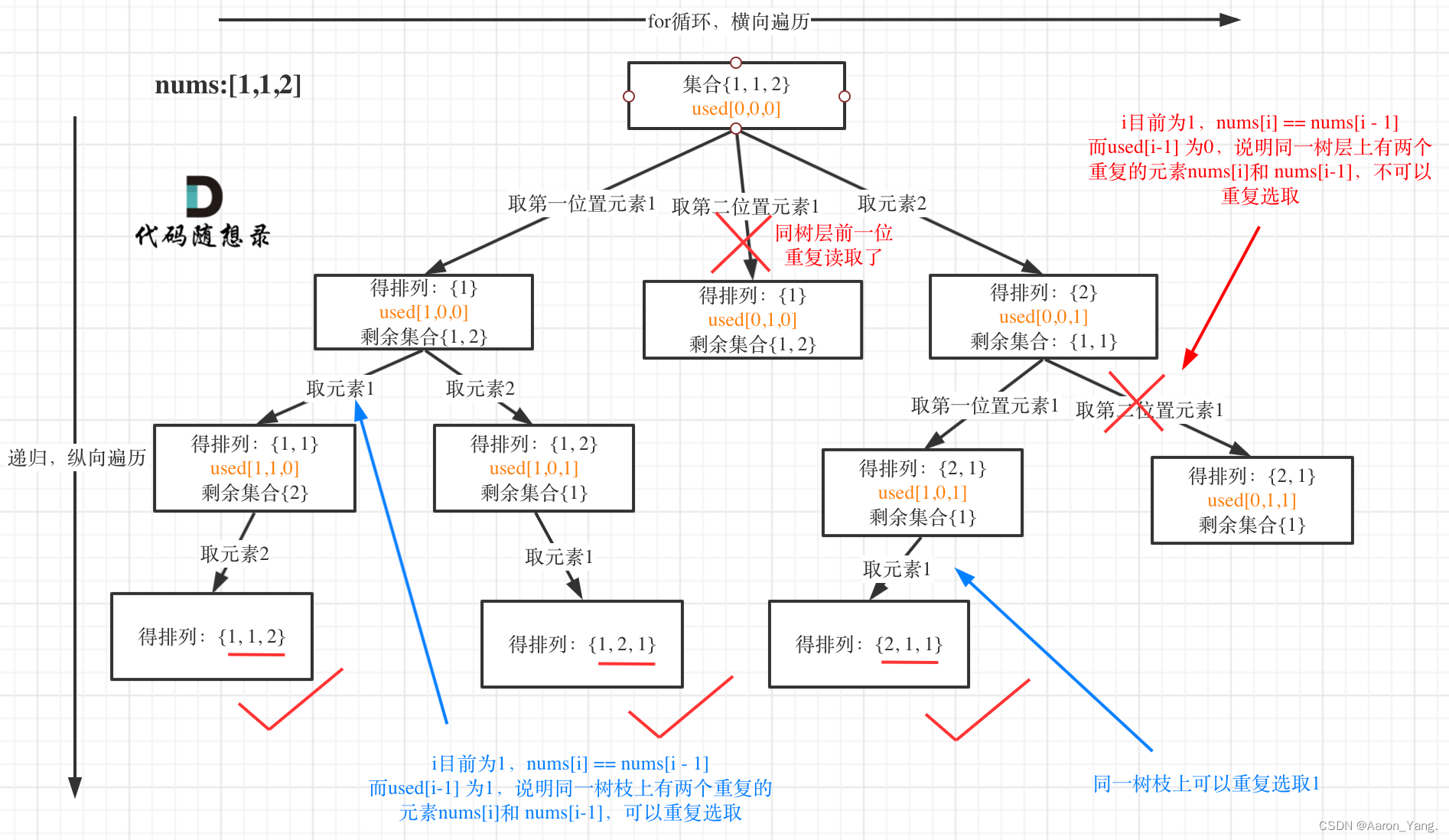
目录:
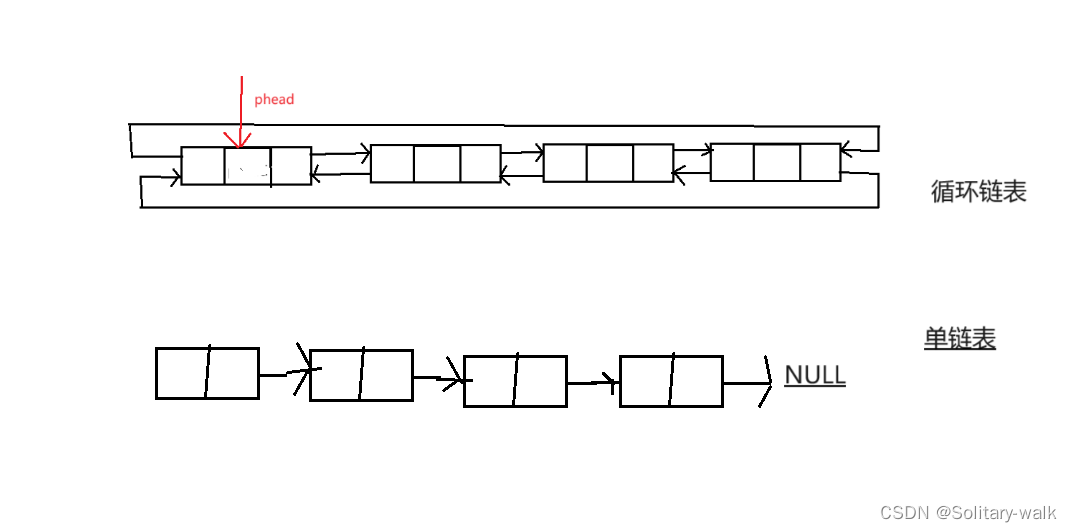
一:单链表(不带头单向不循环)与循环链表(带头双向循环)区别
二:循环链表初始化
三:循环链表头插
四:循环链表尾插
五:循环链表头删
六:循环链表尾删
七:循环链表查找
八:循环链表指定pos 位置的删除
九:循环链表指定pos 位置之前的插入
十:循环链表销毁
十一:结语
1:单链表(不带头单向不循环)与循环链表(带头双向循环)区别
1)结构上
循环链表多了给 前驱指针 pre
2)链表增删查改
有了pre这个指针,效率大大提升
2:循环链表初始化
讲到初始化,这里主要就是对哨兵位 (暂时称为:phead)进行设置
注意:哨兵位只是占一个位置,并不存储任何有效的数据
循环链表初始状态是空的:phead 自己成环

对应代码:
phead -> next = phead ;
phead -> pre = phead ;
那么问题就来了,在设计这个初始化函数的时候用一级指针还是二级指针

想必,前期看过我的单链表的博客,自然会说二级指针呀:
因为是对phead 这个指针进行改变所以是传二级指针。没毛病!不知道大家在做OJ题的时候,我们也涉及到对一级指针的改变,但是我们也可以返回这个一级指针,即可实现
ListNode* ListNodeInit()
{/*哨兵位:val 没有实际意义(自行赋值)初始化的目的就是对哨兵位进行设置因为整个接口都是用一级指针,若是初始化用二级指针有点不顺眼此函数返回哨兵位地址即可实现对哨兵位的初始化*/ListNode* phead = NULL;ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}phead = newnode;phead->val = -1;phead->pre = phead->next = phead;//够成环return phead;
}3:循环链表头插
头插:即在哨兵位的后面进行头插(若是链表为空,此时的头插也即是尾插)
头插分析:显然我们只需改变指针走向即可
注意指针先后问题
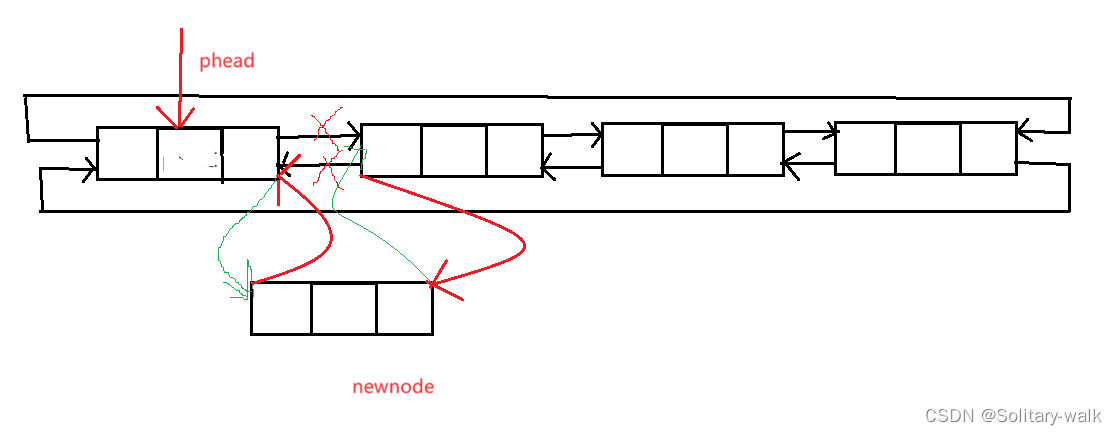
各位老铁康康这样的代码是否之正确:
phead-> next = newnode;
newnode-> next = phead-> next;
newnode-> pre = phead;
newnode->next-> pre = newnode;

此代码结合画图,来看, 显然这样是不对的,因为newnode-> next = phead-> next;这句代码让newnode 这个节点自己成环了,所以又怎么可能头插进去呢?
实质性原因是:当我们头插进来newnode 时,应该先执行
newnode-> next = phead->next; //注意指针先后问题
phead->next->pre = newnode; //让原来头结点的 pre 指向newndoe
newnode-> pre = phead;
phead-> next = newnode;
ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);newnode->next = phead->next;newnode->pre = phead;phead->next->pre = newnode;//原来第一个节点pre与新的头结点连接phead->next = newnode;//新的头结点对于以上问题还可以这样解决:定义一个 next指针来保留一下原来的头结点
4:循环链表尾插
尾差之前我们需要先思考一个问题:对于单链表(不循环,不带头,单向)而言,每次尾插之前都需要遍历链表,来找尾结点
但是对于循环链表而言我们就不需要:找尾结点直接一步到位 phead-> pre
真的是没有对比就没有伤害,所以在这块,咱循环链表还是比较好搞滴
尾插分析:
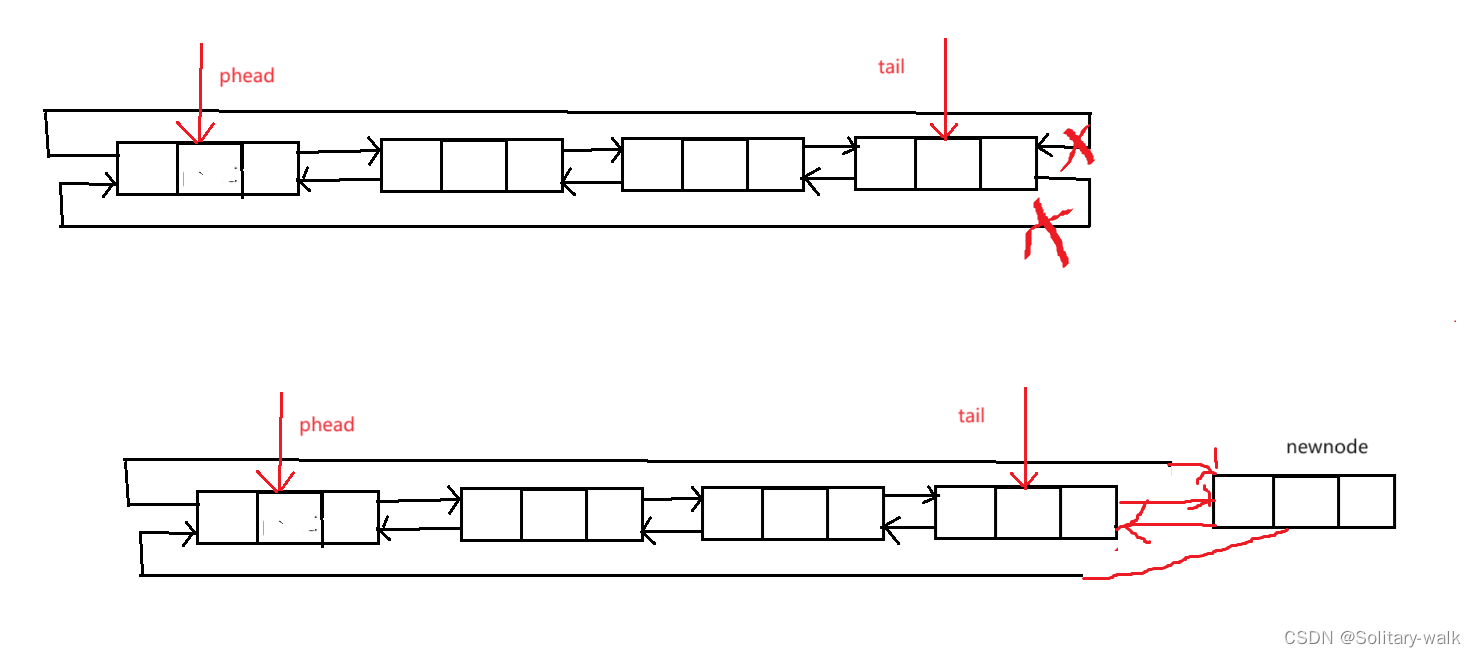
这里只需改变指针走向即可
代码:
void ListNodePushBack(ListNode* phead,DataType x)
{assert(phead);/*1:找尾结点 phead->pre2:指针连接 */ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);newnode->next = phead;newnode->pre = phead->pre;phead->pre->next = newnode;//原来尾结点与newnode进行连接phead->pre = newnode;//新的尾结点}5:循环链表头删
依然如此,按照“国际惯例”:找头结点 phead -> next
删除之前先保留一下 第二个节点
当把链表所以节点删除后(除哨兵位),会自动保存一个循环链表
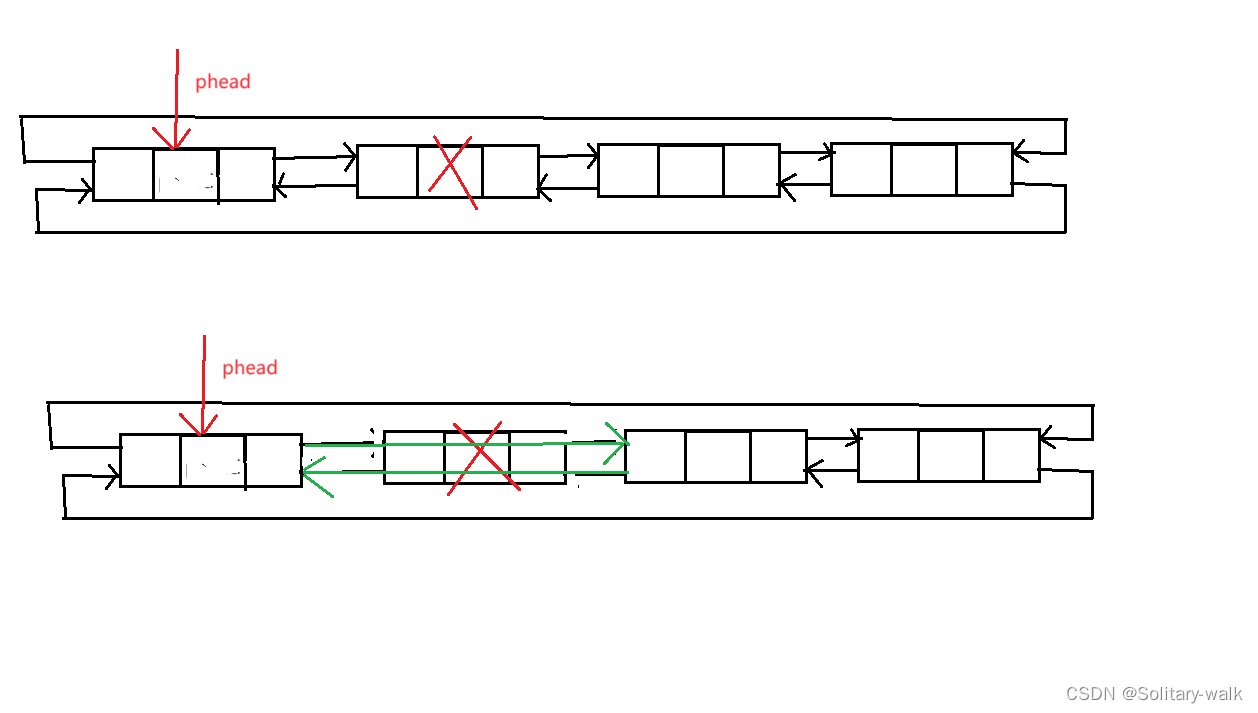
代码见下:
void ListNodePopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead->next != phead);//不相等说明不为空ListNode* newFirst = phead->next->next;newFirst->pre = phead;phead->next = newFirst;//成为新的头结点//以下写法也对,但可读性差phead->next = phead->next->next;phead->next->pre = phead;}6:循环链表尾删
既然谈到尾删,咱这里不得不提一嘴,单链表的尾删
单链表尾删逻辑:
1:链表不为空
2:只有一个节点:传二级指针
3:多个节点:传一级指针
4:找尾结点: 条件 tail -> next != NULL;
咱就是说,是不是事很多。
相比较之下,循环链表就比较友好:找啥尾结点,直接一步到位 phead-> pre
直接改变指针走向即可。
老问题:保留一下尾结点的前一个节点 tailPre
void ListNodePopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);/*空链表: 1:找尾结点 phead->pre2:成环: 改变新的尾结点与phead 直接的链接*/assert(phead->next != phead);//不相等说明链表不为空,为空不能删除ListNode* tail = phead->pre;ListNode* tailPre = tail->pre;phead->pre = tailPre;//新的尾结点tailPre->next = phead;free(tail);
}7:循环链表查找
此函数可以实现2个功能:一个是查找;另一个是修改
逻辑:按值查找,若是存在,直接返回当前节点,否则返回 NULL
注意是从 第一个节点开始 而不是从哨兵位 开始
ListNode* Find(ListNode* phead, DataType x) //指定数据查找
{/*从第一个节点开始查找: phead->next依次遍历,若是存在返回节点否则返回NULL*/assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead ) //phead 是哨兵位{if (x == cur->val){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;//没有找到
}8:循环链表指定pos 位置的删除
这个接口的逻辑其实说白了与尾删没啥不同
注意:pos 这个节点是查找函数返回的
void ListNodeErase(ListNode* pos)//指定位置删除 pos是查找函数返回的
{assert(pos);ListNode* posPre = pos->pre;ListNode* posNext = pos->next;posPre->next = posNext;posNext->pre = posPre;free(pos);
}9:循环链表指定pos 位置之前的插入
void ListNodeInsert(ListNode* pos, DataType x)//指定位置之前插入
{/*1:找到pos 前一个节点 pos->pre2:注意避免节点找不到3:改变指针连接: posPre,newnode,pos*/assert(pos);//为空直接不玩了ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);ListNode* posPre = pos->pre;posPre->next = newnode;newnode->pre = posPre;newnode->next = pos;pos->pre = newnode;}10:循环链表销毁
这里的销毁就是一个节点一个节点进行删除
注意:包括哨兵位在内
void ListNodeDestroy(ListNode* phead)
{/*注意哨兵位也需要删除一个节点一个节点删除*/assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}各位老铁们,别走开,接下来的问题你值得一看,或许哪天自己面试会遇到类似问题呢?

前段时间看到过样一个问题:
有个求职者去面试:在他的简历上写着自己是比较熟练数据结构这个模块的。
面试官问了这样一个问题:你能否在10分钟之内,搞一个链表出来?
听到这,求职者心里多多少少是有点担忧“搞,是没有问题,但是这个时间能否在宽裕点……”
进过这种协商,时间定在15分钟
对于这个问题的答卷:很显然,这个求职者没有拿到100分

屏幕前的各位铁子们,假设你是那个求职者,你又会如何回答好这份答卷?
是的,要是我,我一定会用循环链表来搞呀(因为面试官有没有指定具体是8中链表的哪一种)
你仔细想想:循环链表效率多高呀
对于一个链表的基本操作无非不就是:
头删头插
尾删,尾插
任意位置的插入和删除
不知道你是否考虑过这样问题:
循环链表的尾插,头插其实就是任意位置插入的一个特例
尾删,头删其实就是任意位置的删除的一个特例
完整代码如下:
DList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"
void ListNodePrint(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;printf("guard<==>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<==>", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}
ListNode* ListNodeInit()
{/*哨兵位:val 没有实际意义(自行赋值)初始化的目的就是对哨兵位进行设置因为整个接口都是用一级指针,若是初始化用二级指针有点不顺眼此函数返回哨兵位地址即可实现对哨兵位的初始化*/ListNode* phead = NULL;ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}phead = newnode;phead->val = -1;phead->pre = phead->next = phead;//够成环return phead;
}ListNode* BuyNode(DataType x)
{ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->pre = NULL;return newnode;
}
void ListNodePushBack(ListNode* phead,DataType x)
{assert(phead);/*1:找尾结点 phead->pre2:指针连接 *///ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);//newnode->next = phead;//newnode->pre = phead->pre;//phead->pre->next = newnode;//原来尾结点与newnode进行连接//phead->pre = newnode;//新的尾结点ListNodeInsert(phead, x);//注意ListNodeInsert 这个函数功能是在pos 之前插入,所以要想实现尾插,需要传phead ,而不是phead->pre }
void ListNodePushFront(ListNode* phead, DataType x)
{/*注意phead不是头结点(第一个节点),phead 只是一个哨兵位,只占位置第一个节点:phead->next考虑指针先后问题,避免找不到第一个节点(链表不为空)*/assert(phead);//ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);//newnode->next = phead->next;//newnode->pre = phead;//phead->next = newnode;//新的头结点以上代码不对//ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);//newnode->next = phead->next;//newnode->pre = phead;//phead->next->pre = newnode;//原来第一个节点pre与新的头结点连接//phead->next = newnode;//新的头结点ListNodeInsert(phead->next, x);}void ListNodePopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);/*空链表: 1:找尾结点 phead->pre2:成环: 改变新的尾结点与phead 直接的链接*/assert(phead->next != phead);//不相等说明链表不为空,为空不能删除ListNodeErase(phead->pre);//ListNode* tail = phead->pre;//ListNode* tailPre = tail->pre;//phead->pre = tailPre;//新的尾结点// tailPre->next = phead;//free(tail);
}
void ListNodePopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead->next != phead);//不相等说明不为空ListNodeErase(phead->next);//ListNode* newFirst = phead->next->next;//newFirst->pre = phead;//phead->next = newFirst;//成为新的头结点以下写法也对,但可读性差//phead->next = phead->next->next;//phead->next->pre = phead;}
ListNode* Find(ListNode* phead, DataType x) //指定数据查找
{/*从第一个节点开始查找: phead->next依次遍历,若是存在返回节点否则返回NULL*/assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead ) //phead 是哨兵位{if (x == cur->val){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;//没有找到
}void ListNodeInsert(ListNode* pos, DataType x)//指定位置之前插入
{/*1:找到pos 前一个节点 pos->pre2:注意避免节点找不到3:改变指针连接: posPre,newnode,pos*/assert(pos);//为空直接不玩了ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);ListNode* posPre = pos->pre;posPre->next = newnode;newnode->pre = posPre;newnode->next = pos;pos->pre = newnode;}void ListNodeErase(ListNode* pos)//指定位置删除 pos是查找函数返回的
{assert(pos);ListNode* posPre = pos->pre;ListNode* posNext = pos->next;posPre->next = posNext;posNext->pre = posPre;free(pos);
}
void ListNodeDestroy(ListNode* phead)
{/*注意哨兵位也需要删除一个节点一个节点删除*/assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}
DList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int DataType;
typedef struct DListNode
{DataType val;struct DListNode* next;struct DListNode* pre;//前驱指针}ListNode;
void ListNodePrint(ListNode*phead);
ListNode* ListNodeInit();void ListNodePushBack(ListNode* phead,DataType x);
void ListNodePushFront(ListNode* phead, DataType x);void ListNodePopBack(ListNode* phead);
void ListNodePopFront(ListNode* phead);ListNode* Find(ListNode* phead,DataType x); //指定数据查找(此函数可以实现2个功能:查找 + 修改)void ListNodeInsert(ListNode* pos, DataType x);//指定位置之前插入,pos是查找函数返回的void ListNodeErase(ListNode* pos);//指定位置删除void ListNodeDestroy(ListNode* phead);
/*
面试题目: 10分钟之内写一个链表
注意:头删,尾删 都只是 ListNodeErase 这个函数一个特例
头插,尾插,同理,是ListNodeInsert 一个特例
所以 可以借用
*/test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"void TestPush()
{ListNode* plist = ListNodeInit();//ListNodeInit(&plist);//ListNodePushBack(plist, 1);//ListNodePushBack(plist, 2);//ListNodePushBack(plist, 3);ListNodePushFront(plist, 1);ListNodePushFront(plist, 2);ListNodePushFront(plist, 3);ListNodePushFront(plist, 4);ListNodePushFront(plist, 5);ListNodePushFront(plist, 6);ListNodePushFront(plist, 7);ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodePushBack(plist, 0);ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodeDestroy(plist);}
void TestPop()
{//ListNode* plist = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//if (plist == NULL)// return;//plist->val = -1;//plist->next = plist;//plist->pre = plist;//等价于以下代码ListNode* plist = ListNodeInit();ListNodePushBack(plist, 1);ListNodePushBack(plist, 2);ListNodePushBack(plist, 3);ListNodePrint(plist);//ListNodePopFront(plist);//ListNodePrint(plist);//ListNodePopFront(plist);//ListNodePrint(plist);//ListNodePopFront(plist);//ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodePopBack(plist);ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodePopBack(plist);ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodePopBack(plist);ListNodePrint(plist);ListNodeDestroy(plist);}
void Test()
{ListNode* plist = ListNodeInit();ListNodePushBack(plist, 1);ListNodePushBack(plist, 2);ListNodePushBack(plist, 3);ListNode* pos = Find(plist, 3);if (pos != NULL){ListNodeInsert(pos, 10);ListNodePrint(plist);}else{printf("操作失败\n");}ListNodeDestroy(plist);}void Test1()
{ListNode* plist = ListNodeInit();ListNodePushBack(plist, 1);ListNodePushBack(plist, 2);ListNodePushBack(plist, 3);ListNode* pos = Find(plist, 3);if (pos != NULL){ListNodeErase(pos);ListNodePrint(plist);}else{printf("操作失败\n");}ListNodeDestroy(plist);}int main()
{TestPush();//TestPop();//Test();//Test1();return 0;
}11:结语
以上就是我今日要为大家share的内容。其实说白了,循环链表的结构看似复杂,实际操作起来,非常简单。(就是多了一个 pre这样的一个前驱指针)。希望各位老铁们能够从这篇博客中学到一些知识,同时欢迎大家随时指正,那咱话不多说,你懂滴!