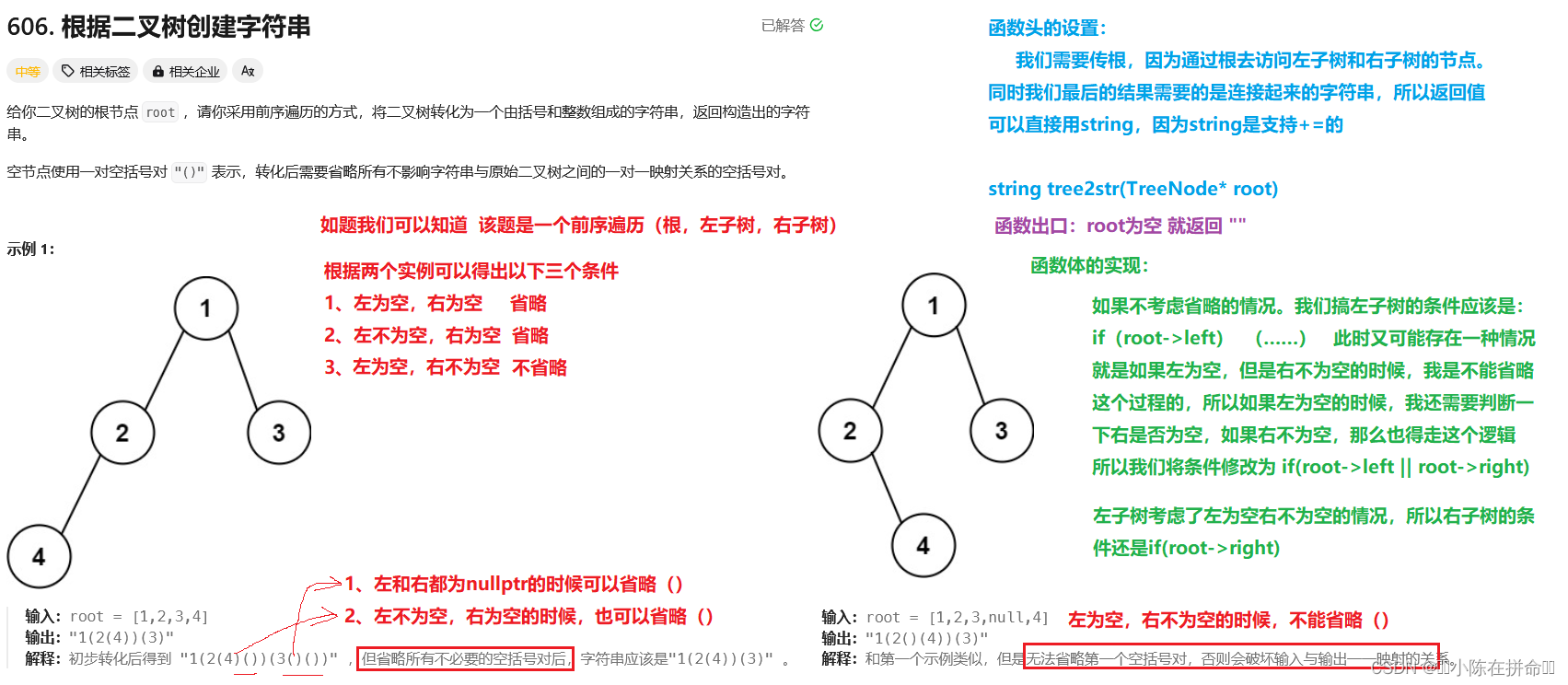
一、根据二叉树创建字符串
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public://前序遍历:根 左 右//左子树为空,右子树不为空的时候,不能省略左//左不为空,右子树为空的时候,可以省略右//都为空,可以省略string tree2str(TreeNode* root) { if(root==nullptr) return "";string str=to_string(root->val);if(root->left||root->right) {str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->left);str+=')';}if(root->right){str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->right);str+=')';}return str;}};二、二叉树的最近公共祖先
. - 力扣(LeetCode)


思路1:
//策略1 1、如果一个在我的左子树,一个在我的右子树,那么我就是最近公共祖先// 2、如果两个走在我的左,就去左找 都不在我的左,那就去我的右找// 3、如果我自己就是,那另一个必然是我的孩子 返回我自己
class Solution {
public:bool isintree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x){if(root==nullptr) return false;else return root==x||isintree(root->left,x)||isintree(root->right,x);}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*&p, TreeNode*&q){if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;if(root==p||root==q) return root;//此时就要去看看我的左子树和右子树找一找bool pleft=isintree(root->left,p);bool pright=!pleft;bool qleft=isintree(root->left,q);bool qright=!qleft;if(pleft&&qright ||qleft&&pright) return root;else if(pleft&&qleft) return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);else return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}
};思路2:
class Solution {
public://策略2:利用dfs将p和q的路径存到容器中,然后转化成链表相交的问题 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q){if(root==p||root==q) return root;stack<TreeNode*> Ppath;stack<TreeNode*> Qpath;dfs(root,p,Ppath);//找pdfs(root,q,Qpath);//找q//此时已经找到了两条目标路径,然后让长的那一条pop直到和另一条相等while(Ppath.size()!=Qpath.size()){if(Ppath.size()>Qpath.size()) Ppath.pop();else Qpath.pop();}//此时两个一起出,直到相等就返回while(Ppath.top()!=Qpath.top()){Ppath.pop();Qpath.pop();}return Ppath.top();}bool dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x,stack<TreeNode*>&path){if(root==nullptr) return false;//此时可以入栈,然后去左边和右边找一下path.push(root);//无论如何都入if(root==x||dfs(root->left,x,path)||dfs(root->right,x,path)) return true;//左边或右边找到,返回true//两边都没有找到,说明root不是我们想要的,出栈并返回false;path.pop();//都没找到,就得回溯return false;}
};三、二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网

class Solution {
public:void inorder(TreeNode* cur,TreeNode*&prev){if(cur==nullptr) return;//cur指向的就是中序遍历的结果inorder(cur->left,prev);//这里出现的cur就是中序的结果cur->left=prev;if(prev) prev->right=cur;prev=cur;inorder(cur->right,prev);}TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree){TreeNode*prev=nullptr;inorder(pRootOfTree,prev);TreeNode*head=pRootOfTree; //不断往左找,找到最链表头while(head&&head->left) head=head->left;return head;}
};技巧:在递归过程中,我们想要有一个变量记录全过程(该题中的prev),第一种方法就是设置成全局变量,第二种方法就是传引用。
四、前序和中序遍历序列构建二叉树
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int&pi,int begin,int end) {//先创建该节点if(begin>end) return nullptr;TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(preorder[pi]);//然后根据该节点分割左右区间 在中序数组中找到树int rooti=begin;while(rooti<=end){if(inorder[rooti]==preorder[pi]) break;++rooti;}//划分区间去左子树和右子树找++pi;root->left=_buildTree(preorder,inorder,pi,begin,rooti-1);root->right=_buildTree(preorder,inorder,pi,rooti+1,end);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {//前序遍历:根 左子树 右子树 一个指针去遍历前序找根//中序遍历:左子树 根 右子树 划分左右区间//前序帮我们找根,中序帮我们划分区间int pi=0;//帮助我们按顺序遍历前序数组return _buildTree(preorder,inorder,pi,0,inorder.size()-1);}
};五、中序和后序序列遍历构建二叉树
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int&pi,int begin,int end){if(begin>end) return nullptr;TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(postorder[pi]);//肯定要先建立根//开始划分区间int rooti=begin;while(rooti<=end) {if(inorder[rooti]==postorder[pi]) break;++rooti;}//开始延伸,先延伸右子树,再延伸左子树--pi;root->right= _buildTree(inorder,postorder,pi,rooti+1,end);root->left= _buildTree(inorder,postorder,pi,begin,rooti-1);return root;}//后序遍历 左子树 右子树 根//中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树//后序遍历帮我们找根。 中序遍历帮我们划分左右区间TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){int n=inorder.size();int pi=n-1;return _buildTree(inorder,postorder,pi,0,n-1);}
};六、非递归实现二叉树的前序遍历
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public://根 左子树 右子树//根、左子树、然后再栈里面搞右子树vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;vector<int> ret;if(root==nullptr) return ret;TreeNode*cur=root;//1、访问左路节点//2、访问左路节点的右子树while(!st.empty()||cur) //cur不为空表示当前的树还没访问,栈不为空表示还有右子树没有访问{while(cur){ret.push_back(cur->val);st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}//开始去访问右子树TreeNode* t=st.top();st.pop();//转化成子问题,去访问节点的右树cur=t->right;}return ret;}
};七、非递归实现二叉树的中序遍历
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
//中序 左子树 根 右子树
//1 左路节点
//2 左子树的右路节点
//从栈里取到左路节点,意味着左路节点,以为着这个节点的左子树已经访问完了。
// 非递归实现 vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;vector<int> ret;if(root==nullptr) return ret;TreeNode*cur=root;while(cur||!st.empty()){while(cur){st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}//此时,从栈中拿出来TreeNode* t=st.top();st.pop();ret.push_back(t->val);cur=t->right;}return ret;}
};八、非递归实现二叉树的后序遍历
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st;vector<int> ret;if(root==nullptr) return ret;TreeNode*cur=root;//1、访问左路节点//2、访问左路节点的右子树TreeNode*prev=nullptr;while(!st.empty()||cur) //cur不为空表示当前的树还没访问,栈不为空表示还有右子树没有访问{while(cur){st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}//开始去访问右子树TreeNode* t=st.top();if(t->right==nullptr||t->right==prev){ret.push_back(t->val);st.pop();prev=t;}//从栈中弹出的节点,我们只能确定其左子树肯定访问完了,但是无法确定右子树是否访问过。else cur=t->right;}return ret;}
};还有一种思路就是,因为我们的结果是存在一个数组去返回的,因此我们可以按照前序遍历的逻辑:将问题拆分成 右路节点和右路节点的左子树。然后按照 根、右子树、左子树的顺序去访问(和后序相反),最后再逆置我们的返回数组即可。这是一种取巧的方法,但是能成功是因为该题是将结果放到一个数组中返回的,如果该题是要求我们边遍历边访问,比如打印,那么该方法就不可行。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;vector<int> ret;if(root==nullptr) return ret;TreeNode*cur=root;//1、访问右路节点//2、访问右路节点的左子树while(!st.empty()||cur) //cur不为空表示当前的树还没访问,栈不为空表示还有左子树没有访问{while(cur){ret.push_back(cur->val);st.push(cur);cur=cur->right;}//开始去访问左子树TreeNode* t=st.top();st.pop();//转化成子问题,去访问节点的右树cur=t->left;}reverse(ret.begin(),ret.end());return ret;}
};九、小总结
1、二叉搜索树涉及到升序的情况,一般是根中序遍历建立联系
2、前序和中序构建二叉树,以及中序和后序构建二叉树,本质上是利用一个序列找根,另一个序列去划分问题。同时我们会发现其实后序遍历如果反着来的话大多数情况下可以转化成类似前序遍历,比如4、5题和7、8题,都可以用前序遍历的思路去解决后序遍历。
3、非递归实现二叉树的前中后序遍历,本质上是将问题拆分为1、访问左路节点 2、访问左路节点的右子树。需要用一个辅助栈去帮助我们记录节点。