最近正在备考蓝桥杯,报的java b组,顺便更一下蓝桥的
幸运数字
题目

思路:填空题,暴力即可
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {static int trans(int x, int y){int res = 0;while(x > 0){res += x % y; // 不用求出转换后的数字,求和即可x /= y; }return res;}public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0, j = 0;while(i < 2023){j++;if(j % trans(j, 2) == 0 && j % trans(j, 8) == 0 &&j % trans(j, 10) == 0 && j % trans(j, 16) == 0) i++;}System.out.println(j);}
}数组分割
题目

思路:数学题。
1.加起来的总和为奇数时(有奇数个奇数)显然不可能完成分割.
2.全为偶数(n个偶数):中0个元素:
,
中1个元素:
... 所以分法总数为
(二项式定理,不证明了,想了解的可以网上查一下)。
3.偶数个奇数和偶数(2m个奇数,n个偶数):不妨将2m个奇数看成m个偶数计算,有,而偶数的排法为
个,一共
,即2的偶数个数加奇数个数-1次方
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {static final int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;static int even = 0, odd = 0;static int fun(){ if(odd % 2 == 1) return 0; // 奇数个奇数,无法排if(odd == 0) return quick_pow(2, even); // 0个奇数,2^偶数个数return quick_pow(2, odd - 1 + even); // 奇数个数加偶数个数减1}static int quick_pow(int a, int b){int res = 1;for(; b > 0; b >>= 1){if((b & 1) == 1) res = (int)((long)res * a % mod);a = (int)((long)a * a % mod);}return res;}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int t = scan.nextInt();while(t-- > 0){int n = scan.nextInt();even = 0; odd = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int a = scan.nextInt();if(a % 2 == 1) odd ++;else even ++;}System.out.println(fun());}scan.close();}
}矩形总面积
题目

思路:数学题
只要两个矩形有相交区域,一定满足
相交区域面积=(min(x2,x4)-max(x1,x3))*(min(y2,y4) - max(x1,x3)。
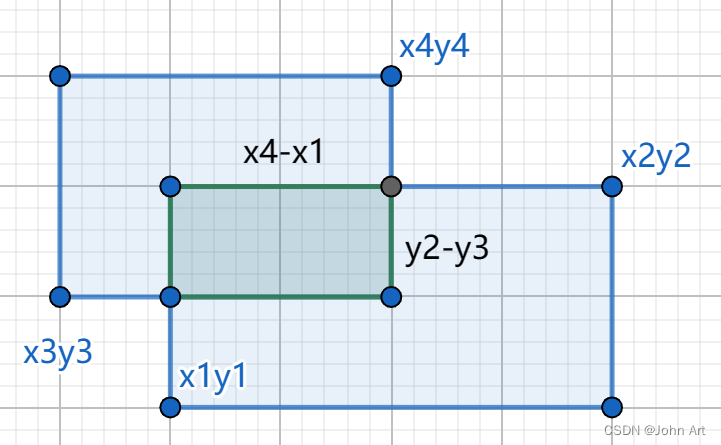
不会证明,但是是对的...(也许可以列出所有的情况证明但是有点麻烦,懒得证了)。
这道题还有个小坑,10^10会爆int,因此用long存面积。读题仔细一点就ok。
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int x1 = scan.nextInt(); int y1 = scan.nextInt();int x2 = scan.nextInt(); int y2 = scan.nextInt();int x3 = scan.nextInt(); int y3 = scan.nextInt();int x4 = scan.nextInt(); int y4 = scan.nextInt();// 总面积long ans = (long)(y2 - y1) * (x2 - x1) + (y4 - y3) * (x4 - x3);// 不相交,不减,相交,减去相交面积if(x2 < x3 || x4 < x1 || y3 > y2 || y1 > y4) System.out.println(ans);else System.out.println(ans - (long)((Math.min(y2, y4) - Math.max(y1, y3))* (Math.min(x2, x4) - Math.max(x1, x3))));scan.close();}
}蜗牛
题目

思路:dp
f[i][0]:到达第i根竹竿底部的最短用时 f[i][1]:到达第i根竹竿上传送门的最短用时
从第i点去i+1点:
底部:1.从i进入传送门,i+1出来,往下爬。 2.从i底部直接爬到i+1底部
传送门入口:1.从i进入传送门,i+1出来,往传送门爬(可能往上或下) 2.从i底部直接爬到i+1底部,再往上爬到传送门入口。
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {static final int N = 100010;static int n;static int[] x = new int[N], a = new int[N], b = new int[N];static double[][] f = new double[N][2];public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);n = scan.nextInt();for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) x[i] = scan.nextInt();for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){a[i] = scan.nextInt();b[i + 1] = scan.nextInt();}f[1][0] = x[1];f[1][1] = x[1] + a[1] / 0.7;for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){// 从下面走或者走传送门f[i][0] = Math.min(f[i - 1][0] + x[i] - x[i - 1], f[i - 1][1] + b[i] / 1.3);// 如果传送门出口在入口上面,往上,否则往下,或者直接走下面if(a[i] > b[i]) f[i][1] = Math.min(f[i - 1][0] + x[i] - x[i - 1] + a[i] / 0.7, f[i - 1][1] + (a[i] - b[i]) / 0.7);else f[i][1] = Math.min(f[i - 1][0] + x[i] - x[i - 1] + a[i] / 0.7, f[i - 1][1] + (b[i] - a[i]) / 1.3);}System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", f[n][0]));scan.close();}
}合并区域
题目

思路:dfs + 暴力
思路很简单,但是我估计大家都懒得写(
把地A和读入,旋转3次全部存入数组中,B同理。然后列出两块地的所有位置可能,dfs一下就ok
import java.util.*;
public class Main {static final int N = 60;static int n;static char[][][] A = new char[4][N][N], B = new char[4][N][N];static char[][] M = new char[3 * N][2 * N]; // M储存每种排列方式static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0}, dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};static void readAndFillArray(Scanner scan, int n, char[][][] array) {for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { // 读入4种旋转char val = (char) (scan.nextInt() + '0');array[0][i][j] = val;array[1][j][n - 1 - i] = val;array[2][n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j] = val;array[3][n - 1 - j][i] = val;}}static int solve() {int res = 0;for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++)for (int j = 0; j < M[i].length; j++)if (M[i][j] == '1') // 每找到一个为1的点就dfsres = Math.max(res, dfs(i, j, 0));return res;}static int dfs(int i, int j, int cnt) {if (i < 0 || i >= M.length || j < 0 || j >= M[i].length || M[i][j] == '0')return cnt; // 边界返回M[i][j] = '0'; cnt++;for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) cnt = dfs(i + dx[k], j + dy[k], cnt);return cnt;}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);n = scan.nextInt(); int move = 2 * n - 1;readAndFillArray(scan, n, A);readAndFillArray(scan, n, B);int max = 0;for(int a = 0; a < 4; a++) // A旋转for(int b = 0; b < 4; b++) // B旋转for(int m = 0; m < move; m++) {// M归零防止上一次结果影响for(int i = 0; i < 3 * n; i++) Arrays.fill(M[i], '0');for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {// A,B放入MSystem.arraycopy(A[a][i], 0, M[n - 1 + i], 0, n);System.arraycopy(B[b][i], 0, M[m + i], n, n);}max = Math.max(max, solve());}System.out.println(max);scan.close();}
}
买二赠一
题目
思路:双指针
从贵的往便宜的买,买两个后找到能免费的最贵的物品,重复此操作即可
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {static final int N = 500010;static int n;static int[] a = new int[N];static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 数据量比较大,用BufferedReader读入BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = Integer.parseInt(str[i]);// 从小到大排序,从后往前取,先买贵的Arrays.sort(a, 0, n);// i买的,j送的,count记录买第几个,free表示免费最高价格int i = n, j = n, count = 0, free = 0;long ans = 0;while(j >= 0) {if(count != 2) { // 没买两个,不送count++;do i--; while(i >= 0 && st[i]); // 已经买过/送过的不能再买/送了if(i < 0) break;st[i] = true; // 没买/送,买它!ans += a[i];free = a[i] / 2; // 从大往小取,取到的第二个一定是便宜的物品}else {count = 0;do j--; while(j >= 0 && (st[j] || a[j] > free)); // 已经买过/送过的不能再买/送了,并且价格要小于free才能送if(j < 0) break; // 不满足送东西的要求了st[j] = true;}}for(i = 0; i < n; i++) // 还没买的全给它买了if(!st[i]) ans += a[i];System.out.println(ans);reader.close();}
}合并石子
题目

思路:dp
在二维数组基础上多加一维表示石子颜色,我们可以直接枚举三个状态,当左右都合法时,我们就可以合并两堆石子,也就是dp(i1,j1,k)和dp[i2,j2,k]都合法就可以合并两个区间
注意,我们此时跑完区间(l,r)得到的num(l,r)跟cost(l,r)不一定是最小的,
我们还要再跑一次循环,得到最小的堆数和价值
import java.util.*;public class Main {static final int N = 310, MAX = Integer.MAX_VALUE;static int n;static int[][][] dp = new int[N][N][3]; //dp[i][j][c] 表示从i到j且颜色为c的石碓合并后所花费的最小石头数static int[] sum = new int[N]; //sum[i] 表示从第1堆到第i堆的石头数之和static int[][] num = new int[N][N]; //num[i][j] 表示从i到j合并后的最小堆数 ,即第一个输出答案static int[][] cost = new int[N][N]; //cost[i][j] 表示从i到j合并后的所花费的最小石头数,即第二个输出答案public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);n = scan.nextInt();for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) {num[i][j] = j - i + 1; //初始化从i到j的堆数和Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], MAX); //全部石碓初始化为maxValue方便判断}}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) // 用前缀和计算合并的花费sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + scan.nextInt();for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)dp[i][i][scan.nextInt()] = 0; // 初始化存在的石碓// i,len表示本次排i到i+len的石子,令j=i+len只是为了减少代码长度for (int len = 1; len < n; len++) {for (int i = 1; i + len <= n; i++) {int j = i + len;for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++) { //三种颜色int min = MAX;for (int k = i; k < j; k++)//判断两堆石碓是否合法存在,如果值为maxValue,则表示不存在;只有两堆都存在才能合并if (dp[i][k][c] != MAX && dp[k + 1][j][c] != MAX)min = Math.min(min, dp[i][k][c] + dp[k + 1][j][c] + sum[j] - sum[i - 1]);if (min != MAX) {dp[i][j][(c + 1) % 3] = Math.min(dp[i][j][(c + 1) % 3], min); // 找到最优合并后的值minnum[i][j] = 1; //合并后,从第i堆到第j堆成为1堆cost[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j][0], Math.min(dp[i][j][1], dp[i][j][2])); // 合并后,从第i堆到第j堆找到最少的花费}}}}for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {for (int j = k + 1; j <= n; j++) {//找到从i到j堆中,合并过后的,最少堆数,在此最少堆数的基础上再找对应的最少花费if (num[i][j] > num[i][k] + num[k + 1][j]) {num[i][j] = num[i][k] + num[k + 1][j];cost[i][j] = cost[i][k] + cost[k + 1][j];}else if (num[i][j] == num[i][k] + num[k + 1][j]) //如果堆数相同,则找到最少的花费cost[i][j] = Math.min(cost[i][j], cost[i][k] + cost[k + 1][j]);}}}System.out.println(num[1][n] + " " + cost[1][n]);}
}最大开支
题目

思路:贪心
i个人,需要花(B+K*i)*i, i + 1人则要花(B+K*(i + 1))*(i+1),多花more = B-(2*i + 1)*K块;
因此新建个类,包含K,B,i,more,再建个堆,按more从大到小排序,每次加最大的more就ok了。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;public class Main {static final int N = 100010;static int n, m;static PriorityQueue<item> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<item>() {@Overridepublic int compare(item i1, item i2) {return Integer.compare(i2.more, i1.more);}});public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");n = Integer.parseInt(str[0]); m = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {str = reader.readLine().split(" ");int b = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);int k = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);if(k + b > 0) pq.add(new item(k, 1, b, k + b));}long ans = 0;while(!pq.isEmpty() && n > 0) { // 最多只能加n次item i = pq.poll();ans += i.more;i.more = i.k + (2 * i.times + 1) * i.b;if(i.more > 0) pq.add(new item(i.k, i.times + 1, i.b, i.more));n--;}System.out.println(ans);}static class item {int k, times, b, more;item(int k, int times, int b, int more) {this.k = k;this.times = times;this.b = b;this.more = more;}}
}魔法阵
题目

思路:dijkstra+dp
这道题如果没有魔法减伤就是一道非常标准的dijkstra算法题,加入减伤后,我们可以用dp来记录。
dp[i][j]表示的是到达第i点并且消除了连续j段的伤害。
我们可以列出状态计算公式(i是t的下一个点):
1.dp[i][0] = dp[t][0]+w[i, t]; (正常dijkstra) 2.dp[i][k] = min(dp[t][k-1],dp[i][k])
3.dp[i][K] = min(dp[t][K] + g[i][t],dp[i][K])
M是N^2级的,因此采用邻接矩阵来存路线。本来朴素dijkstra是用bool类型来储存点是否经过,但是本题有可能会重复走某一个点,所以用队列来存改变距离的点。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;public class Main {static final int N = 1010;static int n, m, k;static int[][] dp = new int[N][N], g = new int[N][N];static void dijkstra() {for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)dp[i][j] = 0x3f3f3f3f;dp[0][0] = 0;Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();q.add(0);while (!q.isEmpty()) {int t = q.poll();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if(g[t][i] < 0x3f3f3f3f) {boolean flag = false;if (dp[i][0] > dp[t][0] + g[i][t]) {dp[i][0] = dp[t][0] + g[i][t];flag = true;}for (int k1 = 1; k1 <= k; k1++) {if (dp[i][k1] > dp[t][k1 - 1]) {dp[i][k1] = dp[t][k1 - 1];flag = true;}}if (dp[i][k] > dp[t][k] + g[i][t]) {flag = true;dp[i][k] = dp[t][k] + g[i][t];}if (flag) q.add(i);}}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");n = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);k = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);m = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)g[i][j] = 0x3f3f3f3f;for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {str = reader.readLine().split(" ");int a = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);int b = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);int w = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);g[a][b] = Math.min(w, g[a][b]); g[b][a] = g[a][b];}dijkstra();System.out.println(Math.min(dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][k]));}
}阶乘求和
题目

思路
找末尾0的数量,i>40时,i!末尾一定大于9个0(i!中乘了9个以上的5和2),由此暴力即可
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改public class Main {static final int MOD = (int)1e9;public static void main(String[] args) {long ans = 0;long p = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= 40; i++){ans = (ans + p) % MOD;p = p * (i + 1) % MOD;}System.out.println(ans);}
}