目录
- 链表的概念和结构
- 单链表
- OJ练习
1. 链表的概念和结构
1.1 链表的概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
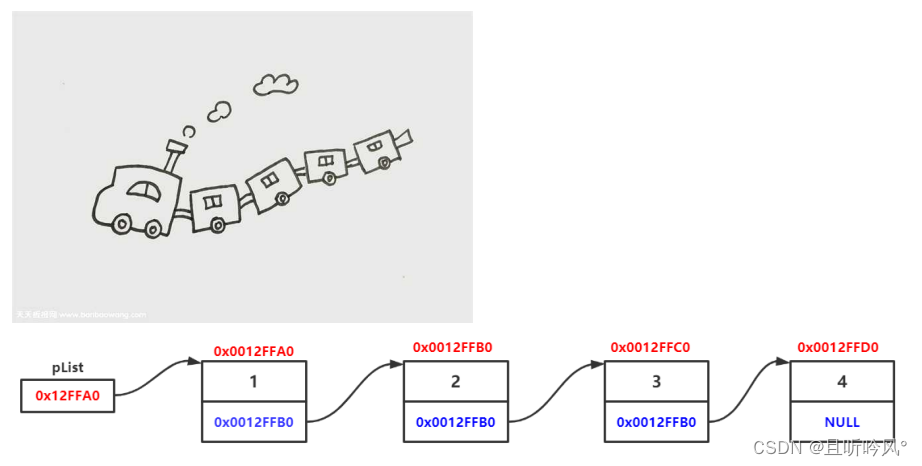 1.从上图可以看出链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,物理上不一定连续
1.从上图可以看出链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,物理上不一定连续
2.现实中的节点一般都是从堆上申请出来的
3.从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续
1.2 链表的分类
以下情况组合起来可能有8种链表结构
1.单向或者双向
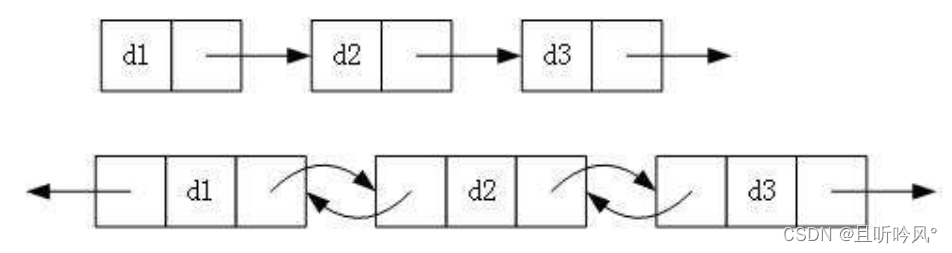
2.带头或者不带头
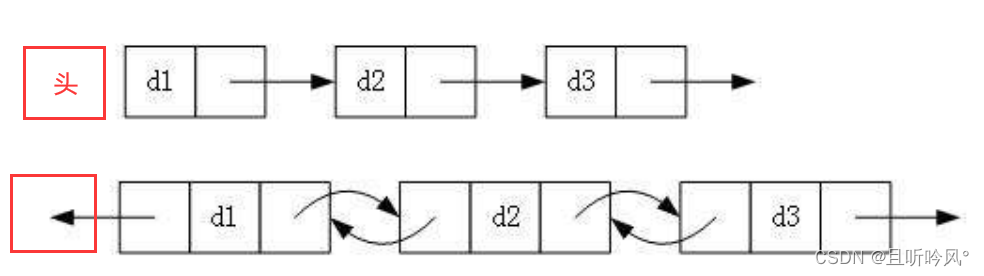
3.循环或非循环
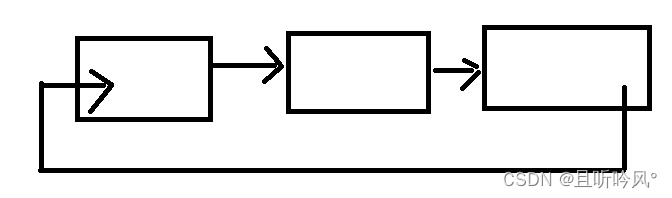
虽然有这么多链表结构,但我们常用的还是两种结构
无头单向非循环链表
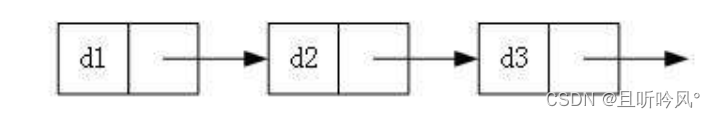 带头双向循环
带头双向循环
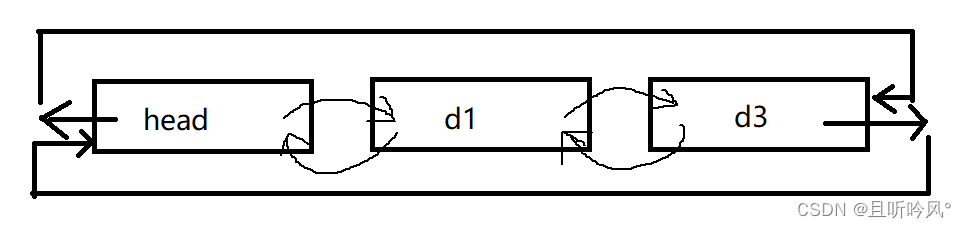 1.无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现更多
1.无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现更多
2.带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现
2. 单链表
头文件
#pragma once//数据类型
typedef int DataType;
//结构
typedef struct _SListNode
{DataType data;struct _SListNode* pNext;
}SListNode;//插入
void PushFront(SListNode** pHead, DataType data);
void PushBack(SListNode** pHead, DataType data);
//pos之前插入
void Insert(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pPos, DataType data);
//pos之后插入
void InsertAfter(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pPos, DataType data);
//查找
SListNode* Find(SListNode* pHead, DataType data);
//删除
void PopFront(SListNode** pHead);
void PopBack(SListNode** pHead);
void Erase(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pos);
// 删除pos位置后面的值
void EraseAfter(SListNode* pos);//打印
void PrintList(SListNode* pHead);
//销毁
void Destory(SListNode** pHead);
实现文件
#include "SList.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>SListNode* BuyNode(DataType data)
{//创建新节点SListNode* NewNode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (NewNode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}NewNode->data = data;NewNode->pNext = NULL;return NewNode;
}void PushFront(SListNode** pHead, DataType data)
{//新节点SListNode* NewNode = BuyNode(data);//连接NewNode->pNext = *pHead;*pHead = NewNode;
}void PushBack(SListNode** pHead, DataType data)
{SListNode* NewNode = BuyNode(data); //分情况,如果链表为空if (*pHead == NULL){*pHead = NewNode;}else{//找链表尾SListNode* pTail = *pHead;while (pTail->pNext != NULL){pTail = pTail->pNext;}pTail->pNext = NewNode;}}void Insert(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pPos, DataType data)
{assert(pHead);assert(pPos);//记录当前节点SListNode* pCur = *pHead;//插入位置为第一个节点,头插if (pCur == pPos){PushFront(pHead, data);}else{//找pos位置链接while (pCur->pNext != pPos){pCur = pCur->pNext;}SListNode* NewNode = BuyNode(data);NewNode->pNext = pPos;pCur->pNext = NewNode;}}void InsertAfter(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pPos, DataType data)
{assert(pPos);//直接将pos位置链接SListNode* NewNode = BuyNode(pHead);NewNode->pNext = pPos->pNext;pPos->pNext = NewNode;
}SListNode* Find(SListNode* pHead, DataType data)
{SListNode* pCur = pHead;while (pCur != NULL){if (pCur->data == data)return pCur;pCur = pCur->pNext;}return NULL;
}void PopFront(SListNode** pHead)
{assert(*pHead);//记录释放指针SListNode* pDel = *pHead;//移动链表首节点*pHead = pDel->pNext;free(pDel);
}void PopBack(SListNode** pHead)
{assert(*pHead);//记录释放指针//如果只有一个节点,需要将链表置空if ((*pHead)->pNext == NULL){free(*pHead);*pHead = NULL;}else{//找链表尾SListNode* pTail = *pHead;while (pTail->pNext->pNext != NULL){pTail = pTail->pNext;}free(pTail->pNext);pTail->pNext = NULL;}}void Erase(SListNode** pHead, SListNode* pos)
{assert(pHead);assert(pos);//删第一个节点,头删if (*pHead == pos){PopFront(pHead);}else{//找pos位置SListNode* pPrev = *pHead;while (pPrev->pNext != pos){ pPrev = pPrev->pNext;}pPrev->pNext = pos->pNext;free(pos);}}void EraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->pNext);//断开pos位置SListNode* Del = pos->pNext;pos->pNext = Del->pNext;free(Del);
}void PrintList(SListNode* pHead)
{SListNode* pCur = pHead;while (pCur != NULL){printf("%d ", pCur->data);pCur = pCur->pNext;}printf("\n");
}
//一级指针无需断言,需要在调用后置空
void Destory(SListNode** pHead)
{assert(pHead);SListNode* cur = *pHead;SListNode* del = NULL;while (cur != NULL){del = cur;cur = cur->pNext;free(del);}*pHead = NULL;
}
主文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "SList.h"
int main()
{//SListNode* pList = NULL;//插入//PushFront(&pList, 3);//PushFront(&pList, 2);//PushFront(&pList, 1);//PushBack(&pList, 4);//PushBack(&pList, 5);//PrintList(pList);//删除//PopFront(&pList);//PopBack(&pList);//PrintList(pList);//Insert();//SListNode* p = Find(pList, 3);//Insert(&pList, p, 8);//PrintList(pList);//InsertAfter(&pList, p, 9);//EraseAfter(p);//PrintList(pList);return 0;
}单链表的实现中需要注意的问题,一个是如果需要改变链表的指针位置,则需要传入二级指针。不用二级指针则需要返回新的头。assert需要断言的地方有哪些,如果操作会崩溃的地方必须断言,断言是一种严厉的检查,if判断则是温柔的检查。
在插入和删除等这些操作的时候,需要考虑只有一个节点的情况,如果传入节点可以为空,也要考虑为空的情况,pos位置的合理性也需要断言或考虑在内
在插入的时候也有一种取巧的办法,将新节点和前一个节点的值直接替换,这样在之前插入只需要遍历一次
3. OJ练习
3.1 移除元素
移除链表元素:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
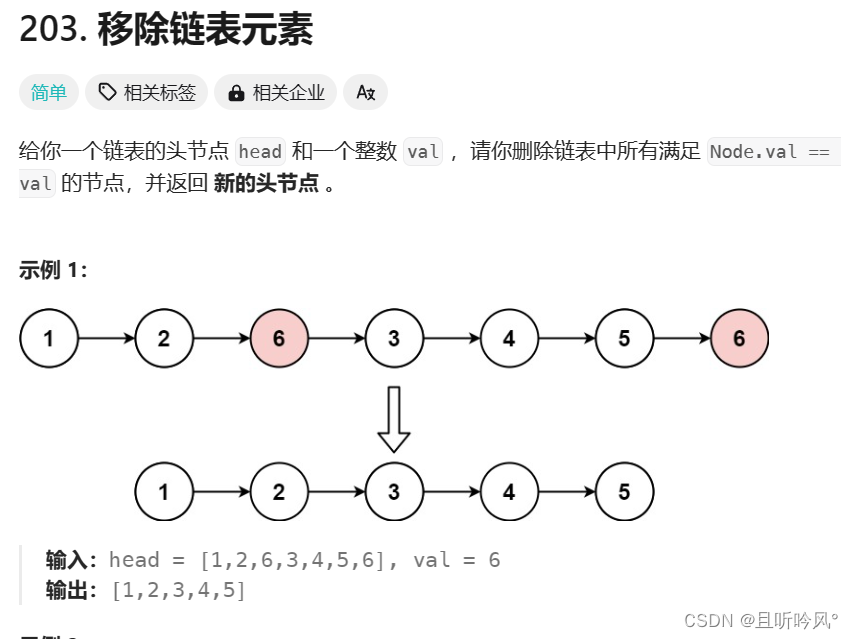
解析
这个考虑的是链表的删除操作,需要一前一后两个指针才能删除当前节点。同时,不要忘了考虑只有一个节点,头删的情况
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {struct ListNode* pPrev = NULL;struct ListNode* pCur = head;while (pCur != NULL)
{if (pCur->val == val){//判断是不是第一个节点if (pCur == head){//头删pCur = pCur->next;free(head);head = pCur;}else{//不是头删,移除元素pPrev->next = pCur->next;free(pCur);pCur = pPrev->next;}}else{pPrev = pCur;pCur = pCur->next;}}return head;
}
另一种思路,可以将不是6的元素放入新链表尾插,然后返回新的链表头。需要考虑第一个节点的情况和每次插入后下节点置空
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {struct ListNode* pCur = head;struct ListNode* NeoHead = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;while (pCur != NULL) {//不是该值的放入新链表if (pCur->val != val) {if (tail == NULL) {NeoHead = pCur;} else {tail->next = pCur;}tail = pCur;pCur = pCur->next;}//是该值释放else {struct ListNode* del = pCur;pCur = pCur->next;free(del);}//第一个节点或空链表tail不能置空if (tail != NULL) {//最后一个节点断掉tail->next = NULL;}}return NeoHead;
}
3.2 反转单链表
反转链表: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
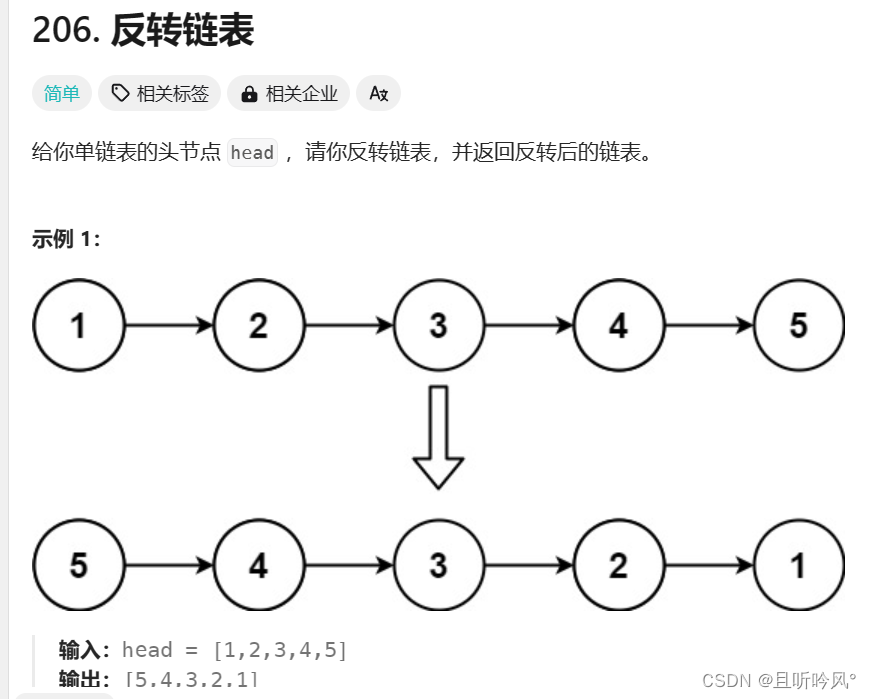
解析
两种思路大体差不多,第一种是将每个节点的指向反过来,第二种是每拿到一个节点直接头插。这里演示第二种思路,可以少一些判断
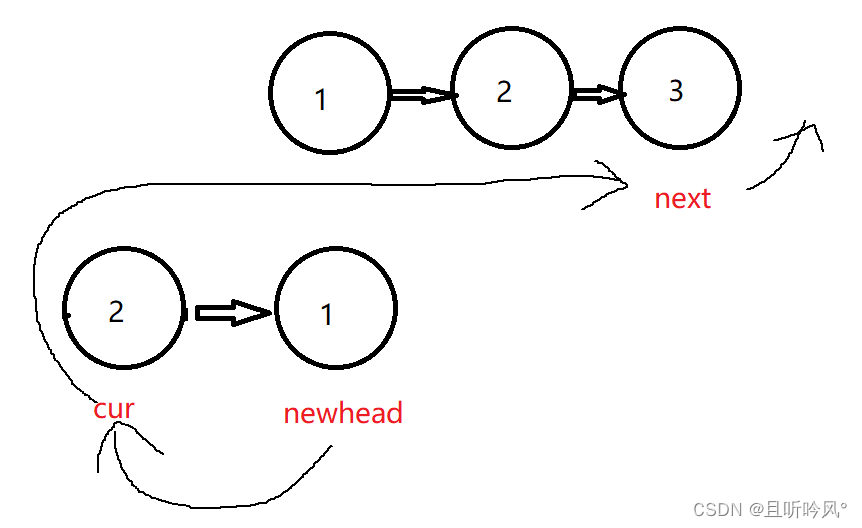
需要三个变量,cur和newhead用来头插交换指向,newhead记录新的头节点,next记录下一个用来插入的元素
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while(cur != NULL){//记录下一个插入的元素struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//头插cur->next = newhead;//移动头节点newhead = cur;//迭代cur = next;}return newhead;
}
3.3 中间节点
链表中间节点https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
第一种思路:
遍历求出链表长度返回需要的中间节点的链表
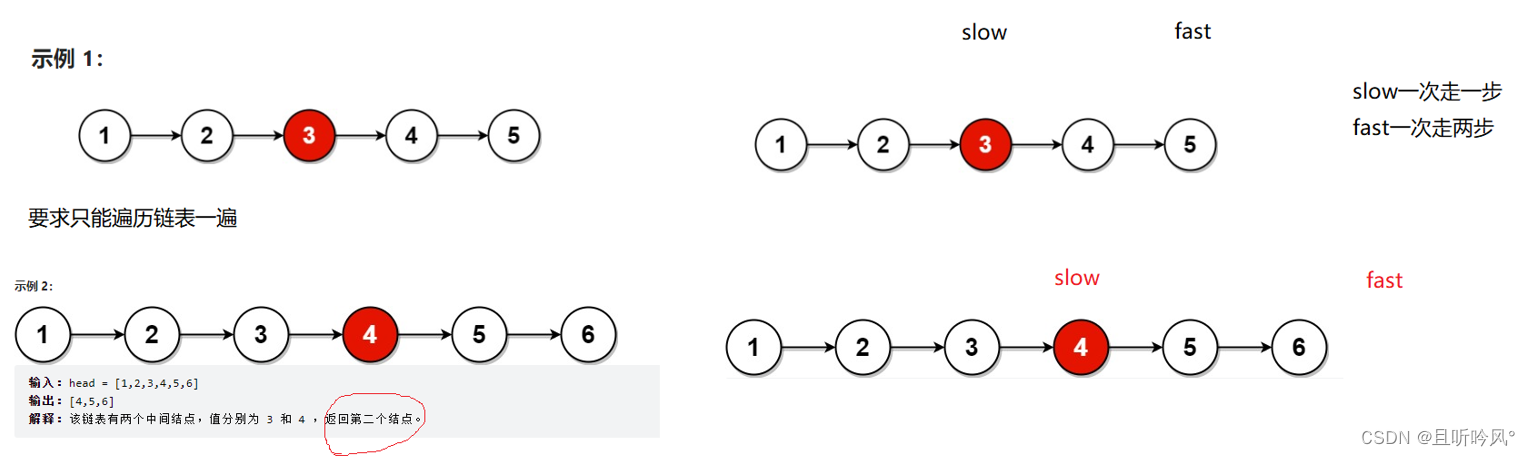
第二种思路:
慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步,当快指针走完的时候,慢指针刚好走了链表一半,画图来分开链表奇数个和偶数个的情况
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}
3.4 倒数第k节点
链表倒数第k个节点:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
第一个方法: 求链表总长度,减去k就知道返回哪个节点的值
第二个方法:和上面思路一样,用一个快慢指针,让两个指针拉开差距,返回第k个节点就让快指针走几步,然后同时移动两个指针,直到快指针为空返回慢指针的值
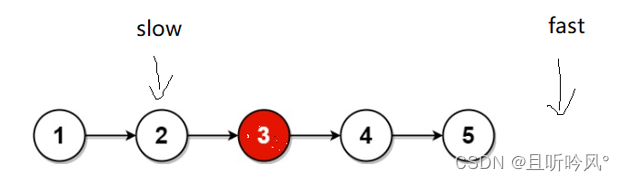
其中有两点需要判断,如果传入的是空指针返回空,如果快指针在拉开距离的时候是空,说明要返回的值超出链表范围,也返回空
/*** struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*//**** @param pListHead ListNode类* @param k int整型* @return ListNode类*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {// write code herestruct ListNode* slow = pListHead;struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;//空链表if (pListHead == NULL) {return NULL;}while (k > 0) {//快指针为空,返回空if (fast == NULL)return NULL;fast = fast->next;k--;}while (fast != NULL) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return slow;}
3.5 合成链表
合并两个有序链表:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/

将两个列表的元素挨个比较,较小的插入新链表。首先需要判断两个链表中可能有一个或两个链表都为空的情况,如果其中一个是空链表,直接返回另一个即可。在插入的过程中需要判断是不是第一个节点的情况,也就是新链表第一次插入。最后有一个链表迭代后为空时,需要将尾巴与另一个链表连接上
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {//如果有一个链表为空,返回另一个if(list1 == NULL)return list2;if(list2 == NULL)return list1;struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL) {if (list1->val <= list2->val) {//是不是第一个节点if (tail == NULL) {newnode = list1;tail = list1;} else {tail->next = list1;tail = list1;}list1 = list1->next;} else {//同上if (tail == NULL) {newnode = list2;tail = list2;} else {tail->next = list2;tail = list2;}list2 = list2->next;}}//一个链表走完,链接另一个if (list1 == NULL) {tail->next = list2;}if (list2 == NULL) {tail->next = list1;}return newnode;
}
3.6 链表分割
链表分割https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking

约瑟夫环,所与人围成一个圈,数到3或数到4的人自杀,什么位置才能让自己幸存到最后一个
用数组解决,挪动删除比较麻烦,所以可以直接用标记-1为已经删除的。这种更适合用链表做,删除必剪方便
思路
可以用两个链表,为了保证数据的顺序不变,将这个值大和小的节点分别尾插到两个链表。在最后,要把后面的链表尾置空,不然会循环起来。可以设置哨兵位,也可以不设置,头节点的尾插会方便很多
不带哨兵位
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {// write code here//记录链表头和当前链表尾ListNode* list1 = NULL;ListNode* cur1 = NULL;ListNode* list2 = NULL;ListNode* cur2 = NULL;ListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur != NULL) {//插入第一个链表if (cur->val < x) {//第一次插入if (list1 == NULL) {list1 = cur;} else {cur1->next = cur;}cur1 = cur;} else {if (list2 == NULL) {list2 = cur;} else {cur2->next = cur;}cur2 = cur;}cur = cur->next;}//链表为空的三种情况,分别将尾节点置空if (list1 == NULL) {cur2->next = NULL;return list2;} else if (list2 == NULL) {cur1->next = NULL;return list1;} else {cur1->next = list2;cur2->next = NULL;return list1;}}
带哨兵位
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {// write code here\
//两个链表的哨兵位和尾结点,哨兵位不存数据ListNode* head1 = NULL;ListNode* head2 = NULL;ListNode* tail1 = NULL;ListNode* tail2 = NULL;head1 = tail1 = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));head2 = tail2 = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));ListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur != NULL) {//判断大小插入哪个链表if (cur->val < x) {tail1->next = cur;tail1 = cur;} else {tail2->next = cur;tail2 = cur;}cur = cur->next;}//链接两个链表tail1->next = head2->next;//尾结点置空tail2->next = NULL;//更新头节点到第一个链表pHead = head1->next;//释放资源free(head1);free(head2);return pHead;}
3.7 回文结构
链表的回文结构:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
思路
先找到链表的中间节点将后面的逆置,从中间节点开始和头部不断向后比。可以利用前面做过的逆置和中间节点的题
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while (cur != NULL) {//记录下一个插入的元素struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//头插cur->next = newhead;//移动头节点newhead = cur;//迭代cur = next;}return newhead;}bool chkPalindrome(ListNode * A) {// write code hereListNode* mid = middleNode(A);ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid);ListNode* fast = A;while (rmid != NULL) {if(A->val != rmid->val)return false;//迭代A= A->next;rmid = rmid->next;}return true;}
3.8 相交
相交链表:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
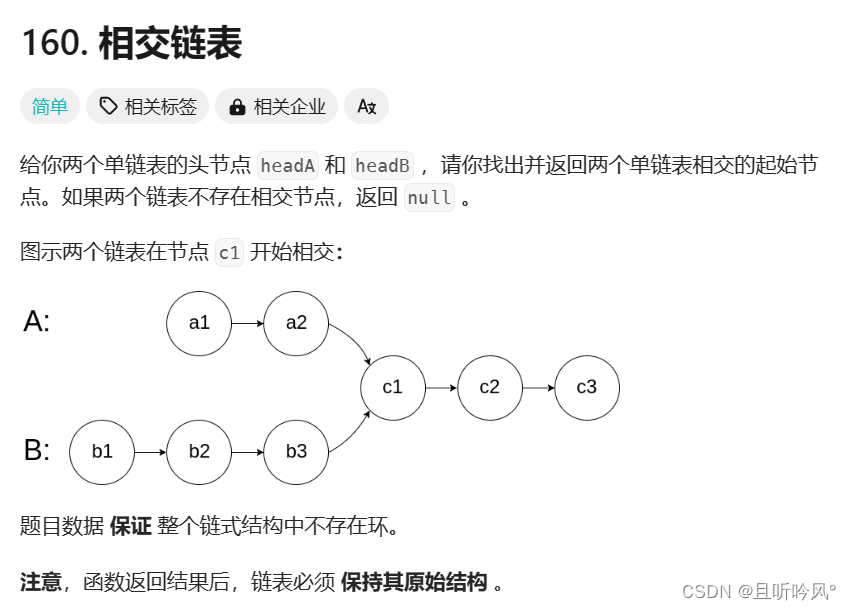
思路
如何判断两个链表有没有相交,可以看两个链表的尾节点是不是一样,因为一个节点不能指向两个节点,所以相交的链表尾结点是一样的。计算出两个链表的长度,让长的链表先走两个的差值,这样再同时走就能找到相交的节点了
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {//记录尾结点struct ListNode * tail1 = headA;struct ListNode * tail2 = headB;//记录长度int len1 = 0;int len2 = 0;//题干链表不是空链表,所以可以直接判断下一个节点while(tail1->next != NULL){tail1 = tail1->next;len1++;}while(tail2->next != NULL){tail2 = tail2->next;len2++;}//有没有交点if(tail1 != tail2){return NULL;}int gap = abs(len1 - len2);//短的移动struct ListNode * shortlist = headA;struct ListNode * longlist = headB;while(gap--){if(len1 > len2)shortlist = shortlist->next;elselonglist = longlist->next;}//找交点返回while(shortlist != longlist){shortlist = shortlist->next;longlist = longlist->next;}return shortlist;
}
3.9 环形链表
是否环形: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
分析
环形链表的一些图示
 当进入到环形里就会不断绕着环转圈,要想看是不是环形链表,就看它遍历后的节点是否会重复,直接判断有些麻烦。可以用快慢指针,如果是环形,快指针肯定会和慢指针相遇,快指针可以一次走n步,每走一步判断是否和慢指针相等。为了方便,这里快指针一次走两步,原因在下面说明
当进入到环形里就会不断绕着环转圈,要想看是不是环形链表,就看它遍历后的节点是否会重复,直接判断有些麻烦。可以用快慢指针,如果是环形,快指针肯定会和慢指针相遇,快指针可以一次走n步,每走一步判断是否和慢指针相等。为了方便,这里快指针一次走两步,原因在下面说明
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode * slow =head;struct ListNode * fast = head;//走到空或只有一个节点结束while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast)return true; }return false;
}
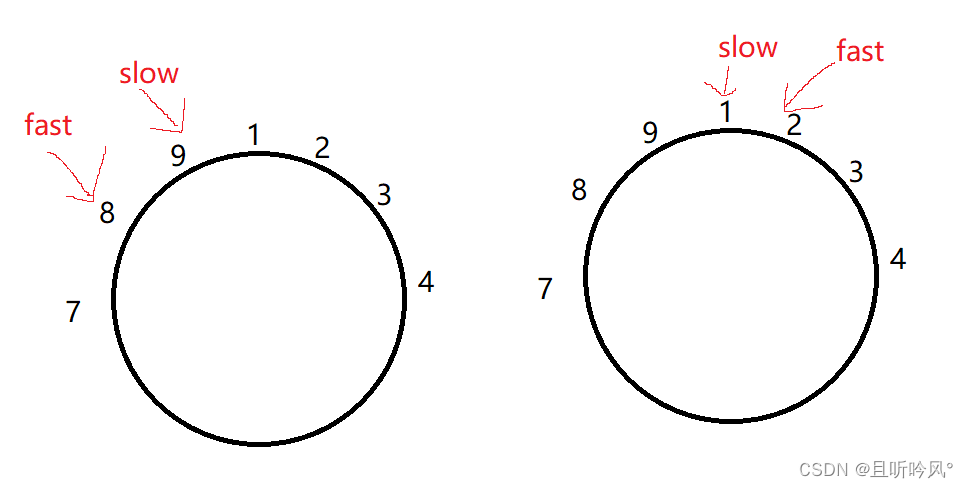
为什么快指针走两步,慢指针走一步就可以
当链表是有环的,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进时,就可能相遇,最差的情况两个指针距离刚好走了环的长度。假设两个指针都进环时距离是N,快指针每走两步就是N+2,慢指针就是N+1,两个相减后,就是距离缩小了一步,这样循环下去,总会有追上的时候
如果快指针走N步,3步5步行不行
这种情况就会有可能一直追不上,还是上面的N,N+3减去N+1,走3步距离每次缩小两步,当之间的距离只有一步时,如果不是快指针每走一步就判断的话就会错过。因为他们的距离每次缩短N-2,可能会越过某一点。就会分环内总长度是奇数还是偶数,如果是奇数,就可能会一直错过
3.10 环链表环节点
返回环形链表入环第一个节点:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/

思路
第一种:
假设快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步。链表头到入环点的距离为L,环型的长度是C,慢指针入环后走的距离是N,慢指针走的总路程L + N,因为不存在会错过的情况,所以快指针必然在一圈内追上慢指针。快指针总路程为L + n * C + N,快指针在相遇时可能已经走了n圈,下图所示:
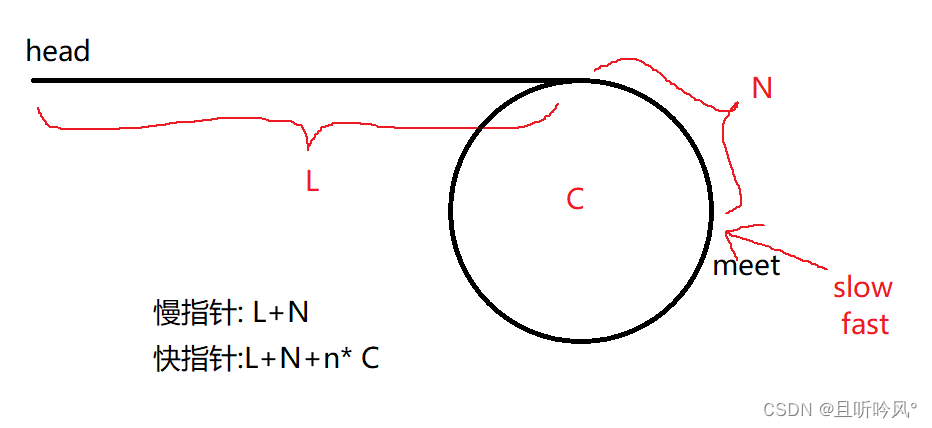
因为每次走两步,所以快指针的总路程是慢指针的2倍,所以有公式:
2(L+N)= L+N+nC
L和N移到左边减去有:
L+N = n C
L = n*C - N
可以理解为: L=(n-1) * (C- N)
C-N的部分刚好是入口点到meet的长度,所以L的长度和meet移动C-N后刚好是入口点
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode * slow =head;struct ListNode * fast = head;//走到空或只有一个节点结束while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){//定义相遇节点struct ListNode * meet = slow;//没遇到继续走while(head != meet){meet = meet->next;head = head->next;}return meet;}}return false;
}
第二种思路:
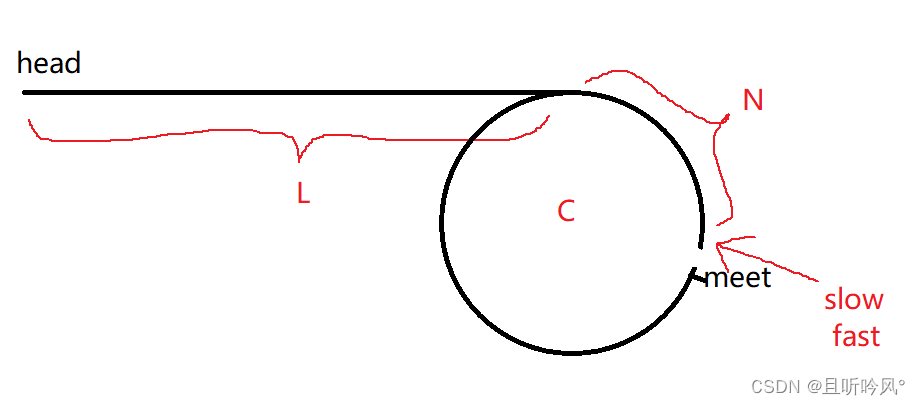
将环内从meet的next处断开,看为新的链表头,和head这个链表找交点,就是入口点
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode * slow =head;struct ListNode * fast = head;//走到空或只有一个节点结束while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if(slow == fast){//定义新链表,尾节点为slowstruct ListNode * meet = slow->next;struct ListNode * tail1 = meet;int len1 = 0;//长链表先走while(tail1 != slow){tail1 = tail1->next;len1++;}struct ListNode * tail2 = head;int len2 = 0;while(tail2 != slow){tail2 = tail2->next;len2++;}int gap = abs(len1 - len2);while(gap--){if(len1 > len2){meet = meet->next;}else{head = head->next;}}//同时走找第一个交点while(head != meet){head =head->next;meet= meet->next;}return meet;}}return NULL;
}