调用函数和定义我们自己的函数,并使用Python内置的文档,是成为一位Pythoner的开始。
通过我的上篇文章,相信您已经看过并使用了print和abs等函数。但是Python还有许多其他函数,并且定义自己的函数是Python编程的重要部分。
在本课程中,你将学习更多关于使用和定义函数的知识。

获取帮助信息
你在上一篇教程中看到了abs函数,但如果你忘记了它做什么怎么办?
help()函数可能是你能学到的最重要的Python函数。如果你记得如何使用help(),你就掌握了理解大多数其他函数的关键。
以下是一个示例:
help(round)执行如下(Python 3.11.7):

这里,help()会显示两件事情:
1.该函数round(number, ndigits=None)实现的头部注释信息。
这信息里告诉我们round()接受一个我们可以描述为number的参数。此外,我们可以选择性地提供一个独立的参数,可以描述为ndigits。
2. 该函数所做的功能的简要英文描述。
常见问题:当你查找一个函数时,记得传入的是函数本身的名称,而不是调用该函数的结果。
如果我们在调用函数round()上使用help会发生什么?解开下面单元格的输出以查看结果。
help(round(-2.01))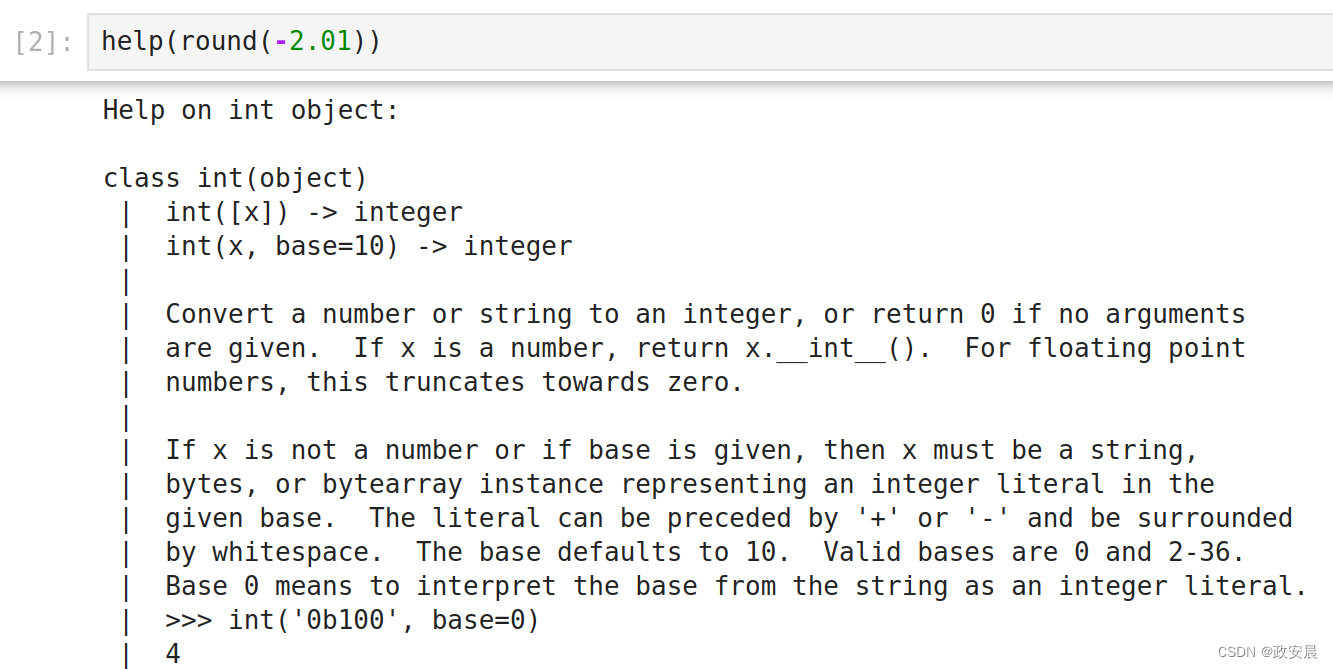
刚刚显示的完整的详细信息见下面:
Help on int object:class int(object)| int([x]) -> integer| int(x, base=10) -> integer| | Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments| are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point| numbers, this truncates towards zero.| | If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,| bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the| given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded| by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.| Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.| >>> int('0b100', base=0)| 4| | Built-in subclasses:| bool| | Methods defined here:| | __abs__(self, /)| abs(self)| | __add__(self, value, /)| Return self+value.| | __and__(self, value, /)| Return self&value.| | __bool__(self, /)| True if self else False| | __ceil__(...)| Ceiling of an Integral returns itself.| | __divmod__(self, value, /)| Return divmod(self, value).| | __eq__(self, value, /)| Return self==value.| | __float__(self, /)| float(self)| | __floor__(...)| Flooring an Integral returns itself.| | __floordiv__(self, value, /)| Return self//value.| | __format__(self, format_spec, /)| Default object formatter.| | __ge__(self, value, /)| Return self>=value.| | __getattribute__(self, name, /)| Return getattr(self, name).| | __getnewargs__(self, /)| | __gt__(self, value, /)| Return self>value.| | __hash__(self, /)| Return hash(self).| | __index__(self, /)| Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list.| | __int__(self, /)| int(self)| | __invert__(self, /)| ~self| | __le__(self, value, /)| Return self<=value.| | __lshift__(self, value, /)| Return self<<value.| | __lt__(self, value, /)| Return self<value.| | __mod__(self, value, /)| Return self%value.| | __mul__(self, value, /)| Return self*value.| | __ne__(self, value, /)| Return self!=value.| | __neg__(self, /)| -self| | __or__(self, value, /)| Return self|value.| | __pos__(self, /)| +self| | __pow__(self, value, mod=None, /)| Return pow(self, value, mod).| | __radd__(self, value, /)| Return value+self.| | __rand__(self, value, /)| Return value&self.| | __rdivmod__(self, value, /)| Return divmod(value, self).| | __repr__(self, /)| Return repr(self).| | __rfloordiv__(self, value, /)| Return value//self.| | __rlshift__(self, value, /)| Return value<<self.| | __rmod__(self, value, /)| Return value%self.| | __rmul__(self, value, /)| Return value*self.| | __ror__(self, value, /)| Return value|self.| | __round__(...)| Rounding an Integral returns itself.| | Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer.| | __rpow__(self, value, mod=None, /)| Return pow(value, self, mod).| | __rrshift__(self, value, /)| Return value>>self.| | __rshift__(self, value, /)| Return self>>value.| | __rsub__(self, value, /)| Return value-self.| | __rtruediv__(self, value, /)| Return value/self.| | __rxor__(self, value, /)| Return value^self.| | __sizeof__(self, /)| Returns size in memory, in bytes.| | __sub__(self, value, /)| Return self-value.| | __truediv__(self, value, /)| Return self/value.| | __trunc__(...)| Truncating an Integral returns itself.| | __xor__(self, value, /)| Return self^value.| | as_integer_ratio(self, /)| Return integer ratio.| | Return a pair of integers, whose ratio is exactly equal to the original int| and with a positive denominator.| | >>> (10).as_integer_ratio()| (10, 1)| >>> (-10).as_integer_ratio()| (-10, 1)| >>> (0).as_integer_ratio()| (0, 1)| | bit_count(self, /)| Number of ones in the binary representation of the absolute value of self.| | Also known as the population count.| | >>> bin(13)| '0b1101'| >>> (13).bit_count()| 3| | bit_length(self, /)| Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.| | >>> bin(37)| '0b100101'| >>> (37).bit_length()| 6| | conjugate(...)| Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int.| | to_bytes(self, /, length=1, byteorder='big', *, signed=False)| Return an array of bytes representing an integer.| | length| Length of bytes object to use. An OverflowError is raised if the| integer is not representable with the given number of bytes. Default| is length 1.| byteorder| The byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is 'big',| the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If| byteorder is 'little', the most significant byte is at the end of the| byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use| `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. Default is to use 'big'.| signed| Determines whether two's complement is used to represent the integer.| If signed is False and a negative integer is given, an OverflowError| is raised.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Class methods defined here:| | from_bytes(bytes, byteorder='big', *, signed=False) from builtins.type| Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes.| | bytes| Holds the array of bytes to convert. The argument must either| support the buffer protocol or be an iterable object producing bytes.| Bytes and bytearray are examples of built-in objects that support the| buffer protocol.| byteorder| The byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is 'big',| the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If| byteorder is 'little', the most significant byte is at the end of the| byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use| `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. Default is to use 'big'.| signed| Indicates whether two's complement is used to represent the integer.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Static methods defined here:| | __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors defined here:| | denominator| the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms| | imag| the imaginary part of a complex number| | numerator| the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms| | real| the real part of a complex number
我的天呐,好多啊。大家看到了吧,上述结果说明了一件我们平时忽略的事情:
Python从内到外评估表达式。
首先它计算round(-2.01)的值,然后提供关于该表达式输出的帮助。
(事实证明Python对整数有很多要说!在我们稍后讨论Python中的对象,方法和属性之后,上面的帮助输出将更有意义。)
round是一个非常简单的函数,有一个简短的文档字符串。当处理更复杂,可配置的函数(如print)时,帮助功能更加突出。
如果下面的输出看起来难以理解,请不要担心…现在只是看看是否能从这个帮助中找到任何新信息。
help(print)
如果你在寻找的话,你可能会发现print函数可以接受一个叫做sep的参数,它描述了我们在打印其他参数时放在它们之间的内容。
定义函数
内置函数非常好用,很多情况下,需要定义自己的函数,以下是一个简单的例子。
def least_difference(a, b, c):diff1 = abs(a - b)diff2 = abs(b - c)diff3 = abs(a - c)return min(diff1, diff2, diff3)咱们创建了一个名为least_difference的函数,它接受三个参数a、b和c。
函数定义以使用def关键字引入的标头开头。冒号后的缩进代码块在调用函数时运行。
return是与函数唯一相关的另一个关键字。
当Python遇到return语句时,它立即退出函数,并将右侧的值传递给调用上下文。
从源代码中清楚least_difference()的功能吗?如果我们不确定,我们可以在几个示例上尝试它:
print(least_difference(1, 10, 100),least_difference(1, 10, 10),least_difference(5, 6, 7), # Python allows trailing commas in argument lists. How nice is that?
)以下是执行:

或者也许help()函数可以告诉我们一些关于它的信息。
help(least_difference)可以看到帮助信息中展示的是刚才咱们定义的函数:

Python不足以智能地阅读我的代码并将其转化为优美的英文描述。然而,当我编写一个函数时,我可以在所谓的文档字符串中提供描述。当咱们添加了这个描述,就可以在帮助信息中被看到啦。
Docstrings是一种在程序代码中文档化函数、模块和类的方法。它是由开发者编写的字符串,用于描述代码的功能、输入参数、返回值等信息。这些文档字符串可以被Python解释器读取,并在交互式环境中使用help()函数查看。同时,它们也可以被一些工具自动生成的文档或IDE使用,以提供代码的说明和提示。Docstrings一般放在函数、类或模块的开头,在三个引号之间编写。常见的Docstrings格式有多种,比如Google风格、reStructuredText风格和numpy风格等。
def least_difference(a, b, c):"""Return the smallest difference between any two numbersamong a, b and c.>>> least_difference(1, 5, -5)4"""diff1 = abs(a - b)diff2 = abs(b - c)diff3 = abs(a - c)return min(diff1, diff2, diff3)docstring是一个用三引号括起来的字符串(可以跨多行),紧跟在函数的头部之后。当我们对一个函数调用help()时,它会显示出docstring。
help(least_difference)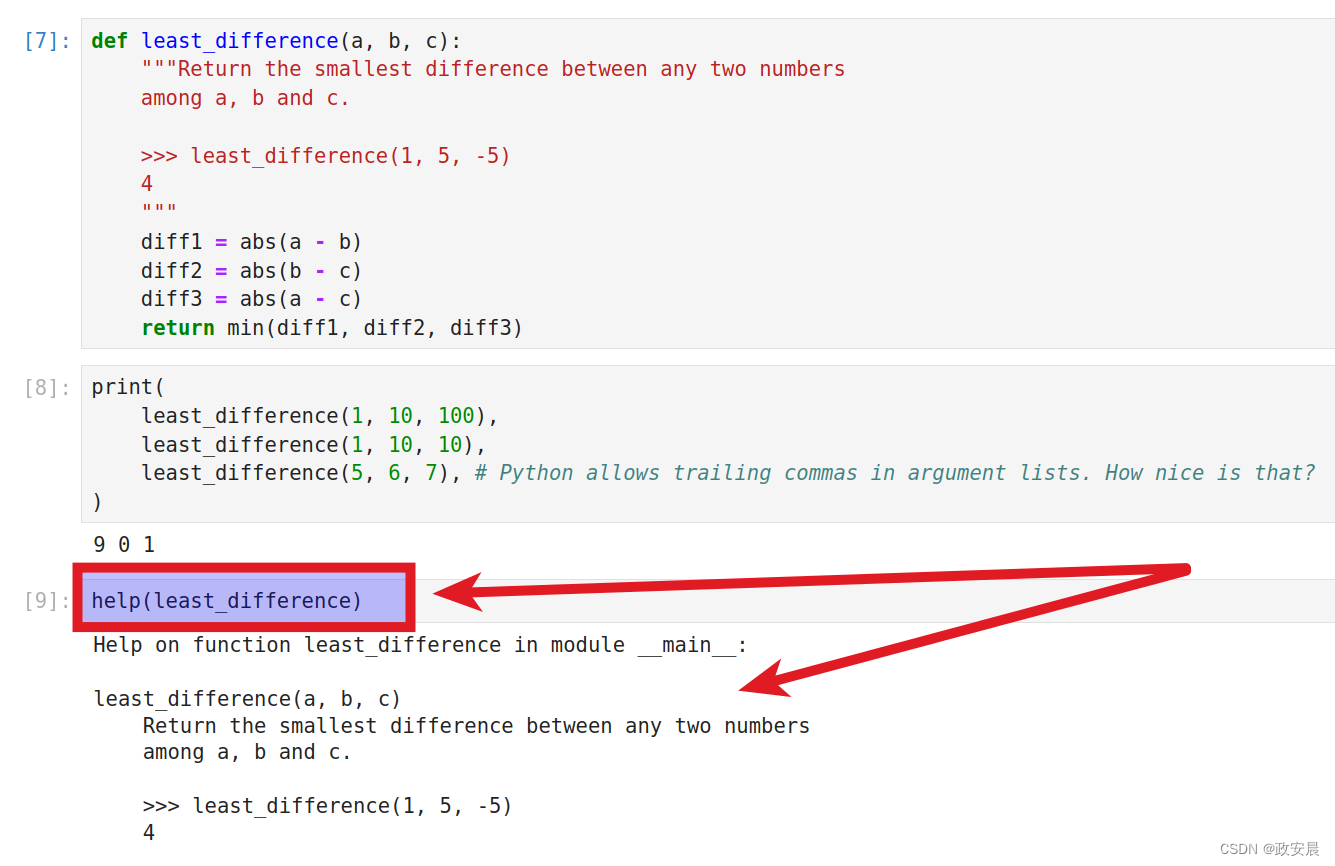
备注:
文档字符串的最后两行是一个示例函数调用和结果。
(>>>是对Python交互式shell中使用的命令提示符的引用。)
Python不会运行示例调用-它只是为了读者的方便而存在。在函数的文档字符串中包含一个或多个示例调用的惯例远非普遍遵守,但它可以非常有效地帮助人们理解您的函数。
好的程序员会使用文档字符串,除非他们预计在使用后不久就会丢弃代码(这种情况很少见)。所以,你也应该开始编写文档字符串!
没有返回值的函数
如果我们在函数中没有包含return关键字会发生什么?

Python允许我们定义这样的函数。调用它们的结果是特殊的值None。
(这类似于其他语言中的“null”概念。)
没有return语句,least_difference函数就毫无意义,但是具有副作用的函数可能在不返回任何内容的情况下执行一些有用的操作。
我们已经看到了两个例子:print()和help()不返回任何内容。我们只是为了它们的执行作用(在屏幕上输出一些文本)而调用它们。其他有用的仅靠执行作用的例子包括写入文件或修改输入。
mystery = print()
print(mystery)
默认参数
当我们调用help(print)时,我们发现print函数有几个可选参数。例如,我们可以为sep指定一个值,在我们打印的参数之间放入一些特殊的字符串:
print(1, 2, 3, sep=' < ')
但是如果我们不指定一个值,sep会被视为具有默认值' '(一个空格)。
print(1, 2, 3)
给我们定义的函数添加具有默认值的可选参数其实非常简单:
def greet(who="Colin"):print("Hello,", who)greet()
greet(who="Kaggle")
# (In this case, we don't need to specify the name of the argument, because it's unambiguous.)
greet("world")
函数调用
这里有一些很强大的东西,尽管一开始可能感觉很抽象。你可以将函数作为参数传递给其他函数。一些示例可能会更加清楚:
def mult_by_five(x):return 5 * xdef call(fn, arg):"""Call fn on arg"""return fn(arg)def squared_call(fn, arg):"""Call fn on the result of calling fn on arg"""return fn(fn(arg))print(call(mult_by_five, 1),squared_call(mult_by_five, 1), sep='\n', # '\n' is the newline character - it starts a new line
)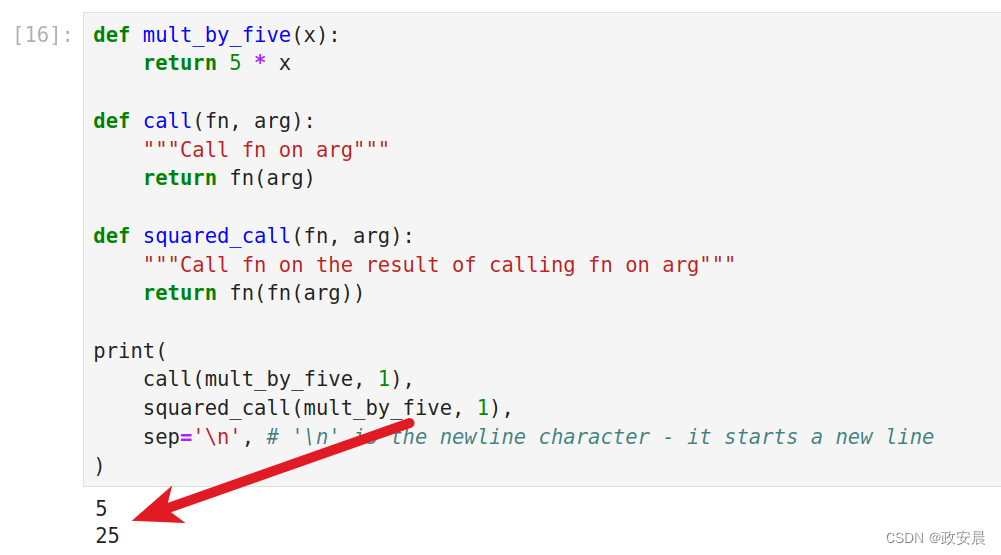
可以操作其他函数的函数被称为“高阶函数”。你可能不会立即编写自己的高阶函数。但Python内置了一些高阶函数,你可能会发现调用它们很有用。
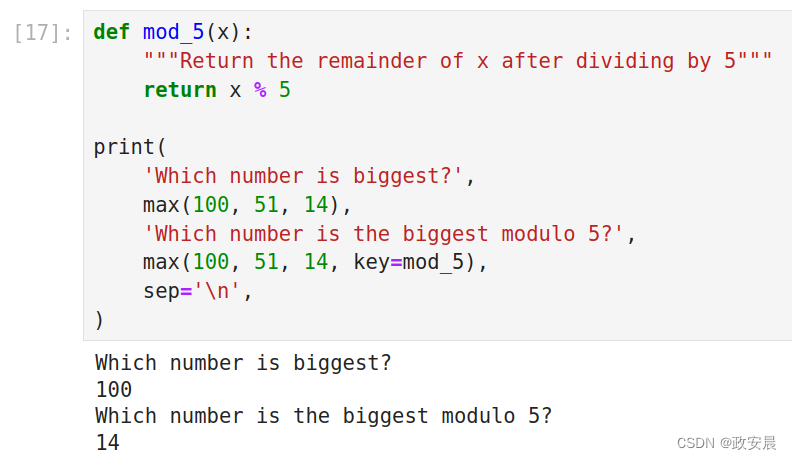
下面是一个有趣的例子,使用了max函数。
默认情况下,max返回其参数中的最大值。但是如果我们使用可选的key参数传入一个函数,它将返回使key(x)(也被称为'argmax')最大化的参数x。
def mod_5(x):"""Return the remainder of x after dividing by 5"""return x % 5print('Which number is biggest?',max(100, 51, 14),'Which number is the biggest modulo 5?',max(100, 51, 14, key=mod_5),sep='\n',
)
轮到你啦
函数在Python编程中打开了一个全新的世界。