作为入门教程,本章是最后一章教程,Dgraph 还有很多东西可以介绍,如果有时间,后面在出Dgraph的进阶教程。对数据库最重要的操作就是增删改查。本章将详细介绍。
1、查询
Dgraph 在你创建GraphQL的时候会自动创建查询。查询用的是Queries。
比如创建
type Post {id: ID!title: String! @searchtext: Stringscore: Float @searchcompleted: Boolean @searchdatePublished: DateTime @search(by: [year])author: Author!
}type Author {id: ID!name: String! @searchposts: [Post!]friends: [Author]
}
下面的查询会自动创建
getPost(postID: ID!): Post
queryPost(filter: PostFilter, order: PostOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Post]
aggregatePost(filter: PostFilter): PostAggregateResult
第一个查询根据ID获取数据,第二个查询允许你根据一些过滤条件,排序查询数据,第三个查询允许你获得一些聚合参数。
执行下面的语句让你获取Post和关联对象
query {getPost(id: "0x1") {idtitletextdatePublishedauthor {namefriends {name}}}
}
你也可以通过Author去查询Post 甚至可以对Post在添加查询过滤条件
query {getAuthor(id: "0x1") {nameposts(filter: {title: {allofterms: "GraphQL"}}) {titletextdatePublished}}
}
注意,这些查询支持哪些查询还去觉得定义Shema的时候给的条件,比如tile 后面的指令 @search。
Dgraph 支持一些聚合查询,比如获取Post的数量
query {aggregatePost {count}}
聚合查询时,也可以加入一些判断条件
query {aggregatePost(filter: {title: {anyofterms: "GraphQL"}}) {count}}
也可以对子节点做高级聚合查询。比如
query {queryAuthor {namepostsAggregate {scoreMinscoreMaxscoreAvg}}}
支持 And,Or和Not,类似下面的语句
queryPost(filter: {title: { allofterms: "GraphQL"},or: { title: { allofterms: "Dgraph" } }
} ) { ... }
支持排序和分页
queryPost(order: { desc: datePublished, then: { desc: numLikes } }, first: 5) { ... }
@cascade 指定可以去除不必要的字段。@skip和@include 可以对语句传入需要的参数。skip和include 是反的。
query ($skipTitle: Boolean!) {queryPost {idtitle @skip(if: $skipTitle)text}
}
查询之前在云平台测试过,这里就不作演示了,可以自己去测试。
2、增,删,改
和查询不同,增删改用的是Mutations。和查询一样,在创建Shema 的时候,下面的Mutaion的将被自动创建
type Mutation {addAuthor(input: [AddAuthorInput!]!): AddAuthorPayloadupdateAuthor(input: UpdateAuthorInput!): UpdateAuthorPayloaddeleteAuthor(filter: AuthorFilter!): DeleteAuthorPayloadaddPost(input: [AddPostInput!]!): AddPostPayloadupdatePost(input: UpdatePostInput!): UpdatePostPayloaddeletePost(filter: PostFilter!): DeletePostPayload
}type AddAuthorPayload {author(filter: AuthorFilter, order: AuthorOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Author]numUids: Int
}type AddPostPayload {post(filter: PostFilter, order: PostOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Post]numUids: Int
}type DeleteAuthorPayload {author(filter: AuthorFilter, order: AuthorOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Author]msg: StringnumUids: Int
}type DeletePostPayload {post(filter: PostFilter, order: PostOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Post]msg: StringnumUids: Int
}type UpdateAuthorPayload {author(filter: AuthorFilter, order: AuthorOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Author]numUids: Int
}type UpdatePostPayload {post(filter: PostFilter, order: PostOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Post]numUids: Int
}
里面涵盖了三个操作:增加 Add,删除deleta 和改 update。
2.1、Add
用add 添加的时候,会自动创建input 类型。下面是自动创建的input 类型和添加一个对象的示例
input AddAuthorInput {name: String!dob: DateTimeposts: [PostRef]
}mutation {addAuthor(input: {name: "A.N. Author",lastName: "2000-01-01",}){...}
}
Dgraph 可以一次执行多个添加,且是互不影响的
mutation ($post: AddPostInput!, $author: AddAuthorInput!) {addAuthor(input: [$author]) {author {name}}addPost(input: [$post]) {post {postIDtitletext}}
}
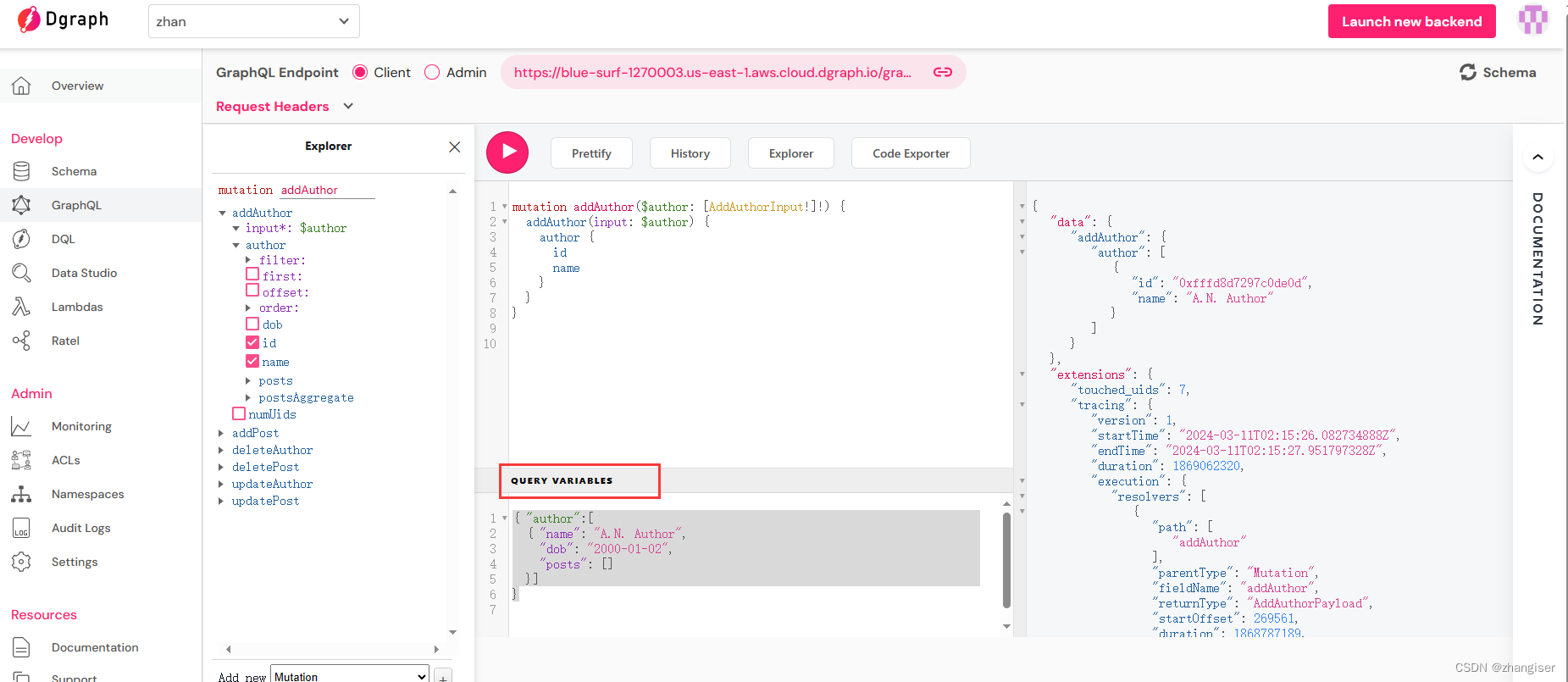
在云平台中应用Schema后,打开GraphQL,在Explorer里面可以看到下面的自动创建的Mutation,在中间输入输入我们的查询语句,点击运行,右侧可以看到添加成功。

我们可以在云平台中用变量的方式测试,输入语句和变量如下
mutation addAuthor($author: [AddAuthorInput!]!) {addAuthor(input: $author) {author {idname}}
}
//变量的写法一
{ "author":[{ "name": "A.N. Author","dob": "2000-01-02","posts": []}]
}
//变量的写法二
{ "author":[{ "name": "A.N. Author","dob": "2000-01-02","posts": []}]
}如下,其中红框内输入变量,按照$author的原型是一个数组,变量的上面两种写法都是可以的。
如果想知道在代码中如何写,请查看Dgraph 入门教程四(开发环境的搭建)-CSDN博客
2.2 、update
update的原型如下
updatePost(input: UpdatePostInput!): UpdatePostPayloadinput UpdatePostInput {filter: PostFilter!set: PostPatchremove: PostPatch
}type UpdatePostPayload {post(filter: PostFilter, order: PostOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Post]numUids: Int
}
先验证下set和remove。在验证之前,先增加下面两条两条post
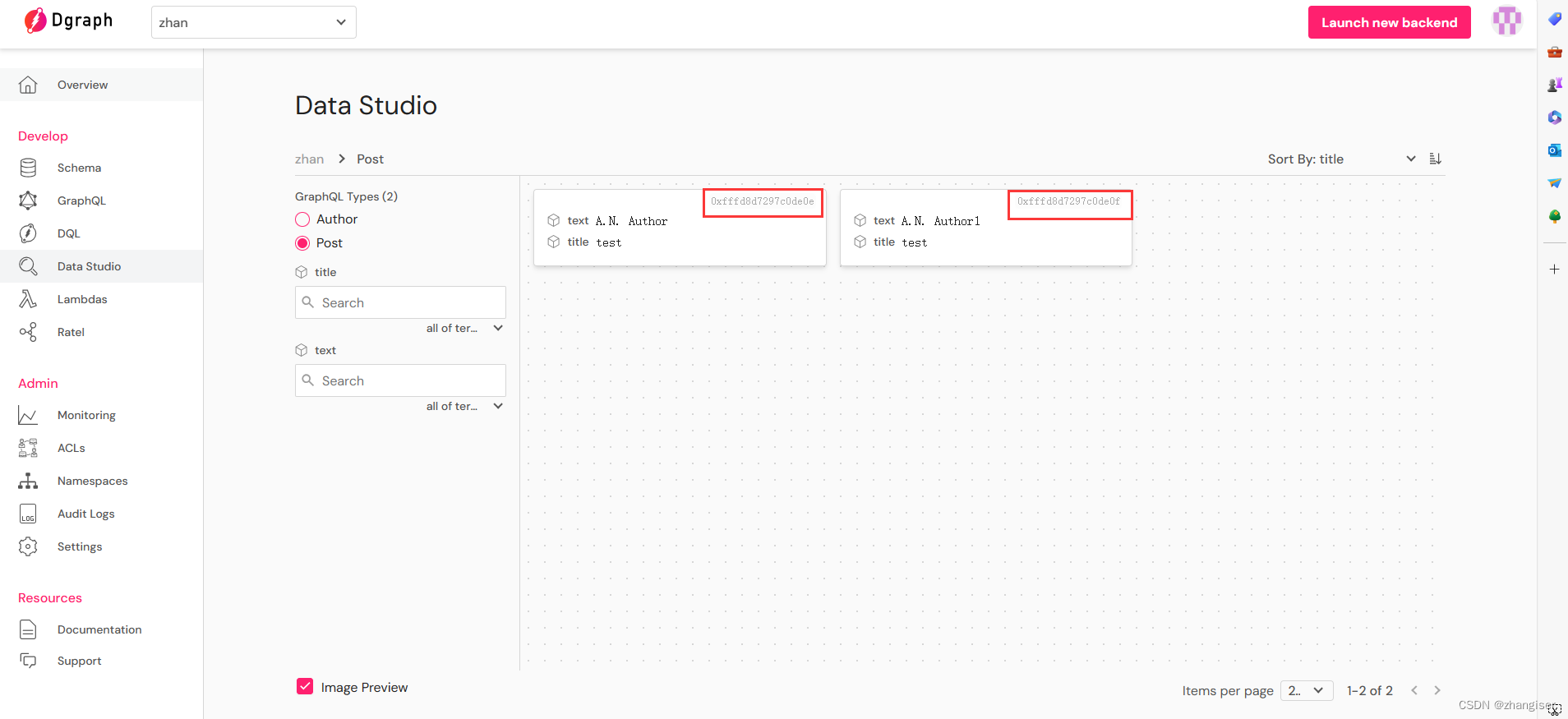
mutation {addPost(input: {text: "A.N. Author", title: "test"}){post{postID,text,title}}}
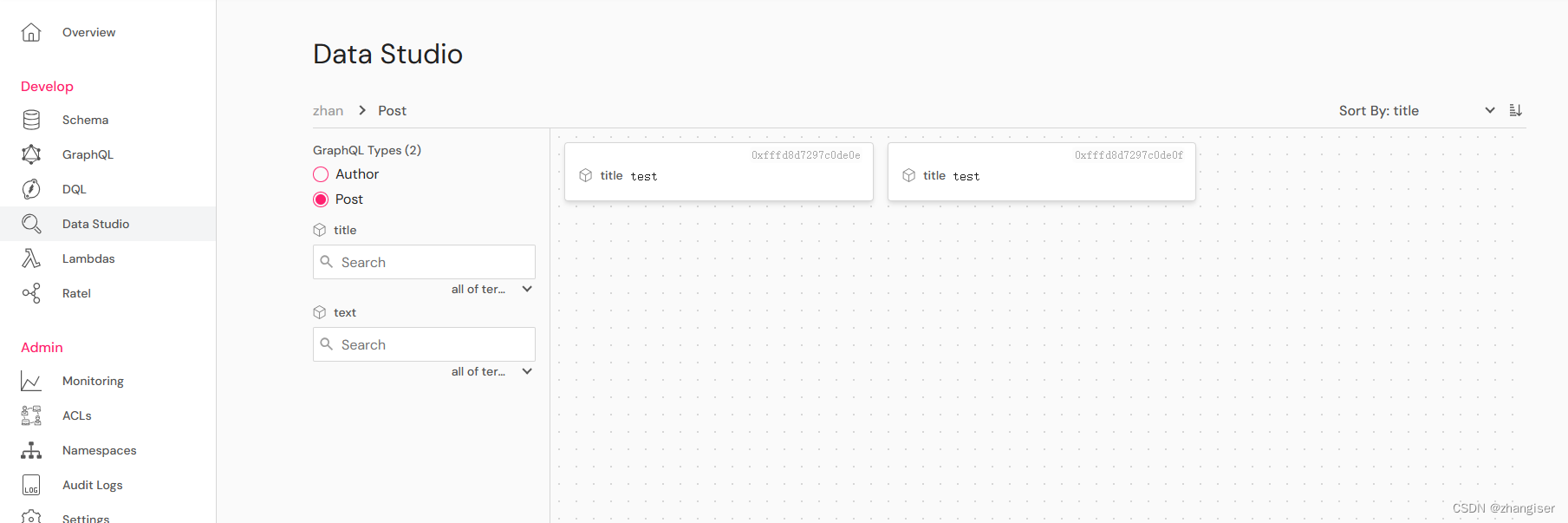
mutation {addPost(input: {text: "A.N. Author1", title: "test"}){post{postID,text,title}}}添加完成后,可以通过Data Studio 去查看,可以看到Post 里面已经有两个对象,红框中是我们需要记住ID,用于后面的更新。
用带变量的验证set,输入下面的语句和变量
语句:
mutation updatePost($patch: UpdatePostInput!) {updatePost(input: $patch) {post {postIDtitletext}}
}变量
{ "patch":{ "filter": {"postID": ["0xfffd8d7297c0de0e", "0xfffd8d7297c0de0f"]},"set": {"text": "updated text"}}
}输入执行界面

查看数据,可以看到text已经变了。这个就是根据id更新text
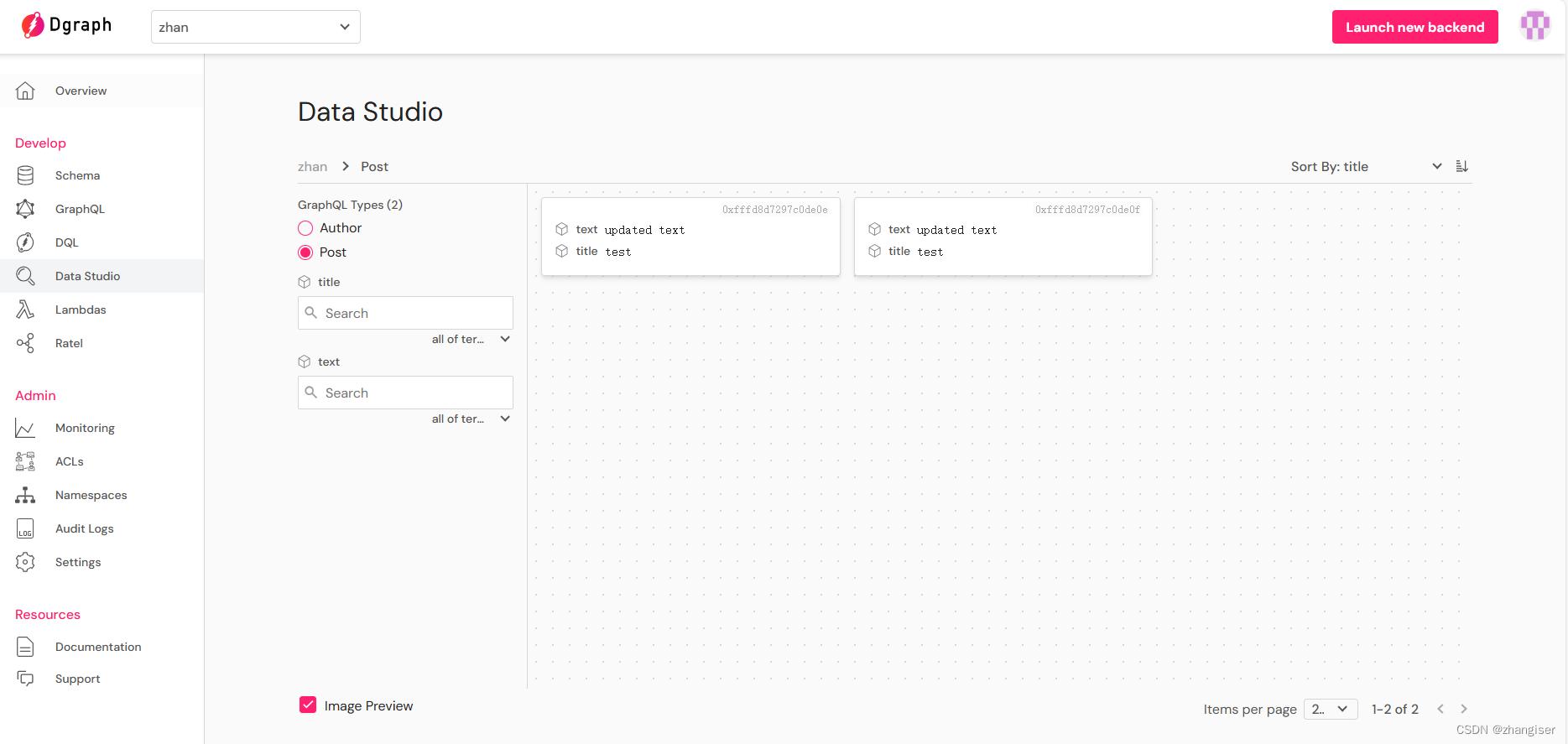
如果想要删除text 属性 ,我们可以执行remove。如下
语句
mutation updatePost($patch: UpdatePostInput!) {updatePost(input: $patch) {post {postIDtitletext}}
}变量
{ "patch":{ "filter": {"postID": ["0xfffd8d7297c0de0e", "0xfffd8d7297c0de0f"]},"remove": {"text": "updated text"}}
}结果,可以看到已经只有title了。这里的remove 是对属性控制了。
2.3、delete
删除的原型
deleteAuthor(filter: AuthorFilter!): DeleteAuthorPayloadtype DeleteAuthorPayload {author(filter: AuthorFilter, order: AuthorOrder, first: Int, offset: Int): [Author]msg: StringnumUids: Int
}
删除示例
语句:
mutation deleteAuthor($filter: AuthorFilter!) {deleteAuthor(filter: $filter) {msgauthor {namedob}}
}
变量
{ "filter":{ "name": { "eq": "A.N. Author" } }
}
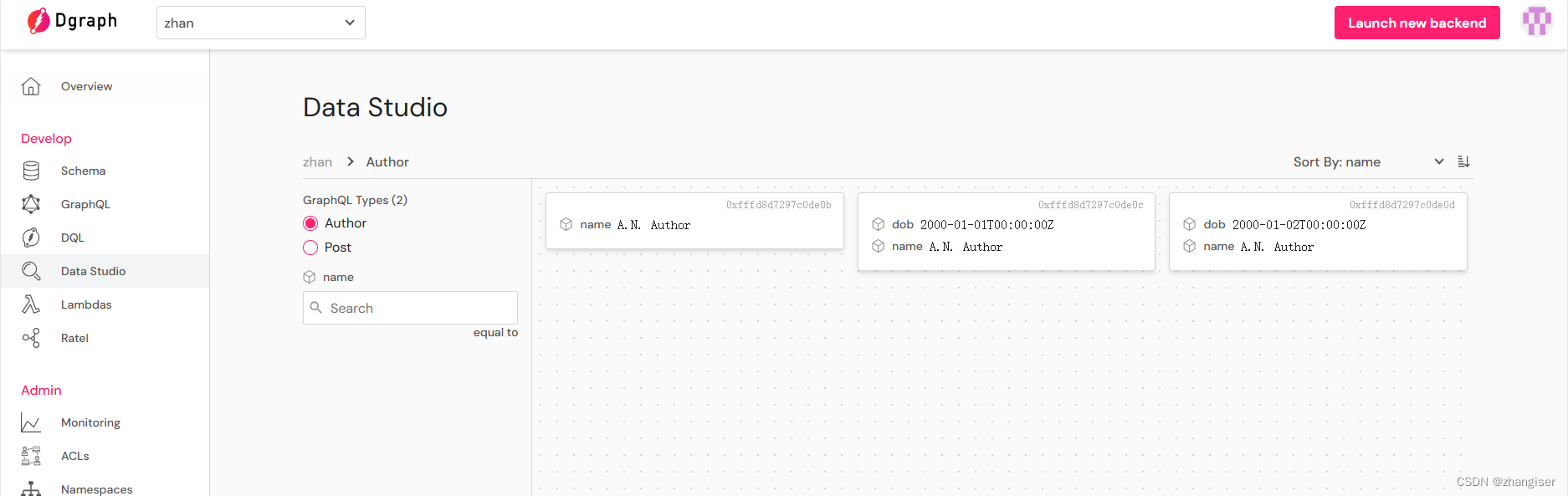
验证:
删除之前:
删除之后:
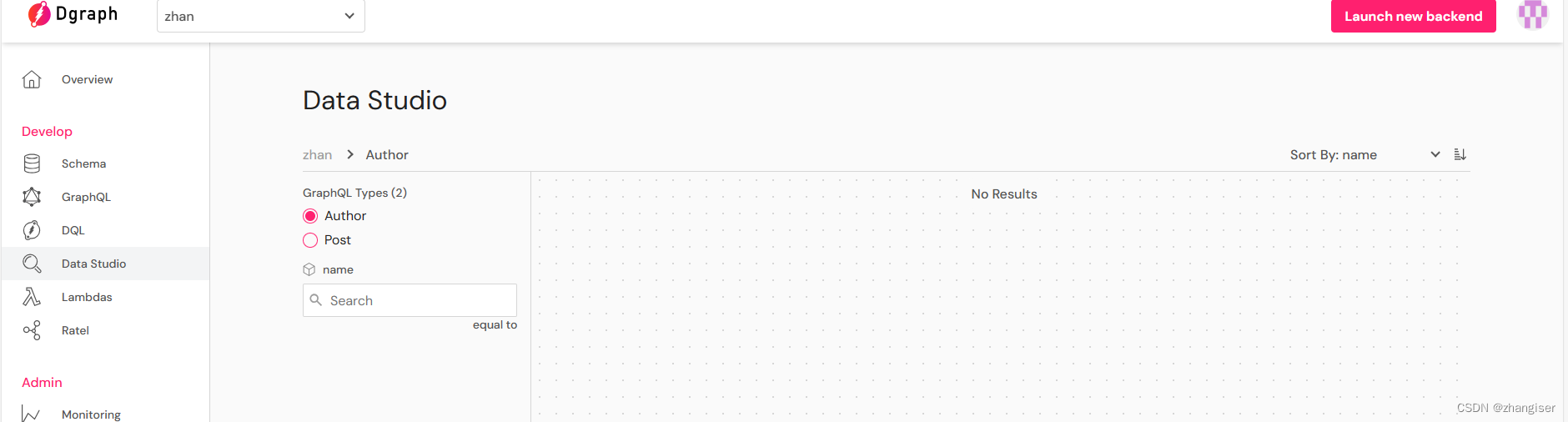
因为都是一个名字,所以全部删除了。
另外可以用Upsert 去增加,更新,如果有就更新,如果没有则直接添加,是个二合一的操作。还可以用deep 父子节点一起操作,需要的可以自己去云平台上测试,这里就不做演示了。