Spring 除了支持通过XML形式配置Bean外,也支持通过注解的形式来配置Bean。需要简洁、易于维护和低耦合度场景下,注解是更好的选择;需要可读性强、可扩展性和分离关注点的场景下,XML是一个更好的选择。
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
| 注解 |
|
|
| xml |
|
|
表 注解与xml 形式配置Bean的优缺点
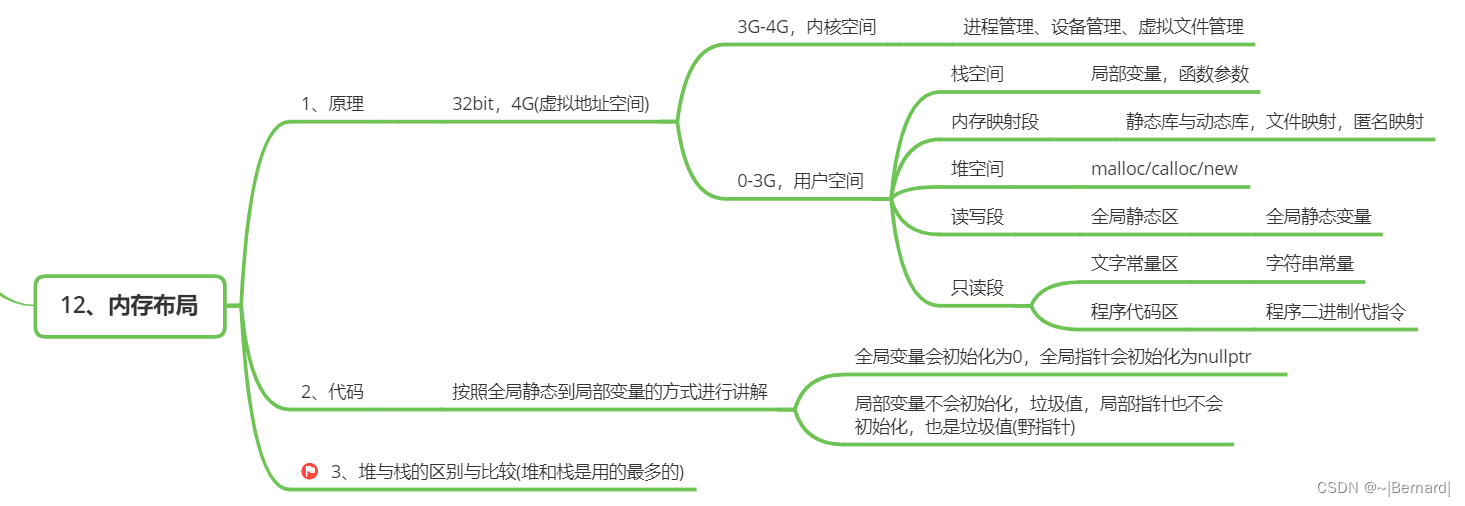
1 常用注解
1.1 @Configuration
是Spring中一个核心注解,用于应用程序的配置信息(类似于xml配置文件)。作用于类,被注解的类里面可以配置和管理Bean。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext可用来创建支持注解的上下文。其接受一个@Configuration注解的类型,在创建上下文时,其注解的类会被容器创建实例。被创建的实例可以像其他bean一样被容器管理及获取。
1.1.1 @ComponentScan
用于定位扫描Bean的位置。@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans") 表示扫描beans包下的所有Bean。与@Configuration配合一起使用时,beans包下所有有注解Bean的类都会被容器注册为bean。
1.2 @Autowired、@Resource与@Inject
这三个注解功能类似,都是用于自动装配Bean。但是在Spring 5.1之后@Autowired 与 @Resource被废弃了,可以使用@Inject来代替。
1.2.1 @Autowired
@Autowired 用于自动装配bean,有以下作用:
- 自动装配,当一个类中声明了@Autowired,Spring容器会自动寻找匹配(或创建)的Bean并注入到该类中。这大大简化了Bean的装配过程。
- 配置灵活,可标注在成员变量、方法或构造函数上。
- 可根据类型、字段名称(与bean的类型名称小写做匹配)及名称自动匹配(名称需要配合@Qualifier一起使用)。
还可以对集合类型及Map进行自动装配。把容器中符合的类型实例注入到集合中,或者将bean名作为key,bean实例作为value注入到Map中。
对于有多种同类型的Bean,如果使用@Autowired的字段名在这些bean中匹配不上,则会报错,这时可以在配置bean的地方,对其中一个bean加上@Primary 用来指定该类型的一个首要的bean。
public interface Mapper {
}@Repository
public class OrderMapper implements Mapper{public OrderMapper() {System.out.println("OrderMapper实例化");}
}@Repository
public class UserMapper implements Mapper{public UserMapper() {System.out.println("UserMapper实例化");}
}@Service
public class OrderService {public OrderService() {System.out.println("实例化");}@Autowiredprivate Mapper userMapper;@Autowiredprivate Mapper orderMapper;@Autowiredprivate List<Mapper> mappers;@Autowiredprivate Map<String,Mapper> mapperMap;public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);OrderService service = context.getBean(OrderService.class);System.out.println(service);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "OrderService{" +"userMapper=" + userMapper +", orderMapper=" + orderMapper +", mappers=" + mappers +", mapperMap=" + mapperMap +'}';}
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class SpringConfig {public SpringConfig() {System.out.println("SpringConfig实例化");}
}1.2.2 @Qualifier
用于解决自动装配时的歧义问题,可以帮助指定要注入的确切Bean。可以用来指定Bean的名称及类型。注意:使用@Qualifier 指定类型时,必须确保所指定的类型是唯一的,否则仍会抛出异常。
public interface MyService {
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans.qualifier")
public class MyConfig {@Bean@Qualifier("service1")public MyService myService1() {return new MyService() {};}@Bean@Qualifier("service2")public MyService myService2() {return new MyService() {};}}@Controller
public class MyController {@Autowired@Qualifier("service1")private MyService service1;@Autowired@Qualifier("service2")private MyService service2;public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);System.out.println(context.getBean(MyController.class));}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyController{" +"service1=" + service1 +", service2=" + service2 +'}';}
}1.2.3 @Autowired 被废弃的原因
1)保持与Java规范的一致性。@Autowired是Spring特有的注解,而@Inject是Java规范中的注解。(@Resource 被废弃也是因为这个原因,其是Java EE规范和Spring的一个注解,不是Java规范的注解)
2)处理多个匹配的依赖项时,如果没有明确指定依赖名称,Spring会抛出异常,这可能会导致代码的不稳定性。
3)类的成员变量如果使用了@Autowired,这个类必须交给Spring管理,否则该注解就会失效。
1.3 被废弃的注解
JSR 是Java依赖注入标准的规范,它提供了一种标准的依赖注入机制。其中有些注解可以代替Spring的某些注解。JSR-330中,像@Autowired 一样,有些注解已被Spring废弃,用JSR-330的注解代替(需要引入javax.inject包)。
| Spring | JSR-330 |
| @Autowired | @Inject |
| @Component | @Names/@ManagedBean |
| @Scope(“singleton”) | @Singleton |
| @Qualifier | @Qualifier/@Named |
| @Required | 无,但是该注解在Spring 5.1后被废弃,Spring 5.1 引入构造函数注入和自定义InitializingBean接口来实现初始化逻辑来替换这个注解。 |
表 JSR330 可替换 Spring中的注解
2 @ComponentScan组件扫描
用于指定Spring在哪些包中搜索被@Component(报告@Service、@Controller等)注解的类,并将它们自动注册为Spring容器中的Bean。还可以指定一些属性来自定义扫描行为:
| basePackages/value | 要扫描的包名,接受字符串数组类型。 |
| basePackageClasses | 要扫描的包中的一个类,将扫描该类所在包及其子包。 |
| includeFilters | 用于指定只包含满足特定条件的组件。是一个Filter类型数组,每个Filter对象包含type、classes属性和pattern属性等,classes属性是一个包含需要过滤的类的数组。pattern是指定匹配的正则表达式。 |
| excludeFilteres | 用于指定需要排除的组件。 |
| useDefaultFilters | 是一个bool类型,用于指定是否需要使用Spring的默认扫描规则。规则包括被@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller或者已经声明过@Component自定义注解标记的注解。 |
| nameGenerator | 自定义Bean的名称的Generator。 |
| scopeResolver | 自定义作用域的Generator。 |
| scopedProxy | 用于支持作用域Bean的属性,决定了是否需要创建代理对象。 |
| resourcePattern | 字符串类型,用于指定要扫描的资源模式的正则表达式。 |
| lazyInit | bool类型,是否懒加载。 |
表 @ComponentScan 的属性
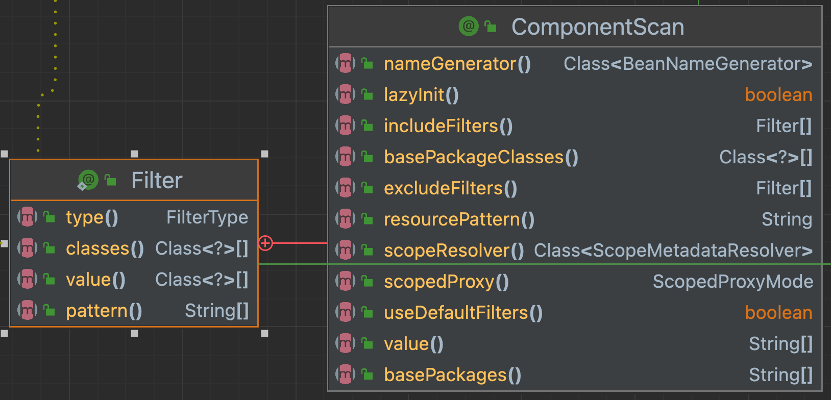
图 @ComponentScan注解的结构图
2.1 @Filter
@Filter注解是@ComponentScan内部定义的注解。用来定义过滤类型。其属性type 是FilterType 类型的枚举。
| annotation | 默认值。指定注解,用于过滤被特定注解标注的类。 |
| assignable | 指定类型,用于过滤特定类型的类。 |
| aspectj | Aspect语法指定。 |
| regex | 正则表达式指定,用于过滤满足表达式的类名。 |
| custom | 自定义规则及过滤逻辑,通过实现ApplicationContextAware接口并覆盖getbeanDefinitionNames方法来指定自己的过滤规则。 |
表 FilterType的枚举值
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan(lazyInit = true,basePackages = "scan.beans", includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {MyComponent.class})})
public class ScanConfig {
}@MyComponent
public class UserService {public UserService() {System.out.println("UserService实例化");}public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ScanConfig.class);UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);System.out.println(userService);}}