenPackages()); // 设置隐藏包return CacheHandler.invoke(context); // 执行缓存处理在进一步分析 CacheHandler类的静态方法invoke之前,我们需要看一下JetCache是如何创建JetCacheInterceptor和CacheAdvisor的Bean,实现逻辑很简单,就是在JetCacheProxyConfiguration中直接实现的,源码如下:
/*** 创建一个名为CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME的CacheAdvisor Bean,并设置其角色为BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE。* 使用JetCacheInterceptor创建CacheAdvisor的缓存拦截器。* 设置CacheAdvisor的缓存拦截器为jetCacheInterceptor。* 设置CacheAdvisor的基包为enableMethodCache.getStringArray("basePackages")。* 设置CacheAdvisor的顺序为enableMethodCache.getNumber("order")。* 返回创建的CacheAdvisor Bean。*/@Bean(name = CacheAdvisor.CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)public CacheAdvisor jetcacheAdvisor(JetCacheInterceptor jetCacheInterceptor) {CacheAdvisor advisor = new CacheAdvisor();advisor.setAdvice(jetCacheInterceptor);advisor.setBasePackages(this.enableMethodCache.getStringArray("basePackages"));advisor.setOrder(this.enableMethodCache.<Integer>getNumber("order"));return advisor;}/*** 创建一个名为jetCacheInterceptor的JetCacheInterceptor Bean,并设置其角色为BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE。* 返回创建的JetCacheInterceptor Bean。*/@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)public JetCacheInterceptor jetCacheInterceptor() {return new JetCacheInterceptor();}
至此,当目标函数被调用时,Spring就会执行JetCacheInterceptor类的invoke函数,接下来,我们就需要针对CacheHandler类的静态方法invoke(CacheInvokeContext)做进一步的分析。源码如下:
public static Object invoke(CacheInvokeContext context) throws Throwable {if (context.getCacheInvokeConfig().isEnableCacheContext()) {try {CacheContextSupport._enable();return doInvoke(context);} finally {CacheContextSupport._disable();}} else {return doInvoke(context);}}上面的方法会首先判断缓存执行上下文是否启用缓存上下文,只有目标函数上带有@EnableCache注解时,context .getCacheInvokeConfig( ).isEnableCacheContext()才会返回true。当启用缓存上下文时就会在函数doInvoke执行前后分别调用CacheContextSupport类的_enable()和_disable()方法。否则就会直接调用doInvoke函数继续进行处理,doInvoke源码如下:
private static Object doInvoke(CacheInvokeContext context) throws Throwable {CacheInvokeConfig cic = context.getCacheInvokeConfig();CachedAnnoConfig cachedConfig = cic.getCachedAnnoConfig();if (cachedConfig != null && (cachedConfig.isEnabled() || CacheContextSupport._isEnabled())) {return invokeWithCached(context);} else if (cic.getInvalidateAnnoConfigs() != null || cic.getUpdateAnnoConfig() != null) {return invokeWithInvalidateOrUpdate(context);} else {return invokeOrigin(context);}}invokeWithCached
如果目标函数的缓存调用配置实例不为空,即目标方法有@Cached注解,且开启缓存就会调用invokeWithCached方法。注意,CachedAnnoConfig中的isEnabled()函数是取自@Cached注解的enabled,默认为true。方法invokeWithCached的源码如下:
/*** 使用缓存调用方法** @param context 缓存调用上下文* @return 方法返回值* @throws Throwable 可抛出异常*/private static Object invokeWithCached(CacheInvokeContext context) throws Throwable {CacheInvokeConfig cic = context.getCacheInvokeConfig(); // 获取缓存调用配置CachedAnnoConfig cac = cic.getCachedAnnoConfig(); // 获取缓存注解配置Cache cache = context.getCacheFunction().apply(context, cac); // 获取缓存函数并应用得到缓存if (cache == null) { // 判断缓存是否为空logger.error("no cache with name: " + context.getMethod()); // 记录错误日志return invokeOrigin(context); // 调用原始方法}Object key = ExpressionUtil.evalKey(context, cic.getCachedAnnoConfig()); // 根据表达式计算缓存的keyif (key == null) { // 判断key是否为空return loadAndCount(context, cache, key); // 加载并统计缓存}if (!ExpressionUtil.evalCondition(context, cic.getCachedAnnoConfig())) { // 判断缓存条件是否满足return loadAndCount(context, cache, key); // 加载并统计缓存}try {CacheLoader loader = new CacheLoader() { // 创建缓存加载器@Overridepublic Object load(Object k) throws Throwable { // 加载缓存Object result = invokeOrigin(context); // 调用原始方法context.setResult(result); // 设置调用上下文的结果return result;}@Overridepublic boolean vetoCacheUpdate() { // 判断是否禁止缓存更新return !ExpressionUtil.evalPostCondition(context, cic.getCachedAnnoConfig()); // 根据表达式判断是否禁止缓存更新}};Object result = cache.computeIfAbsent(key, loader); // 根据key计算缓存结果return result; // 返回缓存结果} catch (CacheInvokeException e) { // 捕获缓存调用异常throw e.getCause(); // 抛出异常原因}}
这个函数是一个私有的静态方法,用于在给定的缓存上下文中执行方法调用。它首先获取缓存配置和注解配置,然后根据配置获取缓存。如果缓存为空,它会记录错误并调用原始方法。接下来,它通过表达式计算缓存的键,并根据条件判断是否需要加载缓存。如果需要加载,它会创建一个缓存加载器,并使用该加载器计算缓存结果。最后,它会返回缓存结果。如果发生缓存调用异常,它会抛出该异常的原因。
上面的函数主要的核心逻辑概括起来,可以用下面的源码来解释:
Cache cache = context.getCacheFunction().apply(context, cac); // 获取缓存函数并应用得到缓存
CacheLoader loader = new CacheLoader() { // 创建缓存加载器@Overridepublic Object load(Object k) throws Throwable { // 加载缓存Object result = invokeOrigin(context); // 调用原始方法context.setResult(result); // 设置调用上下文的结果return result;}@Overridepublic boolean vetoCacheUpdate() { // 判断是否禁止缓存更新return !ExpressionUtil.evalPostCondition(context, cic.getCachedAnnoConfig()); // 根据表达式判断是否禁止缓存更新}
};
Object result = cache.computeIfAbsent(key, loader); // 根据key计算缓存结果
return result; // 返回缓存结果上面的代码逻辑相对比较简单,我们继续看一下computeIfAbsent函数,该函数会先查询Cache对象中是否存在指定的缓存,如果不存在就会调用load函数获取数据并写入Cache对象中。computeIfAbsent函数源码如下:
@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<K, V> loader) {return computeIfAbsent(key, loader, config().isCacheNullValue());}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<K, V> loader, boolean cacheNullWhenLoaderReturnNull) {return AbstractCache.computeIfAbsentImpl(key, loader, cacheNullWhenLoaderReturnNull,0, null, this);}static <K, V> V computeIfAbsentImpl(K key, Function<K, V> loader, boolean cacheNullWhenLoaderReturnNull,long expireAfterWrite, TimeUnit timeUnit, Cache<K, V> cache) {// 获取具体的缓存实现类AbstractCache<K, V> abstractCache = CacheUtil.getAbstractCache(cache);// 创建带有缓存监听的缓存加载器CacheLoader<K, V> newLoader = CacheUtil.createProxyLoader(cache, loader, abstractCache::notify);// 获取缓存获取结果CacheGetResult<V> r;if (cache instanceof RefreshCache) {// 如果缓存是 RefreshCache 类型,则通过该类型的具体方法获取缓存值,并添加刷新任务RefreshCache<K, V> refreshCache = ((RefreshCache<K, V>) cache);r = refreshCache.GET(key);refreshCache.addOrUpdateRefreshTask(key, newLoader);} else {// 否则直接通过缓存的 GET 方法获取缓存值r = cache.GET(key);}if (r.isSuccess()) {// 如果获取成功,则返回获取到的缓存值return r.getValue();} else {// 如果获取失败,则根据条件执行加载和更新逻辑Consumer<V> cacheUpdater = (loadedValue) -> {// 判断是否需要更新缓存if(needUpdate(loadedValue, cacheNullWhenLoaderReturnNull, newLoader)) {// 若需要更新,则根据过期时间和时间单位调用缓存的 PUT 方法if (timeUnit != null) {cache.PUT(key, loadedValue, expireAfterWrite, timeUnit).waitForResult();} else {cache.PUT(key, loadedValue).waitForResult();}}};// 加载值V loadedValue;if (cache.config().isCachePenetrationProtect()) {// 如果开启了缓存穿透保护,则同步加载并更新缓存loadedValue = synchronizedLoad(cache.config(), abstractCache, key, newLoader, cacheUpdater);} else {// 否则直接通过缓存加载器加载值,并执行缓存更新逻辑loadedValue = newLoader.apply(key);cacheUpdater.accept(loadedValue);}// 返回加载的值return loadedValue;}}
invokeWithInvalidateOrUpdate
如果目标函数的缓存调用配置实例不为空,即目标方法有@CacheUpdate或@CacheInvalidate等注解,且开启缓存就会调用invokeWithInvalidateOrUpdate方法。invokeWithInvalidateOrUpdate方法的源码如下:
private static Object invokeWithInvalidateOrUpdate(CacheInvokeContext context) throws Throwable {Object originResult = invokeOrigin(context);context.setResult(originResult);CacheInvokeConfig cic = context.getCacheInvokeConfig();if (cic.getInvalidateAnnoConfigs() != null) {doInvalidate(context, cic.getInvalidateAnnoConfigs());}CacheUpdateAnnoConfig updateAnnoConfig = cic.getUpdateAnnoConfig();if (updateAnnoConfig != null) {doUpdate(context, updateAnnoConfig);}return originResult;}上面的方法首先会执行目标函数,获取相应的结果,然后开始根据目标方法上的@CacheUpdate或@CacheInvalidate注解更新或删除缓存数据。
如果目标方法存在注解@CacheInvalidate,就会调用doInvalidate方法删除缓存数据,源码如下:
// 清除指定缓存private static void doInvalidate(CacheInvokeContext context, List<CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig> annoConfig) {for (CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig config : annoConfig) {doInvalidate(context, config);}}// 清除单个缓存private static void doInvalidate(CacheInvokeContext context, CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig annoConfig) {Cache cache = context.getCacheFunction().apply(context, annoConfig); // 获取指定缓存if (cache == null) {return;}boolean condition = ExpressionUtil.evalCondition(context, annoConfig); // 判断是否满足条件if (!condition) {return;}Object key = ExpressionUtil.evalKey(context, annoConfig); // 获取缓存的键if (key == null) {return;}if (annoConfig.isMulti()) { // 判断是否为多个键Iterable it = toIterable(key); // 将键转为迭代器if (it == null) {logger.error("jetcache @CacheInvalidate key is not instance of Iterable or array: " + annoConfig.getDefineMethod());return;}Set keys = new HashSet();it.forEach(k -> keys.add(k)); // 将键添加到集合中cache.removeAll(keys); // 清除所有指定键的缓存} else {cache.remove(key); // 清除指定键的缓存}}
这段代码定义了两个私有的静态函数:doInvalidate。这两个函数的作用是根据传入的参数,对缓存进行清空操作。其中,doInvalidate函数接受一个CacheInvokeContext对象和一个CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig对象,通过遍历CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig对象的列表,依次调用doInvalidate函数进行清空操作。在doInvalidate函数中,首先通过CacheInvokeContext对象获取缓存对象,并根据CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig对象中的条件判断是否执行清空操作。若满足条件,则根据CacheInvalidateAnnoConfig对象中的配置,对缓存进行清空操作。如果配置中指定了多个key,则将多个key放入Set集合中进行清空操作;如果只指定了一个key,则直接进行清空操作。
如果目标方法存在注解@CacheUpdate,就会调用doUpdate方法更新缓存数据,源码如下:
// 更新缓存private static void doUpdate(CacheInvokeContext context, CacheUpdateAnnoConfig updateAnnoConfig) {// 获取缓存Cache cache = context.getCacheFunction().apply(context, updateAnnoConfig);// 若缓存为空,直接返回if (cache == null) {return;}// 判断是否满足更新条件boolean condition = ExpressionUtil.evalCondition(context, updateAnnoConfig);if (!condition) {return;}// 获取键值Object key = ExpressionUtil.evalKey(context, updateAnnoConfig);Object value = ExpressionUtil.evalValue(context, updateAnnoConfig);// 若键值为空或者获取键值失败,直接返回if (key == null || value == ExpressionUtil.EVAL_FAILED) {return;}// 判断是否为批量更新if (updateAnnoConfig.isMulti()) {// 若值为空,直接返回if (value == null) {return;}// 将键值转换为可迭代对象Iterable keyIt = toIterable(key);Iterable valueIt = toIterable(value);// 若键为null,打印错误日志并返回if (keyIt == null) {logger.error("jetcache @CacheUpdate key is not instance of Iterable or array: " + updateAnnoConfig.getDefineMethod());return;}// 若值为null,打印错误日志并返回if (valueIt == null) {logger.error("jetcache @CacheUpdate value is not instance of Iterable or array: " + updateAnnoConfig.getDefineMethod());return;}// 转换为列表List keyList = new ArrayList();List valueList = new ArrayList();keyIt.forEach(o -> keyList.add(o));valueIt.forEach(o -> valueList.add(o));// 若键列表与值列表大小不一致,打印错误日志并返回if (keyList.size() != valueList.size()) {logger.error("jetcache @CacheUpdate key size not equals with value size: " + updateAnnoConfig.getDefineMethod());return;} else {// 构建键值对映射Map m = new HashMap();for (int i = 0; i < valueList.size(); i++) {m.put(keyList.get(i), valueList.get(i));}// 批量更新缓存cache.putAll(m);}} else {// 批量更新缓存cache.put(key, value);}}
这个函数是一个用于更新缓存的方法。首先根据传入的参数获取缓存对象,如果缓存为空,则直接返回。然后通过判断条件来确定是否执行更新操作。接着通过调用ExpressionUtil的evalKey方法和evalValue方法来获取键和值。如果键或值获取失败,则直接返回。如果updateAnnoConfig.isMulti()为true,则表示是批量更新操作。这时需要将值转换为可迭代对象,并判断是否为空。接着将键和值分别转换为列表,并进行大小判断。如果不相等,则打印错误日志并返回。如果相等,则构建一个键值对映射,然后将该映射批量更新到缓存中。如果updateAnnoConfig.isMulti()为false,则表示是单个更新操作,直接将键值对更新到缓存中。