参考:
[1] LIU Z, MAO H, WU C Y, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C/OL]//2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA. 2022. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cvpr52688.2022.01167. DOI:10.1109/cvpr52688.2022.01167.
[2] 薛导ConvNext博客
[3] DropPath理解
[4] 官方源码Facebook
TOC
- 1 模型学习
- 1.0 训练策略
- 1.1 Macro design
- 1.2 ResNeXt-ify
- 1.3 Inverted bottleneck
- 1.4 Large kernel size
- 1.5 Micro design
- 1.6 框架图
- 2 ConvNext代码实现
- 2.1 DropPath
- 2.2 GELU
- 2.3 LayerNorm
- 2.4 Block的实现
- 2.5 ConvNext网络搭建
- 2.5.1 特征提取部分
- 2.5.2 分类头部分
- 2.5.3 初始化
1 模型学习
1.0 训练策略
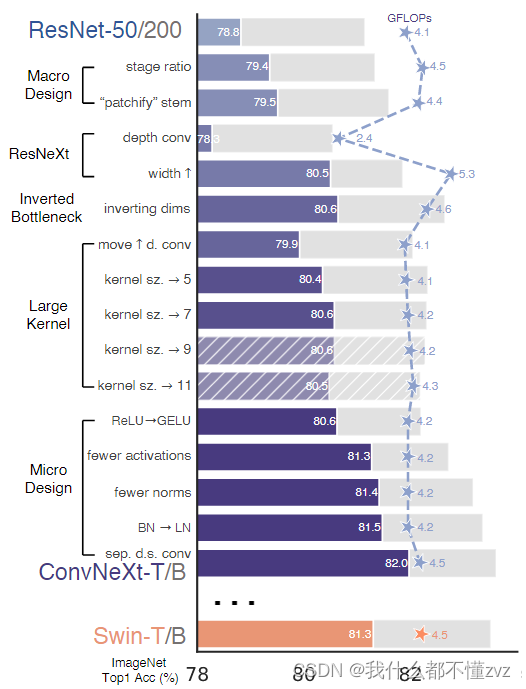
作者以训练Vit的策略用来训练ResNet50,发现比原来要好,以此为基准。
1.1 Macro design
改变stage的计算比例
- 原ResNet50的stage的重复次数为[3,4,6,3],而Swin-T的重复次数比例为1:1:3:1, Swin-L的重复次数比例为1:1:9:1,可见第三层stage的重复次数更多。
- ConvNext将由原来的[3,4,6,4] 魔改为 [3,3,9,3]
改变stem(既开始的部分)
- 原ResNet的stem为卷积7x7,stride为2,padding为3,再经过stride为2的Maxpooling层,将原图像的高宽缩小4倍(224->56)。但在Swim-T中,卷积之间是没有重叠的,既stride=kernel_size
- ConvNext仿照Swin-Transformer,用4x4Conv替代原来的7x7Conv,并将步长设置为4,不使用padding,这样直接将下采样四倍了。
1.2 ResNeXt-ify
替换GroupConv为DW Conv
- 将组卷积替换为depthwise卷积(DW卷积),也就是将groups设置为channel,DW卷积最早出现于MobileNet中,也是GroupConv的一种特殊形式(groups = input channels)
- 然后使用1x1卷积去改变channel数(官方代码中说是使用pointwise 1x1 conv,并且就是一个
nn.Linear)
改变conv的深度
- 原ResNet论文中,卷积的深度为(64,128,256,512), ConvNext将其改为(96,192,384,768)
1.3 Inverted bottleneck
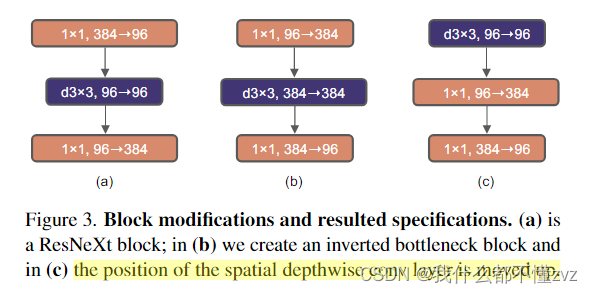
- 原来ResNet结构的Block都是呈现宽-窄-宽结构,在ConvNext中,变成窄-宽-窄结构,如图的(a)->(b)
1.4 Large kernel size
将DW Conv移到第一层
- 为了确保efficiency,large-kernel conv通常有较少的channels,而1x1 conv反而会去做繁杂的事情(比如升维、降维)。故ConvNext将DW Conv移动到第一层,并保持维度不变,而第二、三层的1x1 Conv负责升维降维。
增大kernel size
- ConvNext将DW Conv的3x3 Conv变成7x7 Conv
1.5 Micro design
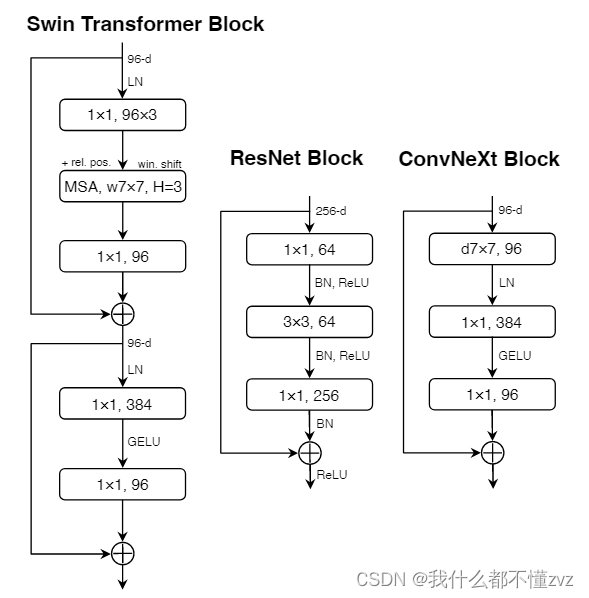
- 将ReLU换成GeLU,GELU可以看作是RELU的smooth版本
- 减小激活函数的使用,由Swim可知,只在最后一个1x1conv之前(降维之前)使用激活函数
- 在第二个1x1 Conv之前使用BN层,减小BN层的使用
- 将BN层换成LN层,BN模块有很多复杂的有害的影响
- 用2x2 Conv with stride 2替换原来的 1x1 Conv with stride 2进行残差下采样,也就是不使用残差下采样了,而是用 identity残差连接+2x2Conv下采样 替代
1.6 框架图


2 ConvNext代码实现
2.1 DropPath
由 DropPath理解可知,droppath是随机失活样本中的一部分,而dropout是随机失活样本的一些权重。需要注意的是,Droppath只在training phase中使用,并且放在block的残差连接之前。
下图分别为DropPath和Dropout的输出。


具体实现
def droppath(x,drop_prob:float=0.,training:bool=False):if drop_prob == 0. or not training:return xkeep_prob = 1. - drop_probshape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,)*(x.dim -1)# 举个例子: # 如果x为[10,3,224,224],那么shape为[10,1,1,1],只保留第0维,扩展后3维random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)# random_tensor介于[0,2)之间random_tensor = random_tensor.floor_() # random_tensor为0或1,表示失活或保留x = x.div(keep_prob)*randoom_tensor# 保持期望值不变,参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dan-baishucaizi/p/14703263.html
官方源码调用库函数
from timm.models.layers import DropPath
...self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
2.2 GELU
参考:https://alaaalatif.github.io/2019-04-11-gelu/
总的来说,GELU要比RELU的训练效果要好,并且GELU具有导数连续,比RELU更加平滑等优点,并且在0以下的值有一定概率不会变为0,避免了梯度消失。由下图可知,GELU安插在1x1conv升维之前。

代码:
self.gelu = nn.GELU()
2.3 LayerNorm
LayerNorm就是对每一个channel独立地进行求均值和方差的操作,然后再去对每一个channel独立地进行标准化。现在分channel维在第二位和第四位的情况,而pytorch官方可直接调用LayerNorm的情况是channel维在第四位的情况。
代码实现
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):def __init__(self,normalized_shape,eps=1e-6,data_format='channels_last')self.eps = epsself.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(normalized_shape)) # learnable gammaself.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(normalized_shape)) # learnable betaself.data_format = data_formatif self.data_format not in ['channels_first','channels_last']:raise NotImplementedErrorself.normalized_shape = (normalized_shape,)def forward(self,x):if self.data_format == 'channels_first':return F.layer_norm(x,self.normalized_shape,self.weight,self.bias,self.eps)elif self.data_format == 'channels_last':u = x.mean(1,keepdim=True)s = (x-u).pow(2).mean(1,keepdim=True) # variancex = (x-u)/torch.sqrt(s+self.eps)x = self.weight[:,None,None]*x+self.bias[:,None,None]return x
2.4 Block的实现
Block的源码中有一个layer_scale的操作是原论文中没有提及的,源于改论文Going deeper with image transformers. ICCV, 2021, 简单来说就是每一个通道的值进行缩放,缩放的因子gamma是一个可学习参数。
官方源码中开头的注释:
ConvNeXt Block. There are two equivalent implementations:
(1) DwConv -> LayerNorm (channels_first) -> 1x1 Conv -> GELU -> 1x1 Conv; all in (N, C, H, W)
(2) DwConv -> Permute to (N, H, W, C); LayerNorm (channels_last) -> Linear -> GELU -> Linear; Permute back
We use (2) as we find it slightly faster in PyTorch
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
drop_path (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
代码实现:
class Block(nn.Module):def __init__(self,dim,drop_path:float=0.,layer_scale_init_value:float=1e-6):self.dwconv = nn.Conv2d(dim,dim,kernel_size=7,padding=3,groups=dim)self.norm = LayerNorm(dim,eps=1e-6)self.pwconv1 = nn.Linear(dim,dim*4)self.gelu = nn.GELU()self.pwconv2 = nn.Linear(dim*4,dim)self.gamma = nn.Parameter(layer_scale_init_value* torch.ones((dim)), require_grad=True) if layer_scale_init_value > 0 else Noneself.Droppath = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()def forward(self,x):input_ = x x = self.dwconv(x)x = x.permute(0,2,3,1) # put channel dim into last dimx = self.norm(x)x = self.pwconv1(x)x = self.gelu(x)x = self.pwconv2(x)if self.gamma is not None:x *= self.gammax = x.permute(0,3,1,2)x = input_ + self.drop_path(x)return x2.5 ConvNext网络搭建
2.5.1 特征提取部分
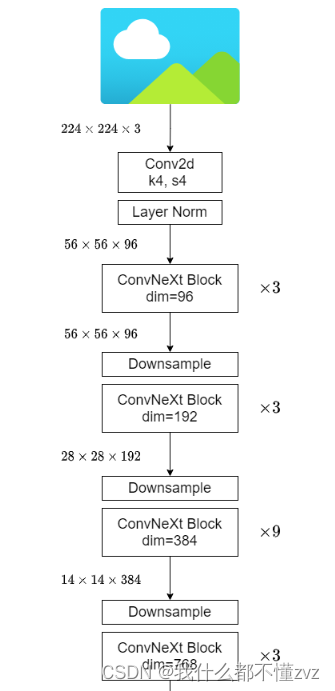
- stem为 [
conv(k=4,s=4) + Layer Norm] - downsample为 [
Layer Norm + conv(dim1,dim2,k=2,s=2)] - stage部分为 [ 多个block ]
2.5.2 分类头部分

- 全局平均: 相当于平均每一维,既[B,C,H,W] - > [B,C]
- Layer Norm + Linear不介绍了
2.5.3 初始化
需要初始化的层包括Linear和Conv,分别初始化其weight和bias
- 分类头Linear: weight和bias都乘以1(保持不变),且这是一个in-place操作,意味着它会直接修改self.head.bias的值,而不是创建一个新的tensor。
- 其他Linear和conv:关于weight使用 truncated normal distribution(截断正态分布),关于bias使用常数constant为0
网络代码:
class ConvNext(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000, depths=[3,3,9,3], dims=[96,192,384,768],drop_path_rate=0.,layer_scale_init_value=1e-6,head_init_scale=1.)super().__init__()# ------------------ 下采样部分 --------------------------------self.downsample_layers = nn.ModuleList() # 保存 stem和3个downsample_layerstem = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3,dims[0],kernel_size=4,stride=4),LayerNorm(dims[0],eps=1e-6,data_format='channels_first'))for i in range(3):downsample_layer = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(dim[i],eps=1e-6,data_format='channels_first'),nn.Conv2d(dim[i],dim[i+1],kernel_size=2,stride=2))self.downsample_layers.append(downsample_layer)# ------------------- stage 部分 --------------------------------self.stages = nn.ModuleList()dp_rate = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths)]cur = 0 # 表示当前在第几层(深度)for i in range(4):stage = nn.Sequential(*[Block(dims[i], drop_path=dp_rate[cur+j],layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value) for j in range(depths[i]))self.stages.append(stage)cur += depths[i]# ------------------ 分类头和初始化部分 ----------------------------self.norm = LayerNorm(dim[-1],eps=1e-6)self.head = nn.Linear(dim[-1],num_classes)self.apply(self._init_weights)self.head.weight.data.mul_(head_init_scale)self.head.bias.data.mul_(head_init_scale)def _init_weight(self,m):if isinstance(m,(nn.Linear, nn.Conv2d)):trunc_normal(m.weight, std=.02),nn.init.constant_(m.bias,0)def forward_features(self,x):# features extraction part(stem, stage and downsample)for i in range(4):x = self.downsample_layers[i](x)x = self.stages[i](x)return self.norm(x.mean([-2,-1])) # GAP(global average pooling) [c,b,h,w] -> [c,b]def forward(self,x):x = self.forward_features(x)x = self.head(x)return x