1. pinia是什么
Pinia 是一个基于 Vue.js 的状态管理库,用于管理应用程序的数据。它提供了一种简单、直观且可扩展的方式来组织和访问应用程序的状态,下面是详细介绍
- 基于 Vue 3:Pinia 是专门为 Vue 3 开发的状态管理库,充分利用了 Vue 3 的响应性系统和 Composition API。
- 类 Vuex 的 API:Pinia 的 API 设计灵感来自于 Vuex,因此对于熟悉 Vuex 的开发人员来说,使用 Pinia 应该会感到非常熟悉。
- 存储库(Stores):Pinia 将应用程序的状态组织为存储库的形式。每个存储库代表一个特定的数据领域或功能。存储库包含状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
- 响应式状态管理:Pinia 使用 Vue 3 的响应性系统,确保状态的变化能够自动追踪和响应,从而实现了高效的状态管理。
- 插件系统:Pinia 提供了插件系统,用于扩展和增强其功能。通过插件,您可以添加中间件、持久化存储、调试工具等来满足特定的需求。
- 类型安全:Pinia 支持 TypeScript,并且提供了类型安全的 API 和开发体验。这使得在开发过程中能够更好地捕获错误和进行静态类型检查。
- 支持异步操作:Pinia 支持在动作(actions)中执行异步操作,如发送网络请求、处理副作用等。
- 适用于大型应用程序:Pinia 的设计使得它非常适用于大型应用程序,可以轻松管理复杂的状态逻辑和数据流。
官方文档:
https://pinia.web3doc.top/introduction.html
2. pinia基本使用
a. 安装依赖
npm install pinia
b. 使用pinia
- 在main.js中引入pinia
import { createPinia } from "pinia";
const pinia = createPinia();createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app')
- 在src目录下创建一个store文件夹,然后在store文件夹内创建index.js文件
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'// useStore 一般命名是use开头,useProductStore、useUserStore 等等
// defineStore 是用于定义存储库(store)的方法。它接受两个参数:storeName 和 storeDefinition。
// 1.storeName(必需):表示存储库的名称,是一个字符串。该名称用于在 Pinia 中唯一标识存储库,因此在应用程序中定义不同的存储库时,应确保每个存储库具有唯一的名称。
// 2.storeDefinition(必需):表示存储库的定义,是一个对象。该对象包含了存储库的配置、状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
export const useStore = defineStore('user', {// 推荐使用 完整类型推断的箭头函数state: () => {return {// 所有这些属性都将自动推断其类型name: "curry",age: 35,};},
})
- 在组件中使用
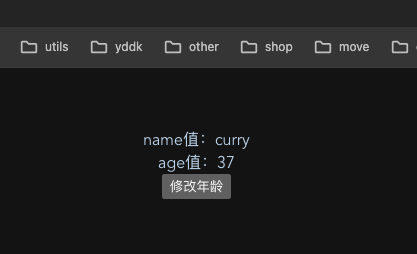
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{ userStore.age }}</div>
</template><script setup>// 引入一下创建的storeimport {useUserStore} from '../store/index'// 因为是个方法,所以我们得调用一下const userStore = useUserStore()</script>
- 页面展示

c. 解构后响应式处理
useStore获取到后不能解构,否则失去响应式,如果想要保持响应式可以使用storeToRefs()函数
- storeToRefs函数使用
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{age }}</div><button @click="addAge">修改年龄</button>
</template><script setup>
// 引入一下创建的store
import {useUserStore} from '../store/index'
import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'const userStore = useUserStore()const {age} = storeToRefs(userStore)function addAge() {userStore.age = userStore.age + 1
}</script>
- 页面展示
d. $patch函数
$patch函数也是常用修改Store的方法
- $patch函数使用
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{ age }}</div><button @click="addAge">修改年龄</button>
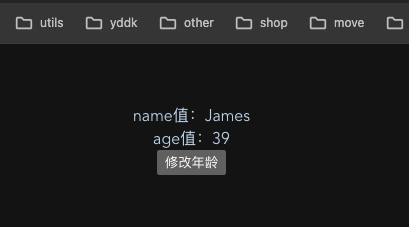
</template><script setup>// 引入一下创建的storeimport {useUserStore} from '../store/index'import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'const userStore = useUserStore()const {age} = storeToRefs(userStore)function addAge() {// userStore.age = userStore.age + 1userStore.$patch({name: "James",age: 39})}</script>
- 页面展示
e. $reset()函数
$reset()函数的作用是重置state中的数据
- $reset()函数使用
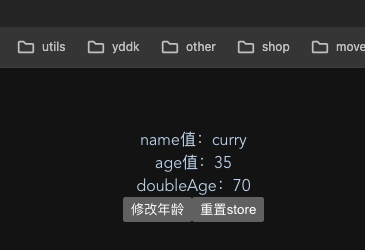
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{ age }}</div><button @click="addAge">修改年龄</button><button @click="restart">重置store</button>
</template><script setup>// 引入一下创建的storeimport {useUserStore} from '../store/index'import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'const userStore = useUserStore()const {age} = storeToRefs(userStore)function addAge() {userStore.age = userStore.age + 1}function restart() {userStore.$reset()}</script>
2.页面展示
3. getters和actions
在Pinia插件中,getters(获取器)和actions(动作)是两个不同的概念,用于处理和访问存储库中的数据。
a. getters
ⅰ. getters介绍
Getter是用于获取存储库中的状态(state)的方法。Getter类似于计算属性,它们基于存储库的状态计算出一个值,并在需要时被调用。Getter可以接受参数,并且可以进行逻辑操作和计算,但不能直接修改状态。
Getter的主要特点包括:
- 用于获取和计算存储库的状态。
- 可以接受参数进行动态计算。
- 在状态发生变化时,Getter会自动重新计算。
- 不能直接修改状态,只能读取状态。
ⅱ. getters使用案例
- getters中添加doubleAge方法
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'// useStore 一般命名是use开头,useProductStore、useUserStore 等等
// defineStore 是用于定义存储库(store)的方法。它接受两个参数:storeName 和 storeDefinition。
// 1.storeName(必需):表示存储库的名称,是一个字符串。该名称用于在 Pinia 中唯一标识存储库,因此在应用程序中定义不同的存储库时,应确保每个存储库具有唯一的名称。
// 2.storeDefinition(必需):表示存储库的定义,是一个对象。该对象包含了存储库的配置、状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {// 推荐使用 完整类型推断的箭头函数state: () => {return {// 所有这些属性都将自动推断其类型name: "curry",age: 35,};},getters: {// 年龄乘以2doubleAge: (state) => state.age * 2,},
})
- 调用addAge
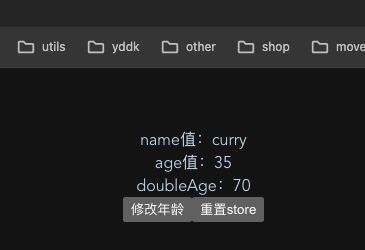
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{ age }}</div><div>doubleAge:{{ userStore.doubleAge }}</div><button @click="addAge">修改年龄</button><button @click="restart">重置store</button>
</template><script setup>// 引入一下创建的storeimport {useUserStore} from '../store/index'import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'const userStore = useUserStore()const {age} = storeToRefs(userStore)function addAge() {userStore.age = userStore.age + 1}function restart() {userStore.$reset()}</script>
- 页面展示
b. actions
ⅰ. actions介绍
Action是用于对存储库中的状态进行操作和修改的方法。Action可以执行异步操作,如发送网络请求、处理副作用等。Action可以接受参数,并且可以修改状态或触发其他动作。
Action的主要特点包括:
- 用于操作和修改存储库的状态。
- 可以接受参数进行动态操作。
- 可以进行异步操作,如发送网络请求。
- 可以修改状态或触发其他动作。
ⅱ. actions使用案例
- actions添加doubleAge方法
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'// useStore 一般命名是use开头,useProductStore、useUserStore 等等
// defineStore 是用于定义存储库(store)的方法。它接受两个参数:storeName 和 storeDefinition。
// 1.storeName(必需):表示存储库的名称,是一个字符串。该名称用于在 Pinia 中唯一标识存储库,因此在应用程序中定义不同的存储库时,应确保每个存储库具有唯一的名称。
// 2.storeDefinition(必需):表示存储库的定义,是一个对象。该对象包含了存储库的配置、状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {// 推荐使用 完整类型推断的箭头函数state: () => {return {// 所有这些属性都将自动推断其类型name: "curry",age: 35,};},getters: {// 年龄乘2doubleAge: (state) => state.age * 2,},actions:{incrementAge(num){this.age += num}}})
- 调用doubleAge方法
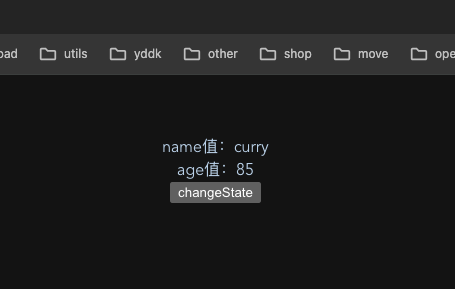
<template><!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了--><div>name值:{{ userStore.name }}</div><div>age值:{{ userStore.age }}</div><button @click="changeState">changeState</button>
</template><script setup>// 引入一下创建的storeimport {useUserStore} from '../store/index'const userStore = useUserStore()function changeState() {userStore.incrementAge(10)}</script>
- 页面展示
总结:
Getter用于获取存储库的状态并进行计算,而Action用于操作和修改存储库的状态。
Getter主要用于获取数据,而Action主要用于执行操作和修改数据。
根据您的需求,选择适当的方式来读取或修改存储库中的数据。
4. 数据的持久化
默认pinia数据是没有持久化的,刷新页面就变成默认值了,持久化需要安装如下插件
ⅰ. 安装插件
npm i pinia-plugin-persist
ⅱ. 在main.js中引入持久化插件
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { createPinia } from "pinia";
import piniaPluginPersist from "pinia-plugin-persist"; //pinia持久化
const pinia = createPinia();
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersist);createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app')
ⅲ. 在store中使用
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'// useStore 一般命名是use开头,useProductStore、useUserStore 等等
// defineStore 是用于定义存储库(store)的方法。它接受两个参数:storeName 和 storeDefinition。
// 1.storeName(必需):表示存储库的名称,是一个字符串。该名称用于在 Pinia 中唯一标识存储库,因此在应用程序中定义不同的存储库时,应确保每个存储库具有唯一的名称。
// 2.storeDefinition(必需):表示存储库的定义,是一个对象。该对象包含了存储库的配置、状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {// 推荐使用 完整类型推断的箭头函数state: () => {return {// 所有这些属性都将自动推断其类型name: "curry",age: 35,};},getters: {// 年龄乘2doubleAge: (state) => state.age * 2,},actions: {incrementAge(num) {this.age += num},changeName(name) {this.name = name}},persist: {// 默认会保存当前模块全部数据enabled: true, // 开启缓存 默认会存储在本地localstoragestorage: sessionStorage, // 缓存使用方式}
})
刷新页面age不会被重置
store中所有的store都被保存了
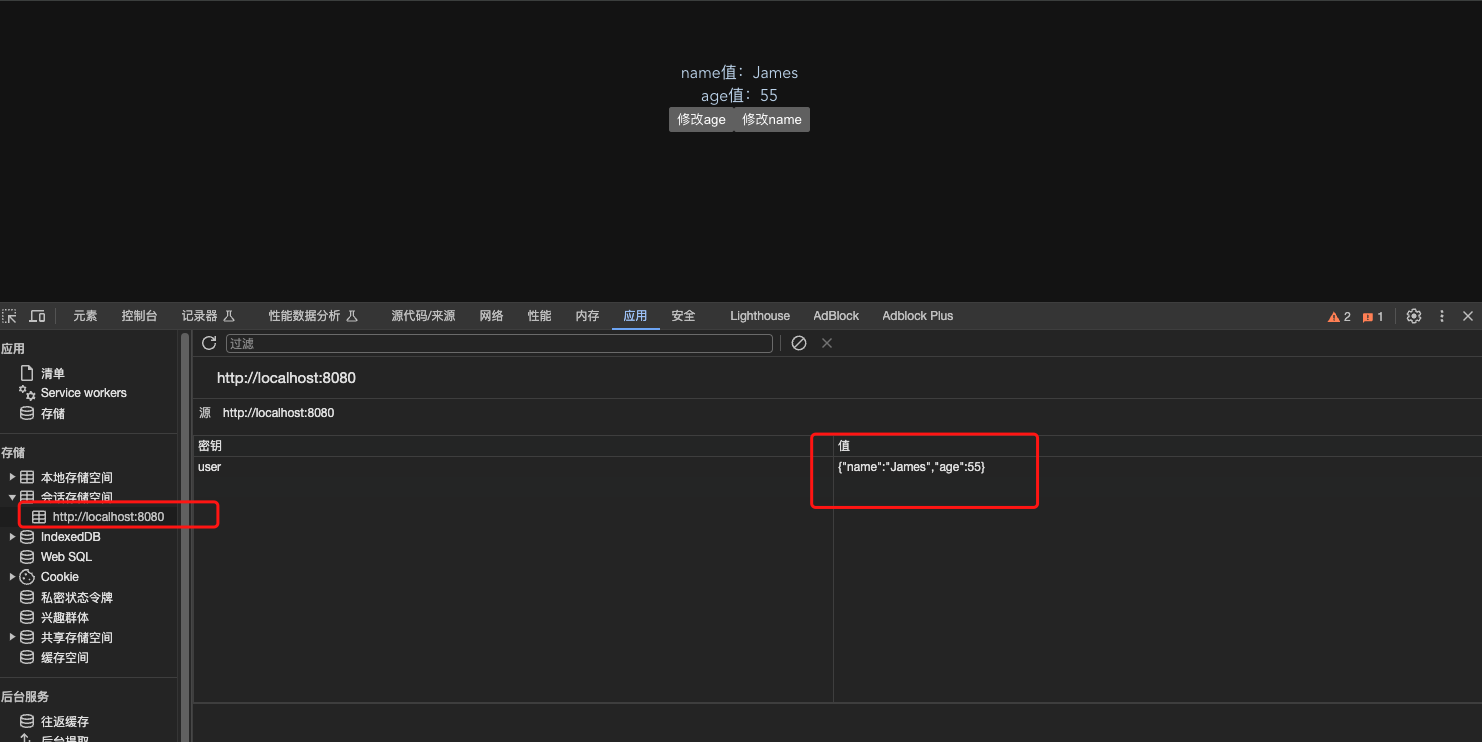
页面刷新后age也不会变成默认值,证明持久化成功
ⅳ. 设置 key 、指定保存内容
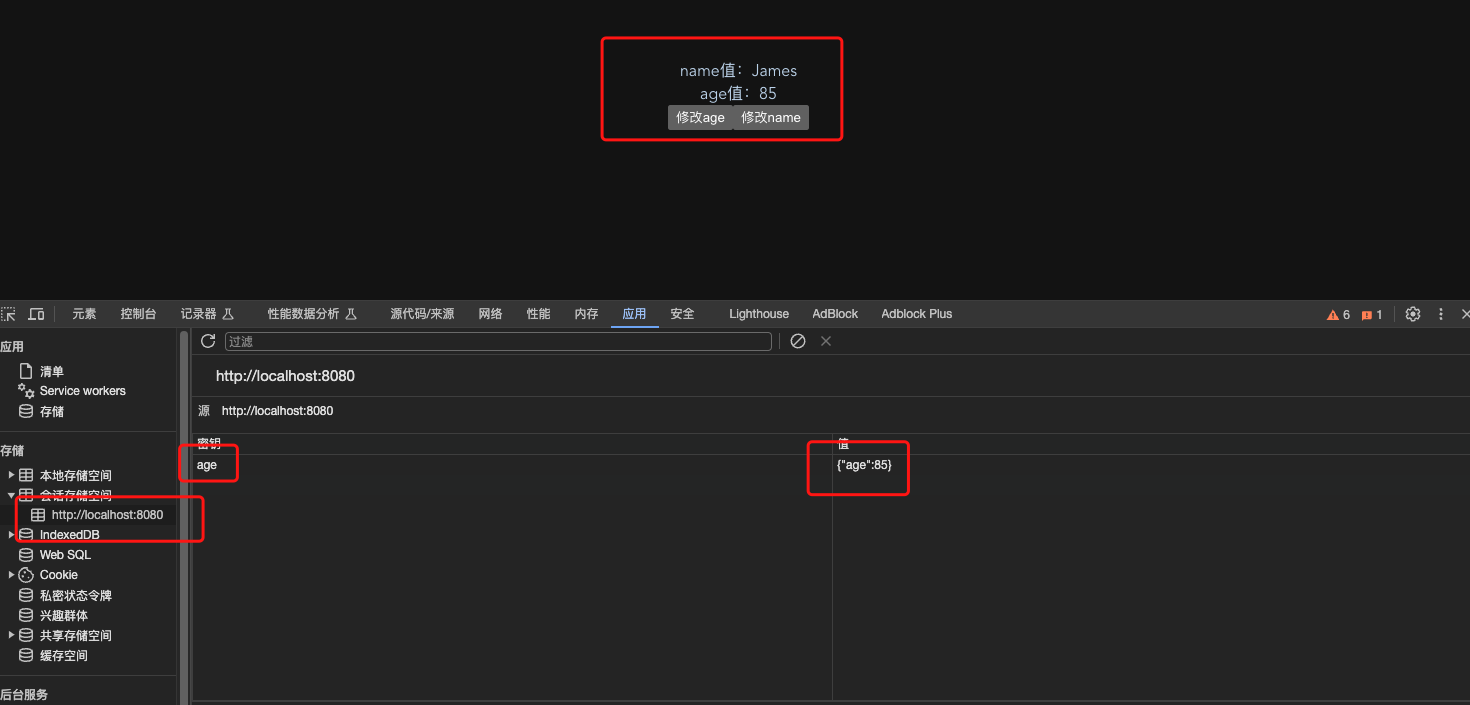
有时可能只要保存部分数据,这是就要用到strategies,在里面自定义保存的内容了
key设置为’age’,paths设置只保存’age’
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'// useStore 一般命名是use开头,useProductStore、useUserStore 等等
// defineStore 是用于定义存储库(store)的方法。它接受两个参数:storeName 和 storeDefinition。
// 1.storeName(必需):表示存储库的名称,是一个字符串。该名称用于在 Pinia 中唯一标识存储库,因此在应用程序中定义不同的存储库时,应确保每个存储库具有唯一的名称。
// 2.storeDefinition(必需):表示存储库的定义,是一个对象。该对象包含了存储库的配置、状态(state)、动作(actions)、获取器(getters)等。
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {// 推荐使用 完整类型推断的箭头函数state: () => {return {// 所有这些属性都将自动推断其类型name: "curry",age: 35,};},getters: {// 年龄乘2doubleAge: (state) => state.age * 2,},actions: {incrementAge(num) {this.age += num},changeName(name) {this.name = name}},// persist: {// 默认会保存当前模块全部数据// enabled: true, // 开启缓存 默认会存储在本地localstorage// storage: sessionStorage, // 缓存使用方式// }//持久化persist: {enabled: true,// 自定义持久化参数strategies: [{// 自定义keykey: "age",// 自定义存储方式,默认sessionStoragestorage: sessionStorage,// 指定要持久化的数据,默认所有 state 都会进行缓存,可以通过 paths 指定要持久化的字段,其他的则不会进行持久化。paths: ["age"],}],},
})
这时看到只有age被保存