qt-Robot-PyQt5
- 一、演示效果
- 二、关键程序
- 三、下载链接
Python 脚本使用 PyQt5 作为窗口框架,OpenGL 作为 3D 环境。 每个机器人都是 DOF3_robot 类的一个实例。
所需模块:
PyQt5的
pyqtgraph/opengl
Numpy。
一、演示效果
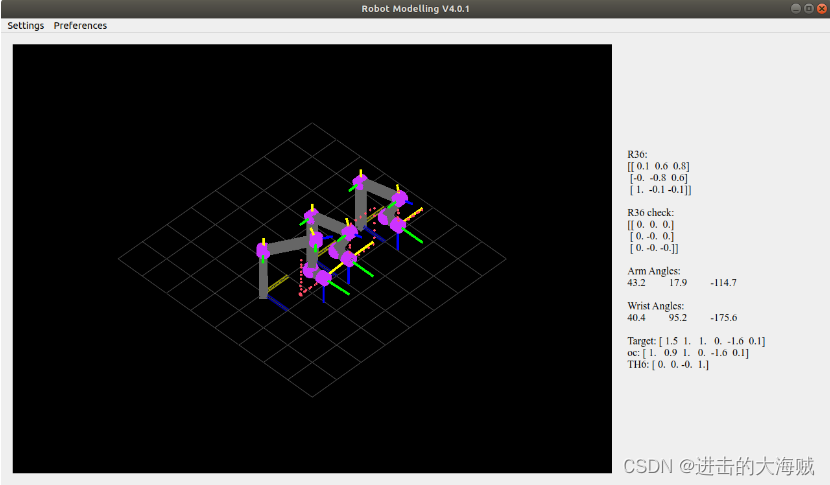
二、关键程序
import rm_utilities as Rm
import numpy as np
import pyqtgraph.opengl as gl"""
Simulation of a 6 DOF robot.
- Cédric Wassenaar & Joeri Verkerk
- C.M.Wassenaar@student.hhs.nl
- 24-09-2018
"""class Link(object):"""Storage type for robot arm object"""def __init__(self):self.arm_length = 0self.arm: gl.GLMeshItem|None = Noneself.frame: gl.GLAxisItem|None = Noneself.joint: gl.GLMeshItem|None = Noneself.DH_parameters = [0, 0, 0, 0]self.homogenious_matrix: np.array|None = Noneself.hg_matrix_list = []self.p = Noneclass Robot(object):"""Class to create robot object for OpenGl implementation"""def __init__(self, view3D):self.view3D = view3D# Presetsself.radius = 0.2self.width = .6 * 2 * self.radiusself.depth = self.widthself.depth_cylinder = 1.2 * self.widthself.segments = 40self.joint_color = (0.8, 0.2, 1, 1) # yellowself.arm_color = (0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1) # light blueself.cycle = 0self.iteration = 0self.N = 0self.ready = Falseself.print_text = []# define arm lengthsself.arm_lengths = [1.75,1.60,1.25,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.50,0.00]# Create a list of arm piecesself.link = [Link()] * (len(self.arm_lengths) + 1)# define Target rotation for the end effector# self.target_rotation = Rm.make_rotation_matrix("x", np.radians(00))self.target_rotation = np.eye(3, 3)# define trajectory# X, Y, Z, Ax, Ay, Az (degrees)self.trajectory = np.array([[-1.5, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0],[1.5, 0.5, 4, 0, 0, np.pi/2],[1.5, 2.0, 1, 0, np.pi, np.pi/2],[-0.0, 2.0, 3, 0, np.pi, 0],[-1.5, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0]])self.setup()def setup(self):"""Function for user defined objects and functions:return:"""# create all arm piecesself.link[0].frame = self.create_main_axis()self.link[1] = self.add_arm(self.link[0], self.arm_lengths[0])self.link[1].frame.setSize(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)self.link[2] = self.add_arm(self.link[1], self.arm_lengths[1])self.link[2].frame.setSize(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)self.link[3] = self.add_arm(self.link[2], self.arm_lengths[2])self.link[3].frame.setSize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)self.link[4] = self.add_arm(self.link[3], self.arm_lengths[3])self.link[4].frame.setSize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)self.link[5] = self.add_arm(self.link[4], self.arm_lengths[4])self.link[5].frame.setSize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)self.link[6] = self.add_arm(self.link[5], self.arm_lengths[5])self.link[6].frame.setSize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)self.link[7] = self.add_arm(self.link[6], self.arm_lengths[6])self.link[7].frame.setSize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)self.link[8] = self.add_arm(self.link[7], self.arm_lengths[7])# Rotate arms to work with Denavit Hartenberg parametersself.link[1].arm.rotate(90, 1, 0, 0)self.link[2].arm.rotate(-90, 0, 1, 0)self.link[3].arm.rotate(-90, 0, 1, 0)# Predefine static values of the Denavit Hartenberg parametersself.link[0].DH_parameters = [0, 0, 0, 0]self.link[1].DH_parameters = [0, 1.57079, self.arm_lengths[0], 0]self.link[2].DH_parameters = [self.arm_lengths[1], 0, 0, 0]self.link[3].DH_parameters = [self.arm_lengths[2], 0, 0, 0]self.link[4].DH_parameters = [0, 1.57079, 0, 1.57079]self.link[5].DH_parameters = [0, -1.57079, 0, 0]self.link[6].DH_parameters = [0, 1.57079, 0, 0]self.link[7].DH_parameters = [0, 0, 0, 0]self.link[8].DH_parameters = [0, 0, self.arm_lengths[6], 0]def set_new_trajectory(self, new_trajectory, precision):"""Sets and calculates new trajectory for robot"""self.trajectory = Rm.interpolate(new_trajectory, precision)self.N = self.trajectory.shape[0]self.iteration = 0self.calculate_path()def calculate_path(self):"""In order to reduce CPU use the inverse kinematics are pre-calculated and saved in a list,the update_window methods will then iterate through this list."""# Clear old pathself.print_text = []for i in range(1, len(self.link)):self.link[i].hg_matrix_list = []# Create new pathlength = len(self.trajectory)for current in range(length):# In order to prevent call by reference the trajectory values are copied.pos = self.trajectory[current].copy()rotation = Rm.rotate_xyz(pos[3:])pos[0] = pos[0] - self.arm_lengths[6] * rotation[0, 2]pos[1] = pos[1] - self.arm_lengths[6] * rotation[1, 2]pos[2] = pos[2] - self.arm_lengths[6] * rotation[2, 2]# The Inverse kinematics are calculated in the rm_utilitiesV3 fileangles, error = Rm.inverse_algorithm_3DOF(self.arm_lengths, pos)# If the robot arm is not capable of reaching the given coordinate it will raise an errorif not error:# The dynamic values of the Denavit Hartenberg parameters are now updated.self.link[1].DH_parameters[3] = angles[0]self.link[2].DH_parameters[3] = angles[1]self.link[3].DH_parameters[3] = angles[2]# The homogenious matrices are created for link 0 to 4for i in range(5):self.link[i].homogenious_matrix = Rm.make_DH_matrix(self.link[i].DH_parameters)# The H03 matrix is calculated using the @ symbol (matrix multiplication)H03 = self.link[0].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[1].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[2].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[3].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[4].homogenious_matrix# The 3x3-rotation matrix R36 is calculatedR36 = np.matrix.transpose(H03[:3, :3]) @ rotation# The inverse kinematics for the wrist is calculated with R36rotate, R_compare = Rm.inverse_kinematics_wrist(R36)self.link[5].DH_parameters[3] = rotate[0]self.link[6].DH_parameters[3] = rotate[1]self.link[7].DH_parameters[3] = rotate[2]for i in range(5, 9):self.link[i].homogenious_matrix = Rm.make_DH_matrix(self.link[i].DH_parameters)# The end effector matrices are calculatedH36 = self.link[5].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[6].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[7].homogenious_matrix @ \self.link[8].homogenious_matrixH06 = H03 @ H36p0 = np.array([self.trajectory[current, 0],self.trajectory[current, 1],self.trajectory[current, 2],1])TH6 = np.linalg.inv(H06).dot(p0)# All flattened homogenious matrices are saved in a listfor i in range(1, len(self.link)):# self.link[i].frame.setTransform(self.link[i].homogenious_matrix.flatten())matrix = self.link[i].homogenious_matrix.flatten()self.link[i].hg_matrix_list.append(matrix)# The positions are saved in textformatangles = str(format(np.degrees(angles[0]), '.1f')) + \"\t" + str(format(np.degrees(angles[1]), '.1f')) + \"\t" + str(format(np.degrees(angles[2]), '.1f')) + "\n\n"rotate = str(format(np.degrees(rotate[0]), '.1f')) + \"\t" + str(format(np.degrees(rotate[1]), '.1f')) + \"\t" + str(format(np.degrees(rotate[2]), '.1f')) + "\n\n"self.print_text.append("R36:\n" + str(R36) +"\n\nR36 check:\n" + str(R_compare) +"\n\nArm Angles:\n" + angles +"Wrist Angles:\n" + rotate +"Target: " + str(self.trajectory[current]) +"\noc: " + str(pos) +"\nTH6: " + str(TH6))# Each 5th step of the trajectory a small block is rendered to show the path of the robotif (current % 6) > 4:self.show_path(H06)else:print("Error Calculating, position possibly out of range")self.ready = Truedef __str__(self):return self.print_text[self.iteration]def add_arm(self, parent_object, length):""":param parent_object::param length::return:"""link = Link()link.frame = self.set_new_axis(parent_object.frame)link.arm = self.create_arm(length)link.arm.setParentItem(link.frame)link.arm_length = lengthlink.arm.rotate(-90, 0, 1, 0)link.arm.translate(self.width / 2, -self.width / 2, self.width / 2)link.joint = self.create_joint()link.joint.setParentItem(link.frame)link.joint.translate(0, 0, -self.depth_cylinder/ 2)return linkdef create_arm(self, length) -> gl.GLMeshItem:"""Creates a box that is attached to a certain object"""size = (length, self.width, self.depth)vertices_arm, faces_arm = Rm.box(size)arm = gl.GLMeshItem(vertexes=vertices_arm, faces=faces_arm,rawEdges=False, drawFaces=True, color=self.arm_color)self.view3D.addItem(arm)return armdef create_joint(self) -> gl.GLMeshItem:"""Creates a joint that is attached to a certain object"""vertices_joint, faces_joint = Rm.cylinder(self.radius, self.depth_cylinder, self.segments)joint = gl.GLMeshItem(vertexes=vertices_joint, faces=faces_joint,drawEdges=False, drawFaces=True, color=self.joint_color)self.view3D.addItem(joint)return jointdef set_new_axis(self, parent_object) -> gl.GLAxisItem:"""Adds axis to given object"""axis = gl.GLAxisItem(antialias=True, glOptions='opaque')axis.updateGLOptions({'glLineWidth': (3,)})axis.setParentItem(parent_object)self.view3D.addItem(axis)return axisdef create_main_axis(self) -> gl.GLAxisItem:"""Create the basis axis"""axis = gl.GLAxisItem()axis.updateGLOptions({'glLineWidth': (6,)})self.view3D.addItem(axis)return axisdef show_path(self, frame):vertices_arm, faces_arm = Rm.box((0.05, 0.05, 0.05))box = gl.GLMeshItem(vertexes=vertices_arm, faces=faces_arm,rawEdges=False, drawFaces=True, color=(1, 0.3, 0.4, 1))box.setParentItem(self.link[0].frame)m1 = np.array_split(frame.flatten(), 4)box.setTransform(m1)self.view3D.addItem(box)def update_window(self):"""Render new frame of 3D view"""if not self.ready:return # When ready the robot is rendered and updated.for i in range(1, len(self.link)):a1 = self.link[i].hg_matrix_list[self.iteration]m1 = np.array_split(a1, 4)self.link[i].frame.setTransform(m1)# increase the counter, such that next time we get the next pointself.iteration += 1# if the counter arives at N, reset it to 0, to repeat the trajectoryif self.iteration == self.N:self.iteration = 0self.cycle += 1三、下载链接
https://download.csdn.net/download/u013083044/88851028