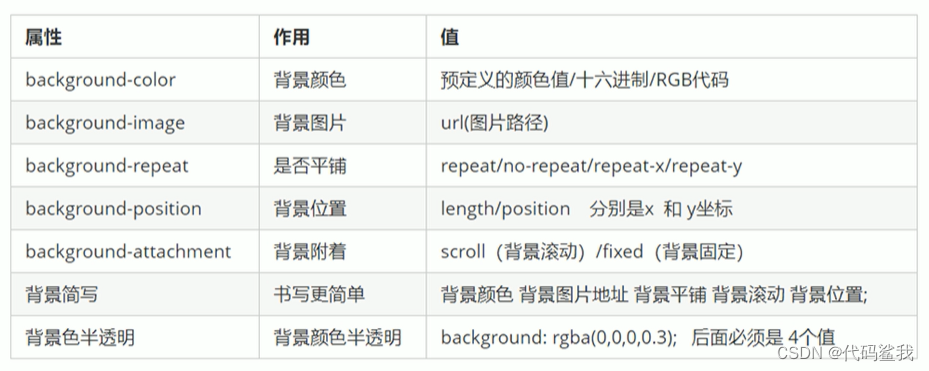
一、注解实现
@EnableAsync注解
创建一个配置类,并在类上添加@EnableAsync注解,用来启用异步支持。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig {
}
或者,在启动类上添加@EnableAsync注解,用来启用异步支持。
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootSampleApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSampleApplication.class, args);}
}
异步任务类
创建一个包含异步方法的类,并在方法上添加@Async注解。
@Service
public class MyAsyncService {// 默认线程池@Asyncpublic void asyncTask() {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 异步执行的任务逻辑System.out.println("异步任务正在执行");}public void task() {// 同步执行的任务逻辑System.out.println("其他任务正在执行");}
}
调用异步方法
asyncTask方法将在一个单独的线程中异步执行,而主线程将继续执行其他任务。
确保项目中添加了spring-boot-starter-async依赖,这样异步任务的支持才能生效。
注意:异步方法 和 调用方法 不能在同一个类中。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@Autowiredprivate MyAsyncService myAsyncService;@GetMapping("/asyncTask")public String asyncTask() {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 调用异步方法myAsyncService.asyncTask();// 主线程的其他逻辑myAsyncService.task();System.out.println("方法结束,执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));return "OK";}
}
对比
使用@Async注解,主线程马上返回,异步任务继续执行。
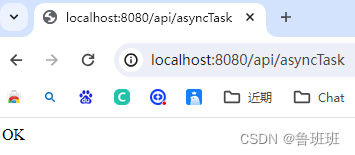
输出:
其他任务正在执行
方法结束,执行耗时:0
异步任务正在执行
不使用@Async注解,主线程方法全部同步执行。
输出:
异步任务正在执行
其他任务正在执行
方法结束,执行耗时:5015
使用自定义线程池
在配置类中创建自定义线程池。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig {@Bean(name = "customTaskExecutor")public TaskExecutor customTaskExecutor() {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();executor.setThreadNamePrefix("CustomThread-");// CPU密集型:corePoolSize = CPU核数 + 1;IO密集型:corePoolSize = CPU核数 * 2int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1;executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize); // 核心线程数目executor.setMaxPoolSize(corePoolSize); // 最大线程数executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(30); // 线程空闲后的最大存活时间executor.setQueueCapacity(100); // 阻塞队列大小,当核心线程使用满时,新的线程会放进队列// 线程执行的拒绝策略executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());executor.initialize();return executor;}
}
在异步服务类上,使用@Async注解并指定value属性为自定义线程池的名字。
@Service
public class MyAsyncService {// 不指定则使用默认线程池@Async("customTaskExecutor")public void asyncTask() {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 异步执行的任务逻辑System.out.println("异步任务正在执行");}
}
asyncTask方法将在名为customTaskExecutor的自定义线程池中执行。
确保异步任务调用方仍然使用@Autowired注解注入MyAsyncService,Spring Boot会自动关联使用相应的自定义线程池执行异步任务。
二、CompletableFuture实现
异步任务类
CompletableFuture是Java 8引入的一种异步编程的方式,它提供了更为灵活和强大的异步操作支持。
@Service
public class MyAsyncService {// 线程池,也可以使用自定义的线程池private final Executor customExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);public CompletableFuture<Void> performAsyncTask() {return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 异步执行的任务逻辑System.out.println("异步任务正在执行");}, customExecutor);}
}
在这个例子中,performAsyncTask方法返回了一个CompletableFuture<Void>,这表示异步任务没有返回值。CompletableFuture.runAsync(...)方法接受一个Runnable作为参数,并使用customExecutor作为执行器执行异步任务。
调用异步方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@Autowiredprivate MyAsyncService myAsyncService;@GetMapping("/triggerAsyncTask")public String triggerAsyncTask() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 调用异步方法myAsyncService.performAsyncTask().get();// 主线程的其他逻辑return "OK";}
}
在Controller中,可以通过CompletableFuture.get()方法来等待异步任务的完成。
需要注意的是,get()方法会阻塞,等待到异步方法执行完成,且get()方法可能会抛出InterruptedException和ExecutionException异常,因此需要进行适当的异常处理。
使用CompletableFuture的好处在于,你可以在异步任务中进行更复杂的操作,例如处理异步任务的结果、合并多个异步任务等。