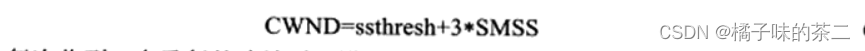目录
1 自适应中值滤波算法
1.1 函数定义
1.2 输入参数检查
1.3 初始化
1.4 自适应中值滤波过程
1.5 处理剩余未处理的像素
1.6 总结
2 计算输入数组的平均值
2.1 函数定义
2.2 注释
2.3 输入验证
2.4 计算平均值
2.5 总结
3 基于高斯模型的贝叶斯分类器
3.1 函数定义
3.2 输入校验和初始化
3.3 参数处理
3.4 计算协方差矩阵的行列式和逆矩阵
3.5 评估决策函数
3.6 分类决策
3.7 总结
4 将4连通边界转换为8连通边界
4.1 函数输入和输出
4.2 代码分析
4.3 关键函数和操作
4.4 总结


1 自适应中值滤波算法
function f = adpmedian(g, Smax)
%ADPMEDIAN Perform adaptive median filtering.
% F = ADPMEDIAN(G, SMAX) performs adaptive median filtering of
% image G. The median filter starts at size 3-by-3 and iterates up
% to size SMAX-by-SMAX. SMAX must be an odd integer greater than 1.% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/11/21 14:19:05 $% SMAX must be an odd, positive integer greater than 1.
if (Smax <= 1) | (Smax/2 == round(Smax/2)) | (Smax ~= round(Smax))error('SMAX must be an odd integer > 1.')
end
[M, N] = size(g);% Initial setup.
f = g;
f(:) = 0;
alreadyProcessed = false(size(g));% Begin filtering.
for k = 3:2:Smaxzmin = ordfilt2(g, 1, ones(k, k), 'symmetric');zmax = ordfilt2(g, k * k, ones(k, k), 'symmetric');zmed = medfilt2(g, [k k], 'symmetric');processUsingLevelB = (zmed > zmin) & (zmax > zmed) & ...~alreadyProcessed; zB = (g > zmin) & (zmax > g);outputZxy = processUsingLevelB & zB;outputZmed = processUsingLevelB & ~zB;f(outputZxy) = g(outputZxy);f(outputZmed) = zmed(outputZmed);alreadyProcessed = alreadyProcessed | processUsingLevelB;if all(alreadyProcessed(:))break;end
end% Output zmed for any remaining unprocessed pixels. Note that this
% zmed was computed using a window of size Smax-by-Smax, which is
% the final value of k in the loop.
f(~alreadyProcessed) = zmed(~alreadyProcessed);
这段代码实现了一种自适应中值滤波算法,用于图像处理中的噪声去除。自适应中值滤波是一种非线性滤波技术,特别适合去除所谓的“胡椒盐”噪声,同时尽量保留图像的边缘和细节。与传统的中值滤波不同,自适应中值滤波可以根据局部区域的特征动态调整滤波器的大小。
下面是对该函数的详细分析:
1.1 函数定义
function f = adpmedian(g, Smax)
g是输入的待处理图像。Smax是滤波器窗口的最大尺寸,必须是大于1的奇数。- 函数返回经过自适应中值滤波处理后的图像
f。
1.2 输入参数检查
if (Smax <= 1) | (Smax/2 == round(Smax/2)) | (Smax ~= round(Smax))error('SMAX must be an odd integer > 1.')
end
这部分代码确保Smax是一个大于1的奇数。如果不是,则抛出错误。
1.3 初始化
[M, N] = size(g);
f = g;
f(:) = 0;
alreadyProcessed = false(size(g));
- 获取输入图像
g的尺寸。 - 创建输出图像
f,并将其所有像素值初始化为0。 - 创建一个与输入图像同尺寸的逻辑矩阵
alreadyProcessed,用于标记每个像素是否已被处理,初始时全部设置为false。
1.4 自适应中值滤波过程
for k = 3:2:Smax...
end
通过从3x3开始,以步长为2(保证窗口尺寸始终为奇数),直至达到Smax的大小,进行迭代滤波。
在每次迭代中:
-
计算当前窗口尺寸下的最小值、最大值和中值滤波结果:
zmin是窗口内的最小值。zmax是窗口内的最大值。zmed是窗口内的中值。
-
确定哪些像素需要使用Level B处理:
- 如果
zmed > zmin且zmax > zmed,则当前像素的中值不是极端值,可以进行Level B处理。
- 如果
-
确定具体的处理方式:
- 如果当前像素值
g处于zmin和zmax之间,则保留原像素值。 - 否则,使用中值
zmed替换当前像素值。
- 如果当前像素值
-
更新已处理标记:
- 将经过处理的像素标记为
true。
- 将经过处理的像素标记为
-
提前终止:
- 如果所有像素都已处理,则提前结束循环。
1.5 处理剩余未处理的像素
f(~alreadyProcessed) = zmed(~alreadyProcessed);
对于那些在迭代过程中未被处理的像素,使用最后一次迭代计算的中值zmed进行填充。
1.6 总结
这段代码通过动态调整滤波窗口的大小,为每个像素选择一个合适的局部区域进行中值滤波,从而有效地去除噪声,尤其是在噪声密度变化较大的情况下,能够比传统的中值滤波器获得更好的效果。
2 计算输入数组的平均值
function av = average(A)
%AVERAGE Computes the average value of an array.
% AV = AVERAGE(A) computes the average value of input array, A,
% which must be a 1-D or 2-D array. % Sample M-file used in Chapter 2.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.2 $ $Date: 2003/03/27 21:23:21 $% Check the validity of the input. (Keep in mind that
% a 1-D array is a special case of a 2-D array.)
if ndims(A) > 2error('The dimensions of the input cannot exceed 2.')
end% Compute the average
av = sum(A(:))/length(A(:));这段代码定义了一个名为 average 的函数,其目的是计算输入数组 A 的平均值。这个函数可以处理一维(1-D)或二维(2-D)数组。以下是对该代码的详细分析:
2.1 函数定义
function av = average(A)
这一行定义了一个名为 average 的函数,它接收一个参数 A,并返回一个值 av。A 是输入数组,而 av 将是计算出的平均值。
2.2 注释
代码中的注释提供了关于函数的基本信息,包括:
- 函数的作用:计算数组的平均值。
- 输入要求:输入
A必须是一维或二维数组。 - 版权信息和参考书籍。
2.3 输入验证
if ndims(A) > 2error('The dimensions of the input cannot exceed 2.')
end
这部分代码检查输入数组 A 的维度。如果 A 的维度超过2(即不是一维或二维数组),函数将抛出一个错误信息,提示用户输入的维度不能超过2。这是通过 ndims 函数来实现的,它返回数组的维度数。如果条件成立(维度大于2),则通过 error 函数显示错误信息。
2.4 计算平均值
av = sum(A(:))/length(A(:));
这行代码是函数的核心,用于计算输入数组的平均值。它首先将数组 A 转换为一个列向量 A(:)。这种转换确保了无论 A 的原始形状如何,计算都能正确进行。然后,使用 sum 函数计算所有元素的总和,再通过 length 函数获取元素的总数(即数组的长度)。最后,将总和除以长度得到平均值,并将结果赋值给 av。
2.5 总结
这个 average 函数是一个简单而有效的工具,用于计算一维或二维数组的平均值。它首先验证输入数组的维度,然后计算并返回平均值。通过将数组转换为列向量并使用 sum 和 length 函数,这段代码以高效且容易理解的方式实现了其功能。
3 基于高斯模型的贝叶斯分类器
function d = bayesgauss(X, CA, MA, P)
%BAYESGAUSS Bayes classifier for Gaussian patterns.
% D = BAYESGAUSS(X, CA, MA, P) computes the Bayes decision
% functions of the n-dimensional patterns in the rows of X.
% CA is an array of size n-by-n-by-W containing W covariance
% matrices of size n-by-n, where W is the number of classes.
% MA is an array of size n-by-W, whose columns are the corres-
% ponding mean vectors. A cov. matrix and a mean vector must be
% specified for each class, even is some are equal. X is of size
% K-by-n, where K is the number of patterns to be classified. P is
% a 1-by-W array, containing the probabilities of occurrence of
% each class. If P is not included in the argument, the classes
% are assumed to be equally likely.
%
% D, is a column vector of length K. Its ith element is the class
% number assigned to the ith vector in X during classification. % Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.8 $ $Date: 2004/01/18 01:34:28 $d = [ ]; % Initialize d.
error(nargchk(3, 4, nargin)) % Verify correct no. of inputs.
n = size(CA, 1); % Dimension of patterns.% Protect against the possibility that the class number is
% included as an (n+1)th element of the vectors.
X = double(X(:, 1:n));
W = size(CA, 3); % Number of pattern classes.
K = size(X, 1); % Number of patterns to classify.
if nargin == 3P(1:W) = 1/W; % Classes assumed equally likely.
elseif sum(P) ~= 1 error('Elements of P must sum to 1.'); end
end
% Compute the determinants.
for J = 1:W DM(J) = det(CA(:, :, J));
end
% Compute inverses, using right division (IM/CA), where IM =
% eye(size(CA, 1)) is the n-by-n identity matrix. Re-use CA.
IM = eye(size(CA,1));
for J = 1:W CA(:, :, J) = IM/CA(:, :, J);
end% Evaluate the decision functions. Note the use of
% function mahalanobis discussed in Section 12.2.
MA = MA'; % Organize the mean vectors as rows.
for J = 1:WC = CA(:,:,J);M = MA(J,:);k1 = log(P(J));k2 = 0.5*log(DM(J));L(1:K,1) = k1;DET(1:K,1) = k2;if P(J) == 0;D(1:K, J) = -inf;elseD(:, J) = L - DET - 0.5*mahalanobis(X, C, M);end
end% Find the coordinates of the maximum value in each row. These maxima
% maxima give the class of each pattern:
[i, j] = find(D==repmat(max(D')',1,size(D,2)));
% Re-use X. It now contains the max value along each column.
X = [i j];
% Eliminate multiple classifications of the same patterns. Since
% the class assignment when two or more decision functions give
% the same value is arbitrary, we need to keep only one.
X = sortrows(X);
[b, m] = unique(X(:,1));
X = X(m, :);
% X is now sorted, with the 2nd column giving the class of the
% pattern no. in the 1st col.; i.e., X(j, 1) refers to the jth
% input pattern, and X(j, 2) is its the class number.% Output the result of classification. d is a col. vector with
% length equal to the total no. of inout patterns. The elements of
% d are the classes into which the patterns were classified.
d = X(:,2);这段代码实现了基于高斯模型的贝叶斯分类器。贝叶斯分类器是一种利用概率模型进行分类的方法,它在统计决策理论中占有重要地位。该代码的目的是对输入的样本集(X)进行分类,根据每个样本属于不同类别的概率,将样本分配到最可能的类别中。
下面是对这段代码的详细分析:
3.1 函数定义
function d = bayesgauss(X, CA, MA, P)
这个函数名为bayesgauss,接收四个参数:
X:待分类的样本集,大小为K-by-n,其中K是样本数量,n是特征维度。CA:协方差矩阵数组,大小为n-by-n-by-W,W是类别数。每个类别都有一个n-by-n的协方差矩阵。MA:均值向量数组,大小为n-by-W,每列代表一个类别的均值向量。P:类别出现的概率数组,大小为1-by-W。如果没有提供此参数,则假设所有类别出现的概率相等。
3.2 输入校验和初始化
error(nargchk(3, 4, nargin)) % Verify correct no. of inputs.
检查输入参数的数量是否正确,必须是3个或4个。
d = [ ]; % Initialize d.
初始化输出向量d为空,后续将填充这个向量以表示每个样本的分类结果。
3.3 参数处理
n = size(CA, 1); % Dimension of patterns.
X = double(X(:, 1:n));
W = size(CA, 3); % Number of pattern classes.
K = size(X, 1); % Number of patterns to classify.
获取样本特征维度n、类别数W、待分类样本数K。并确保X是双精度类型。
if nargin == 3P(1:W) = 1/W; % Classes assumed equally likely.
elseif sum(P) ~= 1 error('Elements of P must sum to 1.'); end
end
如果没有提供P参数,则假设所有类别出现的概率相等。如果提供了P,则检查其元素之和是否为1。
3.4 计算协方差矩阵的行列式和逆矩阵
for J = 1:W DM(J) = det(CA(:, :, J));
end
IM = eye(size(CA,1));
for J = 1:W CA(:, :, J) = IM/CA(:, :, J);
end
对于每个类别,计算其协方差矩阵的行列式(DM)和逆矩阵(更新CA存储逆矩阵)。
3.5 评估决策函数
MA = MA'; % Organize the mean vectors as rows.
for J = 1:W...D(:, J) = L - DET - 0.5*mahalanobis(X, C, M);
end
转置均值向量数组MA使其行表示均值向量。对于每个类别,计算决策函数的值,这里使用了马氏距离(mahalanobis函数)。
3.6 分类决策
[i, j] = find(D==repmat(max(D')',1,size(D,2)));
X = [i j];
X = sortrows(X);
[b, m] = unique(X(:,1));
X = X(m, :);
d = X(:,2);
找出每个样本在所有类别中决策函数值最大的类别,即为该样本的分类结果。处理可能的多重分类情况,保证每个样本只被分到一个类别中。最后,d向量包含了所有样本的分类结果。
3.7 总结
这段代码实现了一个基于高斯模型的贝叶斯分类器,通过计算每个样本属于不同类别的概率,并将样本分配到最可能的类别中。它涵盖了从参数检验、协方差矩阵处理、决策函数评估到最终的分类决策等多个步骤。
4 将4连通边界转换为8连通边界
function rc_new = bound2eight(rc)
%BOUND2EIGHT Convert 4-connected boundary to 8-connected boundary.
% RC_NEW = BOUND2EIGHT(RC) converts a four-connected boundary to an
% eight-connected boundary. RC is a P-by-2 matrix, each row of
% which contains the row and column coordinates of a boundary
% pixel. RC must be a closed boundary; in other words, the last
% row of RC must equal the first row of RC. BOUND2EIGHT removes
% boundary pixels that are necessary for four-connectedness but not
% necessary for eight-connectedness. RC_NEW is a Q-by-2 matrix,
% where Q <= P. % Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.6 $ $Date: 2003/11/21 14:19:38 $if ~isempty(rc) & ~isequal(rc(1, :), rc(end, :))error('Expected input boundary to be closed.');
endif size(rc, 1) <= 3% Degenerate case.rc_new = rc;return;
end% Remove last row, which equals the first row.
rc_new = rc(1:end - 1, :);% Remove the middle pixel in four-connected right-angle turns. We
% can do this in a vectorized fashion, but we can't do it all at
% once. Similar to the way the 'thin' algorithm works in bwmorph,
% we'll remove first the middle pixels in four-connected turns where
% the row and column are both even; then the middle pixels in the all
% the remaining four-connected turns where the row is even and the
% column is odd; then again where the row is odd and the column is
% even; and finally where both the row and column are odd.remove_locations = compute_remove_locations(rc_new);
field1 = remove_locations & (rem(rc_new(:, 1), 2) == 0) & ...(rem(rc_new(:, 2), 2) == 0);
rc_new(field1, :) = [];remove_locations = compute_remove_locations(rc_new);
field2 = remove_locations & (rem(rc_new(:, 1), 2) == 0) & ...(rem(rc_new(:, 2), 2) == 1);
rc_new(field2, :) = [];remove_locations = compute_remove_locations(rc_new);
field3 = remove_locations & (rem(rc_new(:, 1), 2) == 1) & ...(rem(rc_new(:, 2), 2) == 0);
rc_new(field3, :) = [];remove_locations = compute_remove_locations(rc_new);
field4 = remove_locations & (rem(rc_new(:, 1), 2) == 1) & ...(rem(rc_new(:, 2), 2) == 1);
rc_new(field4, :) = [];% Make the output boundary closed again.
rc_new = [rc_new; rc_new(1, :)];%-------------------------------------------------------------------%
function remove = compute_remove_locations(rc)% Circular diff.
d = [rc(2:end, :); rc(1, :)] - rc;% Dot product of each row of d with the subsequent row of d,
% performed in circular fashion.
d1 = [d(2:end, :); d(1, :)];
dotprod = sum(d .* d1, 2);% Locations of N, S, E, and W transitions followed by
% a right-angle turn.
remove = ~all(d, 2) & (dotprod == 0);% But we really want to remove the middle pixel of the turn.
remove = [remove(end, :); remove(1:end - 1, :)];if ~any(remove)done = 1;
elseidx = find(remove);rc(idx(1), :) = [];
end
这段代码定义了一个名为bound2eight的函数,其目的是将4连通边界转换为8连通边界。在数字图像处理中,连通性是用来描述图像区域中像素点之间连接方式的概念。4连通边界意味着每个边界像素与其上下左右的像素相连,而8连通边界还允许与对角线方向的像素相连。这种转换通常用于简化边界表示或改进图像分析算法的性能。
4.1 函数输入和输出
- 输入:
rc,一个P-by-2矩阵,其中每一行包含一个边界像素的行和列坐标。 - 输出:
rc_new,一个Q-by-2矩阵,表示转换后的8连通边界,其中Q <= P。
4.2 代码分析
-
检查闭合边界:
- 首先,函数检查输入的边界是否闭合。闭合边界意味着边界的起点和终点是同一个像素,即
rc的第一行与最后一行相等。如果不满足这一条件,则抛出错误。
- 首先,函数检查输入的边界是否闭合。闭合边界意味着边界的起点和终点是同一个像素,即
-
处理退化情况:
- 如果输入边界非常小(小于或等于3个像素),则没有必要进行转换,直接返回原始边界。
-
移除冗余像素:
- 由于4连通边界转换为8连通边界时某些像素可能变得不必要(特别是在直角转弯的地方),这段代码通过迭代移除这些冗余像素来简化边界。这一过程分为四个步骤,分别处理行坐标和列坐标都是偶数、行坐标偶数列坐标奇数、行坐标奇数列坐标偶数、以及行列坐标都是奇数的情况。
-
计算移除位置:
compute_remove_locations函数用于计算需要移除的像素位置。它通过计算边界向量的差分和这些差分向量之间的点积来识别直角转弯的位置。如果两个连续的差分向量的点积为0且至少有一个维度的差分为0,则表明这是一个直角转弯。
-
重新闭合边界:
- 在移除了所有不必要的像素后,为了保持边界的闭合性,将边界的起点再次添加到边界数组的末尾。
4.3 关键函数和操作
- 向量化操作:代码中大量使用了向量化操作来提高效率,例如
rem(rc_new(:, 1), 2) == 0用于筛选行坐标为偶数的像素。 - 差分和点积:通过计算差分和点积来识别需要移除的像素位置是这个算法的关键,这种方法有效地识别了边界上的直角转弯。
- 逻辑索引:使用逻辑数组作为索引来批量移除数组中的元素,这是MATLAB中处理此类问题的常用技巧。
4.4 总结
这段代码定义了一个名为bound2eight的MATLAB函数,旨在将4连通边界转换为8连通边界,用于数字图像处理中边界简化的目的。它通过先验证输入边界的闭合性,然后逐步移除不必要的像素(特别是在直角转弯处),最终确保输出的8连通边界仍然闭合。该函数利用向量化操作、差分和点积计算等技术高效地识别并移除冗余像素,从而优化边界表示,适用于需要边界简化以提高图像分析性能的场景。总的来说,bound2eight函数通过一系列精心设计的步骤将4连通边界转换为8连通边界,这在图像处理和分析中是一个常见且有用的操作。