Linux系统编程7–线程_写个测试脚本
-
参考博客:
Linux多线程编程初探 - 峰子_仰望阳光 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
-
我的PC是8核*16进程,所以在固定的时间点,我可以同时运行8 * 16的进程,更多的线程(任务管理器)
Linux线程 生产者 消费者(自学)
-
sleep不会让出系统资源,只会堵了自己的线
API

0、测试脚本
-
实验1
//test.sh ./a.out ./a.out ./a.out -
>>> vim test.sh //创建脚本 测试 >>> chmod +x test.sh >>> ./test.sh
system("echo Hello, World!")会调用系统的命令处理程序来执行echo Hello, World!命令,从而在控制台输出"Hello, World!"。
- 第二种
- 实验2
//demo10.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int g_data = 0;//都能用它pthread_mutex_t mutex;//定义锁// int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
void *func1(void *arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//加锁//pthread_self(): 获取id,输出idprintf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));//输出这个函数的参数 *argwhile(1){printf("t1:%d\n",++g_data);sleep(1);if(g_data == 3){pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁printf("t1 quit==============================");//pthread_exit(NULL);exit(0); //如果是exit(0),线程崩了,整个进程也会崩}}
}void *func2(void *arg)
{printf("t2:%ld thread is creat\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t2:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//加锁g_data++;printf("t2:%d\n",g_data);sleep(1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁}
}int main()
{int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;pthread_t t2;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//初始化这把锁//创造线程//返回成功时,返回线程ID给t1//第二个参数定制不同线程属性//第三个参数是要开始执行的函数//第四个参数是给上面函数的参数 param = 100;ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t1 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t2, NULL, func2,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t2 success\n");}printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());while(1){printf("main:creat success\n");sleep(1);}pthread_join(t1,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞pthread_join(t2,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞//可以解释为什么函数中要利用 static ;不用的话,会随机给个数传过来//printf("main:t1 quit:%d\n",*pret);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁这把锁return 0;
}
//test.c 测试脚本
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{int i = 0;for(i = 0;i<100;i++){system("./thread");}
}
>>> gcc demo10.c -o thread
>>> gcc test.c
>>> ./a.out
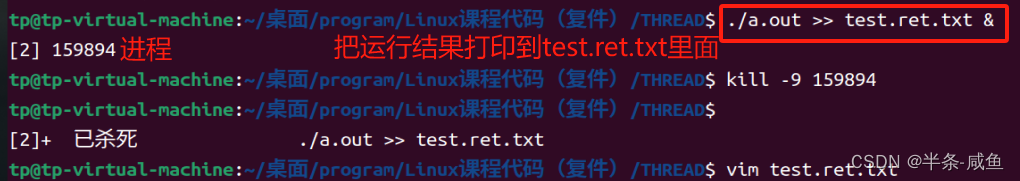
>>> ./a.out >>test.ret.txt & //将运行结果放在test.ret.txt文件中//& 后台运行
>>> [2] 159894 //自动显示进程
>>> kill -9 159894 //杀死进程
>>> vim test.ret.txt //看看这个文件
1、线程的创建、退出&等待
-
基础API
-
//线程ID获取 & 比较 #include <pthread.h> pthread_t pthread_self(void); // 返回:调用线程的ID- 对于线程ID比较,为了可移植操作,我们不能简单地把线程ID当作整数来处理,因为不同系统对线程ID的定义可能不一样。我们应该要用下边的函数:
-
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_equal(pthread_t tid1, pthread_t tid2); // 返回:若相等则返回非0值,否则返回0
1.1 线程创建
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号int param = 100;
ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回
//返回成功时,返回线程ID给t1
//第二个参数定制不同线程属性
//第三个参数是要开始执行的函数
//第四个参数是给上面函数的参数 param = 100;
1.2 线程推出
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_exit(void *rval_ptr);
//rval_ptr是一个无类型指针,与传给启动例程的单个参数类似。进程中的其他线程可以通过调用pthread_join函数访问到这个指针.pthread_exit((void *)p);//线程退出
1.3 线程等待
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **rval_ptr);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号pthread_join(t1,(void **)&pret); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞
printf("main:t1 quit:%s\n",pret);
- 实验
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>// int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
void *func1(void *arg)
{//static int ret = 10;static char *p = "t1 is run out";//pthread_self(): 获取id,输出idprintf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));//输出这个函数的参数 *arg//pthread_exit((void *)&ret);//线程退出pthread_exit((void *)p);//线程退出
}int main()
{int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;//int *pret=NULL;char *pret = NULL;//创造线程ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回//返回成功时,返回线程ID给t1//第二个参数定制不同线程属性//第三个参数是要开始执行的函数//第四个参数是给上面函数的参数 param = 100;if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t1 success\n");}printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());pthread_join(t1,(void **)&pret); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞//可以解释为什么函数中要利用 static ;不用的话,会随机给个数传过来//printf("main:t1 quit:%d\n",*pret);printf("main:t1 quit:%s\n",pret);return 0;
}
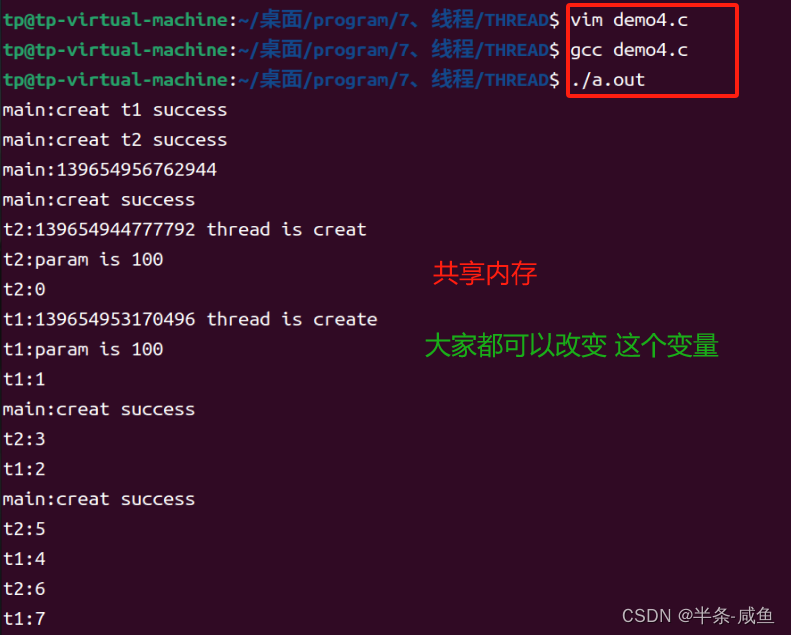
2、线程共享内存
- 实验
- 不同的线程可以共享
g_data变量
//demo4.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int g_data = 0;//都能用它// int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
void *func1(void *arg)
{//pthread_self(): 获取id,输出idprintf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));//输出这个函数的参数 *argwhile(1){printf("t1:%d\n",g_data++);sleep(1);}
}void *func2(void *arg)
{printf("t2:%ld thread is creat\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t2:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));while(1){printf("t2:%d\n",g_data++);sleep(1);}
}int main()
{int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;pthread_t t2;//创造线程 //返回成功时,返回线程ID给t1//第二个参数定制不同线程属性 //第三个参数是要开始执行的函数//第四个参数是给上面函数的参数 param = 100;ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t1 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t2, NULL, func2,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t2 success\n");}printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());while(1){printf("main:creat success\n");sleep(1);}pthread_join(t1,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞pthread_join(t2,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞//可以解释为什么函数中要利用 static ;不用的话,会随机给个数传过来//printf("main:t1 quit:%d\n",*pret);return 0;
}- 实验结果
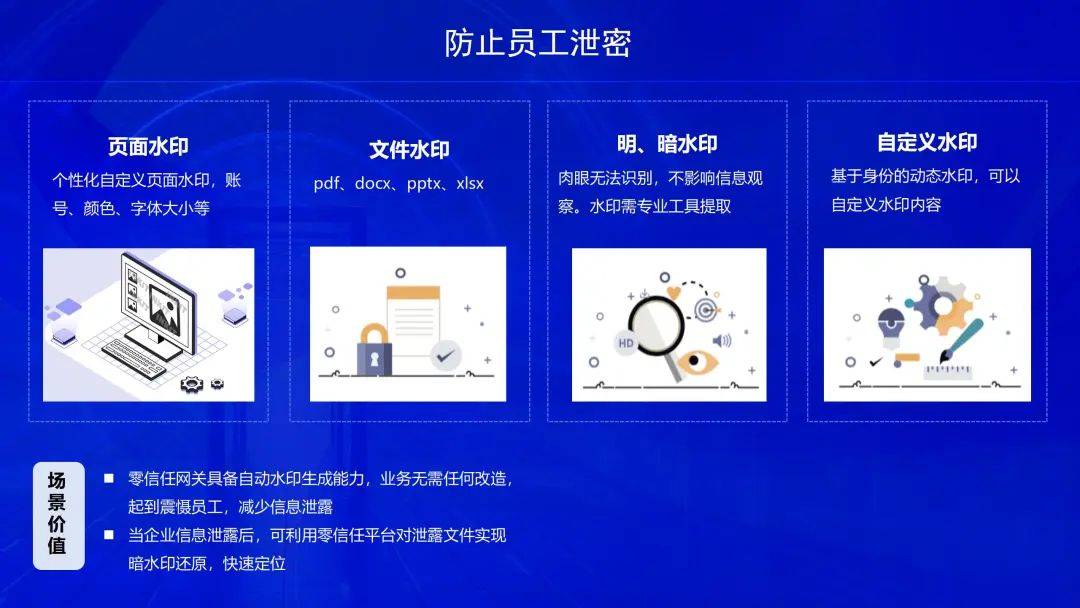
3、互斥锁(同步资源)
- 互斥量 就是 一把锁;
- 加锁—(共享资源)—解锁
- **同步(synchronization)**是指在一定的时间内只允许某一个线程访问某个资源。而在此时间内,不允许其它的线程访问该资源。
- 基础API
3.1 创建及销毁互斥锁
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t mutex);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//初始化这把锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁锁
3.2 加锁及解锁
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t mutex);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁 互斥量mutex
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁
- 实验
//demo8.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int g_data = 0;
//都能用它pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//被锁锁住的都叫互斥量 mutex// int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
void *func1(void *arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁 互斥量mutex//pthread_self(): 获取id,输出id、printf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));//输出这个函数的参数 *argpthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁
}void *func2(void *arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁printf("t2:%ld thread is creat\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t2:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁
}void *func3(void *arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁printf("t3:%ld thread is creat\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t3:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁
}int main()
{int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;pthread_t t2;pthread_t t3;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//初始化这把锁//创造线程//返回成功时,返回线程ID给t1//第二个参数定制不同线程属性//第三个参数是要开始执行的函数//第四个参数是给上面函数的参数 param = 100;ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t1 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t2, NULL, func2,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t2 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t3, NULL, func3,(void*)¶m);//成功返回0,失败返回if(ret == 0){printf("main:creat t3 success\n");}printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());pthread_join(t1,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞pthread_join(t2,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞pthread_join(t3,NULL); //等待t1线程退出,否则阻塞//可以解释为什么函数中要利用 static ;不用的话,会随机给个数传过来//printf("main:t1 quit:%d\n",*pret);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁锁return 0;
}- 实验结果
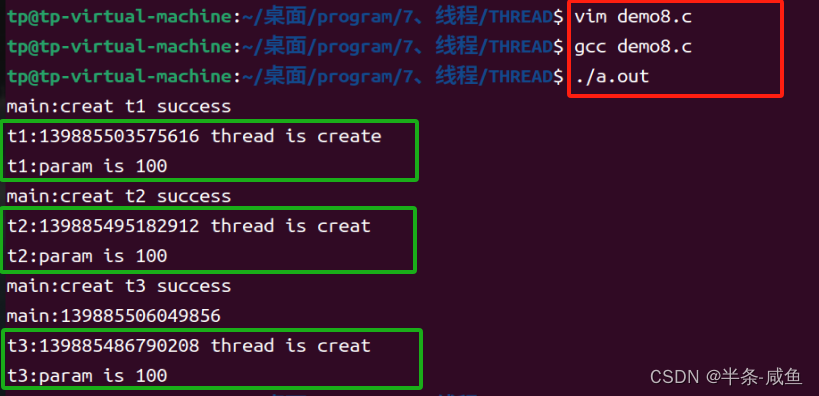
- t1结束后,t2和t3会进行竞争,main函数没有上锁,所以可以穿插进来;
4、互斥锁限制共享资源的访问
见文首–测试脚本demo10 [Link text][#anchor-0]
5、死锁(面试)
-
所谓死锁,是指多个进程在运行过程中因争夺资源而造成的一种僵局,当进程处于这种僵持状态时,若无外力作用,它们都将无法再向前推进
-
造成死锁的条件
- 有两个锁
- 线程a获得了锁1,还想要获得锁2;
- 线程b获得了锁2,还想要获得锁1;
//demo7 #include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h>//int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg); int g_data = 0;pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_mutex_t mutex2;void *func1(void *arg) {int i;pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);sleep(1);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);for(i=0;i<5;i++){printf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));sleep(1);}pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}void *func2(void *arg) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);sleep(1);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("t2:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t2:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}void *func3(void *arg) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("t3:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t3:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}int main() {int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;pthread_t t2;pthread_t t3;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);pthread_mutex_init(&mutex2, NULL);ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void *)¶m);if(ret == 0){printf("main:create t1 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t2, NULL, func2,(void *)¶m);if(ret == 0){printf("main:create t2 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t3, NULL, func3,(void *)¶m);printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());pthread_join(t1,NULL);pthread_join(t2,NULL);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex2);return 0; }
6、线程条件控制,实现线程的同步
- 条件变量是线程另一可用的同步机制。条件变量给多个线程提供了一个会合的场所。
- 动态初始化和静态初始化;二选一
//动态初始化
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //定义一把锁
pthread_cond_t cond; //定义一个条件
//main函数里面定义
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
//静态初始化
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
//使用了静态初始化,main函数可以不用定义pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);&& pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
6.1 创建及销毁条件变量
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t cond);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//销毁条件
- 除非需要创建一个非默认属性的条件变量,否则
pthread_cont_init函数的attr参数可以设置为NULL
6.2 等待
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
// 返回:若成功返回0,否则返回错误编号pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//等待条件发生
//cond:条件 mutex:锁
-
pthread_cond_wait等待条件变为真。如果在给定的时间内条件不能满足,那么会生成一个代表一个出错码的返回变量。 -
传递给
pthread_cond_wait的 互斥量(锁) 对条件进行保护,调用者把锁住的互斥量传给函数。函数把调用线程放到等待条件的线程列表上,然后对互斥量解锁,这两个操作都是原子操作。这样就关闭了条件检查和线程进入休眠状态等待条件改变这两个操作之间的时间通道,这样线程就不会错过条件的任何变化。pthread_cond_wait返回时,互斥量再次被锁住。 -
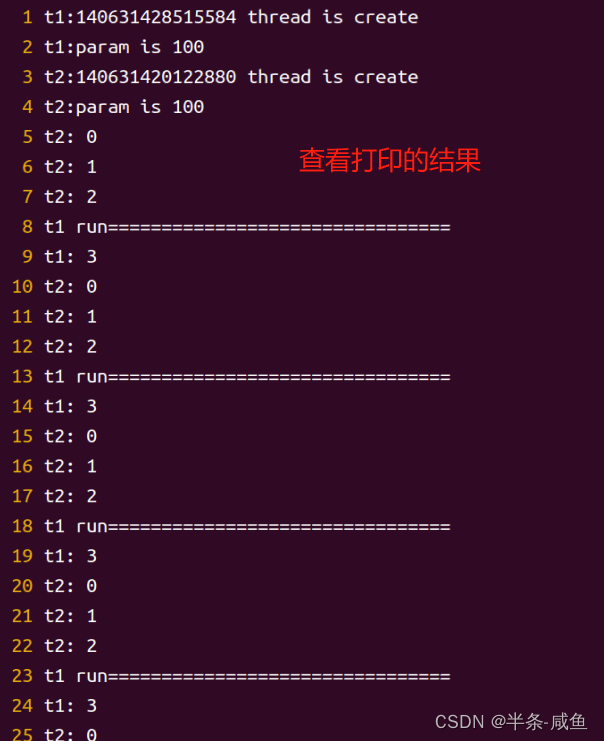
实验
//text.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_rtn)(void *), void *restrict arg);
int g_data = 0;
//动态初始化
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond; //定义一个条件
/*
动态初始化和静态初始化;二选一
//静态初始化
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
//使用了静态初始化,main函数可以不用定义pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);&& pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
*/
void *func1(void *arg)
{printf("t1:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t1:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));static int cnt = 0;while(1){pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//等待条件发生//cond:条件 mutex:锁printf("t1 run================================\n");printf("t1:%d\n",g_data++);g_data = 0;sleep(1);if(cnt++ == 10){exit(1);//全退出,线程退出,全都死掉}}}void *func2(void *arg)
{printf("t2:%ld thread is create\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());printf("t2:param is %d\n",*((int *)arg));//输出参赛 *argwhile(1){printf("t2: %d\n",g_data);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);g_data++;if(g_data==3){pthread_cond_signal(&cond);//触发,t1执行}pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(1);}
}int main()
{int ret;int param = 100;pthread_t t1;pthread_t t2;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, func1,(void *)¶m);if(ret == 0){
// printf("main:create t1 success\n");}ret = pthread_create(&t2, NULL, func2,(void *)¶m);if(ret == 0){
// printf("main:create t2 success\n");}// printf("main:%ld\n",(unsigned long)pthread_self());pthread_join(t1,NULL);//等待pthread_join(t2,NULL);//等待pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//销毁条件return 0;
}
- 结果
- 输出到txt文件
欢迎大家一起交流讨论!