目标
- 关于gin.Default(),gin.New(),gin.Use()
- group与子group之间的关系,多group与middleware之间关系
- 中间件的类型,全局,group,get,不同类型的中间件什么时候执行。中间件 next 和abort行为
- 如何实现http请示请求?http并发如何处理,middleware的context是什么
基本用法
func initMiddleware(ctx *gin.Context) {fmt.Println("全局中间件 通过 r.Use 配置")// 调用该请求的剩余处理程序ctx.Next()// 终止调用该请求的剩余处理程序//ctx.Abort()
}//0. 初始化
r := gin.Default()//1. 全局中间件
r.Use(initMiddleware)//2. group与子group,类型为RouterGroup
adminRouter := router.Group("/admin", initMiddleware)
userRouter := adminRouters.Group("/user", initMiddleware)//3. 请求
userRouters.GET("/user", initMiddleware, controller.UserController{}.Index)//4. 中间件共享数据
ctx.Set("username", "张三")
username, _ := ctx.Get("username")关于初始化
使用流程中涉及到几个重要的结构体
gin.Engine,gin.Context,gin.RouterGroup
gin.Default(),gin.New(),gin.Use()
func Default() *Engine {// 初始化一个新的Egineengine := New()// 默认注册全局中间件Logger()和Recovery()//Logger()定义一个中间件,实现每次请求进来的日志打印//可以配置日志的过滤路径,打印颜色,打印的位置等 //Recovery()定义一个中间件,用来拦截运行中产生的所有panic,输出打印并返回500//同样可以配置全局panic拦截的行为//如果要配置Logger与Recovery则直接在应用中使用gin.New()。然后再在应用中调用//engine.Use(LoggerWithFormatter(xxxx), RecoveryWithWriter(xxxx))。engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery())return engine
}//初始化Engine
func New() *Engine {engine := &Engine{//初始化化第一个RouterGroup, root表示是否为根RouterGroupRouterGroup: RouterGroup{Handlers: nil,basePath: "/",root: true,},FuncMap: template.FuncMap{},TrustedPlatform: defaultPlatform,MaxMultipartMemory: defaultMultipartMemory,//请求方法数组,GET,POST,DELETE,每个方法下面有个链表trees: make(methodTrees, 0, 9),delims: render.Delims{Left: "{{", Right: "}}"},//已删除部分配置项}//给第一个Group配置engine,也就是本engineengine.RouterGroup.engine = engineengine.pool.New = func() any {return engine.allocateContext(engine.maxParams)}return engine
}//注册全局中间件
func (engine *Engine) Use(middleware ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {//把middleware函数append到上面创建的engine的根RouterGroup的Handlers数组中 engine.RouterGroup.Use(middleware...)//初始化404和405处理的中间间engine.rebuild404Handlers()engine.rebuild405Handlers()return engine
}Engine继承了RouterGroup,gin.Default()初始化了Engine与第一个RouterGroup,并初始化了两个默认的中间件,Logger(), Recovery(),他们的作用与配置上面代码中有介绍
gin.Use的核心功能为把传入进来的中间件合并到RouterGroup的Handlers数组中,代码如下
group.Handlers = append(group.Handlers, middleware...)重要的结构体
type HandlerFunc func(*Context)
type HandlersChain []HandlerFunctype RouterGroup struct {Handlers HandlersChainbasePath stringengine *Engineroot bool
}type RoutesInfo []RouteInfotype Engine struct {//继承RouterGroupRouterGroup//此处已省略部分gin的请求配置的字段,//gin的很多请求配置都在这,需要了解的可以看一下注释或官方文档delims render.DelimsHTMLRender render.HTMLRenderFuncMap template.FuncMap//所有的404的回调中间件allNoRoute HandlersChain//所有的405请求类型没对上的回调中间件,使用gin.NoMethod设置allNoMethod HandlersChain//404的回调中间件,使用gin.NoRoute设置,会合并到allNoRoute中noRoute HandlersChain//同上noMethod HandlersChainpool sync.Pooltrees methodTrees
}创建Group
Engine继承RouterGroup,RouterGroup里又有一个engine变量
之前猜测,RouterGroup与RouterGroup之前通过链表连接起来,目前来看上一个RouterGroup与当前RouterGroup没什么连接关系
只是利用上一个RouterGroup的Group函数创建一个新的RouterGroup,并把之前RouterGroup与Engine注册的中间件全部复制过来
//用法:adminRouters := r.Group("/admin", middlewares.InitMiddleware)//参数relativePath:RouterGroup的路径
//参数handlers:处理函数
func (group *RouterGroup) Group(relativePath string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) *RouterGroup {//创建一个新的RouterGroupreturn &RouterGroup{//把上一个Router的中间件,全局中间件与新中间件函数合并到新RouterHandlers: group.combineHandlers(handlers),//把上一个Router的路径与新的Router路径相加得到新的地址basePath: group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath),engine: group.engine,}
}创建Get请求
//使用方法userRouters.GET("/user", middlewares.InitMiddleware, controller.UserController{}.Index)
func (group *RouterGroup) GET(relativePath string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {return group.handle(http.MethodGet, relativePath, handlers)
}func (group *RouterGroup) handle(httpMethod, relativePath string, handlers HandlersChain) IRoutes {absolutePath := group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath)//这里有疑问,为什么要把GET请示所有的执行函数加入到group的handlers里handlers = group.combineHandlers(handlers)//把请求加入到方法树中group.engine.addRoute(httpMethod, absolutePath, handlers)return group.returnObj()
}type node struct {path stringindices stringwildChild boolnType nodeTypepriority uint32children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the arrayhandlers HandlersChainfullPath string
}type methodTree struct {method stringroot *node
}type methodTrees []methodTreefunc (engine *Engine) addRoute(method, path string, handlers HandlersChain) {//engine.trees,是一个methodTrees的切片//trees.get()找到哪一个属于GET请求的树,找不到则new一个root := engine.trees.get(method)if root == nil {root = new(node)root.fullPath = "/"engine.trees = append(engine.trees, methodTree{method: method, root: root})}//插入router的请求树中root.addRoute(path, handlers)//删除部分参数初始化}插入请求树
//第一个路径/list
//第二个路径/list2
//第三个路径/licq
//第四个路径/li:id
func (n *node) addRoute(path string, handlers HandlersChain) {fullPath := pathn.priority++//插入第一个路径时,root node为空,直接插入 if len(n.path) == 0 && len(n.children) == 0 {//insertChild做两件事//1. 解析参数,并插入参数节点 //2. 直接参数节点,第一个路径节点就简单地插入到GET的tree中 //到此/list结点添加完成,type=1, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:无 n.insertChild(path, fullPath, handlers)n.nType = rootreturn}parentFullPathIndex := 0walk:for {// Find the longest common prefix.// This also implies that the common prefix contains no ':' or '*'// since the existing key can't contain those chars.//找出新插入路径path与上一个插入的节点的路径做比较,找出连续相同字符的数量 // /xxx/list与/xxx/list2,前9个字符相同,所以i等于9 i := longestCommonPrefix(path, n.path)// Split edge// 添加list2:list2的i == len(n.path)相同,不走这里 // 添加licq: 走这里,且整棵树下移 if i < len(n.path) {child := node{path: n.path[i:],wildChild: n.wildChild,nType: static,indices: n.indices,children: n.children,handlers: n.handlers,priority: n.priority - 1,fullPath: n.fullPath,}//整棵树下移 n.children = []*node{&child}// []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65n.indices = bytesconv.BytesToString([]byte{n.path[i]})//第一次添加list,第一个节点为的path为list//第二次添加list2,因为与父节点节点前面相同,则父节点path为list,节点path为2//第三次添加licq,新节点与list节点前面li相同,//所以把父节点改为li,原来的list改为st, cq节点与st结点同为li的子节点,//最终结构如下// |->cq//li |// |->st-->2//修改原来的父节点 n.path = path[:i]n.handlers = niln.wildChild = falsen.fullPath = fullPath[:parentFullPathIndex+i]}// 添加list2:list2的i < len(path)走这里 // Make new node a child of this nodeif i < len(path) {//截取list2中的2,path==[2]path = path[i:]c := path[0]// '/' after param// 添加list2:n为上个list的node的nType为root,不走这里 if n.nType == param && c == '/' && len(n.children) == 1 {parentFullPathIndex += len(n.path)n = n.children[0]n.priority++continue walk}// Check if a child with the next path byte exists// 如果父节点有indices,且与c相同,则找下一个节点 for i, max := 0, len(n.indices); i < max; i++ {if c == n.indices[i] {parentFullPathIndex += len(n.path)i = n.incrementChildPrio(i)n = n.children[i]continue walk}}// Otherwise insert itif c != ':' && c != '*' && n.nType != catchAll {// 添加list2:list的node的indices为2 // []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65n.indices += bytesconv.BytesToString([]byte{c})// 添加list2:创建list2的node child := &node{fullPath: fullPath,}// 添加list2:把list2的node插入到list的node children中 n.addChild(child)// 添加list2:设置priority,并把高priority的chdil排在前面n.incrementChildPrio(len(n.indices) - 1)// 这里把n切换为child,做后面的设置n = child} else if n.wildChild {// inserting a wildcard node, need to check if it conflicts with the existing wildcardn = n.children[len(n.children)-1]n.priority++// Check if the wildcard matchesif len(path) >= len(n.path) && n.path == path[:len(n.path)] &&// Adding a child to a catchAll is not possiblen.nType != catchAll &&// Check for longer wildcard, e.g. :name and :names(len(n.path) >= len(path) || path[len(n.path)] == '/') {continue walk}// Wildcard conflictpathSeg := pathif n.nType != catchAll {pathSeg = strings.SplitN(pathSeg, "/", 2)[0]}prefix := fullPath[:strings.Index(fullPath, pathSeg)] + n.pathpanic("'" + pathSeg +"' in new path '" + fullPath +"' conflicts with existing wildcard '" + n.path +"' in existing prefix '" + prefix +"'")}//如上所述,如果路径没有参数,此函数的作用为n.handlers = handlersn.insertChild(path, fullPath, handlers)return}// Otherwise add handle to current nodeif n.handlers != nil {panic("handlers are already registered for path '" + fullPath + "'")}n.handlers = handlersn.fullPath = fullPathreturn}
}路由树图示
下面通过图示来看一下,每次增加一个请求,路由树会有什么变化。
如果插入一个带参数的请求如/list/:id/:sn,流程和上面代码所分析的基本一至,只是会在/list挂两个param结点,id与sn
userRouters.GET("/list", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list2", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list23", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list33", Index)
userRouters.GET("/liicq", Index)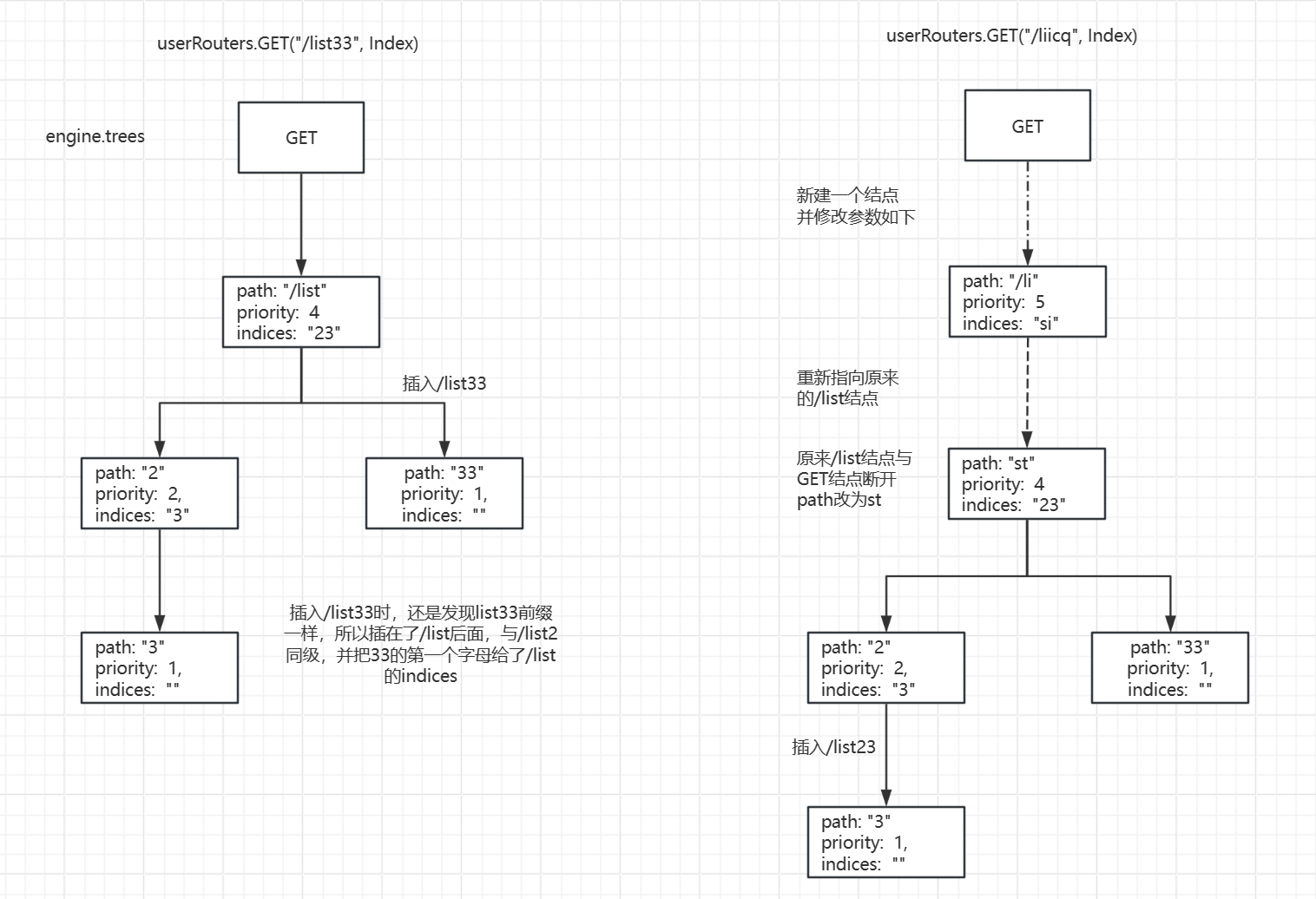
测试代码
自己写了一个代码去打印树结构
func _p(level int, pre string, n *node){for i := 0; i < level+1; i++ {fmt.Print(pre)}fmt.Printf(" path=%v, type=%d, childrenLen=%d, priority:%d, indices:%s, wildChild=%t\n",n.path, n.nType, len(n.children), n.priority, n.indices, n.wildChild)
}func (group *RouterGroup) printNode(level int, node *node) {if len(node.children) != 0 || level == 0 {_p(level, "#", node)}if len(node.children) != 0 {for _, n := range node.children {_p(level, "-", n)}level++for _, n := range node.children {group.printNode(level, n);}}
}打印结果
//测试内容
userRouters.GET("/list", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list2", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list23", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list33", Index)
userRouters.GET("/liicq", Index)//打印结果
# path=/admin/user/li, type=1, childrenLen=2, priority:5, indices:si, wildChild=false
- path=st, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:4, indices:23, wildChild=false
- path=icq, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
## path=st, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:4, indices:23, wildChild=false
-- path=2, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:2, indices:3, wildChild=false
-- path=33, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
### path=2, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:2, indices:3, wildChild=false
--- path=3, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false//测试内容
userRouters.GET("/list", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list2", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list23", Index)
userRouters.GET("/list33", Index)
userRouters.GET("/liicq", Index)userRouters.GET("/lipar/:id/:sn", Index)
userRouters.GET("/lipar2", Index)//打印结果
# path=/admin/user/li, type=1, childrenLen=3, priority:7, indices:spi, wildChild=false
- path=st, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:4, indices:23, wildChild=false
- path=par, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:2, indices:/2, wildChild=false
- path=icq, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
## path=st, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:4, indices:23, wildChild=false
-- path=2, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:2, indices:3, wildChild=false
-- path=33, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
### path=2, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:2, indices:3, wildChild=false
--- path=3, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
## path=par, type=0, childrenLen=2, priority:2, indices:/2, wildChild=false
-- path=/, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=true
-- path=2, type=0, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
### path=/, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=true
--- path=:id, type=2, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
#### path=:id, type=2, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
---- path=/, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=true
##### path=/, type=0, childrenLen=1, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=true
----- path=:sn, type=2, childrenLen=0, priority:1, indices:, wildChild=false
下篇文章了解一下gin启动都做了什么工作,中间件如何被调用,以及request是如何并发的