给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
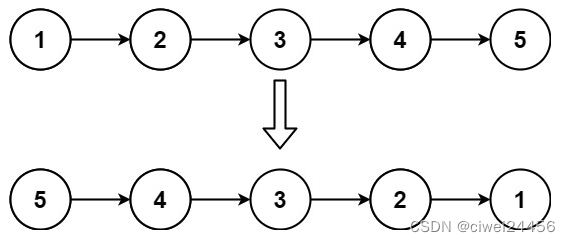
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
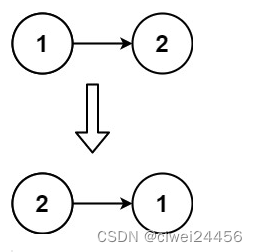
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
方法一:迭代(双指针)
考虑遍历链表,并在访问各节点时修改 next 引用指向
python:
class Solution:def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:cur, pre = head, Nonewhile cur:tmp = cur.next # 暂存后继节点 cur.nextcur.next = pre # 修改 next 引用指向pre = cur # pre 暂存 curcur = tmp # cur 访问下一节点return pre
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N) : 遍历链表使用线性大小时间。
空间复杂度 O(1): 变量 pre 和 cur 使用常数大小额外空间。
方法二:递归
考虑使用递归法遍历链表,当越过尾节点后终止递归,在回溯时修改各节点的 next 引用指向。
recur(cur, pre) 递归函数:
终止条件:当 cur 为空,则返回尾节点 pre (即反转链表的头节点);
递归后继节点,记录返回值(即反转链表的头节点)为 res ;
修改当前节点 cur 引用指向前驱节点 pre ;
返回反转链表的头节点 res ;
reverseList(head) 函数:
调用并返回 recur(head, null) 。传入 null 是因为反转链表后, head 节点指向 null ;
python:
class Solution:def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:def recur(cur, pre):if not cur: return pre # 终止条件res = recur(cur.next, cur) # 递归后继节点cur.next = pre # 修改节点引用指向return res # 返回反转链表的头节点return recur(head, None) # 调用递归并返回
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N) : 遍历链表使用线性大小时间。
空间复杂度 O(N): 遍历链表的递归深度达到 N ,系统使用 O(N)大小额外空间。