Association Pattern Mining 关联模式挖掘

Special case: Frequent Pattern Mining (binary data sets) 频繁模式挖掘
Given data matrix, identify all subsets of columns ( features ) such that at least a fraction of rows (objects ) in the matrix have all the features enabled (i.e., the features take on the value of 1).
Classification 分类
1. The goal is to use training data to learn relationships between a fixed feature (called class label ) and the remaining features in the data
使用训练数据去学习一个固定特征(被叫做 类特征 )和数据中其他特征的关系
2. The resulting learned model may then be used to estimate (predict) values of the class label for records, where the value is not known.
根据学习后得到的模型来 预测 records的 类特征 的值
3. The objects whose class label is unknown are test objects (test data).
类特征未知的对象叫测试对象
4. 监督学习
Examples
1. Targeted marketing
2. Text recognition
Clustering 聚类
1. Given a data set (data matrix), partition its objects (rows) into sets (clusters) C 1 , C 2 , …, C k such that the objects in each cluster are “ similar ” to one another.
2. Specific definitions depend on how the notion of similarity is defined
3. Can be seen as an unsupervised version of classification. 未监督学习版本的分类
Examples
1. Customer segmentation (identify similar customers for targeted product promotion)
2. Data summarisation (cluster can be used to create a summary of the data)
Outlier Detection 异常值检测
Given a data set, determine the outliers , i.e. the objects that are significantly different from the remaining objects.
Examples:• Credit card fraud • Detecting sensor events • Medical diagnosis • Earth science
Linear algebra
1. vector
2. matrices
3. vector arithmetic
4. matrix arithmetic
5. transpose and inverse

6. linear independence
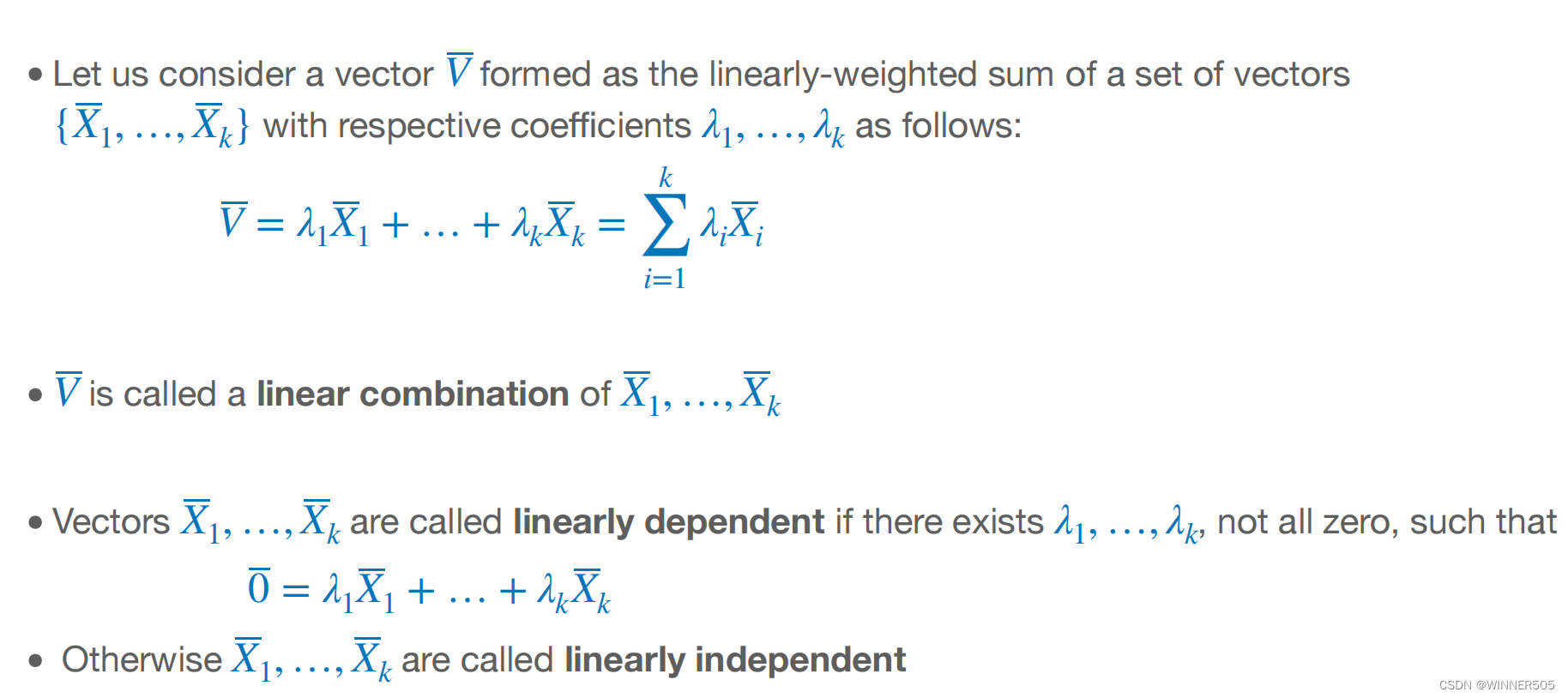
7. rank

invertible 可倒转的
8. matrix trace

9. eigenvalues and eigenvectors