雪雾:
设计一个算法,将一个节点值为自然数的单列表拆分成两个单列表,原表中值为偶数的节点保留,而值为奇数的节点,按他们在原表的相对次序组成一个新的单列表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct Node {int data;struct Node* next;
} Node;void splitList(Node* head, Node** evenList, Node** oddList) {Node* evenTail = NULL;Node* oddTail = NULL;while (head != NULL) {if (head->data % 2 == 0) {if (*evenList == NULL) {*evenList = head;evenTail = head;} else {evenTail->next = head;evenTail = evenTail->next;}} else {if (*oddList == NULL) {*oddList = head;oddTail = head;} else {oddTail->next = head;oddTail = oddTail->next;}}head = head->next;}if (evenTail != NULL) evenTail->next = NULL;if (oddTail != NULL) oddTail->next = NULL;
}// Example usage:
// Call splitList with your original list and two empty lists for even and odd nodes.
// Node* originalList;
// Node* evenList = NULL;
// Node* oddList = NULL;
// splitList(originalList, &evenList, &oddList);雪雾:
顺序表a和b其元素值均被从小到大的顺序排列,编写一个算法,将它们合并成一个顺序表c,要求c的元素也按从小到大的升序排列
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void mergeSortedArrays(int a[], int m, int b[], int n, int c[]) {int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;while (i < m && j < n) {if (a[i] < b[j]) {c[k++] = a[i++];} else {c[k++] = b[j++];}}while (i < m) {c[k++] = a[i++];}while (j < n) {c[k++] = b[j++];}
}// Example usage:
// int a[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
// int b[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
// int c[8]; // Assuming enough space in the array
// mergeSortedArrays(a, 4, b, 4, c);雪雾:
设计快速排序的非递归算法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void swap(int* a, int* b) {int temp = *a;*a = *b;*b = temp;
}int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {int pivot = arr[high];int i = (low - 1);for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) {if (arr[j] < pivot) {i++;swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);}}swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);return (i + 1);
}void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {int stack[high - low + 1];int top = -1;stack[++top] = low;stack[++top] = high;while (top >= 0) {high = stack[top--];low = stack[top--];int pi = partition(arr, low, high);if (pi - 1 > low) {stack[++top] = low;stack[++top] = pi - 1;}if (pi + 1 < high) {stack[++top] = pi + 1;stack[++top] = high;}}
}// Example usage:
// int arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
// int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);雪雾:
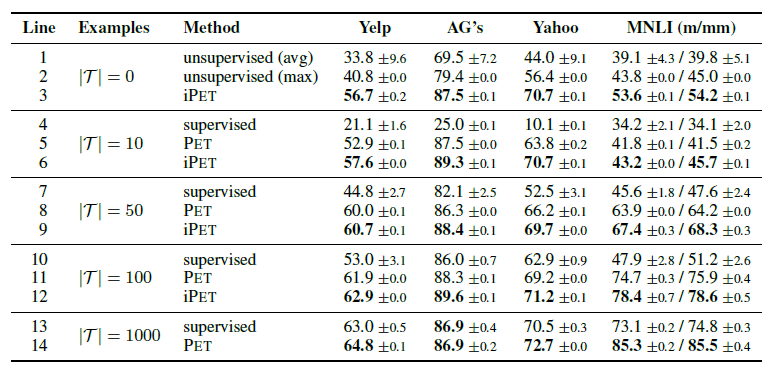
二叉树前序遍历为ABCDRF,中序遍历为CBAEDF,画出此二叉数,并求该树的后序遍历
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct TreeNode {char data;struct TreeNode* left;struct TreeNode* right;
} TreeNode;TreeNode* buildTree(char preorder[], char inorder[], int preStart, int preEnd, int inStart, int inEnd) {if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {return NULL;}TreeNode* root = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));root->data = preorder[preStart];int inIndex = inStart;while (inorder[inIndex] != root->data) {inIndex++;}int leftSubtreeSize = inIndex - inStart;root->left = buildTree(preorder, inorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSubtreeSize, inStart, inIndex - 1);root->right = buildTree(preorder, inorder, preStart + leftSubtreeSize + 1, preEnd, inIndex + 1, inEnd);return root;
}void postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}postorderTraversal(root->left);postorderTraversal(root->right);printf("%c ", root->data);
}// Example usage:
// char preorder[] = "ABCDRF";
// char inorder[] = "CBAEDF";
// TreeNode* root = buildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, 5, 0, 5);
// postorderTraversal(root);雪雾:
对于几个顶点的无向图和有向图均为不带权图,采用邻接矩阵和邻接表表示时如何求解以下问题
1.图中有多少条边
2.任意两个顶点i和j是否有边相连
3.任意一个顶点的度是多少
#define MAX_VERTICES 100// 邻接矩阵表示
typedef struct {int matrix[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];int numVertices;
} GraphMatrix;// 邻接表表示
typedef struct Node {int vertex;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;
} LinkedList;typedef struct {LinkedList array[MAX_VERTICES];int numVertices;
} GraphList;// 问题解答
int countEdges(GraphMatrix* graph) {int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < graph->numVertices; j++) {if (graph->matrix[i][j] != 0) {count++;}}}return count / 2; // For undirected graph
}bool areVerticesConnected(GraphMatrix* graph, int i, int j) {return (graph->matrix[i][j] != 0);
}int calculateVertexDegree(GraphMatrix* graph, int vertex) {int degree = 0;for (int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {if (graph->matrix[vertex][i] != 0) {degree++;}}return degree;
}// 类似的函数也可以定义在GraphList中// Example usage:
// GraphMatrix graph;
// int edgeCount = countEdges(&graph);
// bool connected = areVerticesConnected(&graph, 0, 1);
// int degree = calculateVertexDegree(&graph, 0);雪雾:
假设稀疏矩阵采用3元组表示,编写一个函数计算其转置矩阵b,要求b也采用3元组表示
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct {int row;int col;int value;
} Triplet;void transposeSparseMatrix(Triplet a[], Triplet b[]) {int numTerms = a[0].value;b[0].row = a[0].col;b[0].col = a[0].row;b[0].value = numTerms;if (numTerms > 0) {int currentB = 1;for (int currentA = 0; currentA < numTerms; currentA++) {int currentCol = a[currentA].row;b[currentB].row = currentCol;b[currentB].col = a[currentA].col;b[currentB].value = a[currentA雪雾:
含有60个叶子节点的二叉树的最小高度是多少
最小高度的二叉树是一棵平衡二叉树,其中每个叶子节点都位于最底层或倒数第二层。平衡二叉树的高度可以通过以下方式计算:
对于含有 n 个叶子节点的平衡二叉树,其高度 h 可以通过以下不等式确定:
[2^{h-1} < n \leq 2^h - 1]
在这个问题中,n = 60,我们需要找到最小的 h 满足上述不等式。可以通过迭代计算找到最小的 h:
[2^{h-1} < 60 \leq 2^h - 1]
[2^{h-1} < 60 \leq 2^h - 1]
[2^{h-1} + 1 \leq 60 \leq 2^h - 1]
[2^{h-1} + 1 \leq 60 \leq 2^h - 1]
[2^{h-1} \leq 59 \leq 2^h - 2]
因此,[h-1 \leq \log_2(59) < h]
最小的 h 是 (\lceil \log_2(59) \rceil),其中 (\lceil x \rceil) 表示不小于 x 的最小整数。计算得到:
[h = \lceil \log_2(59) \rceil = 6]
所以,含有 60 个叶子节点的二叉树的最小高度为 6。

雪雾:
在分块检索中,对256个元素的线性表分成多少块最好?每块的最佳长度是多少?若每块的长度为8,其平均检索的长度是多少
在分块检索(或块搜素)中,要确定最佳的块数和每块的最佳长度,可以考虑使用平方根法则。该法则认为,如果有 (n) 个元素,最佳的块数 (m) 和每块的最佳长度 (k) 分别为:
[m = \sqrt{n}]
[k = \frac{n}{m} = \sqrt{n}]
对于 256 个元素的线性表,应该分成 (m = \sqrt{256} = 16) 块,每块的最佳长度 (k = \frac{256}{16} = 16)。
如果每块的长度为 8,而不是最佳长度 16,那么平均检索长度(average search length)可以通过以下公式计算:
[L = \frac{k}{2} + \frac{n}{k}]
其中,(k) 是每块的长度,(n) 是元素的总数。
在这个情况下:
[L = \frac{8}{2} + \frac{256}{8} = 4 + 32 = 36]
所以,如果每块的长度为 8,平均检索长度将为 36。但是,为了达到最佳性能,建议使用平方根法则计算最佳的块数和每块的最佳长度。

雪雾:
设有一组关键字(19 1 23 14 55 20 84 27 68 11 10 77)其哈希函数为h(key)=key%13,采用拉链法解决冲突是在0~18的哈希表中对该关键字序列构造哈希表,并求在查找成功的情况下的平均查找长度

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define HASH_TABLE_SIZE 13typedef struct Node {int key;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;
} Bucket;void insert(int key, Bucket* hashTable) {int hashValue = key % HASH_TABLE_SIZE;Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->key = key;newNode->next = hashTable[hashValue].head;hashTable[hashValue].head = newNode;
}Node* search(int key, Bucket* hashTable) {int hashValue = key % HASH_TABLE_SIZE;Node* current = hashTable[hashValue].head;while (current != NULL) {if (current->key == key) {return current; // 找到了}current = current->next;}return NULL; // 没找到
}double calculateASL(Bucket* hashTable) {int totalLength = 0;int totalCount = 0;for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {Node* current = hashTable[i].head;int length = 0;while (current != NULL) {length++;current = current->next;}totalLength += length;totalCount += (length > 0) ? 1 : 0;}return (double)totalLength / totalCount;
}int main() {int keys[] = {19, 1, 23, 14, 55, 20, 84, 27, 68, 11, 10, 77};int keyCount = sizeof(keys) / sizeof(keys[0]);// 初始化哈希表Bucket hashTable[HASH_TABLE_SIZE];for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {hashTable[i].head = NULL;}// 插入关键字for (int i = 0; i < keyCount; i++) {insert(keys[i], hashTable);}// 计算平均查找长度double averageSearchLength = calculateASL(hashTable);printf("Average Search Length: %.2lf\n", averageSearchLength);return 0;
}