文章目录
- 1. 概念
- 2. 链表分类
- 3. 链表与顺序表对比
- 4. 无头单向非循环链表实现(C语言)
- 4.1 SingleLinkedList.h
- 4.2 Test.c
- 4.3 SingleLinkedList.c
1. 概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
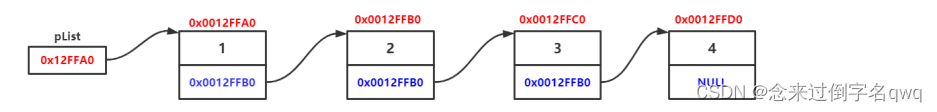
链表在逻辑上是连续的,物理上则不一定连续(因为每个节点内存由操作系统分配),节点一般从堆内存申请,堆内存空间是按照一定策略分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续。
2. 链表分类
以下不同情况下组合起来有8种链表结构:
- 单向或双向;
- 带头或不带头;
- 循环或非循环;
不过实际中最常用还是两种结构:
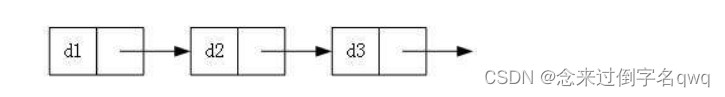
- 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等,另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
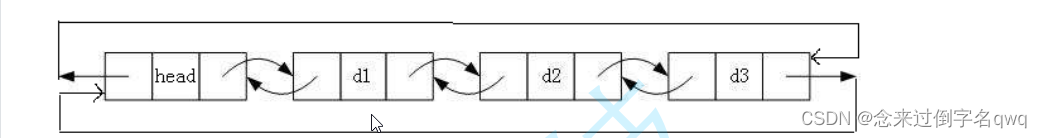
- 带头双向循环链表::结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,不同功能的实现反而简单了。
3. 链表与顺序表对比
| 不同角度 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储结构 | 逻辑、物理连续 | 逻辑连续,物理不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持,效率高 | 不支持,效率较低 |
| 插入或删除 | 效率低 | 效率高 |
| 容量 | 容量不足时需要扩容 | 不需要扩容 |
| 缓存利用率 | 高 | 低 |
| 应用场景 | 高效存储和频繁访问 | 频繁插入和删除 |
4. 无头单向非循环链表实现(C语言)
4.1 SingleLinkedList.h
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>// 单链表结构(无哨兵位)
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct SingleLinkedListNode {datatype val;struct SingleLinkedListNode* next;
} Node, * SingleLinkedList;// malloc返回新节点
Node* CreateNode(datatype val);// 头插尾插
void AddFront(Node** pphead, datatype val);
void AddBack(Node** pphead, datatype val);void Print(Node* phead);// 头删尾删
void RemoveFront(Node** pphead);
void RemoveBack(Node** pphead);// 查找是否存在
bool IsExist(Node** pphead, datatype target);
// 目标节点前面插入
void Insert(Node** pphead, datatype val, datatype target);
// 删除节点
void Erase(Node** pphead, datatype target);
// 删除全部
void Destroy(Node** pphead);// 查找并返回节点
Node* Find(Node** pphead, datatype target);
// 目标节点后面插入
void InsertAfter(Node* targetNode, datatype val);
// 删除目标节点后面的节点
void EraseAfter(Node* targetNode);
4.2 Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "SingleLinkedList.h"void TestAddFront() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;AddFront(&linkedList, 1);AddFront(&linkedList, 2);AddFront(&linkedList, 3);AddFront(&linkedList, 4);printf("\nTestAddFront(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestAddBack() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;AddBack(&linkedList, 1);AddBack(&linkedList, 2);AddBack(&linkedList, 3);AddBack(&linkedList, 4);printf("\nTestAddBack(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestRemoveBack() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;AddBack(&linkedList, 1);AddBack(&linkedList, 2);AddBack(&linkedList, 3);AddBack(&linkedList, 4);RemoveBack(&linkedList);printf("\nTestRemoveBack(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestTestFront() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;AddFront(&linkedList, 1);AddFront(&linkedList, 2);AddFront(&linkedList, 3);AddFront(&linkedList, 4);RemoveFront(&linkedList);printf("\nTestTestFront(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestInsert() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;Insert(&linkedList, 10, 11); // 测试空链表时Insert(&linkedList, 20, 10); // 测试空链表或节点数<=1时Insert(&linkedList, 30, 11); // 测试目标节点不存在时Insert(&linkedList, 40, 10); // 测试正常情况Insert(&linkedList, 1, 20); // 测试目标节点是头结点时printf("\nTestInsert(): ");Print(linkedList); // 1->20->40->10->30->NULL
}void TestErase() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;Insert(&linkedList, 10, 11); Insert(&linkedList, 20, 10); Insert(&linkedList, 30, 11); Insert(&linkedList, 40, 10); Insert(&linkedList, 1, 20); Erase(&linkedList, 30);printf("\nTestDelete(): ");Print(linkedList); // 1->20->40->10->NULL
}void TestDestroy() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;Insert(&linkedList, 10, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 20, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 30, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 40, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 1, 20);Destroy(&linkedList);printf("\nTestDestroy(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestInsertAfter() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;Insert(&linkedList, 10, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 20, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 30, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 40, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 1, 20);InsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 30), 50); // 1->20->40->10->30->50->NULLInsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 50), 100); // 1->20->40->10->30->50->100->NULLInsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 1), 1000); // 1->1000->20->40->10->30->50->100->NULLprintf("\nTestInsertAfter(): ");Print(linkedList);
}void TestEraseAfter() {SingleLinkedList linkedList = NULL;Insert(&linkedList, 10, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 20, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 30, 11);Insert(&linkedList, 40, 10);Insert(&linkedList, 1, 20);InsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 30), 50);InsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 50), 100);InsertAfter(Find(&linkedList, 1), 1000); // 1->1000->20->40->10->30->50->100->NULLEraseAfter(Find(&linkedList, 1)); // 1->20->40->10->30->50->100->NULLEraseAfter(Find(&linkedList, 100)); // 1->20->40->10->30->50->100->NULLEraseAfter(Find(&linkedList, 10)); // 1->20->40->10->50->100->NULLprintf("\nTestEraseAfter(): ");Print(linkedList);
}int main() {TestAddFront();TestAddBack();TestRemoveBack();TestTestFront();TestInsert();TestErase();TestDestroy();TestInsertAfter();TestEraseAfter();return 0;
}
4.3 SingleLinkedList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "SingleLinkedList.h"Node* CreateNode(datatype val) {Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));if (node == NULL) {perror("CreateNode() malloc error");exit(-1);}node->val = val;node->next = NULL;return node;
}void AddFront(Node** pphead, datatype val) {Node* newNode = CreateNode(val);newNode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newNode;
}void AddBack(Node** pphead, datatype val) {Node* newNode = CreateNode(val);if (*pphead == NULL) { // 空链表*pphead = newNode;}else { /* 节点数>=1 */Node* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newNode;}
}void Print(Node* phead) {Node* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL) {printf("%d->", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}void RemoveFront(Node** pphead) {assert(*pphead); // 空链表/* 链表节点数>=1 */Node* pNext = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = pNext;//Node* tmp = *pphead;//*pphead = (*pphead)->next;//free(tmp);//tmp = NULL;
}void RemoveBack(Node** pphead) {assert(*pphead); // 空链表if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) { /* 只有1个节点 */free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else { /* 节点数>=2 */Node* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next->next) {prev = prev->next;}free(prev->next);prev->next = NULL;}
}bool IsExist(Node** pphead, datatype target) {Node* cur = *pphead;while (cur) {if (cur->val == target) {return true;}cur = cur->next;}return false;
}void Insert(Node** pphead, datatype val, datatype target) {// 当 (1)空链表 或 (2)节点数<=1 或 (3)目标节点是头节点时 则直接头插if (*pphead == NULL || (*pphead)->next == NULL || (*pphead)->val == target) {AddFront(pphead, val);}else { // 节点数>=2if (IsExist(pphead, target)) {Node* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next->val != target) {prev = prev->next;}Node* targetNode = prev->next;Node* newNode = CreateNode(val);prev->next = newNode;newNode->next = targetNode;}else { // 当目标节点不存在时尾插AddBack(pphead, val);}}
}void Erase(Node** pphead, datatype target) {assert(*pphead); // 空链表Node* cur = *pphead;Node* pPrev = NULL; // 当节点数>=2必有pPrev != NULLwhile (cur) {if (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->val == target) {pPrev = cur;}if (cur->val == target) {Node* pNext = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;if (pPrev != NULL) {pPrev->next = pNext;}else { // 说明删除的是头结点,pNext=NULL。*pphead = pNext;}break;}cur = cur->next;}
}void Destroy(Node** pphead) {Node* cur = *pphead;Node* del = NULL;while (cur) {del = cur;cur = cur->next;free(del);del = NULL;}*pphead = NULL;
}Node* Find(Node** pphead, datatype target) {Node* cur = *pphead;while (cur) {if (cur->val == target) {return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void InsertAfter(Node* targetNode, datatype val) {assert(targetNode);Node* newNode = CreateNode(val);Node* pNext = targetNode->next;targetNode->next = newNode;newNode->next = pNext;
}void EraseAfter(Node* targetNode) {assert(targetNode);Node* pDel = targetNode->next;if (pDel != NULL) { // 避免targetNode是尾结点时pDel=NULL的情况Node* pNext = pDel->next;free(pDel);pDel = NULL;targetNode->next = pNext;}
}




![计算机网络安全教程(第三版)课后简答题答案大全[6-12章]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a7a88f05dadd4adda150c3c049c4b075.png)

![【算法每日一练]-动态规划 (保姆级教程 篇16) #纸带 #围栏木桩 #四柱河内塔](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1cea3486216242abb2b62aff231340d4.png)