shell学习第7天
- sed的学习
- 1.sed是什么
- 2.sed有两个空间pattern hold
- 3.sed的语法
- 4. sed里单引号和双引号的区别:
- 5.sed的查找方式
- 6.sed的命令
- sed的标签用法
- sed的a命令:追加
- sed的i命令:根据行号插入
- sed的c命令:整行替换
- sed的r命令
- sed的s命令:替换
- sed的d命令:删除
- sed中的&符号
- 7.怎么替换有深度的文件
- 8. 练习(要是awk更好,就用awk)
- 9.小知识点
- 判断进程是否起来 pidof
- 正则中的 \w 和 \W \s和\b
- \1
- 输出文本的第一行和最后一行
- 编写一个一键更换ip地址,并检测ip地址是否合法的脚本。
- 一键更换ip升级版
sed的学习
1.sed是什么
sed - stream editor for filtering and transforming text
用于过滤和转换文本的Sed流编辑器 —>
文字流编辑器Sed is a stream editor. A stream editor is used to perform basic text transformations on
an input stream (a file or input from a pipeline).Sed是一个流编辑器。流编辑器用于在上执行基本的文本转换
输入流(来自管道的文件或输入)。
sed是脚本中修改文本或者文本替换的最佳工具
简单的例子:修改selinux的配置文件 把enforcing改成disabled
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted [root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
2.sed有两个空间pattern hold
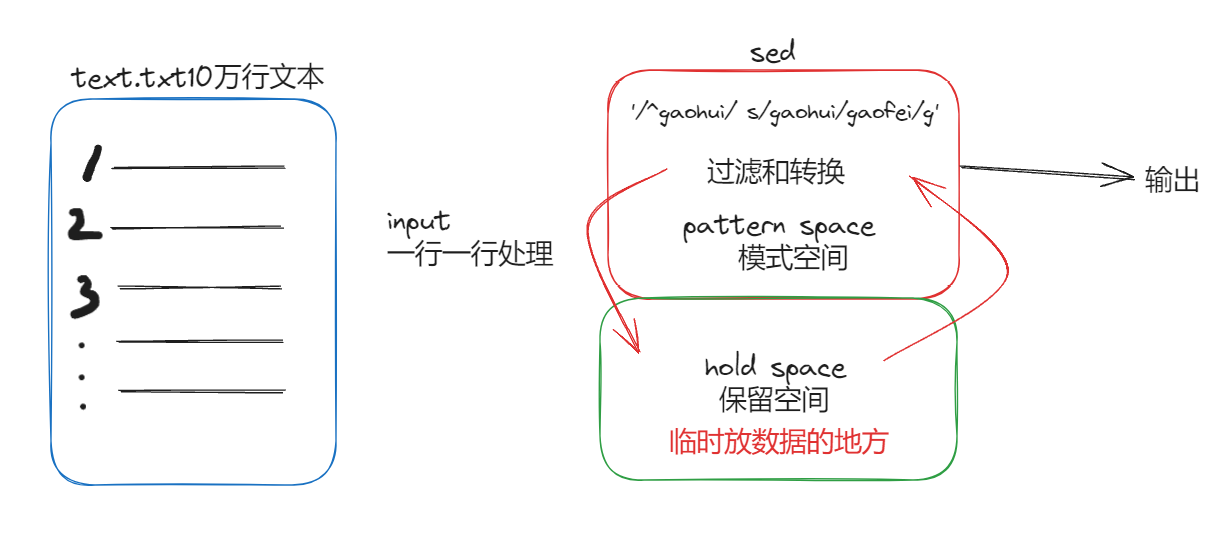
-i选项直接对源文件进行修改
不接-i就是输出到屏幕 不改源文件
pattern space 输出之后就会清空里边的内容
3.sed的语法



执行多条语句,先打印1-10行,再打印20行,30行
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -n '1,10p;20p;30p' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
chrony:x:998:996::/var/lib/chrony:/sbin/nologin
sc13:x:1012:1012::/home/sc13:/bin/bash
[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
cat passwd -n|sed -n ‘1 ~ 3p’:每隔三行输出一下
4. sed里单引号和双引号的区别:

[root@gh-shell 1-22] num1=10
[root@gh-shell 1-22] num2=20
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat -n /etc/passwd|sed -n "${num1},${num2}p"10 operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin11 games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin12 ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin13 nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin14 systemd-network:x:192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin15 dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin16 polkitd:x:999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin17 tss:x:59:59:Account used by the trousers package to sandbox the tcsd daemon:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin18 sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin19 postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin20 chrony:x:998:996::/var/lib/chrony:/sbin/nologin
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 5.sed的查找方式
-
根据行号
通过 -p [root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -n '1p;2p' passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin [root@gh-shell 1-22]# -
根据模式—>正则表达式=字符+特殊符号

[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -n '/bash/p' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
sc1:x:1000:1000::/home/sc1:/bin/bash
sc5:x:1004:1004::/home/sc5:/bin/bash
sc6:x:1005:1005::/home/sc6:/bin/bash
sc7:x:1006:1006::/home/sc7:/bin/bash
sc8:x:1007:1007::/home/sc8:/bin/bash
sc9:x:1008:1008::/home/sc9:/bin/bash
。
。
。
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# -n太好用了,只显示匹配处理的行
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -rn '/^#|^$/!p' /etc/grub2.cfg
'不打印出以#开头,还有空行的行'
//$/p 找出以/结尾的行,需要用到转义符号
[root@gh-shell 1-22] df -h|sed -n '/\/$/p'
/dev/mapper/centos-root 50G 2.1G 48G 5% /
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 6.sed的命令
sed的标签用法

玩一下:
[root@gh-shell 1-22] tail -1 passwd
gaofei12:x:1032:1032::/home/gaofei12:/bin/bash
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i -r 's/(^[0-Z]+)(.*)/\1/' passwd
[root@gh-shell 1-22] tail -1 passwd
gaofei12
[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
{=;p}先执行=号命令,作用输出行号,然后执行打印内容命命sed -E-n'/\b(\w+)\s+\1\b/{=;p}'two-cities-dup1.txt
sed的a命令:追加
[root@gh-shell shell] sed -i '2a gaodafei' user_pwd.txt #第二行的后面加个gaodafei
[root@gh-shell shell] head -5 user_pwd.txt
gf1 01a8589953
gf2 76088a94e6
gaodafei
gf3 e09f493732
gf4 d07af864bb
[root@gh-shell shell]#
[root@gh-shell shell] sed -i '/gf3/a gaodafei123' user_pwd.txt
[root@gh-shell shell] head -5 user_pwd.txt
gf1 01a8589953
gf2 76088a94e6
gaodafei
gf3 e09f493732
gaodafei123
[root@gh-shell shell]# sed的i命令:根据行号插入
[root@gh-shell shell] sed -i '$i gaohui' user_pwd.txt #在匹配的那个前一行加入
[root@gh-shell shell] tail user_pwd.txt
gaodafei123
gf4 d07af864bb
gf5 57196a836a
gf6 2fce65efeb
gf7 2f41fdfa48
gf8 d610f5fcf3
gf9 e5003d62d1
gf10 7e8c0ffca3
gaohui
gaohui
[root@gh-shell shell]#
[root@gh-shell shell] sed -i '/li/i shenmj' user_pwd.txt 匹配的前一行加
[root@gh-shell shell] tail user_pwd.txt
gf5 57196a836a
gf6 2fce65efeb
gf7 2f41fdfa48
gf8 d610f5fcf3
gf9 e5003d62d1
gf10 7e8c0ffca3
gaohui
gaohui
shenmj
lidaliu
[root@gh-shell shell]# sed的c命令:整行替换

sed的r命令
'读入操作'
sed '$r /etc/hosts' /etc/fstab
在fstab文件的末尾后面读入hosts文件的内容
sed的s命令:替换



[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
cali 80 91 82 cali feng cali feng
tom 90 80 99
lucy 99 70 75
jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i 's/cali/fengdeyong/' grade.txt #默认替换第一个
[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
fengdeyong 80 91 82 cali feng cali feng
tom 90 80 99
lucy 99 70 75
jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i 's/cali/fengdeyong/2' grade.txt #替换第二个
[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
fengdeyong 80 91 82 cali feng fengdeyong feng
tom 90 80 99
lucy 99 70 75
jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i 's/cali/fengdeyong/g' grade.txt #全局替换
[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
fengdeyong 80 91 82 fengdeyong feng fengdeyong feng
tom 90 80 99
lucy 99 70 75
jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13]# 换分隔符
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i 's#sbin/nologin#fengdeyong#' passwd
[root@gh-shell 1-13] tail passwd
liu1:x:1023:1023::/home/liu1:fengdeyong
liu2:x:1024:1024::/home/liu2:fengdeyong
liu3:x:1025:1025::/home/liu3:fengdeyong
gaodingjiang:x:1026:1026::/home/gaodingjiang:fengdeyong
gaodingjiang1:x:1027:1027::/home/gaodingjiang1:fengdeyong
gaodingjiang12:x:1028:1028::/home/gaodingjiang12:fengdeyong
gaodingjiang123:x:1029:1029::/home/gaodingjiang123:fengdeyong
gh123:x:1030:1030::/home/gh123:fengdeyong
gaofei123:x:1031:1031::/home/gaofei123:fengdeyong
gaofei12:x:1032:1032::/home/gaofei12:fengdeyong
[root@gh-shell 1-13]# 练习:
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed '/^SELINUX=/ s/disabled/enforcing/' /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted [root@gh-shell 1-13]#
尝试删除grade.txt中lucy的行:
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i 's/lucy//g' grade.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
fengdeyong 80 91 82 fengdeyong feng fengdeyong feng
tom 90 80 9999 70 75
jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13]# sed的d命令:删除

'一般不建议删,而是加个注释'
[root@gh-shell 1-13] sed -i '/^jack/ s/^/#/' grade.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-13] cat grade.txt
name chinese math english
fengdeyong 80 91 82 fengdeyong feng fengdeyong feng
tom 90 80 9999 70 75
#jack 60 89 99
[root@gh-shell 1-13]# sed中的&符号
$代替sed在模式匹配里找到的内容
[root@gh-shell 1-24] vim cat.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-24] sed -i 's/.at/"&"/g' cat.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-24] cat cat.txt
i have a "fat" "cat"
i have a "fat" "cat"
i have a "fat" "cat"
i have a "fat" "cat"
i have a "fat" "cat"
[root@gh-shell 1-24]#
7.怎么替换有深度的文件
'先用find找,再用sed替换'
[root@gh-shell 1-22] mkdir aa/bb/cc -p
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cp ip.txt aa/
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cp ip.txt aa/bb/
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cp ip.txt aa/bb/cc/
[root@gh-shell 1-22] find . -name ip.txt
./ip.txt
./aa/bb/cc/ip.txt
./aa/bb/ip.txt
./aa/ip.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 写个脚本去改:
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat sc_sed.sh
#!/bin/bashfor i in $(find /shell -name ip.txt)
doecho $ised -i 's/192.168.1.8/8.8.8.8/g' $iecho "#####################"cat $i
done
[root@gh-shell 1-22] bash sc_sed.sh
/shell/1-22/ip.txt
#####################
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
/shell/1-22/aa/bb/cc/ip.txt
#####################
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
/shell/1-22/aa/bb/ip.txt
#####################
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
/shell/1-22/aa/ip.txt
#####################
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
sanchaung 8.8.8.8 gao 8.8.8.8
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 8. 练习(要是awk更好,就用awk)
19/Jan/2024:09:51:12 到 19/Jan/2024:10:41:48 日志,显示出来–>sed或者awk
'sed:'
sed -n '/19\/Jan\/2024:09:51:12/,/19\/Jan\/2024:10:41:48/p' access.log'awk:'
awk '/19\/Jan\/2024:09:51:12/,/19\/Jan\/2024:10:41:48/' access.log
例子:

复制/etc/hosts文件到当前目录下,然后进行操作在每行前面加一个字符串sanchuang
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i 's/^/sanchuang/' hosts
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat hosts
sanchuang127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
sanchuang::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 自己编辑一个文件test.txt,内容如下:
0.0.0.0
1.1.1.1
2.2.2.2
使用sed或者awk或者编写脚本(shell,python,go等)实现输出以下形式:
0.0.0.0:80,1.1.1.1:80,2.2.2.2:80
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i.bak 'N;N;s/\n/:80,/g;s/$/:80/' test.txt
0.0.0.0:80,1.1.1.1:80,2.2.2.2:80[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat test.txt.bak|sed -n 's/$/:80/;H;${x;s/\n/,/2g;p}'
0.0.0.0:80,1.1.1.1:80,2.2.2.2:80
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 'awk最简单'
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat test.txt.bak.a |xargs |awk '{print $1":80,"$2":80,"$3":90"}'
0.0.0.0:80,1.1.1.1:80,2.2.2.2:90
[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
x Exchange the contents of the hold and pattern spaces.
h H Copy/append pattern space to hold space.
g G Copy/append hold space to pattern space.
n N Read/append the next line of input into the pattern space.
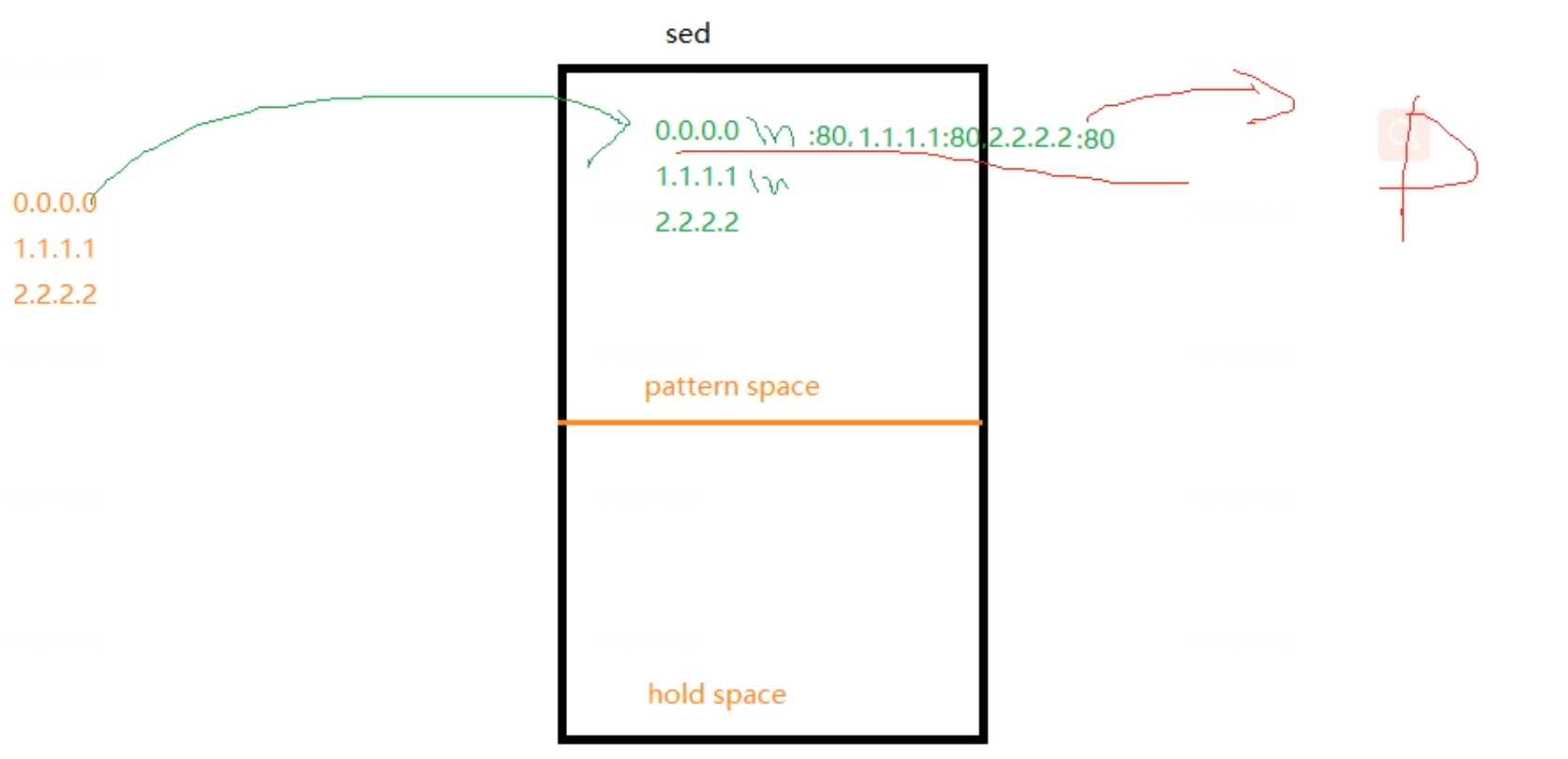
**sed -i.bak ‘N;N;s/\n/:80,/g;s/$/:80/’ test.txt **
这是一个使用
sed命令在文本文件中进行替换的命令。让我逐步解释这个命令:
sed: 流编辑器,用于处理和转换文本流。
-i.bak:-i表示直接在文件中进行修改(in-place),后面的.bak是一个备份文件的扩展名。这样在修改文件的同时会在同级目录下生成一个备份文件,以便于回滚。
'N;N;s/\n/:80,/g;s/$/:80/': 这是sed的编辑脚本,它包含了多个命令。
N;N: 连续两次使用N命令,将下一行添加到当前行的末尾,形成两行的模式空间。
s/\n/:80,/g: 将模式空间中的所有换行符\n替换为:80,。这样,每两行之间的换行符都被替换为:80,,形成了IP地址和端口号的组合。
s/$/:80/: 将模式空间中的行尾$替换为:80,给每一行的最后添加:80。总体来说,这个命令的作用是将每两行之间的换行符替换为
:80,,并在每行的末尾添加:80。最终结果是将test.txt文件中每两行IP地址间的换行符替换为:80,,并在每行的末尾添加:80。
cat test.txt.bak|sed -n 's/$/:80/;H;${x;s/\n/,/2g;p}'这是一个用于处理文本的 LInix 命令行管道,涉及到
sed和cat命令。让我逐步解释这个命令:
cat test.txt.bak:cat命令用于将文件的内容输出到标准输出。这里是将test.txt.bak文件的内容输出。
|:管道符号,将前一个命令的输出传递给下一个命令作为输入。
sed -n 's/$/:80/;H;${x;s/\n/,/2g;p}':sed是一种流编辑器,用于文本流的处理。
-n参数表示关闭默认输出,只输出经过编辑的行。s/$/:80/:正则表达式替换,将每一行的行尾$替换为:80。这样,每个IP地址后都会添加:80。H:将模式空间中的行追加到保持空间(hold space)的末尾。${x;s/\n/,/2g;p}:
${}:表示在最后一行执行的命令。 花括号里边是只对最后一行操作!x:交换模式空间和保持空间的内容。s/\n/,/2g:将保持空间中的所有换行符替换为逗号。这样,每个IP地址与端口号的组合之间的换行符都会被替换为逗号。p:打印最终结果。综合起来,这个命令的作用是将
test.txt.bak文件中的每个IP地址后面添加:80,然后将每个IP地址与端口号的组合之间的换行符替换为逗号,最终输出一行带有IP地址和端口号的字符串。
先复制/etc/passwd文件到当前目录下,然后对当前目录下的passwd进行操作
1.取出passwd文件的第一列
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat passwd|awk -F: '{print $1}'
2.sed将PATH环境变量中的冒号换成 ->可以将PATH变量的内容重定向到一个文件里,例如path.txt
echo $PATH|sed
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# echo $PATH
/shell/1-13/:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# echo $PATH >>gh.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# cat gh.txt
/shell/1-13/:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# sed -i 's/:/->/g' gh.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# cat gh.txt
/shell/1-13/->/usr/local/sbin->/usr/local/bin->/usr/sbin->/usr/bin->/root/bin
[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
3.sed将PATH环境变量斜杠/换成斜杠\
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i 's/\//\\/g' gh.txt
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat gh.txt
\shell\1-13\:\usr\local\sbin:\usr\local\bin:\usr\sbin:\usr\bin:\root\bin
4.sed修改SELINUX配置文件从开启(enforcing)变成禁用(disabled)
/etc/sysconfig/selinux
sed '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
5.去掉passwd文件中第二个字段的x
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat passwd |awk -F: '{print $1":"$3":"$4":"$5":"$6":"$7}'
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i -r '/([0-Z]+)(:X:)(.*)/\1:\3' passwd
6.只显示ip add的ip地址
[root@gh-shell 1-22] ip add|awk -F"[/ ]+" '/ens33$/{print $3}'
192.168.153.166
[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
7.复制/etc/ssh/sshd config到当前目录下,修改里面的端口号修改为8899
将#Port 22 配置修改为Port 8899 要求去掉前面的#号,将22修改为8899
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -i '/^#Port/c Port 8899' ssh_config
9.小知识点
判断进程是否起来 pidof
[root@gh-shell 1-22] pidof nginx
[root@gh-shell 1-22] echo $?
1
[root@gh-shell 1-22] pidof sshd
2740 2719 2133 2109 1109 #获得正在运行的进程号
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 或者直接统计有多少行,一行就是没有启动
[root@gh-shell 1-22] ps -ef|grep nginx
root 3412 2744 0 15:52 pts/3 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@gh-shell 1-22] ps -ef|grep nginx|wc -l
1
[root@gh-shell 1-22] ps -ef|grep sshd
root 1109 1 0 12:28 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 2109 1109 0 12:31 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0
root 2133 1109 0 12:31 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/1
root 2719 1109 0 14:52 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/2
root 2740 1109 0 14:52 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/3
root 3426 2744 0 15:52 pts/3 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd
[root@gh-shell 1-22] ps -ef|grep sshd|wc -l
6
[root@gh-shell 1-22]# 正则中的 \w 和 \W \s和\b
- \w表示字母,数组,下划线
- \W表示特殊符号
- \s表示匹配的空白
- \b。。。\b表示单词界定
\1
[root@halou-gf lianxi]echo aaafdfd bbb ccc |sed -nr 's/([a-z]+) ([a+z]+) ([a-z]+)/\3 \2 \1/p'
在 sed 中,
\3,\2,\1属于后向引用,用于引用正则表达式中括号分组的匹配结果。在你提供的示例中,正则表达式
([a-z]+) ([a+z]+) ([a-z]+)匹配了三个部分,每个部分都用括号分组起来了。其中:
([a-z]+): 第一个括号分组,匹配一个或多个小写字母。([a+z]+): 第二个括号分组,匹配一个或多个小写字母和加号+。([a-z]+): 第三个括号分组,匹配一个或多个小写字母。而
\3,\2,\1分别对应这三个括号分组的匹配结果。通过将
\3 \2 \1作为替换字符串,sed 命令会将匹配到的文本进行替换。具体来说,\3将会被匹配到的第三个括号分组的内容替换,\2将会被匹配到的第二个括号分组的内容替换,\1将会被匹配到的第一个括号分组的内容替换。所以,在你的示例中,sed 命令会将匹配到的字符串
aaafdfd bbb ccc进行替换,将括号分组的内容按照\3 \2 \1的顺序重新排列。最终输出结果为ccc bbb aaafdfd。
输出文本的第一行和最后一行
'方式1:'
[root@gh-shell 1-22] head -1 passwd;tail -1 passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
gaofei12:x:1032:1032::/home/gaofei12:/bin/bash'方式2:'
[root@gh-shell 1-22] sed -rn '1p;$p' passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
gaofei12:x:1032:1032::/home/gaofei12:/bin/bash
编写一个一键更换ip地址,并检测ip地址是否合法的脚本。
[root@gh-shell 1-22] cat modify_ip.sh
#!/bin/bash#接受第一个位置变量
new_ip=$1
# 检测IP地址是否合法
ip_regex='^((1[0-9][0-9]|2[0-4][0-9]|25[0-5]\.)([01][0-9]|2[0-4]|25[0-5]\.){2}([01][0-9]|2[0-4]|25[0-5]))$'
if ! [[ $new_ip =~ $ip_regex ]]; thenecho "无效的IP地址"exit 1
fi
#备份
mkdir /backup_network -p
cp /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 /backup_network
#修改ip地址为第一个位置变量的内容
sed -i "/IPADDR/c IPADDR=$new_ip/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
#重启网络服务
service network restart
#获取ip地址
sc_ip=$(ip add|awk '/inet.*ens33$/{print $2}')
#通过ip add命令去查看本机的ip地址,然后截取出来统计ip内容的长度,如果长度大于1就表示有ip,如果长度为小于1就表示没有ip
if ((${#sc_ip}>1));thenecho "modify ip successfully"
else#回滚cp /backup_network/ifcfg-ens33 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ -fservice network restart
fi[root@gh-shell 1-22]#
传个错误的ip会失败
正确的会成功
一键更换ip升级版
编写一个修改ip地址的脚本
提醒用户输入ip、子网掩码、网关、dns服务器地址
直接修改网卡配置文件,然后刷新服务让输入的ip地址信息生效
需要检查输入ip地址是否合法,不能输入空的内容或者字母,如果ip地址不合法或者输入空内容、字母都给予提醒
提醒:空的内容包括回车和空格,可以是多个空格 在我刚才脚本的基础上改
#!/bin/bash# 提醒用户输入IP地址
read -p "请输入新的IP地址: " new_ip# 检查IP地址是否为空或包含非数字字符
if [[ -z "$new_ip" || ! "$new_ip" =~ ^[0-9.]+$ ]]; thenecho "无效的IP地址"exit 1
fi# 提醒用户输入子网掩码
read -p "请输入子网掩码: " subnet_mask# 检查子网掩码是否为空或包含非数字字符
if [[ -z "$subnet_mask" || ! "$subnet_mask" =~ ^[0-9.]+$ ]]; thenecho "无效的子网掩码"exit 1
fi# 提醒用户输入网关
read -p "请输入网关地址: " gateway# 检查网关地址是否为空或包含非数字字符
if [[ -z "$gateway" || ! "$gateway" =~ ^[0-9.]+$ ]]; thenecho "无效的网关地址"exit 1
fi# 提醒用户输入DNS服务器地址
read -p "请输入DNS服务器地址: " dns_server# 检查DNS服务器地址是否为空或包含非数字字符
if [[ -z "$dns_server" || ! "$dns_server" =~ ^[0-9.]+$ ]]; thenecho "无效的DNS服务器地址"exit 1
fi# 备份网络配置
mkdir -p /backup_network
cp /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 /backup_network# 修改网卡配置文件
sed -i "/IPADDR/c IPADDR=$new_ip/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i "/NETMASK/c NETMASK=$subnet_mask/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i "/GATEWAY/c GATEWAY=$gateway/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i "/DNS1/c DNS1=$dns_server/" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33# 重启网络服务
service network restart# 获取修改后的IP地址
sc_ip=$(ip add | awk '/inet.*ens33$/{print $2}')# 检查是否成功修改IP地址
if [ ${#sc_ip} -gt 1 ]; thenecho "成功修改IP地址"
else# 回滚cp -f /backup_network/ifcfg-ens33 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/service network restartecho "无法修改IP地址。回滚操作。"
fi



![[ACM学习] 树形dp之换根](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/00a4838d79eb45dfb1d2c86e1d79e6f0.png)