STL之list容器的介绍与模拟实现+适配器
- 1. list的介绍
- 2. list容器的使用
- 2.1 list的定义
- 2.2 list iterator的使用
- 2.3 list capacity
- 2.4 list element access
- 2.5 list modifiers
- 2.6 list的迭代器失效
- 3. list的模拟实现
- 3.1 架构搭建
- 3.2 迭代器
- 3.2.1 正向迭代器
- 3.2.2反向迭代器+适配器
- 3.3 空间控制模块
- 3.4 数据的访问
- 3.5 增加/删除数据
- 3.6 构造/拷贝构造/析构
- 4. 整体代码逻辑
所属专栏:C“嘎嘎" 系统学习❤️
🚀 >博主首页:初阳785❤️
🚀 >代码托管:chuyang785❤️
🚀 >感谢大家的支持,您的点赞和关注是对我最大的支持!!!❤️
🚀 >博主也会更加的努力,创作出更优质的博文!!❤️
1. list的介绍
list的文档介绍
- list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
- list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向
其前一个元素和后一个元素。 - list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
- 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
- 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list
的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间
开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这
可能是一个重要的因素)
2. list容器的使用
2.1 list的定义
| 构造函数( (constructor)) | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list |
2.2 list iterator的使用
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| begin +end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin +rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |
【注意】
- begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
- rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
2.3 list capacity
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| empty | 检测list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点的个数 |
2.4 list element access
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| front | 返回list的第一个节点中值的引用 |
| back | 返回list的最后一个节点中值的引用 |
2.5 list modifiers
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list中第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |
2.6 list的迭代器失效
前面说过,此处大家可将迭代器暂时理解成类似于指针,迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节
点被删除了。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代
器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
void TestListIterator1()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));auto it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){// erase()函数执行后,it所指向的节点已被删除,因此it无效,在下一次使用it时,必须先给其赋值l.erase(it);++it;}
}// 改正
void TestListIterator()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));auto it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){it = l.erase(it);}
}
3. list的模拟实现
3.1 架构搭建
- 首先,list容器的底层实现是一个双向循环链表。所以在实现本章节的前提下,我们首先要熟知我们学习C语言的时候是怎么实现一个带头双向循环链表的。核心的逻辑思维是一模一样的。
- 所以在实现的前提下,我们可以先从C语言数据结构着手起步。
- 整体的构架就是:1. 要有一个节点的类,里面包含了两个指针next和prev,和一个存放数据的变量val。2. 就是构建list类,在类里面进行一些类的操作。
template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode(const T& val = T()):_pPre(nullptr),_pNext(nullptr),_val(val){}ListNode<T>* _pPre;ListNode<T>* _pNext;T _val;};//list类template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;//typedef Node* PNode;public://正向迭代器typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//反向迭代器typedef Reverse_iterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef Reverse_iterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;public:///// List的构造list(){……}//拷贝构造list(const list<T>& l){……}~list(){……}
//………………private://创建新节点void CreateHead(){_pHead = new Node;_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;}Node* _pHead;
}
3.2 迭代器
同样提供两个版本const 和 非const版本的。
- 但是这里要注意一点就是,我们的迭代器在进行移动的时候无非就是++/–操作,但是我们可由直接进行(iterator)a++吗?如果这是个内置类型的话那自然是可以的。但是组成list容器并非是内置类型,而是自定义类型,每个节点都是一个类,而自定义类型是无法直接进行++/–等一些类的运算符操作的。要想对自定义类型进行运算符操作就必须要使用运算符重载函数。所以为了可以对迭代器进行运算符操作就也要定义一个迭代器类,并在类中包含要进行操作的自定义类型的对象,在类中进行运算符操作。
3.2.1 正向迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class ListIterator
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> PNode;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; PNode* _pNode;ListIterator(PNode* pNode = nullptr):_pNode(pNode){}//ListIterator(const Self& l);Ref operator*(){return _pNode->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_pNode->_val;}Self& operator++(){_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造(浅拷贝)_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return *this;}Self& operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& l){return _pNode != l._pNode;}bool operator==(const Self& l){return _pNode == l._pNode;}
};
- 注:这里我们可以看到我们创建ListIterator类的时候使用了类模板,并且看到模板参数中不止一个参数,而是多了两个Ref和Ptr。至于理由是:我们要实现两个版本的迭代器,一个是const和非const版本的,而这两个版本的区别无非就是返回的引用值是否能被修改该,也就是
重载*解引用的时候,const版本返回的是const T&,非const版本返回的就是T&,除了这个其他的地方都一样。那如果想两个都实现是不是就要copy一份呢?一下写两个出来呢?所以这个时候模板参数起作用了。定义Ref模板参数,不管是T&还是const T&我们都返回Ref只是当我们想调用const版本的时候就给模板传const T&的类型,我们想调用非cosnt版本的时候就传T&类型的给模板就行,这样就可以避免代码重复问题,提高复用度。 - 同样的既然我们定义是一个自定义类型的节点,迭代器可以看作是一个指针,有了自定义类型和之指针我们就可以通过指针+ (->)的方式拿到节点里面的val值,但是->同样也有两个版本,所以做法和上面的是一样的,只需要多个模板参数传一个值Ptr就行,具体调用什么版本的就传什么类型的过去就行。
- 这里同样也要注意的一点就是重载(->)的时候,我们是这样定义的:
Ptr operator->() { return &_pNode->_val; }
本来我们使用的时候应该it->->val这样有两个箭头使用,也就是it.operator->()->val这样去使用的,但是编译为了方便使用做了优化只需要一个箭头就可进行访问了。
3.2.2反向迭代器+适配器
适配器:
适配器是一种设计模式(设计模式是一套被反复使用的、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总
结),该种模式是将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口
用简单话来概括适配器就是——用现有的东西适配出一个新的东西。
我们的反向迭代器其实就是用到了适配器的概念,用到就是正向迭代器适配出来的。
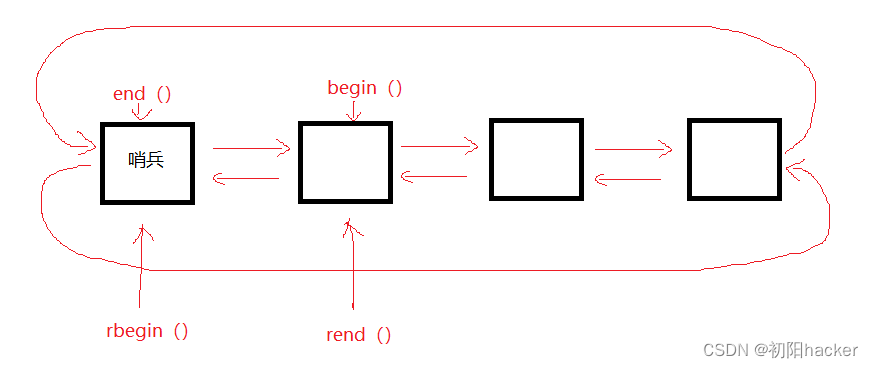
- rbegin的++就是end的–,rend的–就是begin的++,要取rbegin指向的值就是–end()在解引用得到。
所以我们只需要讲正向迭代器的类型当作参数传个我们的反向迭代器的类模板参数就行。 - 同样的这里也需要传三个模板参数,原理和上面是一样的。
template<class Iterator, class Pef, class Ptr>
struct Reverse_iterator
{typedef Reverse_iterator<Iterator, Pef, Ptr> self;Iterator cur;Reverse_iterator(Iterator it):cur(it){}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*());}self& operator++(){--cur;return *this;}self operator++(int){Iterator tmp = cur;--cur;return tmp;}self& operator--(){++cur;return *this;}self operator--(int){Iterator tmp = cur;++cur;return tmp;}Pef operator*(){Iterator tmp = cur;--tmp;return *tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& l){return cur != l.cur;}bool operator==(const self& l){return cur == l.cur;}
};
3.3 空间控制模块
- 返回list容器的大小
size_t size() const
{size_t len = 0;const_iterator it = begin();//这里要用const_iterator迭代器,this被const修饰了while (it != end()){++len;++it;}return len;
}
- list容器是否为空
bool empty()const
{return begin() == end();
}
- resize
void resize(size_t newsize, const T& data = T())
{size_t oldsize = size();if (newsize <= oldsize){// 有效元素个数减少到newsizewhile (newsize < oldsize){pop_back();oldsize--;}}else{while (oldsize < newsize){push_back(data);oldsize++;}}
}
3.4 数据的访问
- 访问头节点的值
T& front()
{return (begin()._pNode)->_pNext->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{return (begin()._pNode)->_pNext->_val;}
- 访问尾节点的值
T& back()
{return (end()._pNode)->_pPre->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{return (end()._pNode)->_pPre->_val;
}
3.5 增加/删除数据
- 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{Node* newnode = new Node;newnode->_val = val;Node* cur = pos._pNode;Node* prev = cur->_pPre;prev->_pNext = newnode;newnode->_pPre = prev;newnode->_pNext = cur;cur->_pPre = newnode;return iterator(newnode);
}
- 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._pNode;Node* prev = cur->_pPre;Node* next = cur->_pNext;prev->_pNext = next;next->_pPre = prev;return iterator(next);}
- push_back/pop_back
void push_back(const T& val)
{insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back()
{ erase(--end());
}
- push_front/pop_front
void push_front(const T& val)
{ insert(begin(), val);
}
void pop_front()
{ erase(begin());
}
- 清除数据
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}
}
3.6 构造/拷贝构造/析构
- 构造函数
list()
{CreateHead();
}list(int n, const T& value = T())
{CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(value);}
}template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}
}
- 拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& l)
{CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位const_iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){push_back(*it);++it;}
}
- 赋值运算符重载
void swap(list<T>& l)
{std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);
}list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{swap(l);return *this;
}
- 析构
~list()
{//iterator it = begin();//while (it != end())//{// Node* cur = it._pNode;// _pHead->_pNext = cur->_pNext;// delete cur;//}clear();delete _pHead;_pHead = nullptr;
}
4. 整体代码逻辑
namespace qfw
{// List的节点类template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode(const T& val = T()):_pPre(nullptr),_pNext(nullptr),_val(val){}ListNode<T>* _pPre;ListNode<T>* _pNext;T _val;};//List的迭代器类template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>class ListIterator{public:typedef ListNode<T> PNode;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; PNode* _pNode;ListIterator(PNode* pNode = nullptr):_pNode(pNode){}//ListIterator(const Self& l);Ref operator*(){return _pNode->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_pNode->_val;}Self& operator++(){_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造(浅拷贝)_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return *this;}Self& operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& l){return _pNode != l._pNode;}bool operator==(const Self& l){return _pNode == l._pNode;}};template<class Iterator, class Pef, class Ptr>struct Reverse_iterator{typedef Reverse_iterator<Iterator, Pef, Ptr> self;Iterator cur;Reverse_iterator(Iterator it):cur(it){}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*());}self& operator++(){--cur;return *this;}self operator++(int){Iterator tmp = cur;--cur;return tmp;}self& operator--(){++cur;return *this;}self operator--(int){Iterator tmp = cur;++cur;return tmp;}Pef operator*(){Iterator tmp = cur;--tmp;return *tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& l){return cur != l.cur;}bool operator==(const self& l){return cur == l.cur;}};//list类template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;//typedef Node* PNode;public://正向迭代器typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//反向迭代器typedef Reverse_iterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef Reverse_iterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;public:///// List的构造list(){CreateHead();}list(int n, const T& value = T()){CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(value);}}template <class Iterator>list(Iterator first, Iterator last){CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}//拷贝构造list(const list<T>& l){CreateHead();//先创建哨兵位const_iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){push_back(*it);++it;}}void swap(list<T>& l){std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> l) {swap(l);return *this;}~list(){//iterator it = begin();//while (it != end())//{// Node* cur = it._pNode;// _pHead->_pNext = cur->_pNext;// delete cur;//}clear();delete _pHead;_pHead = nullptr;}///// List Iteratoriterator begin(){return iterator(_pHead->_pNext);}iterator end(){return iterator(_pHead);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_pHead);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const{return const_reverse_iterator(end());}const_reverse_iterator rend() const{return const_reverse_iterator(begin());}///// List Capacitysize_t size() const{size_t len = 0;const_iterator it = begin();//这里要用const_iterator迭代器,this被const修饰了while (it != end()){++len;++it;}return len;}bool empty()const{return begin() == end();}void resize(size_t newsize, const T& data = T()){size_t oldsize = size();if (newsize <= oldsize){// 有效元素个数减少到newsizewhile (newsize < oldsize){pop_back();oldsize--;}}else{while (oldsize < newsize){push_back(data);oldsize++;}}}// List AccessT& front(){return (begin()._pNode)->_pNext->_val;}const T& front()const{return (begin()._pNode)->_pNext->_val;}T& back(){return (end()._pNode)->_pPre->_val;}const T& back()const{return (end()._pNode)->_pPre->_val;}// List Modifyvoid push_back(const T& val) {insert(end(), val); }void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* newnode = new Node;newnode->_val = val;Node* cur = pos._pNode;Node* prev = cur->_pPre;prev->_pNext = newnode;newnode->_pPre = prev;newnode->_pNext = cur;cur->_pPre = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._pNode;Node* prev = cur->_pPre;Node* next = cur->_pNext;prev->_pNext = next;next->_pPre = prev;return iterator(next);}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}private:void CreateHead(){_pHead = new Node;_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;}Node* _pHead;};