在网络编程中,特别是底层网卡驱动开发时,常常遇到字节序问题。字节序指的是多字节数据类型在内存中存放的顺序,高位保存在低地址还是高地址,以此来划分大端还是小端。
1 大端和小端
大端和小端指的是 cpu 的属性,常见的 intel 的 x86 cpu 是小端的,mips 架构的 cpu 是大端的。
假设有一个 int 类型的数据,值为 0x12345678,保存在地址 0x400 ~ 0x403 这 4 个字节的位置。
大端:
在大端 cpu 上,存储情况如下图所示,高位存储在低地址。0x12 是高位,存储在地址 0x400 上;0x78 是低位,存储才 0x403 上。
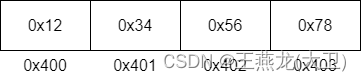
小端:
小端与大端相反,高位存储在高地址。0x12 是高位,存储在 0x403;0x78 是低位,存储在 0x400。
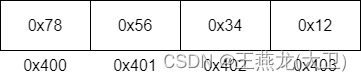
注:
(1)大端更符合我们直观的阅读顺序以及平时的习惯
(2)大端,小端,指的是字节序,大小端不同,字节存储顺序是不一样的。
大端,小端并不影响一个字节内部的 bit 的顺序。
对于一个字节的数据类型,比如 char,不受大端还是小端的影响。
(2)无论是大端序还是小端序,对于上边这个 int 类型的数据来书,这个数据的地址都是 0x400,即数据所在内存空间的低地址
如何判断大端还是小端 ?
如下代码可以判断大端还是小端,使用 union 数据结构的特点,union test 中有两个成员,一个是 char 类型,一个是 int 类型,union 占用 4 个字节,char 类型保存在 4 个字节的低地址。
如果 a 是 0x12,说明高位数据保存在了低地址,是大端;否则,是小端。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>int main() {union test {char a;int b;};union test t;t.b = 0x12345678;if (t.a == 0x12) {printf("大端\n");} else {printf("小端\n");}return 0;
}
程序编译之后运行,打印小端,与 lscpu 查看到的信息是一致的。
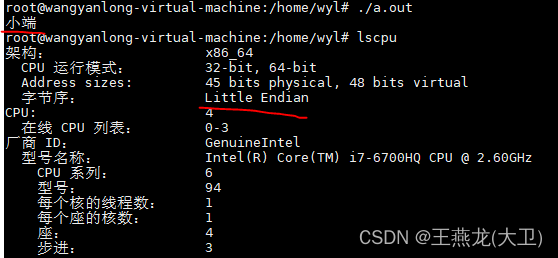
2 网络序和主机序
网络序与大端序是一致的,不管机器是大端的还是小端,发向网络的数据以及从网络中接收的数据都是大端的。大端,网络序与我们平时的思维习惯是一致的。
网络序规定,收到的数据的第一个字节是高位。在数据的发送侧是从低地址发送数据,接收侧先到来的数据也是存储在低地址。所以高位存储在低地址,网络序和大端是一致的。
主机序与 cpu 有关,可能是大端的,也可能是小端的。
3 转换函数
linux 下 的 <arpa/inet.h> 头文件中提供了 4 个函数。4 个函数中的 h 表示 host,主机序;n 表示 net,网络序;l 针对的是 u32 的数据;s 针对的是 u16 的数据。htonl 就是将 32 位的数据从主机序转化为网络序。
uint32_t htonl(uint32_t hostlong);
uint16_t htons(uint16_t hostshort);
uint32_t ntohl(uint32_t netlong);
uint16_t ntohs(uint16_t netshort);
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>int main() {unsigned int a = 0x12345678;unsigned short b = 0x1234;printf("unsigned int 0x%x, host to net: 0x%x\n", a, htonl(a));printf("unsigned int 0x%x, net to host: 0x%x\n", a, ntohl(a));printf("unsigned short 0x%x, host to net: 0x%x\n", b, htons(b));printf("unsigned short 0x%x, net to host: 0x%x\n", b, ntohs(b));return 0;
}
怎么对 64 位数据进行字节序转换 ?
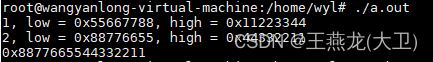
如下代码实现了 64 位数据的字节序转换。最容易出错的是函数的最后一行 return (unsigned long)(((unsigned long)net_low << 32) | net_high);,其中 net_low 需要使用 unsigned long 进行转换,否则会发生数据丢失。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>unsigned long htonll(unsigned long host_ul) {unsigned int host_ul_low = host_ul & 0x00000000ffffffff;unsigned int host_ul_high = host_ul >> 32;printf("1, low = 0x%x, high = 0x%x\n", host_ul_low, host_ul_high);unsigned int net_low = htonl(host_ul_low);unsigned int net_high = htonl(host_ul_high);printf("2, low = 0x%x, high = 0x%x\n", net_low, net_high);return (unsigned long)(((unsigned long)net_low << 32) | net_high);
}int main() {unsigned long a = 0x1122334455667788;printf("0x%llx\n", htonll(a));return 0;
}
运行结果如下: