题目
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
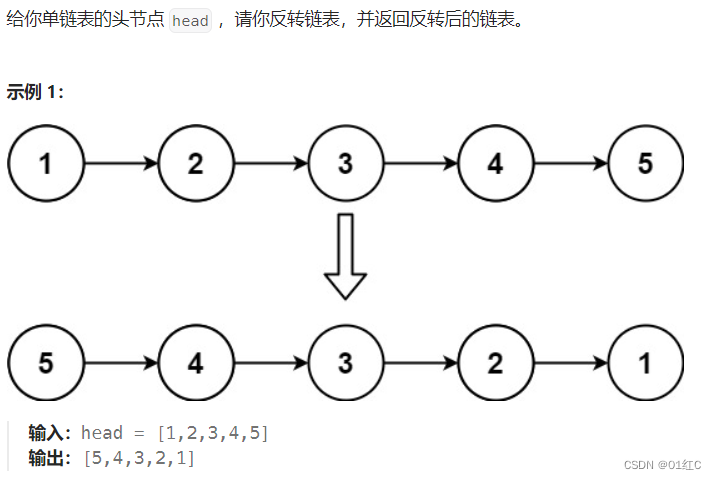
这道题对于刚开始学习数据结构和算法的人来说有点难,是入门的重要典型题目;但等数据结构入门之后,这就会是一道非常简单的题目了。
算法一(算法正确但超出时间限制)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:int lengthLink(ListNode* head){ListNode* p=head;int len=0;while(p){if(p){len++;p=p->next;}else{return len;} }return len;}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr)return head;int len=lengthLink(head);ListNode*p=head;for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){p=p->next;}ListNode* res=head;for(int i=1;i<len;i++){res=res->next;}ListNode* q=p->next;ListNode* L=new ListNode();L->next=head;while(len!=2){ListNode* pre=L;q->next=p;q=p;for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){pre=pre->next;}p=pre;len--;}p->next=nullptr;delete L;return res;}
};逻辑思路
int lengthLink(ListNode* head){ListNode* p=head;int len=0;while(p){if(p){len++;p=p->next;}else{return len;} }return -1;}这个函数是用来计算链表的长度的。将head传入,会返回链表的长度。
求出链表的长度len,之后len会变化,用来表示原链表中未反转的部分的节点的长度
下面是算法主体的逻辑思路:
以下面的链表为例:
使指针p指向倒数第二个节点,使q指向p的下一个节点,也就是倒数第一个节点。
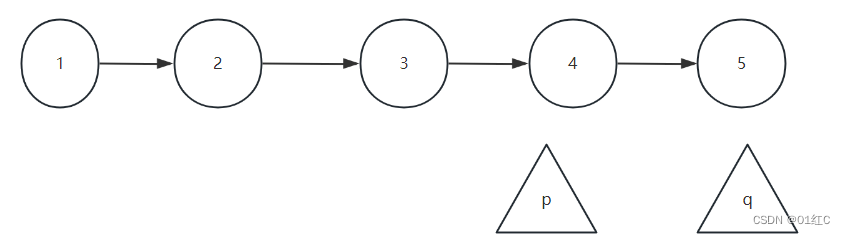
q->next=p;
q=p;
q指向的节点的指针域指向p指向的节点
指针q指到p指向的节点上
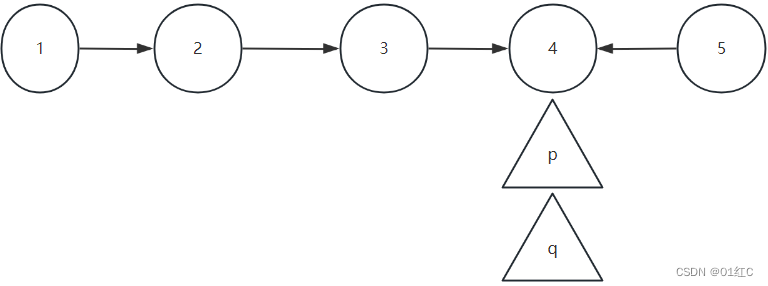
但是这个时候,没法控制p前面的那个节点,所以就需要一个指针pre。
申请一个空节点L作为头结点指向head,使pre刚开始的时候指向L,每次循环遍历到p之前的那个节点。假设p指向倒数第i个节点,pre就循环遍历指向第i+1个节点。
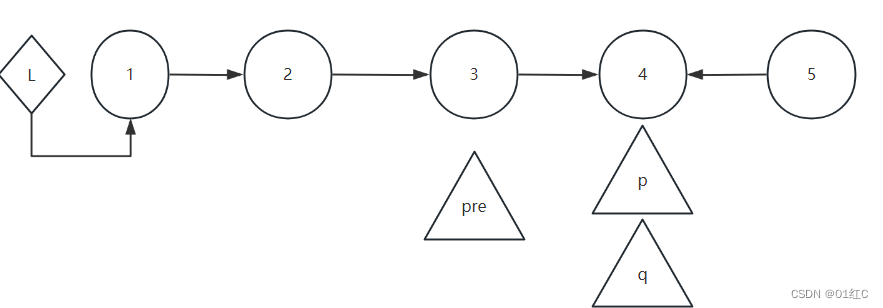
pre指向了p的前一个节点后,让p指向pre指向的节点。然后继续逆置下一个链表的箭头的方向。

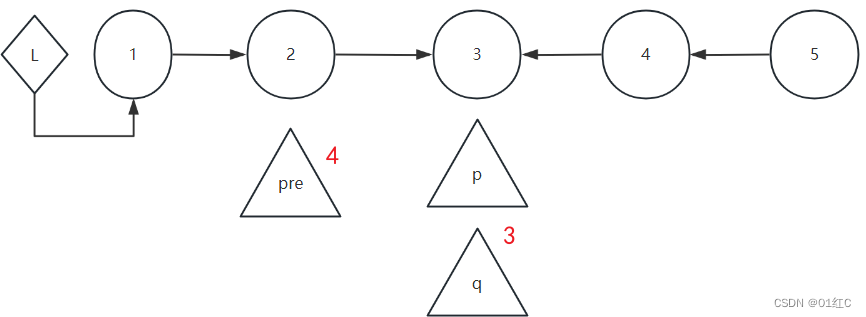
但是,反转链表后,怎么返回这个链表呢?要在还没开始进行链表反转时,使用一个指针res指向尾节点。等最后箭头方向都修改了之后,返回res即可。
代码如下:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr)return head;int len=lengthLink(head);ListNode*p=head;for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){p=p->next;}ListNode* res=head;for(int i=1;i<len;i++){res=res->next;}ListNode* q=p->next;ListNode* L=new ListNode();L->next=head;while(len!=2){ListNode* pre=L;q->next=p;q=p;for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){pre=pre->next;}p=pre;len--;}p->next=nullptr;delete L;return res;}
算法二 双指针
首先使用cur指针指向head节点。
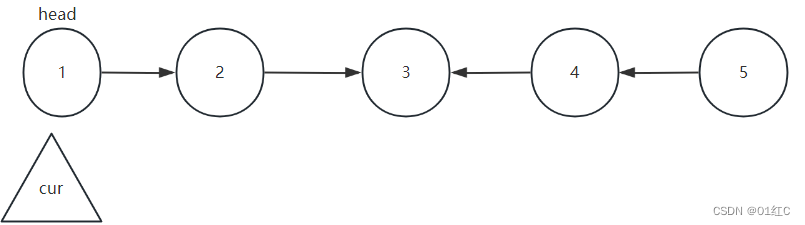
在反转链表的过程中,需要指向当前节点的前一个节点 ,用来改变链表节点的指向。
使用指针pre定义在cur的前面
在初始化的时候:
cur=head;
pre=null;
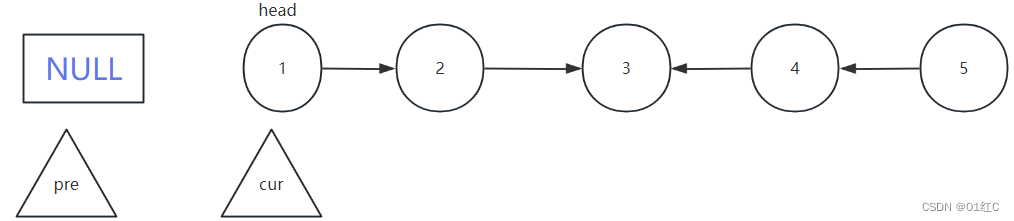
将pre初始为Null,是为了将第一个节点改变指向,指向为Null。
代码如下:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr)return head;ListNode* cur=head;ListNode* pre=nullptr;while(cur!=nullptr){ListNode* temp=cur->next;cur->next=pre;pre=cur;cur=temp;}return pre;}
};方法二和方法一类似,pre和cur类似于p和q,方法一中的pre的作用是为了从后向前执行任务,方法二中的temp的作用是为了从前往后执行任务。
方法三 递归
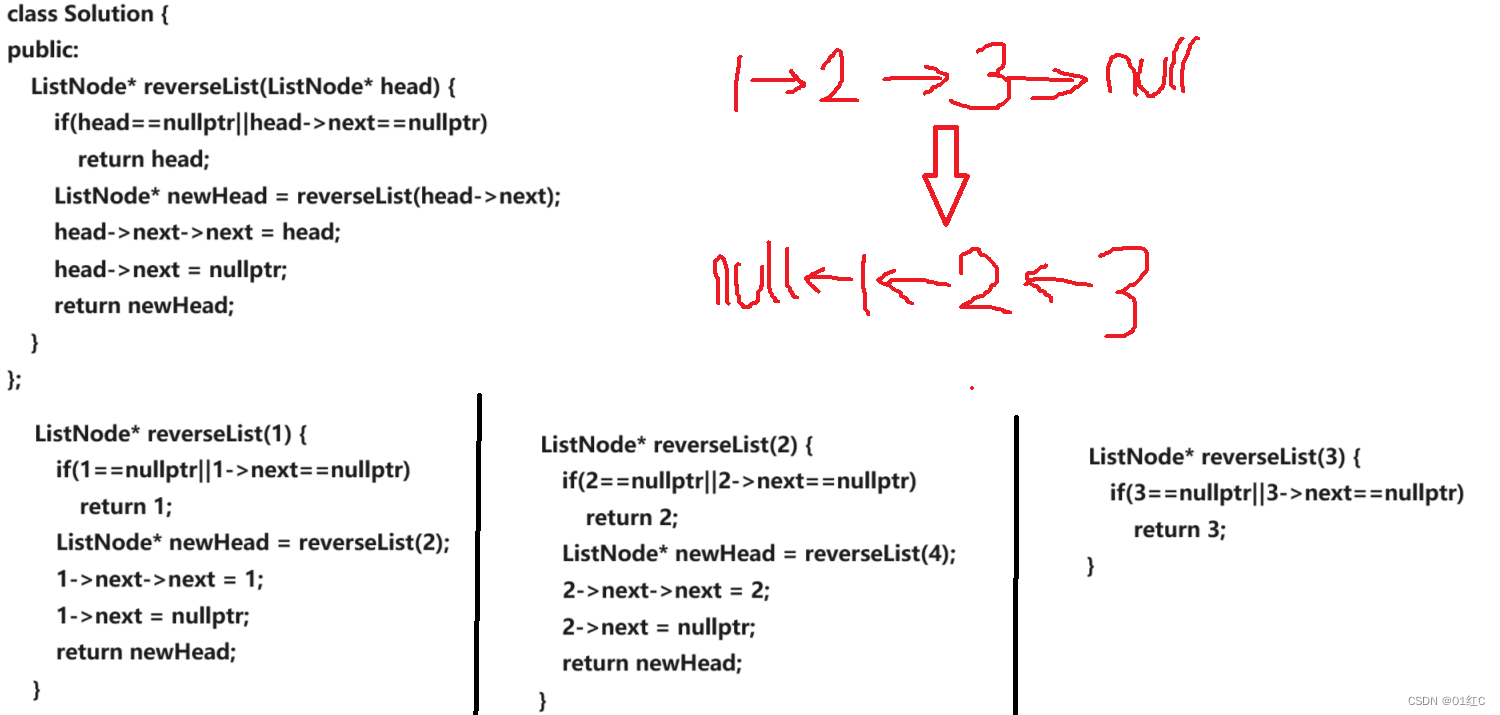
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr)return head;ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next = nullptr;return newHead;}
};