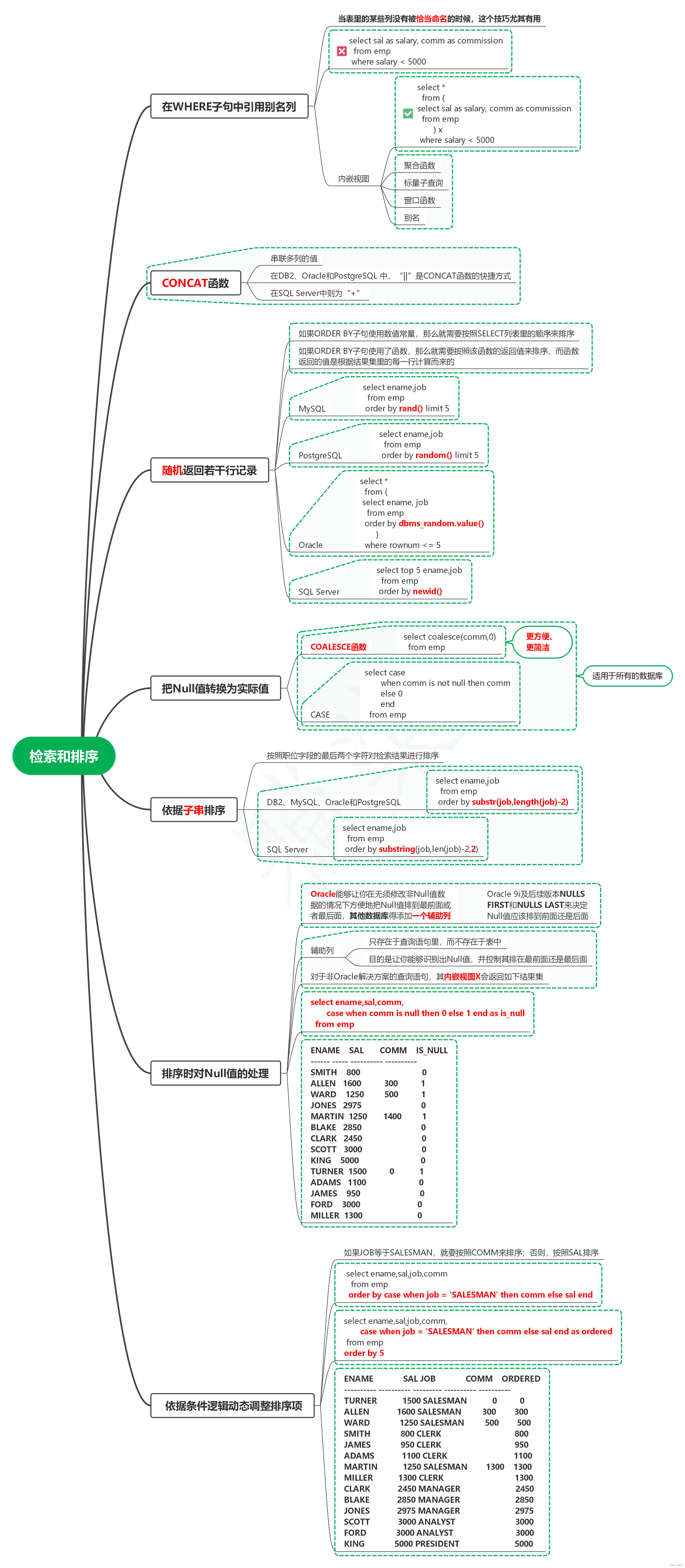
1. 在WHERE子句中引用别名列
1.1. 当表里的某些列没有被恰当命名的时候,这个技巧尤其有用
1.2. sql
select sal as salary, comm as commissionfrom empwhere salary < 5000
1.3. 内嵌视图
1.3.1. sql
select *from (select sal as salary, comm as commissionfrom emp) xwhere salary < 5000
1.3.2. 聚合函数
1.3.3. 标量子查询
1.3.4. 窗口函数
1.3.5. 别名
2. CONCAT函数
2.1. 串联多列的值
2.2. 在DB2、Oracle和PostgreSQL 中,“||”是CONCAT函数的快捷方式
2.3. 在SQL Server中则为“+”
3. 随机返回若干行记录
3.1. 如果ORDER BY子句使用数值常量,那么就需要按照SELECT列表里的顺序来排序
3.2. 如果ORDER BY子句使用了函数,那么就需要按照该函数的返回值来排序,而函数返回的值是根据结果集里的每一行计算而来的
3.3. MySQL
3.3.1. sql
select ename,jobfrom emporder by rand() limit 5
3.4. PostgreSQL
3.4.1. sql
select ename,jobfrom emporder by random() limit 5
3.5. Oracle
3.5.1. sql
select *from (select ename, jobfrom emporder by dbms_random.value())where rownum <= 5
3.6. SQL Server
3.6.1. sql
select top 5 ename,jobfrom emporder by newid()
4. 把Null值转换为实际值
4.1. COALESCE函数
4.1.1. sql
select coalesce(comm,0)from emp
4.1.2. 更方便、更简洁
4.2. CASE
4.2.1. sql
select casewhen comm is not null then commelse 0endfrom emp
4.3. 适用于所有的数据库
5. 依据子串排序
5.1. 按照职位字段的最后两个字符对检索结果进行排序
5.2. DB2、MySQL、Oracle和PostgreSQL
5.2.1. sql
select ename,jobfrom emporder by substr(job,length(job)-2)
5.3. SQL Server
5.3.1. sql
select ename,jobfrom emporder by substring(job,len(job)-2,2)
6. 排序时对Null值的处理
6.1. Oracle能够让你在无须修改非Null值数据的情况下方便地把Null值排到最前面或者最后面,其他数据库得添加一个辅助列
6.1.1. Oracle 9i及后续版本NULLS FIRST和NULLS LAST来决定Null值应该排到前面还是后面
6.2. 辅助列
6.2.1. 只存在于查询语句里,而不存在于表中
6.2.2. 目的是让你能够识别出Null值,并控制其排在最前面还是最后面
6.3. 对于非Oracle解决方案的查询语句,其内嵌视图X会返回如下结果集
6.4. sql
select ename,sal,comm,case when comm is null then 0 else 1 end as is_nullfrom emp
7. 依据条件逻辑动态调整排序项
7.1. 如果JOB等于SALESMAN,就要按照COMM来排序;否则,按照SAL排序
7.2. sql
select ename,sal,job,commfrom emporder by case when job = 'SALESMAN' then comm else sal end
7.3. sql
select ename,sal,job,comm,case when job = 'SALESMAN' then comm else sal end as orderedfrom emp
order by 5