一:递归分治
什么是递归?
- 函数自己调用自己
- 通过函数体来进行循环
- 以
自相似的方法重复进行的过程
递归的过程:先自顶向下找到递归出口,在自底向上回到最初的递归位置
推导路径未知的题目只能用递归不能用循环
比如求多叉树的节点(每个节点的分支都不同)
推导路径未知的题目只能用递归不能用循环
比如求多叉树的节点(每个节点的分支都不同)
递归问题需要考虑
- 确定递归的重叠子问题—数学归纳法
- 确定递归边界,一定要有递归出口—避免死循环
- 保护和还原现场—比如当前层的改变了全局参数回溯会影响结果

一般来说,涉及全局变量和静态变量或者类私有变量,不同层之间可能需要进行数据恢复
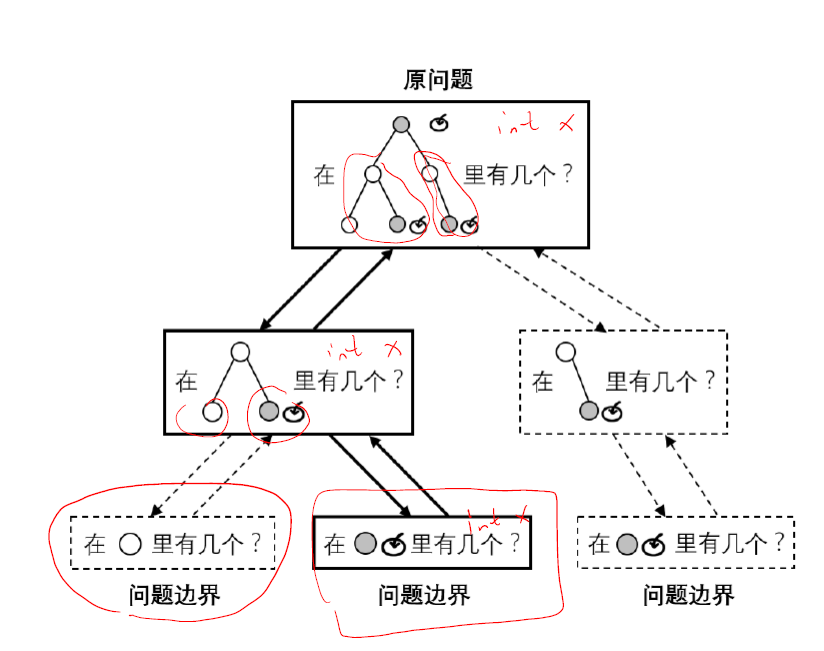
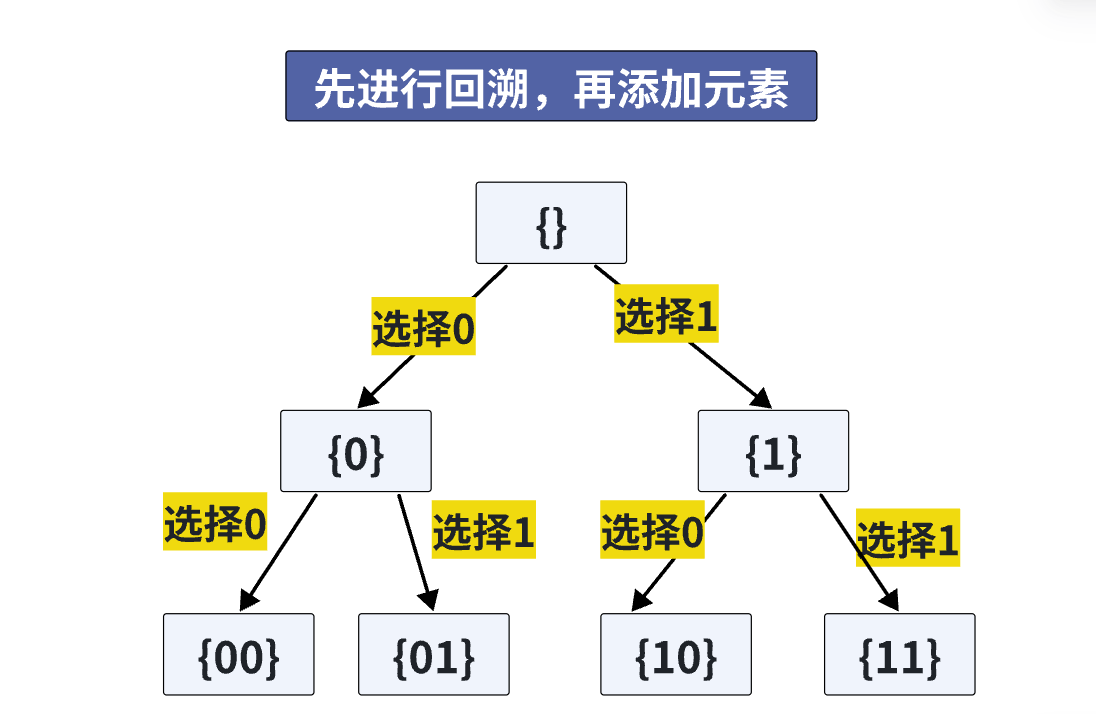
二:打印二进制回溯解法
下图是长度为2的二进制个数
- 从左至右,依次加入0,回溯时放弃0,选择1
先添加元素,后进行递归
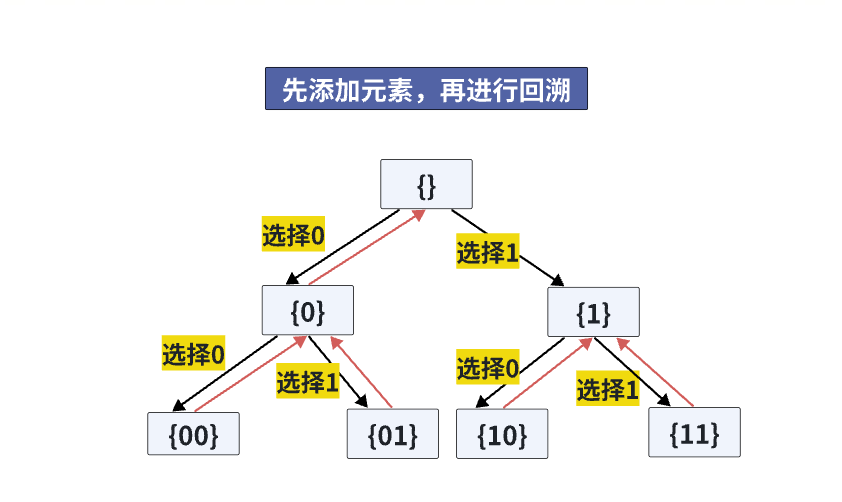
这种方法一定要传递供选项,就是每次进行的选择
- 这里二进制的01选择是隐藏的,需要显式给出
vector<vector<int>> res;
void getAllBin(vector<int> nums,vector<int> ans,int n){for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++){ans.push_back(nums[i]);//先添加元素if(ans.size()==n){//满足存结果,不要returnres.push_back(ans);}else{//不满足长度递归getAllBin(nums, ans, n);}ans.pop_back();}
}
vector<vector<int>> printAllbin(int n){vector<int> nums = {0, 1};//显式给出01供选项vector<int> ans;getAllBin(nums, ans, n);return res;
}
当然也可以把判断语句放在if外,需要return
void getAllBin(vector<int> nums,vector<int> ans,int n){if(ans.size()==n){//满足存结果res.push_back(ans);return;}for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++){ans.push_back(nums[i]);//先添加元素//递归getAllBin(nums, ans, n);ans.pop_back();} }一般选择这种,更清晰
先进行回溯,再添加元素
vector<vector<int>> res;
void getAllBin(vector<int> ans,int n){if(ans.size()==n){res.push_back(ans);return;}//加入0回溯vector<int> tmp1 = ans;tmp1.push_back(0);getAllBin(tmp1, n);//加入1回溯vector<int> tmp2 = ans;tmp2.push_back(1);getAllBin(tmp2, n);
}
vector<vector<int>> printAllbin(int n){vector<int> ans;getAllBin(ans, n);return res;
}
这里是传入新变量,当然也可以用ans,但是需要pop_back(),防止影响结果
void getAllBin(vector<int> ans,int n){if(ans.size()==n){res.push_back(ans);return;}//加入0回溯ans.push_back(0);getAllBin(ans, n);//别忘了pop_back()ans.pop_back();// 加入1回溯ans.push_back(1);getAllBin(ans, n);//pop与否都可以//ans.pop_back(); }
这里ans.size()是隐式递归结束变量,也可以单独用一个参数,但是要注意递归+1
vector<vector<int>> res;
void getAllBin(vector<int> ans,int n,int level){if(level==n){res.push_back(ans);return;}//加入0回溯ans.push_back(0);getAllBin(ans, n, level + 1);//+1ans.pop_back();// 加入1回溯ans.push_back(1);getAllBin(ans, n, level + 1);//+1//pop与否都可以return;
}
vector<vector<int>> printAllbin(int n){vector<int> ans;getAllBin(ans, n,0);//从0开始return res;
}
当然也可以用减法实现,size==0一样可以结束递归
vector<vector<int>> res;
void getAllBin(vector<int> ans,int n){if(n==0){res.push_back(ans);return;}//加入0回溯ans.push_back(0);getAllBin(ans, n-1);//+1ans.pop_back();// 加入1回溯ans.push_back(1);getAllBin(ans, n-1);//+1//pop与否都可以return;
}
vector<vector<int>> printAllbin(int n){vector<int> ans;getAllBin(ans, n);return res;
}
三:用数组初始化一个二叉搜索树
BST数据结构,中序遍历
bst数据结构
struct bst{//节点,左子树,右子树int val;bst *left;bst *right;//带有默认参数的构造函数bst(int v = 0,bst* l=NULL,bst* r=NULL):val(v),left(l),right(r){}
};
- 中序遍历
void midTraverse(const bst* root){if(root==NULL)return;midTraverse(root->left);cout << root->val << " ";midTraverse(root->right);
}
- 程序测试
int main(){bst *aa = new bst(100);bst *bb = new bst(500);bst *cc = new bst(200, aa, NULL);bst *dd = new bst(400, NULL, bb);bst *ee = new bst(300,cc,dd);midTraverse(ee);return 0;
}
运行结果:
100 200 300 400 500
迭代形式创建
先找后插
bst* createBST_loop(int a[],int n){//首先根节点设为第一个元素值bst *root = new bst(a[0]);//插入余下值bst *parent = NULL;for (int i = 1; i < n;i++){//定义指向root节点,防止断链bst *cur = root;//必须从root开始// 先找到插入值的父节点,再进行插值while (cur){if (a[i] < cur->val){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else if (a[i] > cur->val){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else{ // a[i]==root->valreturn root;}}//判断当前值和父节点大小来将新节点插入到左右子树if(parent){//防止NULL->__if(a[i]<parent->val){parent->left = new bst(a[i]);}else{parent->right = new bst(a[i]);}}}//forreturn root;
}
- 需要一个指针指向root,这样每次才能不断链
- 这里是找到插入节点的父节点,单独标记
当然也可以把根节点作为参数,函数没有返回值
-
但是必须传入指针的引用
-
传引用,初始化必须有指向,比如NULL
void create_BST_loop(bst*& root,int a[],int n){root = new bst(a[0]);bst *parent = NULL;for (int i = 1; i < n;i++){bst *cur = root;while(cur){if(a[i]<cur->val){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else if(a[i]>cur->val){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else{return;}}//待插节点bst *tmp = new bst(a[i]);if(parent){if(a[i]<parent->val){parent->left = tmp;}else{parent->right = tmp;}}}//for
}
bst *newnode=NULL;
create_BST_loop(newnode, a, n);
midTraverse(newnode);
边找边插
bst* create_BST_loop(int a[],int n){bst* root = new bst(a[0]);for (int i = 1; i < n;i++){bst *cur = root;while(cur){if(a[i]<cur->val){if(cur->left){cur = cur->left;}else{cur->left = new bst(a[i]);break;//插入后跳出}}else if(a[i]>cur->val){if(cur->right){cur = cur->right;}else{cur->right = new bst(a[i]);break;}}else{return root;}}}//forreturn root;
}
-
这里不需要父节点了,只要往左右子树遍历时判断一下存在性
不存在说明该左子树就是要插值
-
千万别忘了插入后的break
递归形式创建
由于每次插入需要找到插入位置,所以用递归找到插入位置,然后循环多次插入
void getRecursion(bst*& root,int x){if(root==NULL){root = new bst(x);return;}if(x<root->val){getRecursion(root->left, x);}else if(x>root->val){getRecursion(root->right, x);}else{//==return;}
}
bst* create_BSTrecursion(int a[],int n){bst *root = new bst(a[0]);for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){int x = a[i];getRecursion(root, x);}return root;
}
- 父节点形式递归,返回类型bst*
bst* getRecursion(bst* root,int x){if(root==NULL){root = new bst(x);return root;}if(x<root->val){//自己建立链条root->left = getRecursion(root->left, x);}else if(x>root->val){root->right = getRecursion(root->right, x);}return root;
}
bst* create_BSTrecursion(int a[],int n){bst *root = new bst(a[0]);// bst* tmp;for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){int x = a[i];getRecursion(root, x);//tmp=getRecursion(root, x);}return root;//return tmp
}
bst* create_BSTrecursion(int a[],int n){bst *root = new bst(a[0]);bst* tmp;for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){int x = a[i];tmp=getRecursion(root, x);}return tmp }可以定义新变量接受返回值,因为root在函数内部,可以不写
root=getRecyrsion();
- 如果想变成void,就需要把父节点作为参数
void getRecursion(bst* root,bst* parent,int x){if(root==NULL){/*建立parent与root联系*/if(x<parent->val){parent->left = new bst(x);}else{parent->right = new bst(x);}return;//递归结束}//传递父节点if(x<root->val){getRecursion(root->left,root, x);}else if(x>root->val){getRecursion(root->right,root,x);}return;
}
bst* create_BSTrecursion(int a[],int n){bst *root = new bst(a[0]);for (int i = 0; i < n;i++){int x = a[i];getRecursion(root,NULL, x);}return root;
}
主函数形式
bst不可以有重复值,所以生成随机数时候需要去重
int n = 10;int *a = new int[10];for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++){//生成[a,b)的随机数---(rand()%(b-a))+aa[i] = (rand() % 90)+10;//bst不能有重复值,相等去除for (int j = 0; j < i;j++){if(a[j]==a[i]){i-=1;//重新生成a[i]break;}}}// bst *root = create_BSTrecursion(a, n);
四:换一种思路求全排列
也就是变动原数组,选择一个就把自己的选择去掉,然后递归,回溯的时候补上元素
把数组恢复需要用到insert()函数,需要传递插入位置和插入值:
所以在删除的时候提前记录删除元素值和删除的iter位置
vector<vector<int>> res;
void getLine(vector<int> nums ,vector<int> ans,int n){if(n==0){res.push_back(ans);return;}for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++){//记录删除元素xint x = nums[i];ans.push_back(nums[i]);//记录删除元素位置的下一个迭代器itauto it=nums.erase(nums.begin()+i);getLine(nums, ans, n - 1);//别忘了回溯撤销ans的选择ans.pop_back();//恢复原数组,在it前加入xnums.insert(it,x);}
}
vector<vector<int>> fullLine(vector<int> nums){vector<int> tmp;getLine(nums, tmp,nums.size());return res;
}
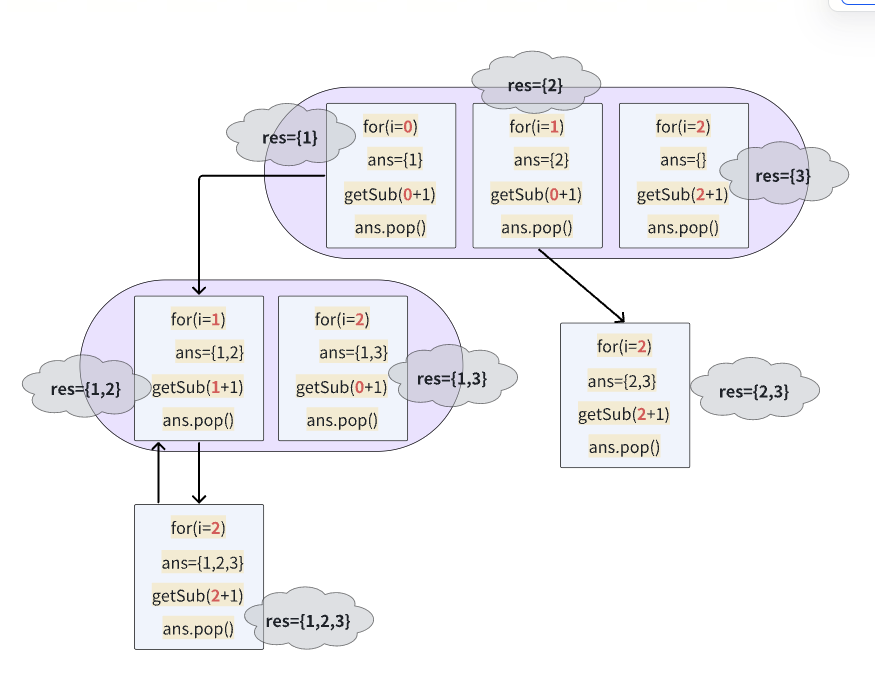
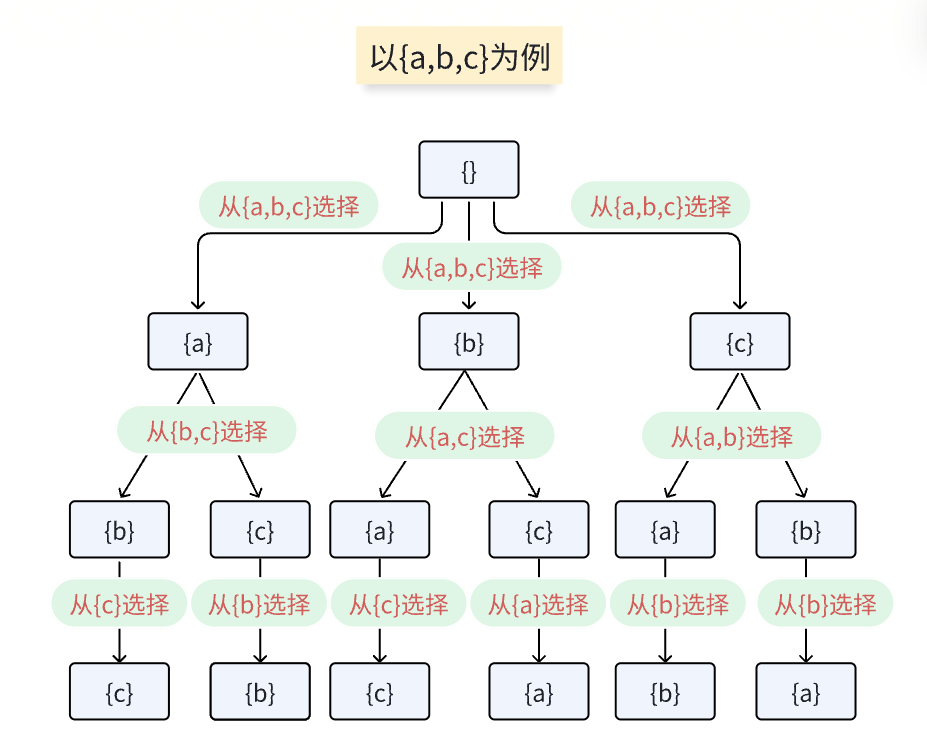
五:求{1,2,3}子集图示
先选元素,再回溯
由于子集中元素可选可不选,每次循环的开始值是上一次的值+1
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {vector<int> mm;findSub(nums, mm, 0);res.push_back({});return res;}private:vector<vector<int>> res;void findSub(vector<int> nums, vector<int> ans, int index) {for (int i = index; i < nums.size(); i++) {ans.push_back(nums[i]);// res.push_back(ans);findSub(nums, ans, i + 1); // 当前i的下一个res.push_back(ans); // 在递归前记录也行ans.pop_back();}}
};
运行结果:

六:组合问题
77. 组合
C n k : 从 n 个元素中选 k 个 C_n^k:\text{从}n\text{个元素中选}k\text{个} Cnk:从n个元素中选k个
其实思路类似子集:
比如{1,2,3}中{1,3}和{3,1}是重复的,所以元素只能以该元素为起点,向后递归,不能往前选
但是组合规定了个数,只要在结果处存储正确的符合条件的结果即可,在所有路径提前剪去不符合要求的
注意:
从i开始的,必须要求[i,...,n]的个数n-i+1加上ans当前的数量大于k即:
n-i+1+ans.size()>k----数量小于k一点不符合题意,提前剪枝
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {this->n=n;this->k=k;vector<int> mm;findCombine(mm,0);return res;}
private:int n;int k;vector<vector<int>> res;void findCombine(vector<int> ans,int index){if(ans.size()==k){res.push_back(ans);return;//递归结束}//[i,...,n]个数:n-i+1+ans.size()<kfor(int i=index;i<(n-k+1)+ans.size();i++){ans.push_back(i+1);findCombine(ans,i+1);ans.pop_back();}}
};
也可以按照选不选元素去回溯,但是要提前结束
- 当前ans的大小超过k了
- 当前ans的大小把后面全选了也不足k
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {this->n = n;this->k = k;vector<int> mm;findCombine(mm, 1);return res;}private:int n;int k;vector<vector<int>> res;void findCombine(vector<int> ans, int index) {// ans.size()+(n-index+1)<kif (ans.size() > k || ans.size() + (n - index + 1) < k) {return; // 提前回溯}if (ans.size() == k) {res.push_back(ans);return;}// 选该元素ans.push_back(index);findCombine(ans, index + 1);// 不选该元素ans.pop_back();findCombine(ans, index + 1);}
};
// 不选该元素findCombine(ans, index + 1);// 选该元素ans.push_back(index);findCombine(ans, index + 1);从不选到选,不需要pop_back(),加上也正确
三种基本类型回溯
分为排列,子集,组合,后一种分别是前一种的子集
类似问题只需在该基础上进行剪枝
七:递归与分治
104. 二叉树的最大深度
自底向上求法
分治求法:
- 求出左子树的最大深度
- 求出右子树的最大深度
- 然后最大深度=max(左子树,右子树)+1(根节点)
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {if(root==NULL) return 0;int l=maxDepth(root->left);int r=maxDepth(root->right);return max(l,r)+1;}
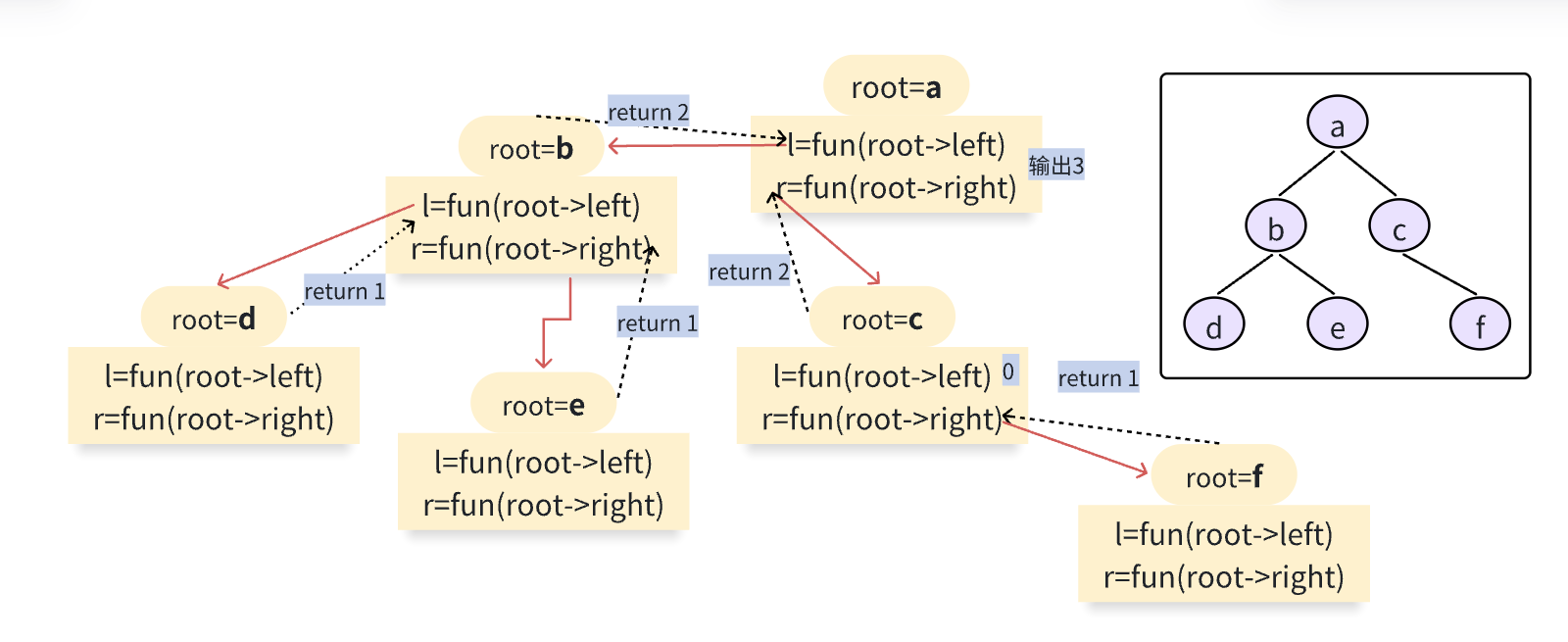
联系在一起的关键是:函数体内求左子树和求右子树的对应一个root
这是典型的自底向上,也就是相当于从下面向前面追溯得到结果
自顶向下求法
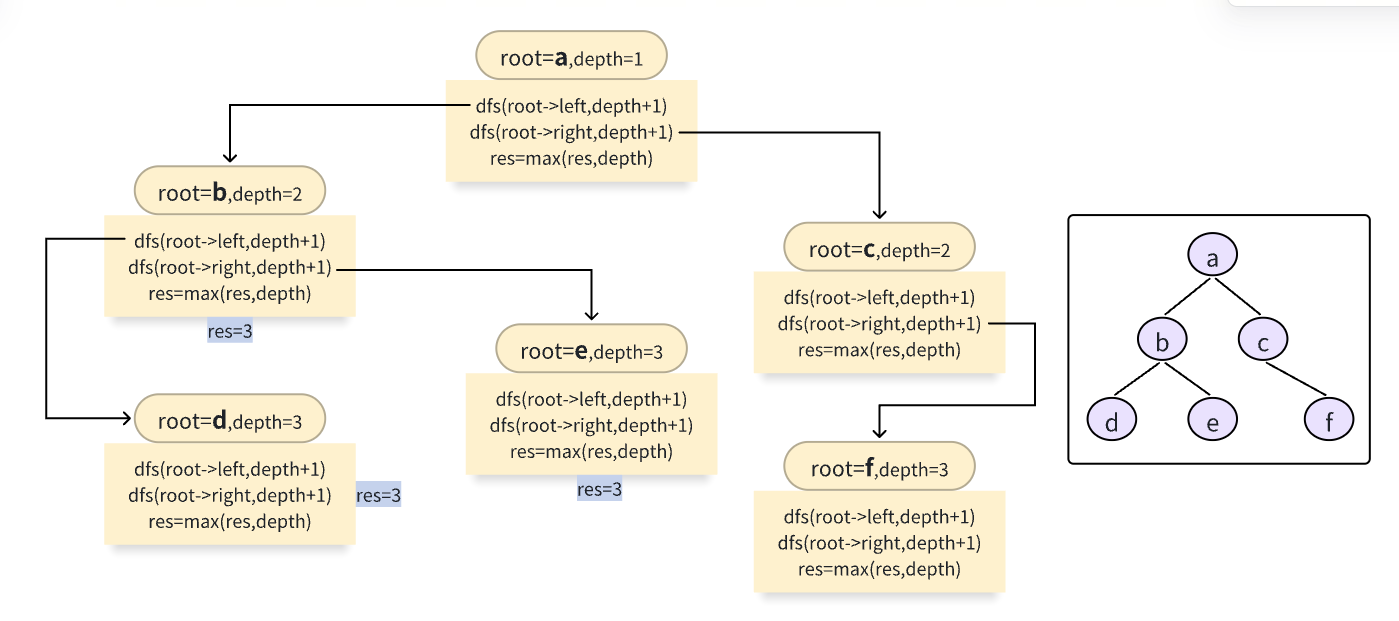
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {res = 0;dfs(root, 1);//根节点为1return res;}private:int res;void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth) {if (root == NULL)return;dfs(root->left, depth + 1);dfs(root->right, depth + 1);res = max(res, depth); // 更新结果}
};
每次递归依次就更新依次结果
递归前或递归后递归不影响
res = max(res, depth); // 更新结果 dfs(root->left, depth + 1); dfs(root->right, depth + 1);
当然也可以把depth设为全局变量,但是要清理现场
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {res = 0;depth=0;dfs(root);return res;}private:int res;int depth;void dfs(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL)return;depth++;//当前层+1res = max(res, depth); // 更新结果dfs(root->left);//depth--;//depth++;dfs(root->right);depth--;//回到上一层,depth-1}
};
bfs—广度优先遍历
队列存储二元组,每次都记录层次大小
using pr=pair<TreeNode*,int>;int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {int res=0;/*广度优先遍历*/queue<pr> que;int level=1;//记录层次if(root==NULL) return 0;que.push(make_pair(root,level));while(!que.empty()){TreeNode* tmp=que.front().first;int level=que.front().second;que.pop();res=max(res,level);//更新resif(tmp->left) que.push(make_pair(tmp->left,level+1));if(tmp->right) que.push(make_pair(tmp->right,level+1));}return res;}
当然也可以利用队列每次存的都是当前层的所有元素
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {int res = 0;/*广度优先遍历*/queue<TreeNode*> que;int level = 1; // 记录层次if (root == NULL)return 0;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()) {int sz = que.size(); // 当前队列元素,当前层个数while (sz > 0) {//当前层所有元素出队TreeNode* tmp = que.front();que.pop();if (tmp->left)que.push(tmp->left);if (tmp->right)que.push(tmp->right);sz--;}res+=1;//层次+1}return res}