文章目录
- 最长递增子序列
- 解法一:动态规划
- 解法二:LIS 和 LCS 的关系
- 解法三:贪心 + 二分查找
- 相关题目
- 673. 最长递增子序列的个数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-longest-increasing-subsequence/
- 1964. 找出到每个位置为止最长的有效障碍赛跑路线 https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-longest-valid-obstacle-course-at-each-position/
- 1671. 得到山形数组的最少删除次数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-number-of-removals-to-make-mountain-array/
- 354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题 https://leetcode.cn/problems/russian-doll-envelopes/
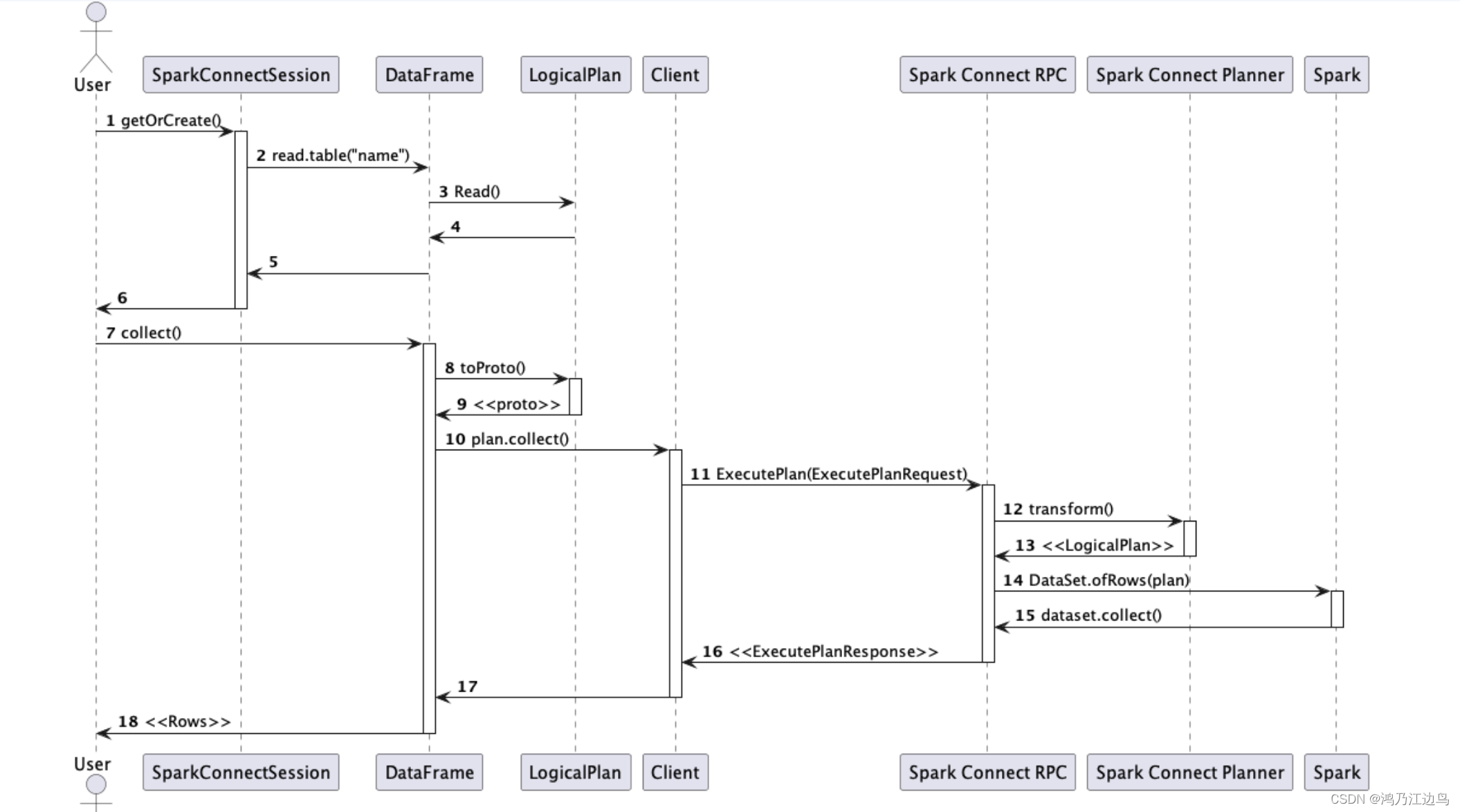
- 1626. 无矛盾的最佳球队 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-team-with-no-conflicts/
本文介绍最长递增子序列的两种解法,以及一些相关题目的简单答案。
本文的重点是学习 时间复杂度为 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2) 的动态规划 和 时间复杂度为 ( N ∗ log 2 N ) (N*\log{2}{N}) (N∗log2N) 的贪心+二分查找 这两种解决 类 最长递增子序列问题的解法。
在最后补充的相关题目中,需要学习当需要考虑的元素有两个时,如何通过自定义排序来避免考虑其中的一个元素。
最长递增子序列
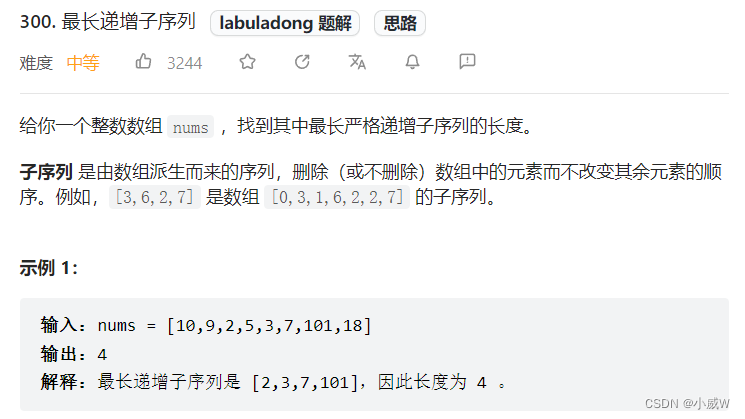
300. 最长递增子序列
解法一:动态规划
双重 for 循环 dp。
class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length, ans = 1;int[] dp = new int[n];Arrays.fill(dp, 1);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {// nums[i]可以作为nums[j]的后续元素if (nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);}ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);}return ans;}
}
还有一种 dp 写法,我感觉比较奇怪还没有理解:
class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length, ans = 1;int[] dp = new int[n];Arrays.fill(dp, 0);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j]);}dp[i]++;}return Arrays.stream(dp).max().getAsInt();}
}
推荐使用第一种写法。
解法二:LIS 和 LCS 的关系

也就是说:
nums = [1, 3, 3, 2, 4]
排序去重后为: [1, 2, 3, 4]
求 nums 和 [1, 2, 3, 4] 的最长公共子序列就好了。方法参见:【算法】最长公共子序列&编辑距离
这种方法 和 上面的 DP 方法的时间复杂度都是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) 的。
解法三:贪心 + 二分查找
进阶技巧:对于动态规划,可以尝试 交换状态与状态值。

例如:
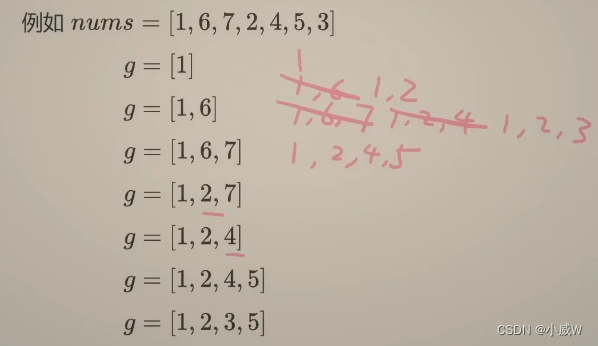
很容易可以理解下面代码的逻辑,从前向后依次遍历各个元素。
- 当前元素大于列表中已有的最后一个元素时,将其加入列表;
- 当前元素不大于列表中已有的最后一个元素时,则找到列表中第一个大于等于当前元素数字的位置,将其替换成当前元素。
class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList();int n = nums.length;ls.add(nums[0]);for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {if (nums[i] > ls.get(ls.size() - 1)) ls.add(nums[i]);else {int l = 0, r = ls.size() - 1; // 找到第一个大于等于nums[i]的位置while (l < r) {int mid = l + r >> 1;if (ls.get(mid) < nums[i]) l = mid + 1;else r = mid;}ls.set(l, nums[i]);}}return ls.size();}
}
相关题目
673. 最长递增子序列的个数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-longest-increasing-subsequence/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-longest-increasing-subsequence/
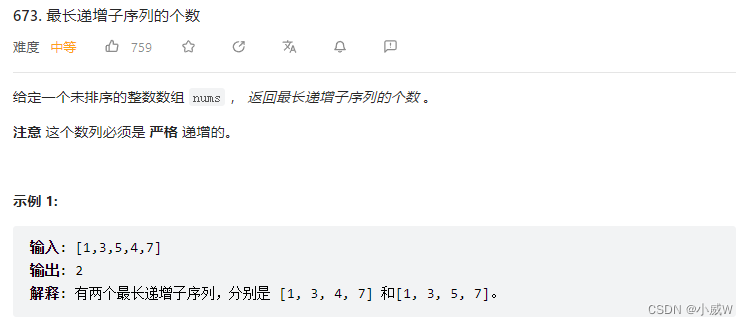
这道题目不仅需要知道最长递增子序列的长度,还需要知道它的数量,因此需要一个额外的 cnt[] 数组。
class Solution {public int findNumberOfLIS(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length, mxL = 1, ans = 0;int[] dp = new int[n], cnt = new int[n]; // 一个记录最大长度,一个记录最大长度的数量Arrays.fill(dp, 1);Arrays.fill(cnt, 1);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {// dp 递推if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {if (dp[j] + 1 > dp[i]) {dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;cnt[i] = cnt[j];} else if (dp[j] + 1 == dp[i]) cnt[i] += cnt[j];}}mxL = Math.max(mxL, dp[i]);}// 统计所有序列长度为最长的数量之和for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (dp[i] == mxL) ans += cnt[i];}return ans;}
}
这题也可以使用 贪心+前缀和+二分查找 来做。(有兴趣的自己看吧:https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-longest-increasing-subsequence/solution/zui-chang-di-zeng-zi-xu-lie-de-ge-shu-by-w12f/)
1964. 找出到每个位置为止最长的有效障碍赛跑路线 https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-longest-valid-obstacle-course-at-each-position/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-longest-valid-obstacle-course-at-each-position/
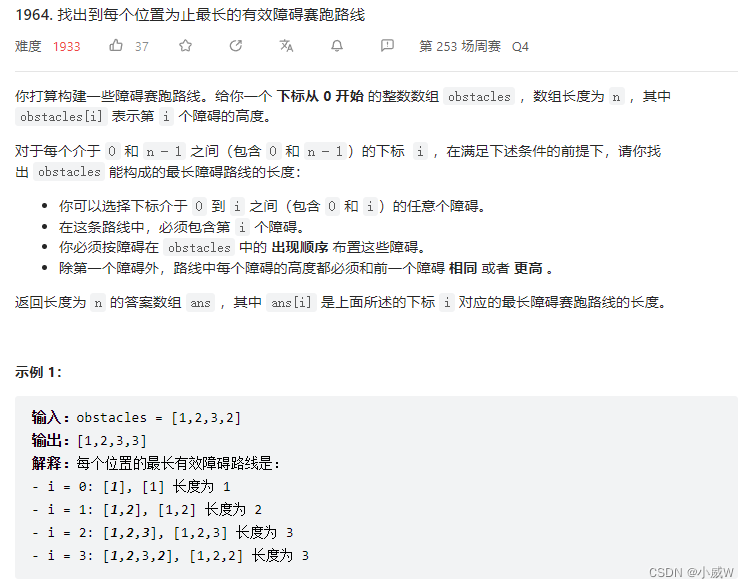
提示:
n == obstacles.length
1 <= n <= 10^5
1 <= obstacles[i] <= 10^7
实际上是求以 i 为结尾的最长非递减子序列长度。
观察到题目给出的数据范围,因此直接使用时间复杂度为 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)的动态规划是会TLE的。
下面给出超时的代码:
class Solution {public int[] longestObstacleCourseAtEachPosition(int[] obstacles) {int n = obstacles.length;int[] ans = new int[n];Arrays.fill(ans, 1);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {if (obstacles[j] <= obstacles[i]) ans[i] = Math.max(ans[j] + 1, ans[i]);}}return ans;}
}
所以,我们需要使用时间复杂度为 O ( N ∗ log 2 N ) O(N*\log_{2}{N}) O(N∗log2N) 的贪心+二分查找方法来做这道题目。
代码如下:
class Solution {public int[] longestObstacleCourseAtEachPosition(int[] obstacles) {int n = obstacles.length;List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList();ls.add(obstacles[0]);int[] ans = new int[n];ans[0] = 1;for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {if (obstacles[i] >= ls.get(ls.size() - 1)) { // 很大,直接放在最后ls.add(obstacles[i]);ans[i] = ls.size();} else {// 寻找第一个大于obstacles[i]的数字int l = 0, r = ls.size() - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = l + r >> 1;if (ls.get(mid) <= obstacles[i]) l = mid + 1;else r = mid;}ls.set(l, obstacles[i]);ans[i] = l + 1;}}return ans;}
}
将代码与 最长递增子序列 这道题目的答案进行比较,可以发现其实只多了两句:
ans[i] = ls.size();
和
ans[i] = l + 1;
1671. 得到山形数组的最少删除次数 https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-number-of-removals-to-make-mountain-array/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-number-of-removals-to-make-mountain-array/
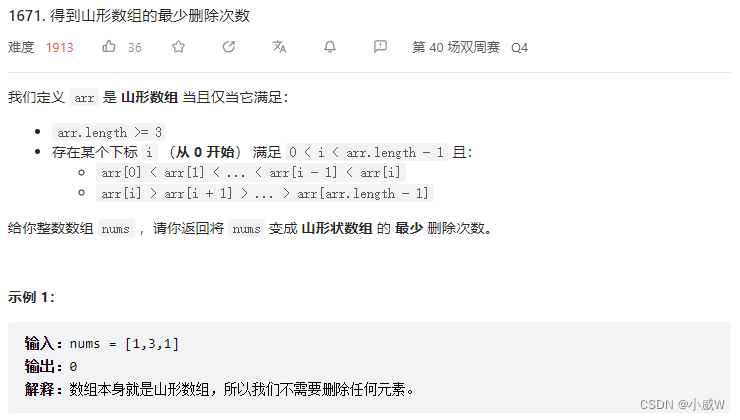
对于数组中的每个元素,求 以它为结尾的从前往后的最长递增子序列长度 和 以它为结尾的从后往前的最长递增子序列的长度,这样它就是山形数组的山顶。
判断哪个元素作为山顶时,两个递增子序列的长度之和最长,结果就取哪个。
(注意题目要求山顶两边都必须有比它小的数字)
class Solution {public int minimumMountainRemovals(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length, ans = n;int[] l1 = new int[n], l2 = new int[n];List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList();// 找从前往后的for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (ls.size() == 0 || nums[i] > ls.get(ls.size() - 1)) ls.add(nums[i]);else ls.set(bs(ls, nums[i]), nums[i]);l1[i] = ls.size();}ls.clear();// 找从后往前的for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {if (ls.size() == 0 || nums[i] > ls.get(ls.size() - 1)) ls.add(nums[i]);else ls.set(bs(ls, nums[i]), nums[i]);l2[i] = ls.size();}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {// 山顶两边都必须有比它小的数字,因此序列长度只有1(只有它自己)是不行的if (l1[i] == 1 || l2[i] == 1) continue; ans = Math.min(n - l1[i] - l2[i] + 1, ans);}return ans;}public int bs(List<Integer> ls, int v) {// 二分查找int l = 0, r = ls.size() - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = l + r >> 1;if (v > ls.get(mid)) l = mid + 1;else r = mid;}return l;}
}
354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题 https://leetcode.cn/problems/russian-doll-envelopes/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/russian-doll-envelopes/
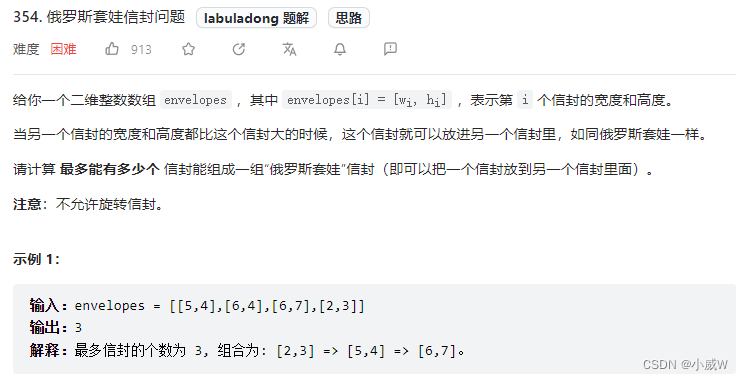
提示:
1 <= envelopes.length <= 10^5
envelopes[i].length == 2
1 <= wi, hi <= 10^5
注意看数据范围,使用 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2) 的动态规划是会超时的。
这道题目一个很牛逼的点在于:使用自定义排序,这样在遍历的过程中就可以忽略信封的宽度了。
忽略宽度后,求排序后高度的最长递增子序列即可。
class Solution {public int maxEnvelopes(int[][] envelopes) {Arrays.sort(envelopes, (a, b) -> {return a[0] == b[0]? b[1] - a[1]: a[0] - b[0]; // 第一元素升序,第二元素降序});// 之后可以忽略第一元素了int n = envelopes.length;List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList();ls.add(envelopes[0][1]);for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {if (envelopes[i][1] > ls.get(ls.size() - 1)) ls.add(envelopes[i][1]);// 二分查找寻找需要放置的位置int l = 0, r = ls.size() - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = l + r >> 1, v = ls.get(mid);if (v < envelopes[i][1]) l = mid + 1;else r = mid;}ls.set(l, envelopes[i][1]);}return ls.size();}
}
Q:为什么要这样自定义排序?
A:首先按第一元素升序排序没有疑问,为了在遍历的过程中可以忽略第一元素,所以在第一元素相等的情况下,需要对第二元素进行降序排序。举个例子如下:

对第二关键字进行降序排序后,这些 h 值就不可能组成长度超过 1 的严格递增的序列了。
(详情解释可见:https://leetcode.cn/problems/russian-doll-envelopes/solution/e-luo-si-tao-wa-xin-feng-wen-ti-by-leetc-wj68/)
1626. 无矛盾的最佳球队 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-team-with-no-conflicts/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-team-with-no-conflicts/
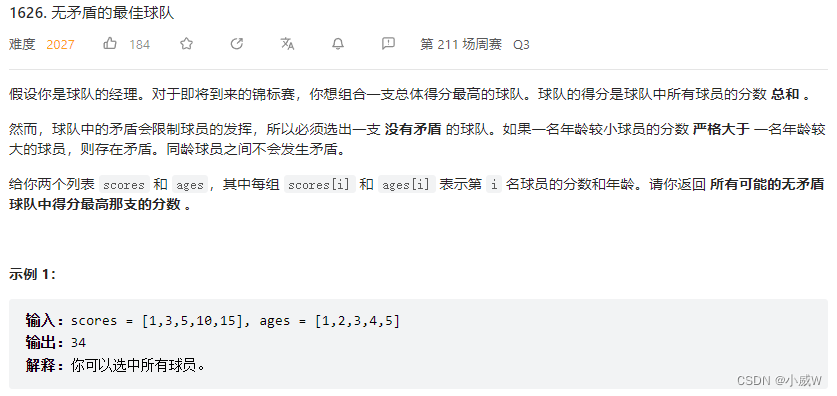
1 <= scores.length, ages.length <= 1000
数据范围比较小,可以使用时间复杂度为 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2) 的动态规划。
对于这种需要同时考虑两种元素的,我们的一个重要策略就是通过自定义排序忽略其中的每一种元素。
在这道题中,先按分数升序排,再按年龄升序排。这样后面遍历到的分数已经时符合条件的,这样只需要判断年龄就可以了。
dp 数组的意义是:dp[i] 表示最后组建的球队中的最大球员序号为排序后的第 i 名球员时的球队最大分数(此时的球员序号为排序后的新序号)
class Solution {public int bestTeamScore(int[] scores, int[] ages) {int n = scores.length;int[][] people = new int[n][2];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {people[i][0] = scores[i];people[i][1] = ages[i];}// 排序 按分数升序排,再按年龄升序排Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> {return a[0] != b[0]? a[0] - b[0]: a[1] - b[1];});int[] dp = new int[n];int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {dp[i] = people[i][0]; // 至少选自己for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {// 我的分数一定大于等于你了,只要年纪也大于等于你就可以和你一起选if (people[i][1] >= people[j][1]) {dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + people[i][0]);}}ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);}return ans;}
}