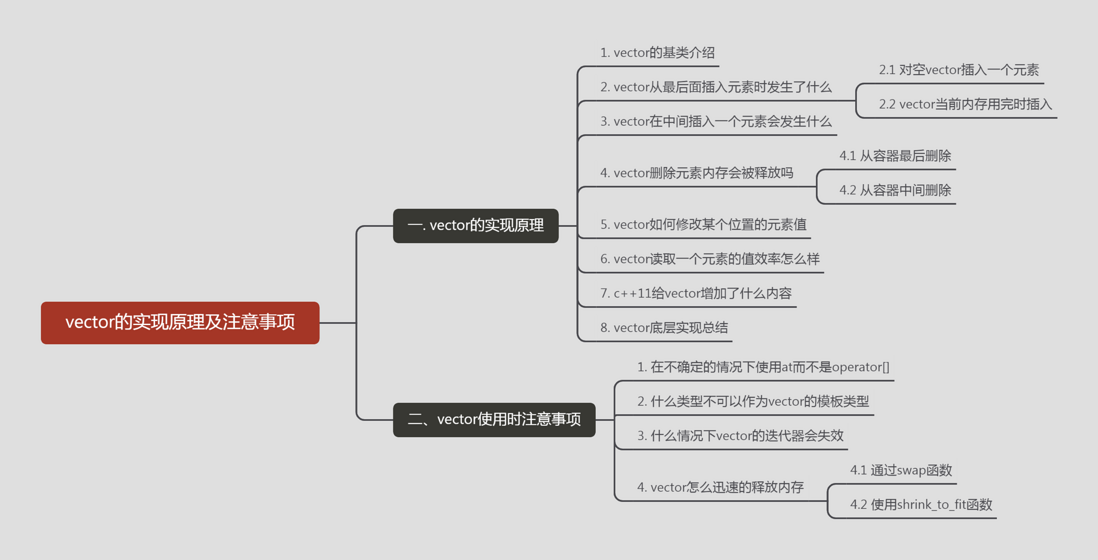
1、什么是空间配置器
空间配置器,顾名思义就是为各个容器高效的管理空间(空间的申请与回收)的,在默默地工作。虽然在常规使用STL时,可能用不到它,但站在学习研究的角度,学习它的实现原理对我们有很大的帮助。
2、为什么需要空间配置器
前面在模拟实现vector、list、map、unordered_map等容器时,所有需要空间的地方都是通过new申请的,虽然代码可以正常运行,但是有以下不足之处:
- 空间申请与释放需要用户自己管理,容易造成内存泄漏。
- 频繁向系统申请小块内存块,容易造成内存碎片。
- 频繁向系统申请小块内存,影响程序运行效率。
- 直接使用malloc与new进行申请,每块空间前有额外空间浪费。
- 申请空间失败怎么应对。
- 代码结构比较混乱,代码复用率不高。
- 未考虑线程安全问题。
为何需要空间配置器
- 如果直接到操作系统上的堆去频繁大量的申请内存,那么效率就会很低,堆就像一个菜市场,虽然有菜,但是未经过加工,有人说那就走malloc(malloc也是一个内存池)来申请内存,但是malloc相当于食堂,服务的是整个进程(所有同学),不是专属于stl容器的,直接malloc多少会有空间的浪费,因此C++需要设计一块高效的内存管理机制(空间配置器–内存池):
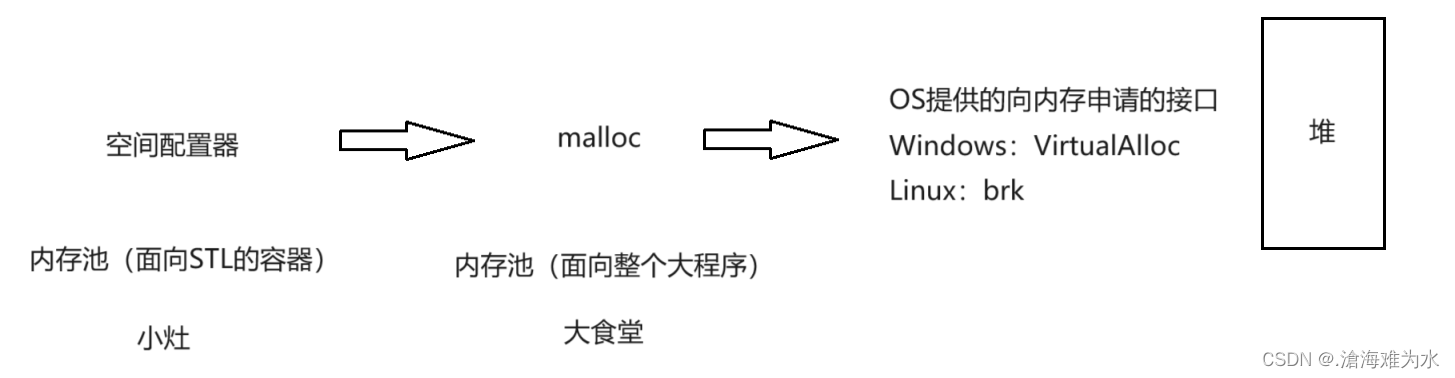
- 此时的空间配置器就像是专门给某种需求提供的小灶,假设我是北方人,爱吃面条,但是公司食堂(malloc)是南方的,多米饭为主,不能满足我的需求,于是空间配置器(小灶)就像是宿舍里头的面条,天然气等材料,可以自给自足。专门服务stl的容器,此时的效率就非常高了。
何为内存碎片?
- 内存碎片又分为外碎片和内碎片,下面展开讨论:
外碎片问题(频繁向系统申请小块内存),就是有足够内存,但是不连续,导致无法申请大块内存,图示如下:
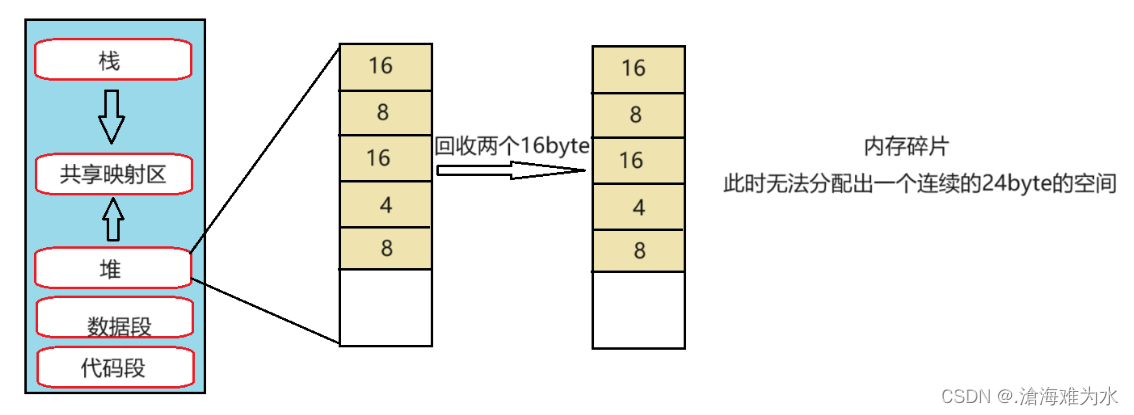
- 如上系统依次分配了16byte、8byte、16byte、4byte,还剩余8byte未分配,此时要分配一个24byte的空间,操作系统回收了上面的两个16byte,总的剩余空间有40byte,但是却无法分配出一个连续24byte的空间,这就是外碎片问题。
内碎片问题(内存挂起来管理,按一定规则对齐,就会导致内存碎片),比如我list it申请12byte,且push_back()操作15次,但是空间配置器给你16byte,也就是说每push_back一次,就会有4byte的浪费,这就是内存碎片。
3、SGI-SGL空间配置器实现原理
以上提到的几点不足之处,最主要还是:频繁向系统申请小块内存造成的。那什么才算是小块内存?SGI-STL以128byte作为小块内存与大块内存的分界线,将空间配置器其分为两级结构:
- 一级空间配置器处理大块内存。
- 二级空间配置器处理小块内存。
一级空间配置器
一级空间配置器原理非常简单,直接对malloc与free进行了封装,并增加了C++中set_new_handle思想。
template <int inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template
{
private:static void* oom_malloc(size_t);
public:// 对malloc的封装static void* allocate(size_t n){// 申请空间成功,直接返回,失败交由oom_malloc处理void* result = malloc(n);if (0 == result)result = oom_malloc(n);return result;}// 对free的封装static void deallocate(void* p, size_t /* n */){free(p);}// 模拟set_new_handle// 该函数的参数为函数指针,返回值类型也为函数指针// void (* set_malloc_handler( void (*f)() ) )()static void (*set_malloc_handler(void (*f)()))(){void (*old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f;return(old);}
};
// malloc申请空间失败时代用该函数
template <int inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_malloc(size_t n)
{void (*my_malloc_handler)();void* result;for (;;){// 检测用户是否设置空间不足应对措施,如果没有设置,抛异常,模式new的方式my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;if (0 == my_malloc_handler){__THROW_BAD_ALLOC;}// 如果设置,执行用户提供的空间不足应对措施(*my_malloc_handler)();// 继续申请空间,可能就会申请成功result = malloc(n);if (result)return(result);}
}
typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;
二级空间配置器
二级空间配置器专门负责处理小于128字节的小块内存。如何才能提升小块内存的申请与释放的方式呢?SGI-STL采用了内存池的技术来提高申请空间的速度以及减少额外空间的浪费,采用哈希桶的方式来提高用户获取空间的速度与高效管理。
内存池
内存池就是:先申请一块比较大的内存块已做备用,当需要内存时,直接到内存池中去去,当池中空间不够时,再向内存中去取,当用户不用时,直接还回内存池即可。避免了频繁向系统申请小块内存所造成的效率低、内存碎片以及额外浪费的问题。
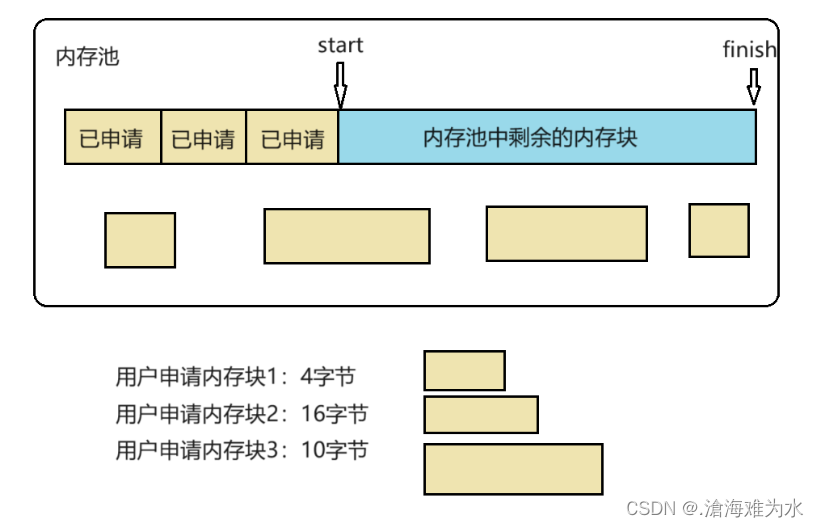
SGI-STL中二级空间配置器设计
SGI-STL中的二级空间配置器使用了内存池技术,但没有采用链表的方式对用户已经归还的空间进行管理(因为用户申请空间时在查找合适的小块内存时效率比较低),而是采用了哈希桶的方式进行管理。那是否需要128桶个空间来管理用户已经归还的内存块呢?答案是不需要,因为用户申请的空间基本都是4的整数倍,其他大小的空间几乎很少用到。因此:SGI-STL将用户申请的内存块向上对齐到了8的整数倍(但为什么是8的整数倍,而不是4?)。
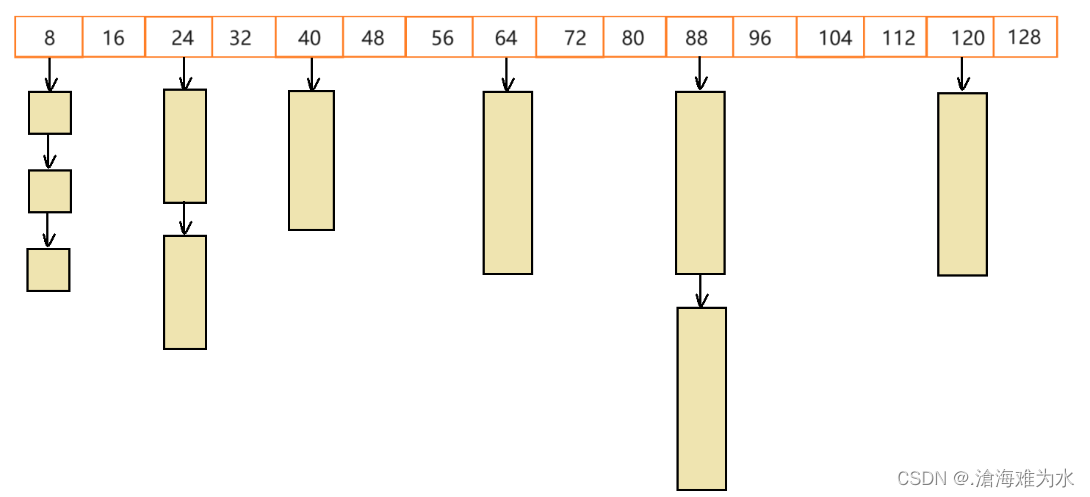
SGI-STL二级空间配置器之空间申请
前期的准备:
// 去掉代码中繁琐的部分
template <int inst>
class __default_alloc_template
{
private:enum { __ALIGN = 8 }; // 如果用户所需内存不是8的整数倍,向上对齐到8的整数倍enum { __MAX_BYTES = 128 }; // 大小内存块的分界线enum { __NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES / __ALIGN }; // 采用哈希桶保存小块内存时所需桶的个数// 如果用户所需内存块不是8的整数倍,向上对齐到8的整数倍static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes){return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1));}
private:// 用联合体来维护链表结构----同学们可以思考下此处为什么没有使用结构体union obj{union obj* free_list_link;char client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */};
private:static obj* free_list[__NFREELISTS];// 哈希函数,根据用户提供字节数找到对应的桶号static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes){return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1);}// start_free与end_free用来标记内存池中大块内存的起始与末尾位置static char* start_free;static char* end_free;// 用来记录该空间配置器已经想系统索要了多少的内存块static size_t heap_size;// ...
};
申请空间:
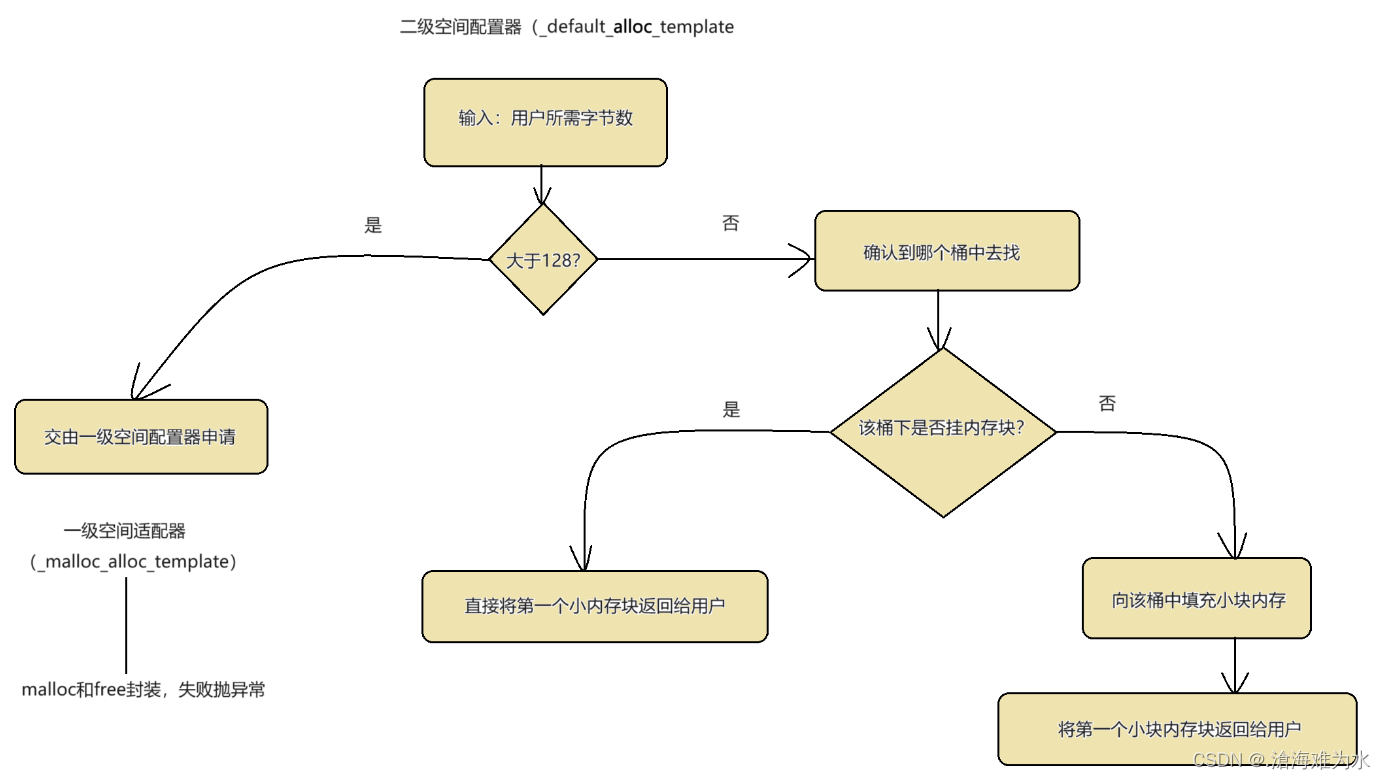
申请空间的规则如下:
- 如果用户所需的空间大于128字节,非小块内存,那么就会跳到一级空间配置器去进行处理。
- 小于128字节就根据用户所需字节找到对应的桶号。
- 若桶中没有内存块时,向桶中补充空间。
- 最后维护桶中剩余内存块的链式关系。
// 函数功能:向空间配置器索要空间
// 参数n: 用户所需空间字节数
// 返回值:返回空间的首地址
static void* allocate(size_t n)
{obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list;obj* __RESTRICT result;// 检测用户所需空间释放超过128(即是否为小块内存)if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES){// 不是小块内存交由一级空间配置器处理return (malloc_alloc::allocate(n));}// 根据用户所需字节找到对应的桶号my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);result = *my_free_list;// 如果该桶中没有内存块时,向该桶中补充空间if (result == 0){// 将n向上对齐到8的整数被,保证向桶中补充内存块时,内存块一定是8的整数倍void* r = refill(ROUND_UP(n));return r;}// 维护桶中剩余内存块的链式关系*my_free_list = result->free_list_link;return (result);
};
填充内存块:
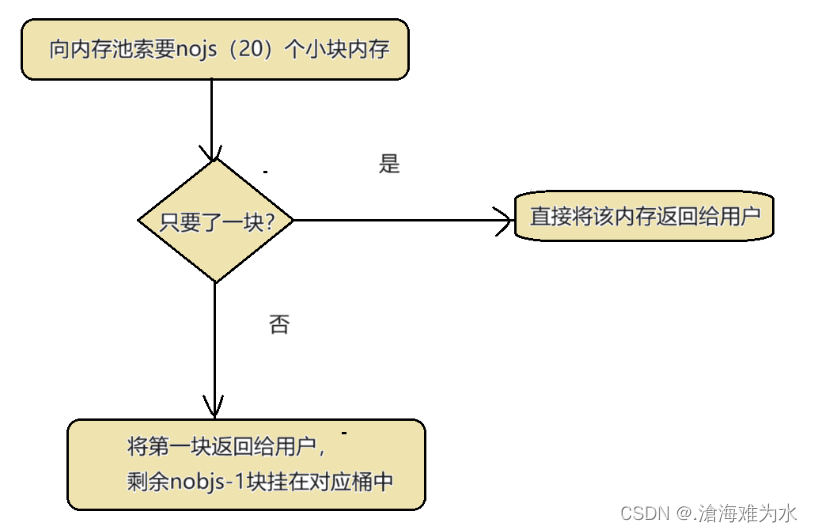
此模块的功能是向哈希桶补充空间,具体步骤如下:
- 一次性向内存池索要20个n字节的小块内存。
- 如果只要了一块,直接返回给用户使用。
- 如果不是,则找到对应的桶号,把第一块返回给用户,其它块链接在对应的桶中。
// 函数功能:向哈希桶中补充空间
// 参数n:小块内存字节数
// 返回值:首个小块内存的首地址
template <int inst>
void* __default_alloc_template<inst>::refill(size_t n)
{// 一次性向内存池索要20个n字节的小块内存int nobjs = 20;char* chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs);obj** my_free_list;obj* result;obj* current_obj, * next_obj;int i;// 如果只要了一块,直接返回给用户使用if (1 == nobjs)return(chunk);// 找到对应的桶号my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);// 将第一块返回值用户,其他块连接在对应的桶中// 注:此处代码逻辑比较简单,但标准库实现稍微有点复杂,同学们可以自己实现result = (obj*)chunk;*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj*)(chunk + n);for (i = 1; ; i++){current_obj = next_obj;next_obj = (obj*)((char*)next_obj + n);if (nobjs - 1 == i){current_obj->free_list_link = 0;break;}else{current_obj->free_list_link = next_obj;}}return(result);
}
向内存池中索要空间:
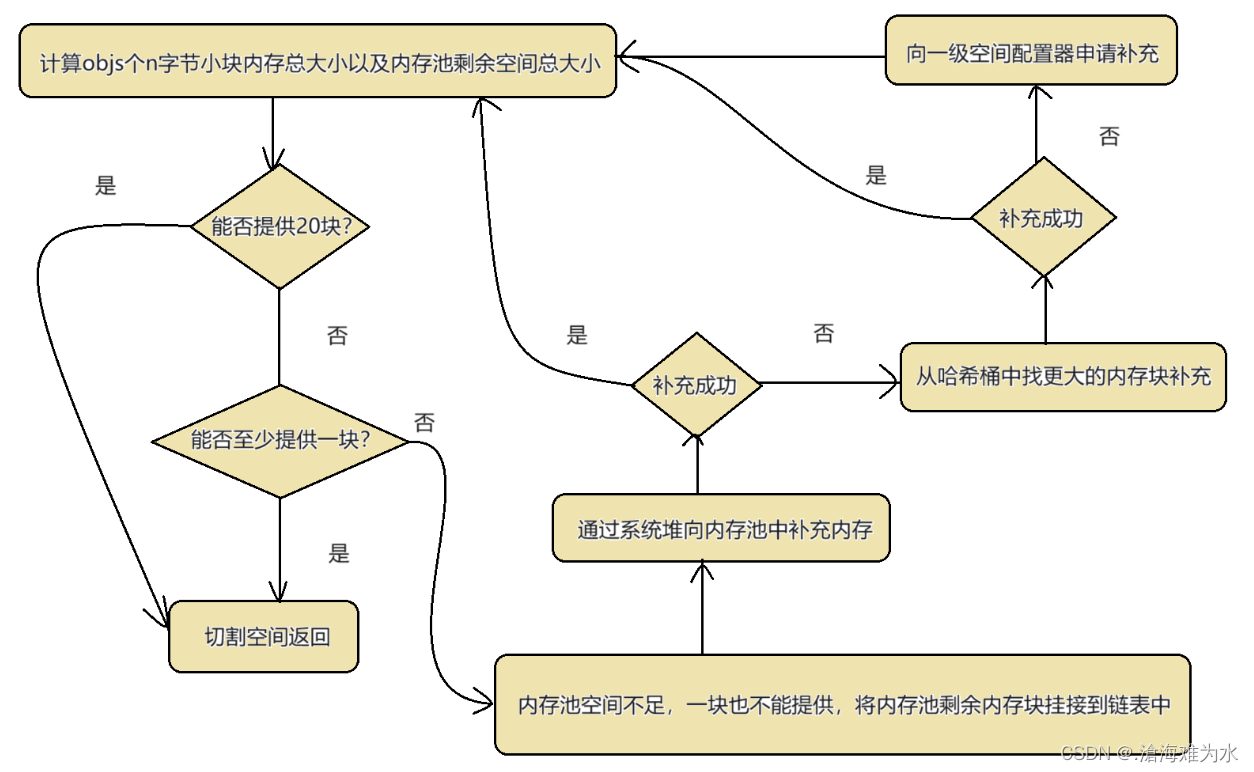
template <int inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<inst>::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs)
{// 计算nobjs个size字节内存块的总大小以及内存池中剩余空间总大小char* result;size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free;// 如果内存池可以提供total_bytes字节,返回if (bytes_left >= total_bytes){result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}else if (bytes_left >= size){// nobjs块无法提供,但是至少可以提供1块size字节内存块,提供后返回nobjs = bytes_left / size;total_bytes = size * nobjs;result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}else{// 内存池空间不足,连一块小块村内都不能提供// 向系统堆求助,往内存池中补充空间
// 计算向内存中补充空间大小:本次空间总大小两倍 + 向系统申请总大小/16size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4);// 如果内存池有剩余空间(该空间一定是8的整数倍),将该空间挂到对应哈希桶中if (bytes_left > 0){// 找对用哈希桶,将剩余空间挂在其上obj** my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_ree_list = (obj*)start_free;}// 通过系统堆向内存池补充空间,如果补充成功,递归继续分配start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);if (0 == start_free){// 通过系统堆补充空间失败,在哈希桶中找是否有没有使用的较大的内存块int i;obj** my_free_list, * p;for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN){my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);p = *my_free_list;// 如果有,将该内存块补充进内存池,递归继续分配if (0 != p){*my_free_list = p->free_list_link;start_free = (char*)p;end_free = start_free + i;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));}}// 山穷水尽,只能向一级空间配置器求助// 注意:此处一定要将end_free置空,因为一级空间配置器一旦抛异常就会出问题end_free = 0;start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);}// 通过系统堆向内存池补充空间成功,更新信息并继续分配heap_size += bytes_to_get;end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));}
}
SGI-STL二级空间配置器之空间回收
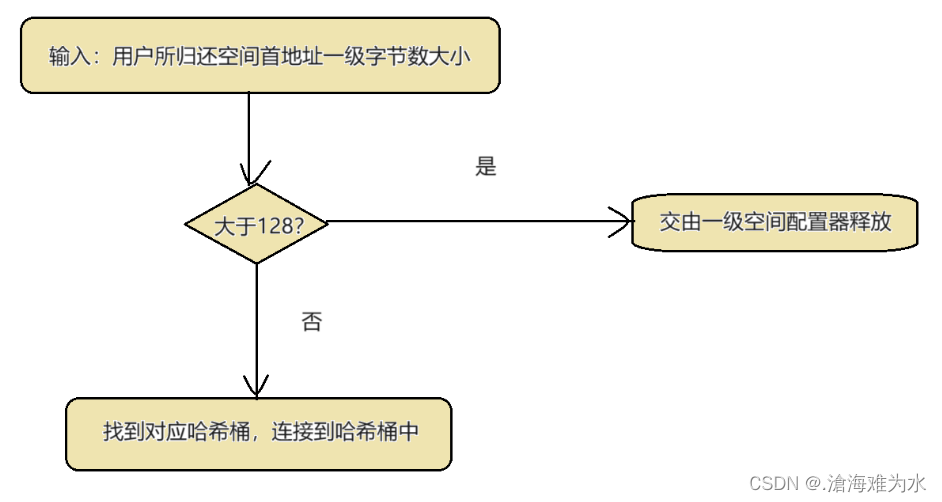
// 函数功能:用户将空间归还给空间配置器
// 参数:p空间首地址 n空间总大小
static void deallocate(void* p, size_t n)
{obj* q = (obj*)p;obj** my_free_list;// 如果空间不是小块内存,交给一级空间配置器回收if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES){malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);return;}// 找到对应的哈希桶,将内存挂在哈希桶中my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);q->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_free_list = q;
}
空间配置器的默认选择
SGI-STL默认使用一级还是二级空间配置器,通过USE_MALLOC宏进行控制:
#ifdef __USE_MALLOC
typedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc;
#else
// 二级空间配置器定义
#endif
在SGI_STL中该宏没有定义,因此:默认情况下SGI_STL使用二级空间配置器。
空间配置器的再次封装
在C++中,用户所需空间可能是任意类型的,有单个对象空间,有连续空间,每次让用户自己计算所需空间总大小不是很友好,因此SGI-STL将空间配置器重新再封装了一层:
// T: 元素类型
// Alloc: 空间配置器
// 注意:该类只负责申请与归还对象的空间,不否则空间中对象的构造与析构
template<class T, class Alloc>
class simple_alloc
{
public:// 申请n个T类型对象大小的空间static T* allocate(size_t n){return 0 == n ? 0 : (T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}// 申请一个T类型对象大小的空间static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof(T));}// 释放n个T类型对象大小的空间static void deallocate(T* p, size_t n){if (0 != n)Alloc::deallocate(p, n * sizeof(T));}// 释放一个T类型对象大小的空间static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p, sizeof(T));}
};
对象的析构与释放
一切为了效率考虑,SGI-STL决定将空间申请释放和对象的构造析构两个过程分离开,因为有些对象的构造不需要调用析构函数,销毁时不需要调用析构函数,将该过程分离开可以提高程序的性能:
// 归还空间时,先先调用该函数将对象中资源清理掉
template <class T>
inline void destroy(T* pointer)
{pointer->~T();
}
// 空间申请好后调用该函数:利用placement-new完成对象的构造
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void construct(T1* p, const T2& value)
{new (p) T1(value);
}
注意:
- 在释放对象时,需要根据对象的类型确定是否调用析构函数(类型萃取)。
- 对象的类型可以通过迭代器获萃取到。
4、与容器结合
本例子给出list与空间配置器是如何结合的,大家参考可给出vector的实现。
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list
{// ...// 实例化空间配置器typedef simple_alloc<list_node, Alloc> list_node_allocator;// ...
protected:link_type get_node(){// 调用空间配置器接口先申请节点的空间return list_node_allocator::allocate();}// 将节点归还给空间配置器void put_node(link_type p){list_node_allocator::deallocate(p);}// 创建节点:1. 申请空间 2. 完成节点构造link_type create_node(const T& x){link_type p = get_node();construct(&p->data, x);return p;}// 销毁节点: 1. 调用析构函数清理节点中资源 2. 将节点空间归还给空间配置器void destroy_node(link_type p){destroy(&p->data);put_node(p);}// ...iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x){link_type tmp = create_node(x);tmp->next = position.node;tmp->prev = position.node->prev;(link_type(position.node->prev))->next = tmp;position.node->prev = tmp;return tmp;}iterator erase(iterator position){link_type next_node = link_type(position.node->next);link_type prev_node = link_type(position.node->prev);prev_node->next = next_node;next_node->prev = prev_node;destroy_node(position.node);return iterator(next_node);}// ...
};
5、总结
引入相对复杂的空间配置器,主要源自两点:
- 频繁使用malloc、free开辟释放小块内存带来的性能效率的低下。
- 内存碎片问题,导致不连续内存不可用的浪费。
引入两层配置器帮我们解决了以上的问题,但是也带来一些问题:
- 内存碎片的问题,自由链表所挂区块都是8的整数倍,因此当我们需要非8倍数的区块,往往会导致浪费。
- 我们并没有释放内存池中的区块。释放需要到程序结束之后。这样子会导致自由链表一直占用内存,其它进程使用不了。
STL下的空间配置器分位两级,他们没有高低之分,只有一个条件,当用户所需要的的内存大小:
- 大于128字节时,交给一级空间配置器处理。
- 小于等于128字节时,交给二级空间配置器处理。
一级配置器的实现思想:
- 实际就是对c下的malloc,relloc,free进行了封装,并且在其中加入了c++的异常。我们要了解对于当内存不足调用失败后,内存不足处理是用户需要解决的问题,STL不处理,只是在你没有内存不足处理方法或有但是调用失败后抛出异常。
二级配置器的实现思想:
- 二级配置器是通过内存池和空闲链表配合起来的一个特别精巧的思想。
- 空闲链表:它每个节点分别维护8,16,32.。。。128字节以8的倍数的各内存大小。
它是按照如下的方式完成的:
- 首先,用户申请内存小于128个字节,进入二级配置器程序,假如第一次用户申请内存为32字节,程序直接调用S_chunk_alloc,直接申请40个大小的32字节空间,一个交给客户,另外19个交给空闲链表,剩下的20个交给内存池。
- 接下来,第二次申请空间,假设这次用户需要64字节的空间,首先,程序检查64字节的空闲链表节点是否有空闲空间,如果有,直接分配,如果没有,就去内存池,然后检查内存池的大小能分配多少个自己大小的节点,完全满足,则拿出一个给用户,剩下的19个给空闲链表,如果不够,尽可能分配内存池的最大个数给用户和空闲链表。如果一个都分配不出,首先把内存池中的剩下没用的小内存分给相应适合的空闲链表,然后继续调用S_chunk_alloc申请内存,内存申请不足,去检索空闲链表有没有尚未使用的大的内存块,如果有,就拿出来给给内存池,递归调用S_chunk_alloc,如果空闲链表也没有了,则交给一级适配器(因为其有对内存不足处理的方法)。内存够,则拿到申请的内存补充内存池。重复上面的操作,将一个给客户,其他的19个交给空闲链表,剩下的给内存池。
二级配置器实现了对小内存的高效管理,使内部碎片出现的概率大大降低。
STL源码:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/** Copyright (c) 1996-1997* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.** Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no* representations about the suitability of this software for any* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.*//* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.* You should not attempt to use it directly.*/#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H#ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
# define __PRIVATE public// Extra access restrictions prevent us from really making some things// private.
#else
# define __PRIVATE private
#endif#ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# define __USE_MALLOC
#endif// This implements some standard node allocators. These are// NOT the same as the allocators in the C++ draft standard or in// in the original STL. They do not encapsulate different pointer// types; indeed we assume that there is only one pointer type.// The allocation primitives are intended to allocate individual objects,// not larger arenas as with the original STL allocators.#if 0
# include <new>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC throw bad_alloc
#elif !defined(__THROW_BAD_ALLOC)
# include <iostream.h>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC cerr << "out of memory" << endl; exit(1)
#endif#ifndef __ALLOC
# define __ALLOC alloc
#endif
#ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
# include <windows.h>
#endif#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#ifndef __RESTRICT
# define __RESTRICT
#endif#if !defined(_PTHREADS) && !defined(_NOTHREADS) \&& !defined(__STL_SGI_THREADS) && !defined(__STL_WIN32THREADS)
# define _NOTHREADS
#endif# ifdef _PTHREADS// POSIX Threads// This is dubious, since this is likely to be a high contention// lock. Performance may not be adequate.
# include <pthread.h>
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK \if (threads) pthread_mutex_lock(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK \if (threads) pthread_mutex_unlock(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile // Needed at -O3 on SGI
# endif
# ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS// The lock needs to be initialized by constructing an allocator// objects of the right type. We do that here explicitly for alloc.
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK \EnterCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK \LeaveCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile // may not be needed
# endif /* WIN32THREADS */
# ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS// This should work without threads, with sproc threads, or with// pthreads. It is suboptimal in all cases.// It is unlikely to even compile on nonSGI machines.extern "C" {extern int __us_rsthread_malloc;
}
// The above is copied from malloc.h. Including <malloc.h>
// would be cleaner but fails with certain levels of standard
// conformance.
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \{ __lock(&__node_allocator_lock); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \{ __unlock(&__node_allocator_lock); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile // Needed at -O3 on SGI
# endif
# ifdef _NOTHREADS
// Thread-unsafe
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS false
# define __VOLATILE
# endif__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endif// Malloc-based allocator. Typically slower than default alloc below.
// Typically thread-safe and more storage efficient.
#ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# ifdef __DECLARE_GLOBALS_HERE
void (*__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0;
// g++ 2.7.2 does not handle static template data members.
# else
extern void (*__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
# endif
#endiftemplate <int inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template {private:static void* oom_malloc(size_t);static void* oom_realloc(void*, size_t);#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUGstatic void (*__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
#endifpublic:static void* allocate(size_t n){void* result = malloc(n);if (0 == result) result = oom_malloc(n);return result;}static void deallocate(void* p, size_t /* n */){free(p);}static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t /* old_sz */, size_t new_sz){void* result = realloc(p, new_sz);if (0 == result) result = oom_realloc(p, new_sz);return result;}static void (*set_malloc_handler(void (*f)()))(){void (*old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f;return(old);}};// malloc_alloc out-of-memory handling#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
template <int inst>
void (*__malloc_alloc_template<inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0;
#endiftemplate <int inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_malloc(size_t n)
{void (*my_malloc_handler)();void* result;for (;;) {my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }(*my_malloc_handler)();result = malloc(n);if (result) return(result);}
}template <int inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_realloc(void* p, size_t n)
{void (*my_malloc_handler)();void* result;for (;;) {my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }(*my_malloc_handler)();result = realloc(p, n);if (result) return(result);}
}typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;template<class T, class Alloc>
class simple_alloc {public:static T* allocate(size_t n){return 0 == n ? 0 : (T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof(T));}static void deallocate(T* p, size_t n){if (0 != n) Alloc::deallocate(p, n * sizeof(T));}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p, sizeof(T));}
};// Allocator adaptor to check size arguments for debugging.
// Reports errors using assert. Checking can be disabled with
// NDEBUG, but it's far better to just use the underlying allocator
// instead when no checking is desired.
// There is some evidence that this can confuse Purify.
template <class Alloc>
class debug_alloc {private:enum { extra = 8 }; // Size of space used to store size. Note// that this must be large enough to preserve// alignment.public:static void* allocate(size_t n){char* result = (char*)Alloc::allocate(n + extra);*(size_t*)result = n;return result + extra;}static void deallocate(void* p, size_t n){char* real_p = (char*)p - extra;assert(*(size_t*)real_p == n);Alloc::deallocate(real_p, n + extra);}static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz){char* real_p = (char*)p - extra;assert(*(size_t*)real_p == old_sz);char* result = (char*)Alloc::reallocate(real_p, old_sz + extra, new_sz + extra);*(size_t*)result = new_sz;return result + extra;}};# ifdef __USE_MALLOCtypedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc;# else// Default node allocator.
// With a reasonable compiler, this should be roughly as fast as the
// original STL class-specific allocators, but with less fragmentation.
// Default_alloc_template parameters are experimental and MAY
// DISAPPEAR in the future. Clients should just use alloc for now.
//
// Important implementation properties:
// 1. If the client request an object of size > __MAX_BYTES, the resulting
// object will be obtained directly from malloc.
// 2. In all other cases, we allocate an object of size exactly
// ROUND_UP(requested_size). Thus the client has enough size
// information that we can return the object to the proper free list
// without permanently losing part of the object.
//// The first template parameter specifies whether more than one thread
// may use this allocator. It is safe to allocate an object from
// one instance of a default_alloc and deallocate it with another
// one. This effectively transfers its ownership to the second one.
// This may have undesirable effects on reference locality.
// The second parameter is unreferenced and serves only to allow the
// creation of multiple default_alloc instances.
// Node that containers built on different allocator instances have
// different types, limiting the utility of this approach.
#ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
// breaks if we make these template class members:
enum { __ALIGN = 8 };
enum { __MAX_BYTES = 128 };
enum { __NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES / __ALIGN };
#endiftemplate <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template {private:// Really we should use static const int x = N// instead of enum { x = N }, but few compilers accept the former.
# ifndef __SUNPRO_CCenum { __ALIGN = 8 };enum { __MAX_BYTES = 128 };enum { __NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES / __ALIGN };
# endifstatic size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes) {return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1));}
__PRIVATE:union obj {union obj* free_list_link;char client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */};
private:
# ifdef __SUNPRO_CCstatic obj* __VOLATILE free_list[];// Specifying a size results in duplicate def for 4.1
# elsestatic obj* __VOLATILE free_list[__NFREELISTS];
# endifstatic size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes) {return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1);}// Returns an object of size n, and optionally adds to size n free list.static void* refill(size_t n);// Allocates a chunk for nobjs of size size. nobjs may be reduced// if it is inconvenient to allocate the requested number.static char* chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs);// Chunk allocation state.static char* start_free;static char* end_free;static size_t heap_size;# ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADSstatic volatile unsigned long __node_allocator_lock;static void __lock(volatile unsigned long*);static inline void __unlock(volatile unsigned long*);
# endif# ifdef _PTHREADSstatic pthread_mutex_t __node_allocator_lock;
# endif# ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADSstatic CRITICAL_SECTION __node_allocator_lock;static bool __node_allocator_lock_initialized;public:__default_alloc_template() {// This assumes the first constructor is called before threads// are started.if (!__node_allocator_lock_initialized) {InitializeCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock);__node_allocator_lock_initialized = true;}}
private:
# endifclass lock {public:lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; }~lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; }};friend class lock;public:/* n must be > 0 */static void* allocate(size_t n){obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list;obj* __RESTRICT result;if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) {return(malloc_alloc::allocate(n));}my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);// Acquire the lock here with a constructor call.// This ensures that it is released in exit or during stack// unwinding.
# ifndef _NOTHREADS/*REFERENCED*/lock lock_instance;
# endifresult = *my_free_list;if (result == 0) {void* r = refill(ROUND_UP(n));return r;}*my_free_list = result->free_list_link;return (result);};/* p may not be 0 */static void deallocate(void* p, size_t n){obj* q = (obj*)p;obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list;if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) {malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);return;}my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);// acquire lock
# ifndef _NOTHREADS/*REFERENCED*/lock lock_instance;
# endif /* _NOTHREADS */q->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_free_list = q;// lock is released here}static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz);};typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc;
typedef __default_alloc_template<false, 0> single_client_alloc;/* We allocate memory in large chunks in order to avoid fragmenting */
/* the malloc heap too much. */
/* We assume that size is properly aligned. */
/* We hold the allocation lock. */
template <bool threads, int inst>
char*
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs)
{char* result;size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free;if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) {result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}else if (bytes_left >= size) {nobjs = bytes_left / size;total_bytes = size * nobjs;result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}else {size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4);// Try to make use of the left-over piece.if (bytes_left > 0) {obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list =free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_free_list = (obj*)start_free;}start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);if (0 == start_free) {int i;obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list, * p;// Try to make do with what we have. That can't// hurt. We do not try smaller requests, since that tends// to result in disaster on multi-process machines.for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) {my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);p = *my_free_list;if (0 != p) {*my_free_list = p->free_list_link;start_free = (char*)p;end_free = start_free + i;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));// Any leftover piece will eventually make it to the// right free list.}}end_free = 0; // In case of exception.start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);// This should either throw an// exception or remedy the situation. Thus we assume it// succeeded.}heap_size += bytes_to_get;end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));}
}/* Returns an object of size n, and optionally adds to size n free list.*/
/* We assume that n is properly aligned. */
/* We hold the allocation lock. */
template <bool threads, int inst>
void* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::refill(size_t n)
{int nobjs = 20;char* chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs);obj* __VOLATILE* my_free_list;obj* result;obj* current_obj, * next_obj;int i;if (1 == nobjs) return(chunk);my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);/* Build free list in chunk */result = (obj*)chunk;*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj*)(chunk + n);for (i = 1; ; i++) {current_obj = next_obj;next_obj = (obj*)((char*)next_obj + n);if (nobjs - 1 == i) {current_obj->free_list_link = 0;break;}else {current_obj->free_list_link = next_obj;}}return(result);
}template <bool threads, int inst>
void*
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void* p,size_t old_sz,size_t new_sz)
{void* result;size_t copy_sz;if (old_sz > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES && new_sz > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) {return(realloc(p, new_sz));}if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz)) return(p);result = allocate(new_sz);copy_sz = new_sz > old_sz ? old_sz : new_sz;memcpy(result, p, copy_sz);deallocate(p, old_sz);return(result);
}#ifdef _PTHREADS
template <bool threads, int inst>
pthread_mutex_t
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock
= PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
#endif#ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
template <bool threads, int inst> CRITICAL_SECTION
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock;template <bool threads, int inst> bool
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock_initialized
= false;
#endif#ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#include <mutex.h>
#include <time.h>
__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
// Somewhat generic lock implementations. We need only test-and-set
// and some way to sleep. These should work with both SGI pthreads
// and sproc threads. They may be useful on other systems.
template <bool threads, int inst>
volatile unsigned long
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock = 0;#if __mips < 3 || !(defined (_ABIN32) || defined(_ABI64)) || defined(__GNUC__)
# define __test_and_set(l,v) test_and_set(l,v)
#endiftemplate <bool threads, int inst>
void
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__lock(volatile unsigned long* lock)
{const unsigned low_spin_max = 30; // spin cycles if we suspect uniprocessorconst unsigned high_spin_max = 1000; // spin cycles for multiprocessorstatic unsigned spin_max = low_spin_max;unsigned my_spin_max;static unsigned last_spins = 0;unsigned my_last_spins;static struct timespec ts = { 0, 1000 };unsigned junk;
# define __ALLOC_PAUSE junk *= junk; junk *= junk; junk *= junk; junk *= junkint i;if (!__test_and_set((unsigned long*)lock, 1)) {return;}my_spin_max = spin_max;my_last_spins = last_spins;for (i = 0; i < my_spin_max; i++) {if (i < my_last_spins / 2 || *lock) {__ALLOC_PAUSE;continue;}if (!__test_and_set((unsigned long*)lock, 1)) {// got it!// Spinning worked. Thus we're probably not being scheduled// against the other process with which we were contending.// Thus it makes sense to spin longer the next time.last_spins = i;spin_max = high_spin_max;return;}}// We are probably being scheduled against the other process. Sleep.spin_max = low_spin_max;for (;;) {if (!__test_and_set((unsigned long*)lock, 1)) {return;}nanosleep(&ts, 0);}
}template <bool threads, int inst>
inline void
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__unlock(volatile unsigned long* lock)
{
# if defined(__GNUC__) && __mips >= 3asm("sync");*lock = 0;
# elif __mips >= 3 && (defined (_ABIN32) || defined(_ABI64))__lock_release(lock);
# else * lock = 0;// This is not sufficient on many multiprocessors, since// writes to protected variables and the lock may be reordered.
# endif
}
#endiftemplate <bool threads, int inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::start_free = 0;template <bool threads, int inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::end_free = 0;template <bool threads, int inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::heap_size = 0;template <bool threads, int inst>
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::obj* __VOLATILE
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst> ::free_list[
# ifdef __SUNPRO_CC__NFREELISTS
# else__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__NFREELISTS
# endif
] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, };// The 16 zeros are necessary to make version 4.1 of the SunPro// compiler happy. Otherwise it appears to allocate too little// space for the array.# ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS// Create one to get critical section initialized.// We do this onece per file, but only the first constructor// does anything.static alloc __node_allocator_dummy_instance;
# endif#endif /* ! __USE_MALLOC */#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif__STL_END_NAMESPACE#undef __PRIVATE#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_H */// Local Variables:// mode:C++// End: